数据结构之栈的讲解
"
春宵一刻值千金,花有清香月有阴。
"
作者:Mylvzi
文章主要内容:leetcode刷题之哈希表的应用(1)
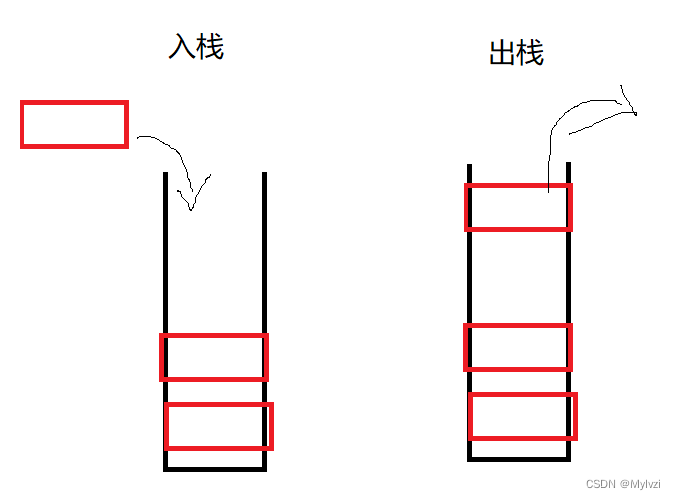
1.栈的概念
栈是一种只允许在一端(栈顶)进行数据操作的数据结构,具有“后进先出”的特性,也叫做Last in First Out
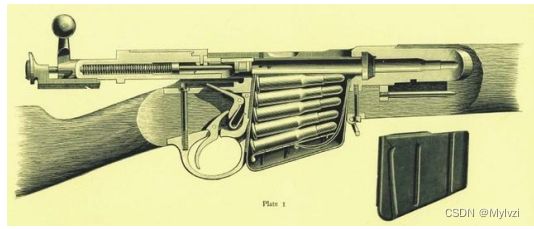
最常见的现实生活中的例子就是压子弹 只能一端压子弹
2.栈的模拟实现
我们想想什么可以实现栈的操作呢?我们知道,栈最大的特性就行只能在一端进行数据操作,使用数组可以更好的模拟栈
数组的末尾就是我的栈顶,操作栈顶就是操作数组的最后一个元素,而数组最后一个元素的添加,删除都很方便!!!
1.使用数组模拟
public class MyStack {
/**
* 栈的实现一:用数组实现栈
*/
private int[] elem;
private int usedSize;
private static final int DEFAULTCAPACITY = 10;
public MyStack() {
this.elem = new int[DEFAULTCAPACITY];
}
public MyStack(int size) {
this.elem = new int[size];
}
public void push(int val) {
if (isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[usedSize] = val;
this.usedSize++;
}
private boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
/* if (this.elem.length == this.usedSize) {
return true;
}
return false;*/
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new StackEmptyException("栈区之内不含有数据,无法删除");
}
// this.usedSize--;
// return this.elem[usedSize];
int oldVal = this.elem[usedSize-1];
this.usedSize--;
return oldVal;
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new StackEmptyException("栈区之内不含有数据,无法删除");
}
return this.elem[usedSize-1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
/* if (this.usedSize == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;*/
}
}2.使用链表模拟
当然除了使用数组模拟栈,使用链表也可以实现栈的功能(Java中的LinkedList本质上是一个无头双向非循环链表)
class Mystack3 {
// 使用链表模拟栈
/**
* 栈只能在一端进行数据的操作
* 在这里我们只在链表的last进行数据的操作
*/
LinkedList mystack = new LinkedList<>();
// push
public void push(int data) {
mystack.addLast(data);
}
// pop
public int pop() {
if(mystack.isEmpty()) {
return -1;// 抛异常也可以
}
return mystack.pollLast();
}
public int peek() {
return mystack.peekLast();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mystack3 mystack3 = new Mystack3();
mystack3.push(1);
mystack3.push(2);
mystack3.push(3);
System.out.println(mystack3.pop());// 3
System.out.println(mystack3.peek());// 2
}
} 3.Java中的栈Stack
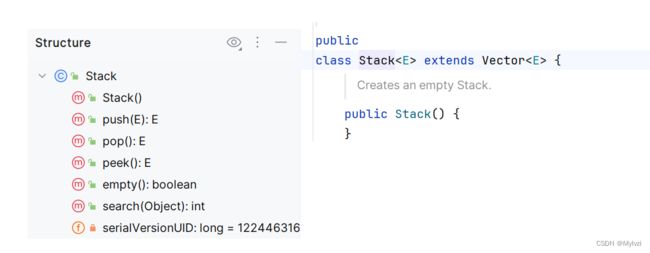
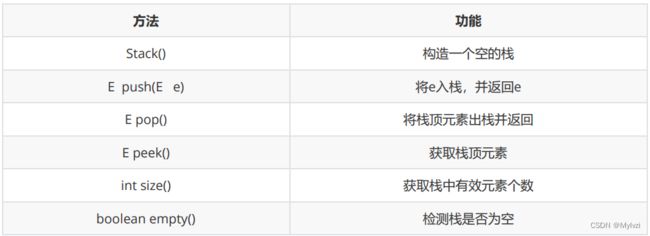
Java中提供了现成的栈供我们使用
代码演示
// 栈的创建 栈在Java中就是一个类!!!
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
// 使用构造器
Iterator it= stack.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next()+" ");// 1 2 3 4
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("============================");
// 重写了toString方法 直接传对象 即可打印内容
System.out.println(stack);// 1 2 3 4
// pop会删除栈顶元素
stack.pop();
System.out.println(stack);// 1 2 3
// peek 瞄一眼 不会把top删除
int x = stack.peek();
System.out.println(x);// 3
} 4.栈的应用场景
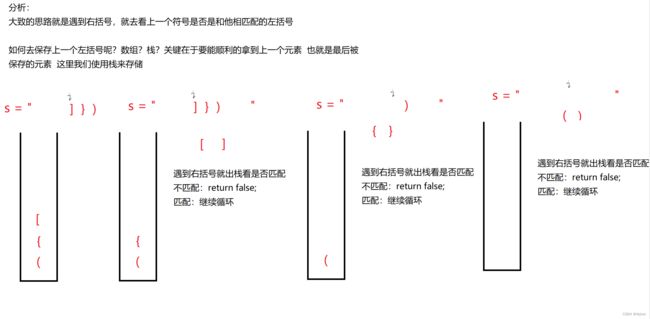
1.括号匹配问题
20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/
分析:
代码实现:
class Solution {
public static boolean isValid(String s) {
if(s.length() % 2 != 0) return false;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
// 获取当前字符
char ch = s.charAt(i);
// 左括号
if(ch == '(' || ch == '{' || ch == '[') {
stack.push(ch);
}else {// 右括号
if(stack.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}else {
// 要进行括号匹配
char top = stack.peek();
if(ch == '}' && top == '{' || ch == ')' && top == '(' ||ch == ']' && top == '[') {
stack.pop();
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
} 也可以使用顺序表实现
class Solution {
public static boolean isValid(String s) {
if(s.length() % 2 != 0) return false;
List list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
// 获取当前字符
char ch = s.charAt(i);
// 左括号
if(ch == '(' || ch == '{' || ch == '[') {
list.add(ch);
}else {// 右括号
if(list.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}else {
// 要进行括号匹配
char top = list.get(list.size()-1);
if(ch == '}' && top == '{' || ch == ')' && top == '(' ||ch == ']' && top == '[') {
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return list.isEmpty();
}
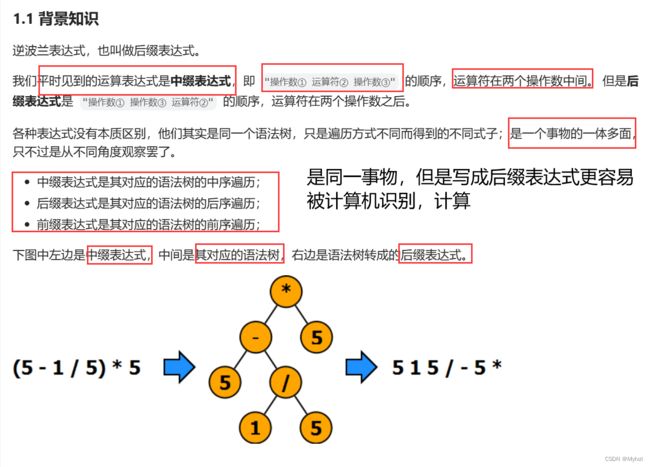
} 2.后缀表达式
代码实现:
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
// 遇到数字存放到栈中
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// 循环遍历所给字符串
for(String s : tokens) {
// 数字
if(!isOperation(s)) {
// 是数字就push
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(s));
}else {// 运算符
// 先弹出的作右运算符 后弹出的是左运算符
int num2 = stack.pop();
int num1 = stack.pop();
switch(s) {
case "+":
stack.push(num1+num2);
break;
case "-":
stack.push(num1-num2);
break;
case "*":
stack.push(num1*num2);
break;
case "/":
stack.push(num1/num2);
break;
}
}
}
// 遍历完 返回栈的最后一个(唯一一个)元素
return stack.pop();
}
// 判断是否是运算符
private boolean isOperation(String s) {
if(s.equals("+") || s.equals("-") || s.equals("*") || s.equals("/")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
} 3.最小栈
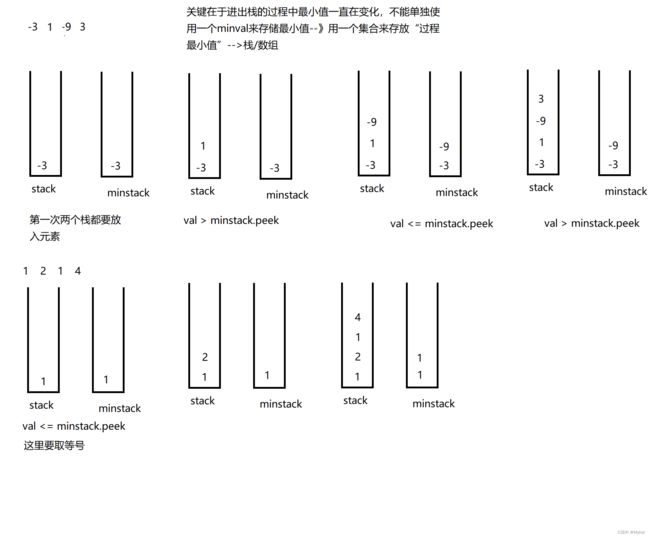
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-stack/submissions/分析思路:
https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-stack/submissions/分析思路:
代码实现:使用两个栈
class MinStack {
//思路1 使用两个栈
private Stack stack;
private Stack minstack;// 存放过程中的最小值
public MinStack() {
this.stack = new Stack<>();
this.minstack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int val) {
if(minstack.isEmpty()) {
minstack.push(val);
}else {
if (val <= minstack.peek()) {
minstack.push(val);
}
}
stack.push(val);
}
public void pop() {
if(!stack.isEmpty()) {
int top = stack.pop();
if (top == minstack.peek()) {
minstack.pop();
}
}
}
public int top() {
if(stack.empty()) {
return -1;
}
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
if (minstack.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return minstack.peek();
}
} 思路2:使用链表实现
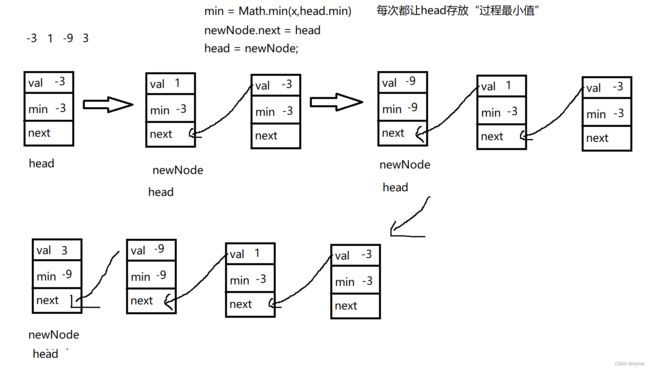
画图分析
代码实现
class MinStack {
// 使用链表实现
private class Node{
int val;
int min;
Node next = null;
public Node(int val, int min) {
this.val = val;
this.min = min;
}
}
private Node head;
public void push(int x) {
if(head == null) {
head = new Node(x,x);
}else {
Node newNode = new Node(x,Math.min(x,head.min));
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
}
}
public void pop() {
head = head.next;
}
public int top() {
return head.val;
}
public int getMin() {
return head.min;
}
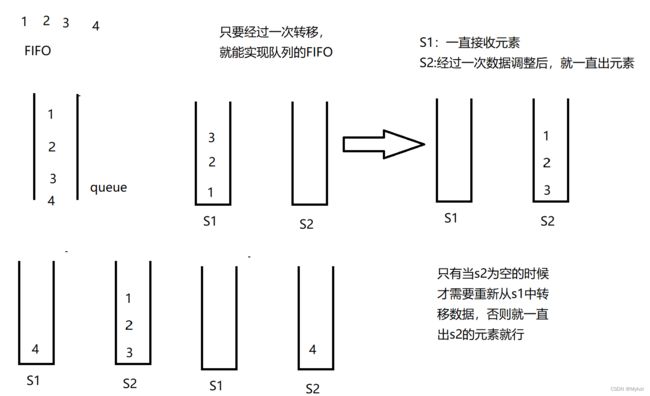
}4.用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class MyQueue {
// 只需要转移一次就能实现顺序的完全颠倒
private Stack stack1;
private Stack stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
// stack1的栈底元素才是我第一个要出的元素
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
// 只有当s2为空的时候才需要从s1中转移数据,否则就一直出s2中的数据即可
if(stack2.empty()) {
while(!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (stack2.empty()) {
while(!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack2.empty() && stack1.empty();
}
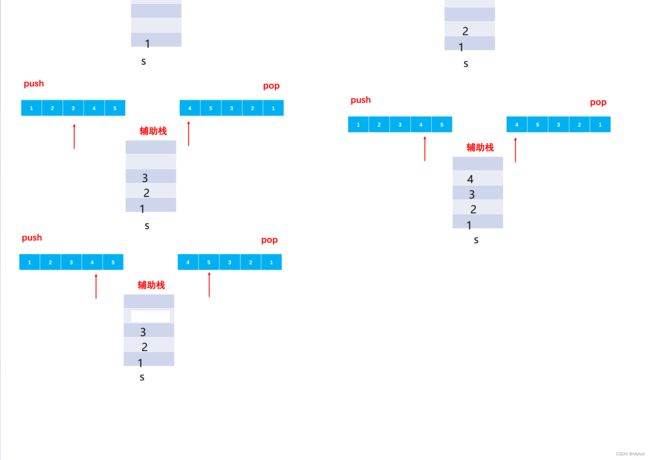
} 5.栈的压入、弹出序列
栈的压入、弹出序列_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
使用一个辅助站来模拟栈的入栈和出栈
代码实现
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pushV int整型一维数组
* @param popV int整型一维数组
* @return bool布尔型
*/
public boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushV, int[] popV) {
// write code here
// 使用辅助栈 模拟出栈的过程
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// j去遍历入栈数组
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < pushV.length; i++) {
// 当j没有遍历完 &&(栈为空 || 栈顶和出栈的数组的元素不同)--入栈
while(j< pushV.length &&(stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek()!=popV[i])) {
stack.push(pushV[j++]);
}
// 出循环 栈顶和popV[i]相等
if(stack.peek() == popV[i]) {
stack.pop();
}else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
} 思路2:开辟辅助栈 遍历入栈序列 相等就出栈 最后判断栈是否为空
public boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushV, int[] popV) {
// write code here
// 使用辅助栈 模拟出栈的过程
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
int j = 0;// 遍历出栈序列
for (int i = 0; i < pushV.length; i++) {
stack.push(pushV[i]);
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == popV[j]) {
stack.pop();
j++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
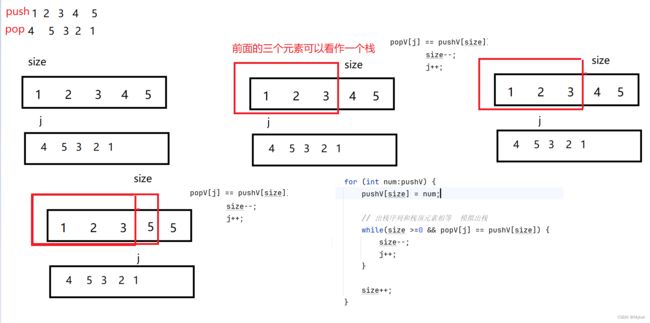
} 思路3:使用size来抽象代替栈的元素个数
把入栈序列遍历完,最后看是否为空
public boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushV, int[] popV) {
// write code here
int size = 0,j=0;
for (int num:pushV) {
pushV[size] = num;
// 出栈序列和栈顶元素相等 模拟出栈
while(size >=0 && popV[j] == pushV[size]) {
size--;
j++;
}
size++;
}
return size == 0;
}使用下标+数组可以模拟栈的操作,使空间复杂度为0(1)