利用Python中的GDAL和OGR模块实现shapefile对栅格DEM数据的裁剪
之前已经把31景DEM数据拼接完成,这篇文章,利用shapefile文件实现对山东DEM数据的裁剪。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/GISShiXiSheng/article/details/72843070?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522161423692216780271562057%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fblog.%2522%257D&request_id=161423692216780271562057&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~blog~first_rank_v1~rank_blog_v1-1-72843070.pc_v1_rank_blog_v1&utm_term=%E6%A0%85%E6%A0%BC%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E8%A3%81%E5%89%AA&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450
Python、GIS基础教程:https://www.osgeo.cn/pygis/ogr-ogrintro.html
1.代码
from osgeo import gdal, gdalnumeric, ogr,gdal_array
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import os
import operator
gdal.UseExceptions()
# This function will convert the rasterized clipper shapefile
# to a mask for use within GDAL.
def imageToArray(i):
"""
Converts a Python Imaging Library array to a
gdalnumeric image.
"""
a = gdalnumeric.fromstring(i.tobytes(), 'b')
a.shape = i.im.size[1], i.im.size[0]
return a
def arrayToImage(a):
"""
Converts a gdalnumeric array to a
Python Imaging Library Image.
"""
i = Image.frombytes('L', (a.shape[1], a.shape[0]),
(a.astype('b')).tobytes())
return i
def world2Pixel(geoMatrix, x, y):
"""
Uses a gdal geomatrix (gdal.GetGeoTransform()) to calculate
the pixel location of a geospatial coordinate
"""
# GetGeoTransform返回值:左上角x坐标, 水平分辨率,旋转参数, 左上角y坐标,旋转参数,竖直分辨率。
ulX = geoMatrix[0]
ulY = geoMatrix[3]
xDist = geoMatrix[1] # 水平分辨率
pixel = int((x - ulX) / xDist)
line = int((ulY - y) / xDist)
return (pixel, line)
#
# EDIT: this is basically an overloaded
# version of the gdal_array.OpenArray passing in xoff, yoff explicitly
# so we can pass these params off to CopyDatasetInfo
#
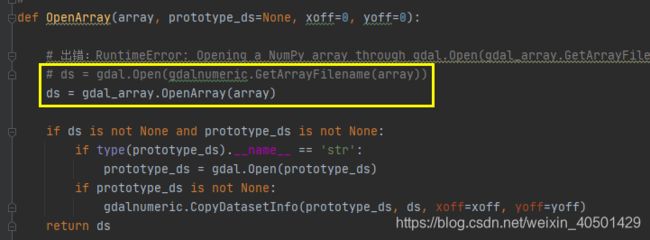
def OpenArray(array, prototype_ds=None, xoff=0, yoff=0):
# 出错:RuntimeError: Opening a NumPy array through gdal.Open(gdal_array.GetArrayFilename()) is no longer supported by default unless the GDAL_ARRAY_OPEN_BY_FILENAME configuration option is set to TRUE. The recommended way is to use gdal_array.OpenArray() instead.
# ds = gdal.Open(gdalnumeric.GetArrayFilename(array))
ds = gdal_array.OpenArray(array)
if ds is not None and prototype_ds is not None:
if type(prototype_ds).__name__ == 'str':
prototype_ds = gdal.Open(prototype_ds)
if prototype_ds is not None:
gdalnumeric.CopyDatasetInfo(prototype_ds, ds, xoff=xoff, yoff=yoff)
return ds
def histogram(a, bins=range(0, 256)):
"""
Histogram function for multi-dimensional array.
a = array
bins = range of numbers to match
"""
fa = a.flat
n = gdalnumeric.searchsorted(gdalnumeric.sort(fa), bins)
n = gdalnumeric.concatenate([n, [len(fa)]])
hist = n[1:] - n[:-1]
return hist
def stretch(a):
"""
Performs a histogram stretch on a gdalnumeric array image.
"""
hist = histogram(a)
im = arrayToImage(a)
lut = []
for b in range(0, len(hist), 256):
# step size
step = reduce(operator.add, hist[b:b + 256]) / 255
# create equalization lookup table
n = 0
for i in range(256):
lut.append(n / step)
n = n + hist[i + b]
im = im.point(lut)
return imageToArray(im)
def main(shapefile_path, raster_path):
# Load the source data as a gdalnumeric array
srcArray = gdalnumeric.LoadFile(raster_path)
# Also load as a gdal image to get geotransform
# (world file) info
srcImage = gdal.Open(raster_path)
geoTrans = srcImage.GetGeoTransform()
# Create an OGR layer from a boundary shapefile
shapef = ogr.Open(shapefile_path)
# os.path.split() 常用于将文件路径与文件名分割开,结果以元组的形式显示(python自带的split()也可以实现相同的效果)。
# os.path.splitext() 将文件名与文件后缀名分割开,结果以元组的形式显示(python自带的split()也可以实现相同的效果)。
# os.path.splitext(shapefile_path)得到一个元组,两部分:文件名+扩展名。[0]是文件名,[1]为扩展名。
# GetLayer()的参数是从0开始的。对于Shapefile而言,它只有一个图层,一般情况下这个参数都是0,如果空着,缺省情况下也是0。
# 该函数是DataSource类的一个成员函数,用来获取第一个图层,返回的是一个Layer类的对象。若返回None,表示获取第一个图层失败。另外,矢量图层的计数是从0开始的,而栅格数据则从1开始,其实shp文件只有一个图层。
lyr = shapef.GetLayer(os.path.split(os.path.splitext(shapefile_path)[0])[1])
# # dir(lyr)返回当前范围内的变量、方法和定义的类型列表
# dir(lyr)
# GetNextFeature可获取层内所有的要素
poly = lyr.GetNextFeature()
# Convert the layer extent to image pixel coordinates
minX, maxX, minY, maxY = lyr.GetExtent()
ulX, ulY = world2Pixel(geoTrans, minX, maxY) # (x方向像素,y方向像素)
lrX, lrY = world2Pixel(geoTrans, maxX, minY) # (x方向像素,y方向像素)
# Calculate the pixel size of the new image
pxWidth = int(lrX - ulX)
pxHeight = int(lrY - ulY)
# clip = srcArray[:, ulY:lrY, ulX:lrX]
clip = srcArray[ulY:lrY, ulX:lrX]
# EDIT: create pixel offset to pass to new image Projection info
#
xoffset = ulX
yoffset = ulY
print
"Xoffset, Yoffset = ( %f, %f )" % (xoffset, yoffset)
# Create a new geomatrix for the image
geoTrans = list(geoTrans)
# 左上角的坐标值
geoTrans[0] = minX
geoTrans[3] = maxY
# Map points to pixels for drawing the boundary on a blank 8-bit, black and white, mask image.
points = []
pixels = []
# 该函数是Feature类的成员函数,作用是获取要素的空间坐标信息,返回值为Geometry类对象。
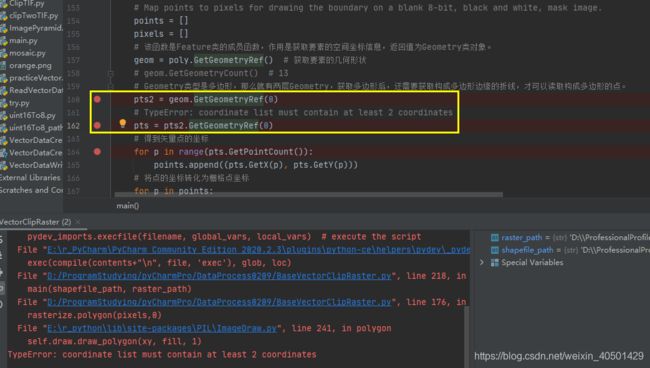
geom = poly.GetGeometryRef() # 获取要素的几何形状
# geom.GetGeometryCount() # 13
# Geometry类型是多边形,那么就有两层Geometry,获取多边形后,还需要获取构成多边形边缘的折线,才可以读取构成多边形的点。
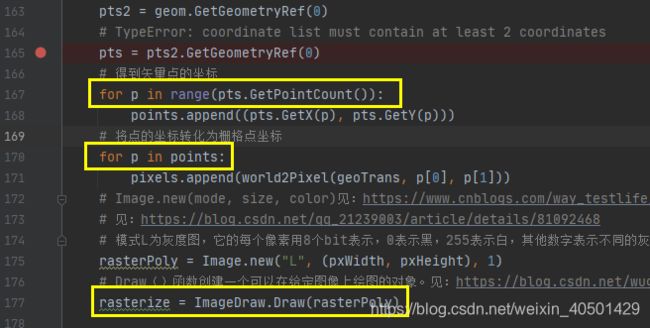
pts2 = geom.GetGeometryRef(0)
# TypeError: coordinate list must contain at least 2 coordinates
pts = pts2.GetGeometryRef(0)
# 得到矢量点的坐标
for p in range(pts.GetPointCount()):
points.append((pts.GetX(p), pts.GetY(p)))
# 将点的坐标转化为栅格点坐标
for p in points:
pixels.append(world2Pixel(geoTrans, p[0], p[1]))
# Image.new(mode, size, color)见:https://www.cnblogs.com/way_testlife/archive/2011/04/20/2022997.html
# 见:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21239003/article/details/81092468
# 模式L为灰度图,它的每个像素用8个bit表示,0表示黑,255表示白,其他数字表示不同的灰度。
rasterPoly = Image.new("L", (pxWidth, pxHeight), 1)
# Draw()函数创建一个可以在给定图像上绘图的对象。见:https://blog.csdn.net/wuguangbin1230/article/details/80348504
rasterize = ImageDraw.Draw(rasterPoly)
# TypeError: coordinate list must contain at least 2 coordinates。将shapefile从multiPolygon换成Polygon时,此句话不会出错。
rasterize.polygon(pixels,0)
mask = imageToArray(rasterPoly)
# Clip the image using the mask
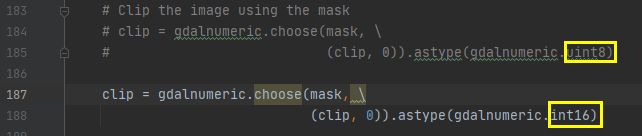
# clip = gdalnumeric.choose(mask, \
# (clip, 0)).astype(gdalnumeric.uint8)
clip = gdalnumeric.choose(mask, \
(clip, 0)).astype(gdalnumeric.int16)
# # This image has 1 bands so we stretch each one to make them visually brighter
# # 无需拉伸,注释掉
# for i in range(3):
# clip[i, :, :] = stretch(clip[i, :, :])
# Save new tiff
#
# EDIT: instead of SaveArray, let's break all the
# SaveArray steps out more explicity so
# we can overwrite the offset of the destination
# raster
#
### the old way using SaveArray
# gdalnumeric.SaveArray(clip, "OUTPUT.tif", format="GTiff", prototype=raster_path)
gtiffDriver = gdal.GetDriverByName('GTiff')
if gtiffDriver is None:
raise ValueError("Can't find GeoTiff Driver")
gtiffDriver.CreateCopy("D:\ProfessionalProfile\DEMdata\OutputDataPython\shandong_int16.tif", OpenArray(clip, prototype_ds=raster_path, xoff=xoffset, yoff=yoffset))
# # Save as an 8-bit jpeg for an easy, quick preview
# clip = clip.astype(gdalnumeric.uint8)
# gdalnumeric.SaveArray(clip, "D:\ProfessionalProfile\DEMdata\OutputDataPython\shandong.jpg", format="JPEG")
gdal.ErrorReset()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# shapefile_path, raster_path
shapefile_path = 'D:\ProfessionalProfile\VectorRelevant\VectorDataofRivers-lakes-etc\ShandongProvince\shandong.shp'
raster_path = 'D:\ProfessionalProfile\DEMdata\OutputDataPython\demMosaic1224.tif'
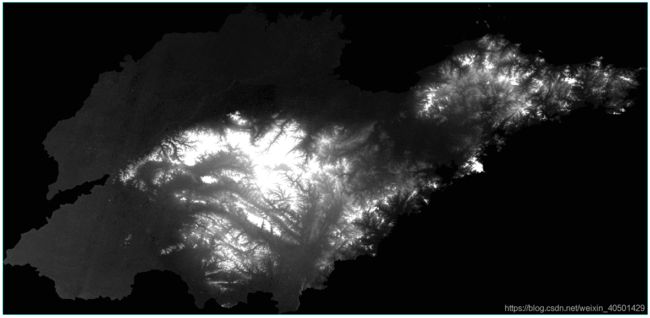
main(shapefile_path, raster_path)最后的运行结果在ENVI中打开:(上侧是用Python处理后的,下侧是用ENVI软件裁剪的)
两幅图明显不一样,看了一下Metadata和统计信息:(1)Python输出的是8bit图像,ENVI裁剪的是16bit图像。(后续再改一下)(2)列数差了一列。因为是30米的精度,个人感觉差一列并不是什么大问题。
修改一下,将数据类型 uint8 修改为 int16 即可。
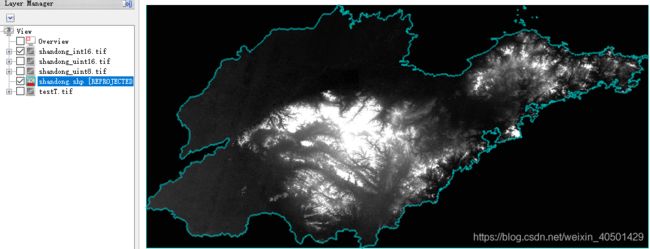
最后,Python运行完的结果如下:
3.代码运行过程中的错误
(1)TypeError: coordinate list must contain at least 2 coordinates
看了一下是因为,points 和 pixels变量都是空的,pts.GetPointCount()函数得不到任何值。查询了一下,Geometry类型是多边形,那么就有两层Geometry,获取多边形后,还需要获取构成多边形边缘的折线,才可以读取构成多边形的点。所以加了一句话:
pts = pts2.GetGeometryRef(0),此时的pts是'LINEARRING',GetPointCount()才能得到点的个数,后续就不报错了。
(2) 出错:RuntimeError: Opening a NumPy array through gdal.Open(gdal_array.GetArrayFilename()) is no longer supported by default unless the GDAL_ARRAY_OPEN_BY_FILENAME configuration option is set to TRUE. The recommended way is to use gdal_array.OpenArray() instead.
将ds = gdal.Open(gdalnumeric.GetArrayFilename(array)) 改成 ds = gdal_array.OpenArray(array),就可以了。
最后没报错,出现一个警告:D:/ProgramStudying/pyCharmPro/DataProcess0209/BaseVectorClipRaster.py:27: DeprecationWarning: The binary mode of fromstring is deprecated, as it behaves surprisingly on unicode inputs. Use frombuffer instead
a = gdalnumeric.fromstring(i.tobytes(), 'b')