算法:(1)剑指offer,python实现
算法:剑指offer,python实现
- 参考
- *. 基础
-
- 0.1 查找和排序
-
- 0.1.1 快速排序
- 0.1.2 二分法
- 2.4.4 动态规划与贪婪算法
- 2.4.5 位运算
- 题目
-
- 11题:旋转数组的最小数字
-
- 分析
- 实现
- 12题:矩阵中的路径
-
- 分析
- 13题:机器人的运动范围
- 14题:剪绳子(动态规划、贪婪算法)
-
- 分析(动态规划)
- 代码
- 分析(贪婪算法)
- 代码
- 15题:二进制中1的个数
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 相关题目
- 18题:删除链表的节点
-
- 题意1:给定单向链表的头指针和节点指针,在 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)时间内删除指定的节点。
- 代码
- 题意2:在一个排序的链表中,删除链表中重复的节点。
- 19题:正则表达式匹配
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 20题:表示数值的字符串判断
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 【3.4】代码的鲁棒性
-
- 23题:链表中环的入口节点
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 24题:反转链表
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 25题:合并两个排序的链表
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 26. 树的子结构(待更)
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 【4.2】画图让抽象问题更加形象化
-
- 27. 二叉树的镜像
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 28. 对称的二叉树
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 【4.3】举例让抽象问题更加形象化
-
- 30. 包含min函数的栈
-
- 分析
- 代码(需要定义类)
- 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 32_1. 从上到下打印二叉树——题目一:不分行,还需要看前序、中序、后序打印
-
- 代码
- 32_2. 从上到下打印二叉树——题目二:分行,还需要看前序、中序、后序打印
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 32_3:从上到下打印二叉树——题目三:分行+之字形
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 【4.4】分解让复杂问题简单化(分治法)
-
- 35. 复杂链表的复制
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 36. 二叉搜索树以及双向链表
-
- 代码(该题先上代码,再分析)
- 分析
- 37. 序列化和反序列化二叉树
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 38. 字符串的排列
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 38-2. 字符串的组合
-
- 分析
- 代码
- 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
-
- 代码
参考
大神
python算法书!
*. 基础
0.1 查找和排序
冒泡排序、插入排序、快速排序、选择排序、归并排序
参考1
参考2
| 顺序查找 | 二分查找 | 哈希表查找 | 二叉排序树查找 |
|---|---|---|---|
| -------- | -------- | 时间O(1),需要额外的空间 |
插入排序、冒泡排序、归并排序、快速排序不同算法的优劣
0.1.1 快速排序
关键在于数组中选择一个数字,根据数组中数字的相对于这个基准值的大小,小的排在基准值左边(前面),大的排在基准值后面。实现的办法是,有两个指针,左指针遍历取相对大的数,和右指针所取的相对小的数,两者进行调换,从而逐渐地将大的数放到右边,小的数放到左边。
def quickSort(alist):
quickSortHelper(alist,0,len(alist)-1)
def quickSortHelper(alist,first,last):
#基本结束条件
if first<last:
#分裂为两部分
splitpoint=partition(alist,first,last)
print(alist)
#递归调用
quickSortHelper(alist,first,splitpoint-1)
quickSortHelper(alist,splitpoint+1,last)
def partition(alist,first,last):
#选定中值
mid=alist[first]
leftmark=first+1
rightmark=last
done=False
while not done:
while leftmark<=rightmark and alist[leftmark]<=mid:
leftmark=leftmark+1
while rightmark>=leftmark and alist[rightmark]>=mid:
rightmark-=1
# 两标相错就结束移动
if rightmark<leftmark:
done=True
# 左右两标指向的值交换,继续移动
else:
temp=alist[leftmark]
alist[leftmark]=alist[rightmark]
alist[rightmark]=temp
# 把mid调换到rightmark因为rightmark是新的分界点,刚好是mid值的排序位置。
temp2=alist[first]
alist[first]=alist[rightmark]
alist[rightmark]=temp2
return rightmark
alist=[10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0]
quickSort(alist)极简法
def quicksort(alist):
if len(alist) >= 2:
mid = alist[0]
left = []
right = []
alist.remove(mid)
for i in alist:
if i <= mid:
left.append(i)
else:
right.append(i)
return quicksort(left) + [mid] + quicksort(right)
else:
return alist
alist=[10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0]
alist_copy = alist.copy()
print(quicksort(alist_copy))0.1.2 二分法
要求在排序(部分排序)的数组中,查找一个数字或者统计某个数字出现的次数,可以用二分查找。
2.4.4 动态规划与贪婪算法
动态规划:大问题分解为小问题,小问题存在最优解,则合并之后成为大问题的最优解。
贪婪算法:每一步都是贪婪选择,最后依靠数学方式证明最后达到最优解。
2.4.5 位运算
数字二进制的表示后进行的运算。5种运算:与、或、异或、左移、右移。
左移n位:最左边的n位将被丢弃,最右边补上n个0。
右移n位:最右边的n位将被丢弃,如果是正数,最左边补n个0;如果是负数,最左边补n个1。
00001010 << 2 = 00101000
10001010 << 3 = 01010000
00001010 >> 2 = 00000010
10001010 >> 3 = 11110001
题目
excel中,用AA 表示第27列,AB表示第28列,写出一个函数,输入用字母表示的列表编码,输出它是第几列。
line = input()
n = len(line)
alist = []
for j in line:
alist.append(int(j,36)-9)
num = 0
for i in range(n):
num += alist[i] * (26**(n-i-1))
print(num)题目
11题:旋转数组的最小数字
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。 输入一个非减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。 例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。 NOTE:给出的所有元素都大于0,若数组大小为0,请返回0。
分析
如果按照从头到尾遍历, O ( n ) O(n) O(n)的时间复杂度,则浪费了旋转数组——部分排序的条件。可以使用二分查找, O ( l o g ( n ) ) O(log(n)) O(log(n))的时间复杂度。
依据题意,能够知道,前半、后半部分都为非减情况,同时一般情况下,第一个数大于等于最小数,最后一个数也大于最小数。
使用两个指针,分别指向第一个和最后一个数字。找到中间元素,如果位于后半序列,说明最小值在中间值前面,更新第二个(位于最后)指针到中间位置;如果位于前半序列,说明最小值在中间值后面,更新第一个(位于开始)指针到中间位置。
实现
考虑一般情况
def find2(alist):
if len(alist)==0: return "enter number list"
index1 = 0
index2 = len(alist)-1
indexmid = index1
# 为了防止是将0个元素旋转,
# 则第一个数判断为小于末尾数则是排序完毕的数组。
while alist[index1] >= alist[index2]:
if index1 == index2 - 1:
indexmid = index2
break
indexmid = (index1 + index2) // 2
# 落于两种位置,结合index1/2判断。
if alist[indexmid] >= alist[index1]:
index1 = indexmid
elif alist[indexmid] <= alist[index2]:
index2 = indexmid
return alist[indexmid]
alist=[5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,1,2,3,4]
alist_copy = alist.copy()
print(find2(alist_copy))12题:矩阵中的路径
请设计一个函数,用来判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向左,向右,向上,向下移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则之后不能再次进入这个格子。 例如
a b c e
s f c s
a d e e
这样的3 X 4 矩阵中包含一条字符串"bcced"的路径,但是矩阵中不包含"abcb"路径,因为字符串的第一个字符b占据了矩阵中的第一行第二个格子之后,路径不能再次进入该格子。
分析
回溯法:像树一样,如果发生条件不符,则回到原位,往别的方向走。
由于有回溯法的递归特质,可以考虑使用栈作为路径。由于不能重复进入路径,所以需要矩阵一样大小的布尔值矩阵。
# 伪代码
def shape()
找到id1(可能有多个位置符合)
上下左右,找id(i-1)
Y:更新i,j
N:返回i,jdef haspath(matrix, rows, cols, path):
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if matrix[i * cols + j] == path[0]:
if findpath(list(matrix), rows, cols, path[1:],i,j):
return True
def findpath(matrix, rows, cols, path, i, j):
if not path:
return True
matrix[i*cols + j] = 0
if j+1 < cols and matrix[i*cols + j + 1]==path[0]:
return findpath(matrix, rows, cols, path[1:],i, j+1)
elif j-1 >= 0 and matrix[i*cols + j - 1]==path[0]:
return findpath(matrix, rows, cols, path[1:],i, j-1)
elif i+1 < rows and matrix[(i+1)*cols + j]==path[0]:
return findpath(matrix, rows, cols, path[1:],i+1, j)
elif i-1 >= 0 and matrix[(i-1)*cols + j]==path[0]:
return findpath(matrix, rows, cols, path[1:],i-1, j)
return False
matrix = 'abcesfcsadee'
path = 'bcced'
print(haspath(matrix, 3,4,path))13题:机器人的运动范围
地上有一个m行和n列的方格。一个机器人从坐标0,0的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。 例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格(35,37),因为3+5+3+7 = 18。但是,它不能进入方格(35,38),因为3+5+3+8 = 19。请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
不确定对否
def movingCount(threshold, rows, cols):
if threshold < 0 or rows <= 0 or cols <= 0:
return 0
visited = [False]*(rows*cols)
count = movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, 0,0, visited)
del(visited)
return count
def movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row, col, visited):
count = 0
if check(threshold, rows, cols, row, col, visited):
visited[row * cols + col] = True
count = 1+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row-1, col, visited)\
+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row+1, col, visited)\
+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row, col-1, visited)\
+ movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row, col+1, visited)
return count
def check(threshold, rows, cols, row, col, visited):
if row >= 0 and row < rows and col >= 0 and col < cols \
and getDigit(row) + getDigit(col) <= threshold \
and not visited[row * cols + col]:
return True
return False
def getDigit(num):
sum1 = 0
while num > 0:
sum1 += num%10
num //= 10
return sum1
print(movingCount(3, 40,40) )14题:剪绳子(动态规划、贪婪算法)
剪成若干段,得到各段的乘积最大。
分析(动态规划)
首先定义 f ( n ) f(n) f(n)为长度为 n n n的绳子,剪成若干段后各段乘积最大值。假设在 i i i处剪了,得到 f ( n ) = f ( i ) ∗ f ( n − i ) , 0 < i < n f(n)=f(i)*f(n-i), 0
代码
length = int(input())
if length < 2: print(0)
if length == 2: print(1)
if length == 3: print(2)
products = [0] * (length + 1)
products[0] = 0
products[1] = 1
products[2] = 2
products[3] = 3
max1 = 0
for i in range(4,length+1):
max1 = 0
for j in range(1,i//2+1):
product = products[j] * products[i-j]
if max1 < product:
max1 = product
products[i] = max1
max2 = products[length]
print(max2)分析(贪婪算法)
如果n大于5,则尽量剪长度为3的绳子;当剩下的绳子长度为4时,剪成两段2的绳子。当n大于等于6时,应该剪更短,所以最后都会出现3的长度。
代码
length = int(input())
if length < 2: print(0)
if length == 2: print(1)
if length == 3: print(2)
timesof3 = length//3
# 此时,余下了1(比如4),所以更好的方法是将其剪成2*2而非3*1
if length - timesof3 * 3 == 1:
timesof3 -= 1
timesof2 = (length - timesof3 * 3) // 2
print((3 ** timesof3)*(2 ** timesof2))15题:二进制中1的个数
分析
将num位右移1位,不断得到最后一位数,并且运算后去除。
num和1进行求“位与运算”,由于1的左边均为0,所以只要是最后一位是1,则求得1,是0则求得0.
注:尽量用位移来代替除以2,以提高效率。
代码
测试用例:
正数(包括边界值)、负数、0
- 可能引起死循环的代码(比如无法处理负数)
def NumberOf1(num):
count = 0
while num:
if num & 1:
count += 1
num = num >> 1
return count
num = int(input())
print(NumberOf1(num))- 常规解法:通过位移flag来进行各个位的比较,但是需要将flag限制int的条件(即232)
def NumberOf1(num):
count = 0
flag = 1
while flag <= 2**32:
if num & flag:
count += 1
flag = flag << 1
return count
num = int(input())
print(NumberOf1(num))- 智商解法。。。
一个例子:1100,该二进制数减去1的情况下,成为1011,两者再求位与关系,即能够将原来最接近右边的1(即1100的第二个1)的右边(包括本身)全变成0,成为新的数,进行另一轮计算。count++
def NumberOf1(num):
count = 0
while num:
count += 1
num = num & (num - 1)
return count
num = int(input())
print(NumberOf1(num))相关题目
- 用一条语句判断一个整数是不是2的整数次方。
分析:易知它的二进制数是只有一位是1,所以在减1 之后,和自己进行位与计算,应该得到全部是0.
def IfSqr(num):
if num & (num - 1) == 0: return True
return False
for _ in range(5):
print(IfSqr(int(input())))- 输入两个整数 m m m和 n n n,计算需要改变 m m m的二进制表示中的多少位才可以得到 n n n。比如10的二进制表示为1010,13的二进制为1101, 需要改变1010中的三位才可以得到1101。
分析:需要得到不同的位的数目,所以运行“异或运算”,再按照此前的手法取得该二进制数的1的数目。
def func(num1,num2):
num = num1 ^ num2
count = 0
while num:
count += 1
num = num & (num - 1)
return count
import sys
for _ in range(5):
line = sys.stdin.readline().strip().split()
print(func(int(line[0]),int(line[1]) ) )18题:删除链表的节点
题意1:给定单向链表的头指针和节点指针,在 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)时间内删除指定的节点。
如果全部都是按照遍历到指定节点的话,会有 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)的复杂时间程度。
(1)如果先把指定的 i i i 节点的下一个节点j节点复制到 i i i,然后把 i i i 的指针指向节点 j j j 的下一个节点,相当于把 i i i 删除了。时间为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)。
(2)此外,如果 i i i 节点在尾部,没有下一个节点,则仍旧需要从最开始进行遍历。
(3)此外,可能存在只有一个节点的情况,则直接删除节点 i i i 即可。
因此时间复杂度为: [ ( n − 1 ) O ( 1 ) + O ( n ) ] / n = O ( 1 ) [(n-1)O(1)+O(n)]/n=O(1) [(n−1)O(1)+O(n)]/n=O(1)
代码
引用链接
class ListNode:
def __init__(self):
self.value = None
self.next_node = None
class Solution:
def list_generate(self, lst):
"""
生成链表
"""
if not lst:
return None
list_node = ListNode()
list_node.value = lst[0]
if len(lst) == 1:
list_node.next_node = None
else:
list_node.next_node = self.list_generate(lst[1:])
return list_node
def find_node(self, node, target_value):
"""
根据给定的目标值,找出指定节点的位置
非题目要求,只是为了测试验证
"""
if not target_value:
return False
while node:
if node.value == target_value:
return node
node = node.next_node
return False
def delete_node(self, head_node, del_node):
"""
删除指定节点
"""
if not (head_node and del_node):
return False
if del_node.next_node:
# 删除的节点不是尾节点,而且不是唯一一个节点
del_next_node = del_node.next_node
del_node.value = del_next_node.value
del_node.next_node = del_next_node.next_node
del_next_node.value = None
del_next_node.next_node =None
elif del_node == head_node:
# 唯一一个节点,删除头节点
head_node = None
del_node = None
else:
# 删除节点为尾节点
node = head_node
while node.next_node != del_node:
node = node.next_node
node.next_node = None
del_node = None
return head_node题意2:在一个排序的链表中,删除链表中重复的节点。
# 接上例
def is_repeat(self, node):
"""
题目二:判断是否与后面的节点重复
"""
if node.next_node:
if node.value == node.next_node.value:
return True
return False
def delete_repeat_node(self, head_node):
"""
题目二:删除重复节点
"""
node = head_node
flag = False
"""
flag说明:例如'a'->'a',第一次循环删除第二个'a',然后通过这个flag来进行判断上一次操作是否删除重复节点
如果是的话,再次判断后面还有没有'a'了,没有,则通过这个flag把第一个'a'也应该删除,
"""
while node:
if solution.is_repeat(node):
# 删除重复节点,并且不进行node=node.next_node,可能出现连续多个重复节点
head_node = self.delete_node(head_node, node)
flag = True
else:
if flag:
head_node = self.delete_node(head_node, node)
flag = False
node = node.next_node
return head_node
if __name__ == '__main__':
solution = Solution()
head_node = solution.list_generate(['a', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'e', 'd', 'd'])# 测试用例
# ----------------------------------------------------
# 题目一: 删除指点节点
# target_value = 'a'
# target_node = solution.find_node(head_node, target_value)
# if target_node:
# print target_node.value
# head_node = solution.delete_node(head_node, target_node)
# ---------------------------------------------------
# ---------------------------------------------------
# 题目二:删除重复节点
head_node = solution.delete_repeat_node(head_node)
# --------------------------------------------------
# 输出,打印新链表
node = head_node
if node:
while node:
print(node.value,'->')
node = node.next_node
else:
print('wrong')19题:正则表达式匹配
分析
请实现一个函数用来匹配包括’.‘和’‘的正则表达式。模式中的字符’.‘表示任意一个字符,而’'表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(包含0次)。 在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式。例如,字符串"aaa"与模式"a.a"和"abaca"匹配,但是与"aa.a"和"ab*a"均不匹配
分析:参考链接
当模式中的第二个字符不是*时:
- 如果字符串第一个字符和模式中的第一个字符相匹配,那么字符串和模式都后移一个字符,然后匹配剩余的。
- 如果字符串第一个字符和模式中的第一个字符相不匹配,直接返回false。
而当模式中的第二个字符是*时:
如果字符串第一个字符跟模式第一个字符不匹配,则模式后移2个字符,继续匹配。如果字符串第一个字符跟模式第一个字符匹配,可以有3种匹配方式:
- 模式后移2字符,相当于x*被忽略;
- 字符串后移1字符,模式后移2字符;
- 字符串后移1字符,模式不变,即继续匹配字符下一位,因为*可以匹配多位;
代码
class Solution:
def match(self, s, pattern):
if s == pattern:
return True
if not pattern:
return False
if len(pattern)>1 and pattern[1] == "*":
if (s and s[0]==pattern[0]) or (s and pattern[0]=="."):
# 1. 跳过当下的pattern
# 2. 算该s匹配,再继续该*的第二次作用。
# 3.算该s匹配,*只发挥该次作用。
return self.match(s, pattern[2:]) \
or self.match(s[1:], pattern) \
or self.match(s[1:], pattern[2:])
else:
return self.match(s, pattern[2:])
elif s and (s[0]==pattern[0] or pattern[0]=="."):
return self.match(s[1:], pattern[1:])
return False
alist = 'abcd'
test1 = 'a.c.'
test2 = 'ac*bcg*ds*d*'
print(alist,' and ',test1,Solution().match(alist,test1))
print(alist,' and ',test2,Solution().match(alist,test2))20题:表示数值的字符串判断
分析
请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。例如,字符串"+100",“5e2”,"-123",“3.1416"和”-1E-16"都表示数值。 但是"12e",“1a3.14”,“1.2.3”,"±5"和"12e+4.3"都不是。
可能的模式: A [ . [ B ] ] [ e ∣ E C ] A[.[B]][e|EC] A[.[B]][e∣EC] 或者 . B [ e ∣ E C ] .B[e|EC] .B[e∣EC], e ∣ E e|E e∣E 表示 e e e或 E E E。
其中,
A A A和 C C C都可能是以 + + +或 − - −号开头的 0 − 9 0-9 0−9的数位串, C C C是紧跟着 E E E或者 e e e的指数部分。
B B B是 0 − 9 0-9 0−9的数位串,但不能有开头正负号。
E E E表示指数部分。
代码
参考大神
def scanUnsignedInteger(string):
if len(string) == 0:
return False, 0
i = 0
while i < len(string) and string[i].isdigit():
i += 1
return i > 0, i
def scanInteger(string):
if len(string) == 0:
return False, 0
if string[0] == "-" or string[0] == "+":
found, index = scanUnsignedInteger(string[1:])
return found, index + 1
else:
return scanUnsignedInteger(string)
def isNumeric(string):
if len(string) == 0:
return False
found_1 = found_2 = found_3 = False
found_1, index = scanInteger(string)
string = string[index:]
is_numeric = found_1
# 如果出现'.',则接下来是小数部分
if len(string) > 0 and string[0] == ".":
string = string[1:]
found_2, index = scanUnsignedInteger(string)
string = string[index:]
# 使用'or'的原因:小数点前面或者后面都可以没有数字
is_numeric = found_2 or is_numeric
# 如果出现'e'或者'E',则接下来的数字是指数部分
if len(string) > 0 and (string[0] == 'e' or string[0] == 'E'):
string = string[1:]
found_3, index = scanInteger(string)
string = string[index:]
# 使用'and'的原因:e的前面或者后面没有数字,都不合法
is_numeric = found_3 and is_numeric
# print("found_1: ", found_1, ",found_2: ", found_2, ",found_3: ", found_3, "is_numeric: ", is_numeric)
return is_numeric and len(string) == 0【3.4】代码的鲁棒性
23题:链表中环的入口节点
分析
如:在1->2->3->4->5->6->3的链表中,包含一个环,环的入口节点是3。
- 确定一个链表里面有环
用两个指针解决问题。P1一次走一步,P2一次走两步(不一定是2倍,较快即可)。当P2(走得快)能够追上P1,说明有环;如果P2走到了链表的末尾,还没有追上P1,说明不包含环。
解释: 因为是两倍,所以假如环的总长度是N,那么P2能够走2N,P1能够走N,P2能够“套圈”。能够套圈说明差距是N。 - 找到环的入口
用两个指针解决问题。P1和P2指向链表的头结点,如果环例有n个节点,那么P1先在环上移动n步,P2再出发,以相同的速度向前移动。当P2到达环的入口节点时,P1应该回到了该入口节点。
使用同样速度一前一后的两个指针,前面的指针先走n步,然后后面的指针和前面的指针一起走,当二者第一次相遇时,慢指针正好走了k步,快指针走了n+k步,都在环入口处。
代码
参考大神
class ListNode:
"""List node."""
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
def MeetingNode(headNode):
if headNode is None:
return
slow = headNode.next
# slow = n1.next = n2
if slow is None:
return
fast = slow.next
# fast = n2.next = n3
while fast is not None and slow is not None:
if fast == slow:
return fast # 两者相遇
# 如果不相遇,继续前进
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
# 需要两倍前进
if fast is not None:
fast = fast.next
return
def entryNodeOfLoop(headNode):
meeting_node = MeetingNode(headNode)
if meeting_node is None:
return
# 计算环的长度
n = 1 # 最短两个节点组成环,差距只有 n = 1
node = meeting_node
while node.next != meeting_node:
node = node.next
n += 1
# 先移动前面的指针n次
ahead = headNode
for i in range(n):
ahead = ahead.next
# 再同时移动两个指针,直到相遇
behind = headNode
while ahead != behind:
ahead = ahead.next
behind = behind.next
return ahead
n1 = ListNode(10)
n2 = ListNode(20)
n3 = ListNode(30)
n4 = ListNode(40)
n5 = ListNode(50)
n6 = ListNode(60)
n1.next = n2
n2.next = n3
n3.next = n4
n4.next = n5
n5.next = n6
n6.next = n3
# n6.next = n3
entry = entryNodeOfLoop(n1)
if entry != None: print(entry.val)
else: print(entry)24题:反转链表
定义一个函数,输入链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
分析
- 递归
- 正向遍历
代码
class ListNode:
"""List node."""
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
def print_list(head_node):
"""Traverse a list and print."""
vals = []
while head_node:
vals.append(head_node.val)
head_node = head_node.next
if len(vals) > 0:
print(" ".join(map(str, vals)))
else:
print("This node list is empty!")
def reverseListRecursive(headNode):
# 防止输入空节点
if headNode is None:
return None, None
# 行进至最后一个,返回本身
if headNode.next is None:
return headNode, headNode
# 递归处:
new_tail, new_head = reverseListRecursive(headNode.next)
new_tail.next = headNode # 新的尾部,接现在输入的headNode,实现该部分翻转
headNode.next = None # 现在输入的headNode应该有None的next,
return headNode, new_head
# new_head 就一直不变,
# 保持是原来最后一个节点作为new_head保持后续的输出。
def reverseList(headNode):
if headNode is None:
return
if headNode.next is None:
return headNode
prevNode = headNode
node = headNode.next
headNode.next = None
while node.next != None:
nextNode = node.next
node.next = prevNode
prevNode = node
node = nextNode
node.next = prevNode
return node
n1 = ListNode(10)
n2 = ListNode(20)
n3 = ListNode(30)
n4 = ListNode(40)
n5 = ListNode(50)
n6 = ListNode(60)
n1.next = n2
n2.next = n3
n3.next = n4
n4.next = n5
n5.next = n6
new_tail, new_head = reverseListRecursive(n1)
print(new_head.val)
print("Recursive solution: ")
print_list(new_head)
print("new tail: ")
print_list(new_tail)
n1 = ListNode(10)
n2 = ListNode(20)
n3 = ListNode(30)
n4 = ListNode(40)
n5 = ListNode(50)
n6 = ListNode(60)
n1.next = n2
n2.next = n3
n3.next = n4
n4.next = n5
n5.next = n6
print("Regular solution: ")
new_head2 = reverseList(n1)
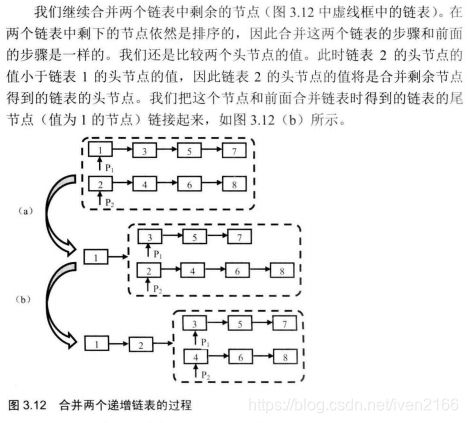
print_list(new_head2)25题:合并两个排序的链表
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
分析
代码
class ListNode:
"""List node."""
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
def print_list(head_node):
"""Traverse a list and print."""
vals = []
while head_node:
vals.append(head_node.val)
head_node = head_node.next
if len(vals) > 0:
print(" ".join(map(str, vals)))
else:
print("This node list is empty!")
def CombineTwoSortedListNode(head_node1, head_node2):
# robust
if head_node1 is None and head_node2 is None:
return None
if head_node1 is None:
return head_node2
if head_node2 is None:
return head_node1
# begin merge
alistnode = [] # 难以用链表直接保存
while head_node1 and head_node2:
if head_node1.val <= head_node2.val:
alistnode.append(head_node1)
head_node1 = head_node1.next
else:
alistnode.append(head_node2)
head_node2 = head_node2.next
while head_node1:
alistnode.append(head_node1)
head_node1 = head_node1.next
while head_node2:
alistnode.append(head_node2)
head_node2 = head_node2.next
for i in range(len(alistnode)-1):
alistnode[i].next = alistnode[i+1]
alistnode[len(alistnode)-1].next = None
return alistnode[0]
# test
n1 = ListNode(1)
n2 = ListNode(2)
n3 = ListNode(3)
n4 = ListNode(4)
n5 = ListNode(5)
n6 = ListNode(6)
n1.next = n3
n3.next = n5
n2.next = n4
n4.next = n6
alistnode = CombineTwoSortedListNode(n1,n2)
print("CombineTwoSortedListNode: ")
print_list(alistnode)
def mergeListNode(head1, head2):
if head1 is None:
return head2
if head2 is None:
return head1
if head1.val <= head2.val:
new_head = mergeListNode(head1.next, head2)
head1.next = new_head
# head1由于比较小,直接接上head1.next和head2处理之后的new_head结果。
return head1
else:
new_head = mergeListNode(head1, head2.next)
head2.next = new_head
return head2
# test
n1 = ListNode(1)
n2 = ListNode(2)
n3 = ListNode(3)
n4 = ListNode(4)
n5 = ListNode(5)
n6 = ListNode(6)
n1.next = n3
n3.next = n5
n2.next = n4
n4.next = n6
alistnode = mergeListNode(n1,n2)
print("mergeListNode: ")
print_list(alistnode)26. 树的子结构(待更)
输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构。
分析
代码
【4.2】画图让抽象问题更加形象化
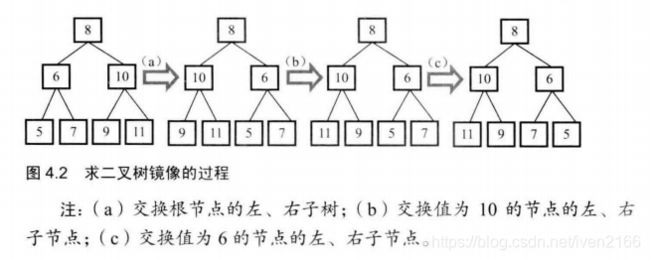
27. 二叉树的镜像
分析
代码
class TreeNode:
"""Tree node."""
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def print_tree(root_node):
"""Travers a tree by level and print."""
travers = []
queue = [root_node]
while len(queue) > 0:
farther = queue.pop()
travers.append(farther.val)
if farther:
if farther.left:
queue.insert(0, farther.left)
if farther.right:
queue.insert(0, farther.right)
print(" ".join(map(str, travers)))
def MirrorRecursively(ptree):
if ptree is None:
return
if (ptree.left is None) and (ptree.right is None):
return
ptemp = ptree.left
ptree.left = ptree.right
ptree.right = ptemp
if ptree.left:
MirrorRecursively(ptree.left)
if ptree.right:
MirrorRecursively(ptree.right)
n1 = TreeNode(8)
n2 = TreeNode(6)
n3 = TreeNode(10)
n4 = TreeNode(5)
n5 = TreeNode(7)
n6 = TreeNode(9)
n7 = TreeNode(11)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
print_tree(n1)
MirrorRecursively(n1)
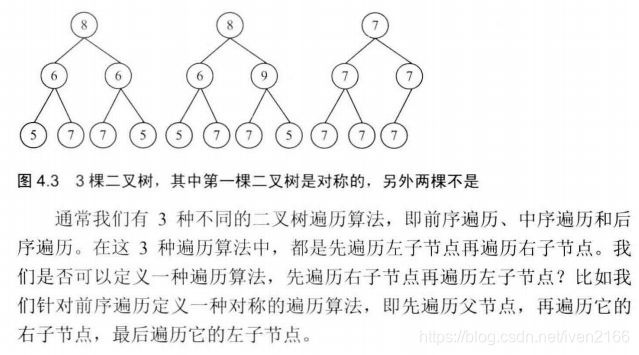
print_tree(n1)28. 对称的二叉树
分析
注:笔者没法考虑到第三个情况,即全部一样的情况下,“根左右”与“根右左”会一样的结果——但其实并不对称。

代码
class TreeNode:
"""Tree node."""
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def print_tree(root_node):
"""Travers a tree by level and print."""
travers = []
queue = [root_node]
while len(queue) > 0:
farther = queue.pop()
travers.append(farther.val)
if farther:
if farther.left:
queue.insert(0, farther.left)
if farther.right:
queue.insert(0, farther.right)
print(" ".join(map(str, travers)))
def isTreeSymmetrical(root):
return isTwoTreeSymmetrical(root, root)
def isTwoTreeSymmetrical(root1, root2):
if root1 is None and root2 is None:
return True
if root1 is None or root2 is None:
return False
if root1.val != root2.val:
return False
return isTwoTreeSymmetrical(root1.left, root2.right) \
and isTwoTreeSymmetrical(root1.right, root2.left)
n1 = TreeNode(8)
n2 = TreeNode(6)
n3 = TreeNode(6)
n4 = TreeNode(5)
n5 = TreeNode(7)
n6 = TreeNode(7)
n7 = TreeNode(5)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
print_tree(n1)
print(isTreeSymmetrical(n1))
print("----------------")
print("change n3.val to 9")
n3.val = 9
print_tree(n1)
print(isTreeSymmetrical(n1))
print("----------------")
print("change n3.val to 6, and n3.right is none")
n3.val = 6
n3.right = None
print_tree(n1)
print(isTreeSymmetrical(n1))29. 顺时针打印矩阵
分析
P r i n t M a t r i x C l o c k w i s e l y PrintMatrixClockwisely PrintMatrixClockwisely 是主方程,用于放入list和列、行说明。
P r i n t M a t r i x I n C i r c l e PrintMatrixInCircle PrintMatrixInCircle 是内层的函数,其中只有start作为左上角的出发点,不断地改变。而且能够想到,出发点自加1到最后,必定小于中间半段。
代码
def PrintMatrixClockwisely(numbers, columns, rows):
if numbers == None or columns<=0 or rows<=0:
return
start = 0
while columns > start *2 and rows > start*2:
PrintMatrixInCircle(numbers, columns, rows, start)
start += 1
def PrintMatrixInCircle(numbers, columns, rows, start):
endX = columns - 1 - start
endY = rows - 1 - start
# 从左到右打印一行
for i in range(start, endX+1):
number = numbers[start][i]
print(number)
# 从上到下打印一列:“终止行号大于起始行号”,才有下方可以走
if start < endY:
for i in range(start+1, endY+1):
number= numbers[i][endX]
print(number)
# 从右到左打印一行:“至少有两行两列”
if start < endX and start < endY:
for i in range(endX-1, start-1, -1):
number = numbers[endY][i]
print(number)
# 从下到上打印一列:“至少有两列三行”
if start < endX and start < endY-1:
for i in range(endY-1, start, -1):
number = numbers[i][start]
print(number)
# test
numbers1 = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12],[13,14,15,16]]
PrintMatrixClockwisely(numbers1, 4,4)
print("=============================")
numbers2 = [[1,2,3,4]]
PrintMatrixClockwisely(numbers2, 4,1)
print("=============================")
numbers3 = [[1],[2]]
PrintMatrixClockwisely(numbers3, 1,2)【4.3】举例让抽象问题更加形象化
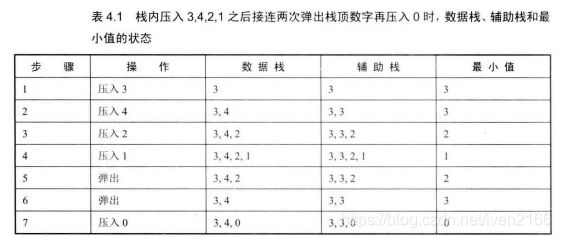
30. 包含min函数的栈
分析
首先注意是栈,需要满足,pop的是栈顶。可以有以下渐进的想法:
- 每次压入一个新元素进栈时,将所有元素排序,最小的元素位于栈顶,所以可以在 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)的情况下得到该最小值。——但是不能保证最后压入的元素最先出栈,因为这样不是栈的定义。
- 添加一个变量,存放最小的元素。但是如果当前最小的数被弹出,如何得到第二小的数呢?因为你这个变量只能够存放一个。
- 增加一个辅助栈!
代码(需要定义类)
class StackWithMin:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
self.stackMin = []
self.top = -1 # 之后初始化top加1,才开始在0位开始添加
def push_func(self, value):
if len(self.stack)==0:
self.stackMin.append(value)
elif value < self.stackMin[self.top]:
self.stackMin.append(value)
else:
self.stackMin.append(self.stackMin[self.top])
self.stack.append(value)
self.top += 1
def pop_func(self):
if len(self.stack) > 0 and len(self.stackMin) > 0:
self.stack.pop()
self.stackMin.pop()
self.top -= 1
def min_func(self):
if len(self.stack) > 0 and len(self.stackMin) > 0:
return self.stackMin[self.top]
###测试例
##alist = StackWithMin()
##alist.push_func(5)
##alist.push_func(3)
##alist.push_func(5)
##alist.push_func(1)
##alist.push_func(4)
##for i in range(len(alist.stack)):
## print(alist.stack, alist.stackMin)
## print(alist.min_func())
## alist.pop_func()
##
##
####[5, 3, 5, 1, 4] [5, 3, 3, 1, 1]
####1
####[5, 3, 5, 1] [5, 3, 3, 1]
####1
####[5, 3, 5] [5, 3, 3]
####3
####[5, 3] [5, 3]
####3
####[5] [5]
####531. 栈的压入、弹出序列
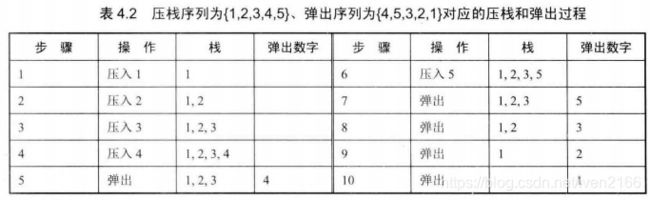
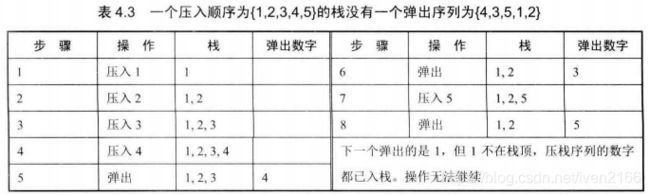
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。

分析
总结规律是:
如果下一个弹出的数字是栈顶的数字,那么直接弹出;如果下一个弹出的数字不在栈顶,则把压栈序列中还没有入栈的数字压入辅助栈,直到把下一个需要弹出的数字压入栈顶位置;如果全部的数字都压入栈顶之后,仍旧没有找到下一个弹出的数字,那么该序列不可能是弹出序列。
- 如果下一个弹出的数字是栈顶的数字,那么直接弹出
- 如果下一个弹出的数字不在栈顶
- 则把压栈序列中还没有入栈的数字压入辅助栈,直到把下一个需要弹出的数字压入栈顶位置
- 如果全部的数字都压入栈顶之后,仍旧没有找到下一个弹出的数字,那么该序列不可能是弹出序列。
- 则把压栈序列中还没有入栈的数字压入辅助栈,直到把下一个需要弹出的数字压入栈顶位置
代码
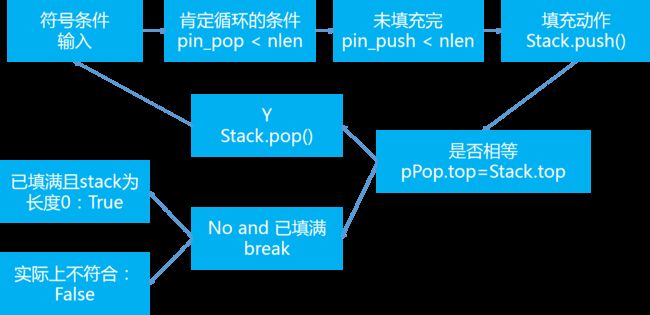
通过牛客网测试
def IsPopOrder(pPush, pPop, nlength):
bPossible = False
if pPush != None and pPop!=None and nlength >0:
pin_push = 0
pin_pop = 0
stack_data = []
while pin_pop < nlength:
if pin_push < nlength:
stack_data.append(pPush[pin_push])
pin_push += 1
if pPop[pin_pop] == stack_data[len(stack_data)-1]:
stack_data.pop()
pin_pop += 1
elif pin_push==nlength and \
pPop[pin_pop] != stack_data[len(stack_data)-1]:
break
if stack_data == []:
bPossible = True
return bPossible
else:
return bPossible
alist_push = [1,2,3,4,5]
alist_pop = [4,5,3,2,1]
alist_pop_false = [4,3,5,1,2]
print(IsPopOrder(alist_push, alist_pop, len(alist_push))) # True
print(IsPopOrder(alist_push, alist_pop_false, len(alist_push))) # False32_1. 从上到下打印二叉树——题目一:不分行,还需要看前序、中序、后序打印
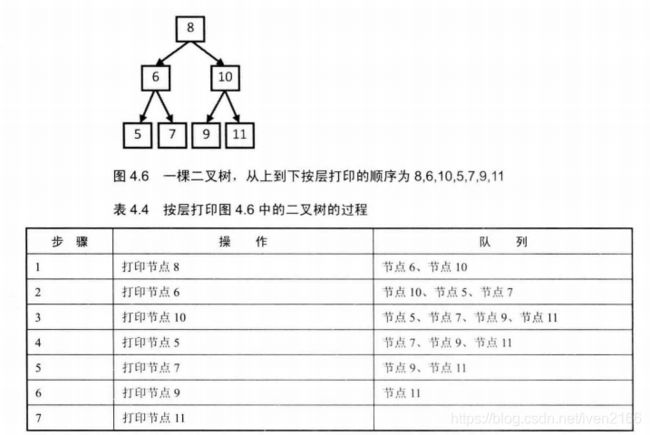
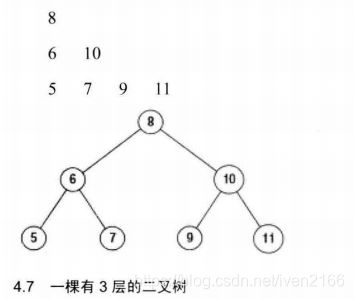
从上到下打印二叉树的每个节点,同一层的节点按照从左到右的顺序打印。例如,输入图4.6的二叉树,则打印出8,6,10,5,7,9,11
代码
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.right = None
self.left = None
def print_tree(root_node):
travelers = []
queue = [root_node]
while len(queue) > 0:
father = queue.pop() # 不断地取queue中的最新的一个tree_node,
# father是一个更新值
travelers.append(father.val)
if father:
if father.left:
queue.insert(0, father.left)
if father.right:
queue.insert(0, father.right)
print(" ",join( map(str, travelers)) )
# test
n1 = TreeNode(8)
n2 = TreeNode(6)
n3 = TreeNode(10)
n4 = TreeNode(5)
n5 = TreeNode(7)
n6 = TreeNode(9)
n7 = TreeNode(11)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
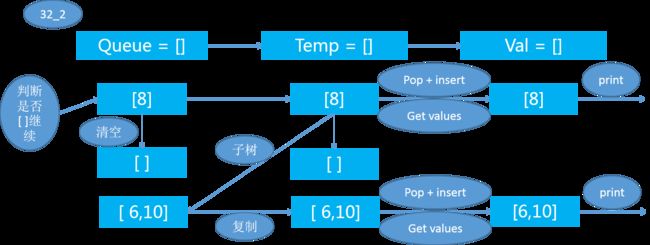
print_tree(n1)32_2. 从上到下打印二叉树——题目二:分行,还需要看前序、中序、后序打印
分析
跟上题类似,实际上就是考虑queue及temp两个栈,用来存放当前的node和要打印出来的node,然后再传入子树。
代码
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.right = None
self.left = None
def print_tree_by_row(root_node):
queue = [root_node]
temp = []
val_PrintNow = []
while len(queue) > 0:
temp = queue
queue = []
for node in temp:
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
while len(temp) > 0:
val_PrintNow.insert(0, temp.pop().val)
print(" ".join(map(str, val_PrintNow)))
val_PrintNow = []
# test
n1 = TreeNode(8)
n2 = TreeNode(6)
n3 = TreeNode(10)
n4 = TreeNode(5)
n5 = TreeNode(7)
n6 = TreeNode(9)
n7 = TreeNode(11)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
print_tree_by_row(n1)32_3:从上到下打印二叉树——题目三:分行+之字形
分行打印。然后第一行从左到右,第二行从右到左,第三行从左到右,以此类推。
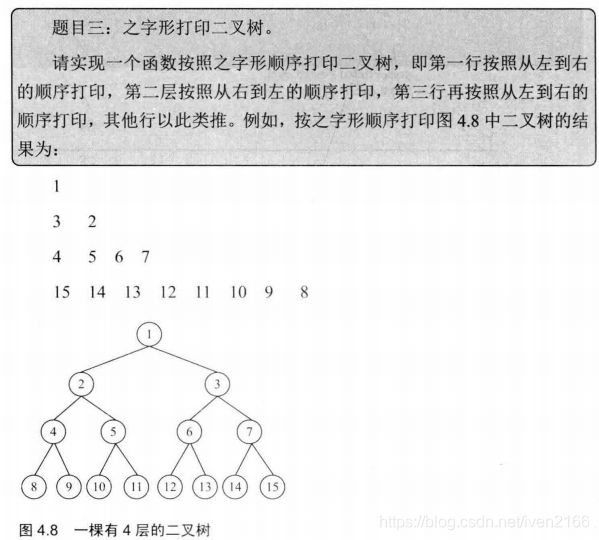
分析
基于上一道题目,同样是分行,我们只需要再加入一个计数器,每print一行就加一,在循环的开头进行计数器的判断,应该给queue左到右还是右到左放入。
代码
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.right = None
self.left = None
def print_tree_by_row_zhitype(root_node):
queue = [root_node]
temp = []
val_PrintNow = []
timer = 1
while len(queue) > 0:
temp = queue
queue = []
for node in temp:
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
if timer%2 == 1:
while len(temp) > 0:
val_PrintNow.insert(0, temp.pop().val)
else:
while len(temp) > 0:
val_PrintNow.append(temp.pop().val)
timer = (timer+1)%2
print(" ".join(map(str, val_PrintNow)))
val_PrintNow = []
# test
n1 = TreeNode(8)
n2 = TreeNode(6)
n3 = TreeNode(10)
n4 = TreeNode(5)
n5 = TreeNode(7)
n6 = TreeNode(9)
n7 = TreeNode(11)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
print_tree_by_row_zhitype(n1)33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),(又:二叉搜索树,二叉排序树)它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值; 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树。
分析
由于每个节点的左子树的值都小于该节点,右子树则值都大于该节点,可以利用循环来判断。
转载大神
代码
def VarifySequenceOfBST(seq):
return vs_core(seq, 0, len(seq) - 1)
def vs_core(seq, s, e):
if len(seq) == 0:
return False
if len(seq) == 1:
return True
root = seq[e]
# 判断左子树是否小于根
i = s
while i < e and seq[i] < root:
i += 1
if i == e:
return True
# 记录左子树的最后一个点的下标
left_e = i - 1
# 判断右子树是否大于根
while i < e:
if seq[i] < root:
return False
i += 1
# 递归判断
is_left = True
is_right = True
if left_e >= s:
is_left = vs_core(seq, s, left_e)
if left_e + 1 < e:
is_right = vs_core(seq, left_e+1, e-1)
return is_left and is_right
# test
seq = [5,7,6,9,11,10,8]
# seq = [7,4,6,5]
print(VarifySequenceOfBST(seq))34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
给出一个二叉树,以及预期的路径(到达叶节点)求和,求所有可能的路径。
分析
- 从根节点开始遍历,只能够进行前序遍历
- 有一个序列储存当前所有遍历值,能够判断加和是否为预期值
- 如果想要更方便地遍历,需要加入递归
- 每一个结点,由于到达它的路径唯一,所以当前求和值也是唯一的,可以储存起来作为形参,供给下一步递归所用!
- 更多注意点在代码中
代码
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def FindPath(root_node, expect_sum):
current_sum = 0 # 第一个递归的值,起点为0
current_path = []
FindPathCore(root_node, expect_sum, current_sum, current_path)
def FindPathCore(root_node, expect_sum, current_sum, current_path):
current_sum = current_sum
current_path = current_path
current_sum += root_node.val
current_path.append(root_node.val)
# 判断递归终止条件,遍历到了叶节点
isLeaf = root_node.left==None and root_node.right==None
if isLeaf and current_sum == expect_sum:
print("We have found a path: ")
print(" ".join(map(str, current_path)) )
print()
# 如果不是叶节点,则前序遍历它
if root_node.left != None:
FindPathCore(root_node.left, expect_sum, current_sum, current_path)
if root_node.right != None:
FindPathCore(root_node.right, expect_sum, current_sum, current_path)
current_path.pop()
'''
最后一句:要注意肯定要在退出子节点返回父节点时,要删除该子节点,
这一块比较难想出来。理解:假设我们在A层进入了 “if root_node.left != None:”
这一行,导入的是当前的current_path,那么进入之后到达B层,
假设它立刻就跳到叶节点,所以不用跳进“if root_node.left != None:”
和 “if root_node.right != None:”这两行,那么它要接着到刚才A层的下一行,
也就是"if root_node.right != None:",它必须要返回父节点,那么在B层那会最后,
需要把path最后一个pop出来。
*!可以验证的是,当程序跑完之后,我们再调用current_path,
会发现它实际上是最后那个符合条件的path,去掉最后一个元素。
'''
# test
n1 = TreeNode(1)
n2 = TreeNode(2)
n3 = TreeNode(3)
n4 = TreeNode(4)
n5 = TreeNode(5)
n6 = TreeNode(11)
n7 = TreeNode(4)
n8 = TreeNode(8)
n9 = TreeNode(3)
n10 = TreeNode(7)
n11 = TreeNode(7)
n12 = TreeNode(7)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right=n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
n4.left = n8
n4.right = n9
n5.left = n10
n7.left = n11
n7.right = n12
FindPath(n1, 15)【4.4】分解让复杂问题简单化(分治法)
35. 复杂链表的复制
题目:请实现ComplexListNodeClone(ComplexListNode)函数,复制一个复杂链表。复杂链表中,每个节点有一个指针指向下一个节点,还有另外一个指针,可以指向任意节点或者是null。
分析
哈希表介绍
最后还是用了书本第三种方法,哈希表还不会用。
分析见代码。
代码
class ComplexListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
self.sibling = None
def printListNode(phead):
pnode = phead
while(pnode != None):
if pnode.next!=None:
print(pnode.val, " next => ", pnode.next.val)
if pnode.sibling != None:
print(pnode.val, " sibling => ", pnode.sibling.val)
pnode = pnode.next
# (1)把clone复制到每个listnode后面
def CloneNodes(phead):
pnode = phead
while(pnode != None):
# 1. 创建clone,并且复制内容和next
Comlistnode_clone = ComplexListNode(pnode.val)
Comlistnode_clone.next = pnode.next
Comlistnode_clone.sibling = None
# 2. 接到后面
pnode.next = Comlistnode_clone
pnode = Comlistnode_clone.next # 到达下一个原生listnode
# (2)把sibling复制到每一个clone的listnode里面
def ConnectSiblingNodes(phead):
pnode = phead
while(pnode != None):
Comlistnode_clone = pnode.next
if(pnode.sibling != None):
# 需要为原生node的sibling的next,是跳到这个sibling复制的node
Comlistnode_clone.sibling = pnode.sibling.next
pnode = Comlistnode_clone.next
# (3)把这个包含原生链以及复制链,拆分为两个
def ReconnectNodes(phead):
pnode = phead
Comlistnode_clone_head = None
Comlistnode_clone = None
# 处理第一个
if(pnode != None):
Comlistnode_clone_head = pnode.next
Comlistnode_clone = pnode.next
# 到原生node的复制的后面,也就是原生node第二位
pnode.next = Comlistnode_clone.next
pnode = pnode.next
while(pnode != None):
Comlistnode_clone.next = pnode.next # 赋值第二位的复制
Comlistnode_clone = Comlistnode_clone.next
pnode.next = Comlistnode_clone.next
pnode = pnode.next
return Comlistnode_clone_head
def ComplextListNode_clone(phead):
CloneNodes(phead)
ConnectSiblingNodes(phead)
return ReconnectNodes(phead)
n1 = ComplexListNode(1)
n2 = ComplexListNode(2)
n3 = ComplexListNode(3)
n4 = ComplexListNode(4)
n5 = ComplexListNode(5)
n1.next = n2
n2.next = n3
n3.next = n4
n4.next = n5
n5.next = None
n1.sibling = n3
n2.sibling = n5
n4.sibling = n2
clonenodehead = ComplextListNode_clone(n1)
print("n1")
printListNode(n1)
print()
print("clonenodehead")
printListNode(clonenodehead)
'''
结果
n1
1 next => 2
1 sibling => 3
2 next => 3
2 sibling => 5
3 next => 4
4 next => 5
4 sibling => 2
clonenodehead
1 next => 2
1 sibling => 3
2 next => 3
2 sibling => 5
3 next => 4
4 next => 5
4 sibling => 2
'''36. 二叉搜索树以及双向链表
题目:输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该树转化为排序的双向二叉树。要求不创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中的指针的指向。(在原有的二叉搜索树上操作)
代码(该题先上代码,再分析)
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def convert(root_node):
last_node_in_list = [None]
convert_core(root_node, last_node_in_list)
head_node = last_node_in_list[0]
while head_node is not None and head_node.left is not None:
head_node = head_node.left
return head_node
def convert_core(root_node, last_node_in_list):
if root_node is None:
return
curr = root_node
if curr.left is not None:
convert_core(curr.left, last_node_in_list)
curr.left = last_node_in_list[0]
if last_node_in_list[0] is not None:
last_node_in_list[0].right = curr
last_node_in_list[0] = curr
if curr.right is not None:
convert_core(curr.right, last_node_in_list)
# test
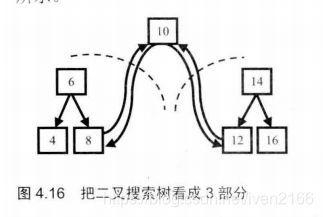
n1 = TreeNode(10)
n2 = TreeNode(6)
n3 = TreeNode(14)
n4 = TreeNode(4)
n5 = TreeNode(8)
n6 = TreeNode(12)
n7 = TreeNode(16)
n1.left = n2
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n1.right = n3
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
head = convert(n1)
while head:
print(head.val, end = " ")
head = head.right
'''result
4 6 8 10 12 14 16
'''分析
- 二叉搜索树的特点是,中序遍历即为排序的遍历
- 需要进行抽象化的迭代
- 利用分拆的方式分析:
设定一个convert_core()函数作为处理的函数,传入n1(10)
- 由于需要遍历,所以需要在第一行判断是否为None,如果是则return,不是则往下走
- curr作为根节点,判断左子树是否为None,不是则进行左子树的处理,迭代convert_core()
- 需要将新的左子树以及n1(10)用双向链连接起来;此时,n5(8)为储存的last_node_in_list[0],因此,n5和n1用
curr.left = last_node_in_list[0]
进行连接;此外,如果现在的last_node_in_list[0]不为None的话(需要判断因为可能为子树的None子树),它的right为curr
也就是n5(8)的right需要为n1(10)。至此,左子树处理完毕,并且和根curr进行left以及right的连接- 此时,last_node_in_list[0] 应该储存根curr也就是n1(10),然后再处理右子树。
为什么最后不用定义n1(10)和n6(12)的连接呢?因为,n6作为新的根curr,届时函数会处理left连接到n1.
37. 序列化和反序列化二叉树
题目:设计两个函数,分别来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
分析
- 第一种思路是,给出前序和中序,来唯一地构建二叉树
- 其实,应该设计一种,可以唯一地进行构建,也就是在子节点为None时,加入特殊的分别字符
- 再于该序列化的序列,生成二叉树
代码
class TreeNode:
"""Tree node."""
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def print_tree_by_row(root_node):
queue = [root_node]
temp = []
val_PrintNow = []
while len(queue) > 0:
temp = queue
queue = []
for node in temp:
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
while len(temp) > 0:
val_PrintNow.insert(0, temp.pop().val)
print(" ".join(map(str, val_PrintNow)))
val_PrintNow = []# 函数开始
def Serialize(root_node, new_serial_list):
if (root_node is None):
new_serial_list.append("$,")
return
new_serial_list.append(str(root_node.val)+',')
Serialize(root_node.left, new_serial_list)
Serialize(root_node.right, new_serial_list)
def BeforeDeSerialize(serial_list):
serial_list = "".join(map(str,serial_list))
return DeSerialize(serial_list.split(",") )
def DeSerialize(serial_list_num):
if len(serial_list_num) == 0:
return None, ""
if serial_list_num[0] == "$":
return None, serial_list_num[1:]
root_node = TreeNode(serial_list_num[0])
root_node.left, serial_list_num = DeSerialize(serial_list_num[1: ])
root_node.right, serial_list_num= DeSerialize(serial_list_num)
return root_node, serial_list_num
n1 = TreeNode(1)
n2 = TreeNode(2)
n3 = TreeNode(3)
n4 = TreeNode(4)
n5 = TreeNode(5)
n6 = TreeNode(6)
n1.left = n2
n2.left = n4
n1.right= n3
n3.left = n5
n3.right= n6
serial_list1 = []
Serialize(n1, serial_list1)
print(" ".join(map(str, serial_list1)))
# 1, 2, 4, $, $, $, 3, 5, $, $, 6, $, $,
new_root_node, slist = BeforeDeSerialize(serial_list1)
print(slist)
print_tree_by_row(new_root_node)
''' result
1, 2, 4, $, $, $, 3, 5, $, $, 6, $, $,
['']
1
2 3
4 5 6
'''38. 字符串的排列
题目:输入一个字符串,打印出字符的所有排列。比如输入abc,返回abc,acb,bac,bca,cab,cba
分析
把大问题拆解为小问题,获得原序列后,
(1)固定第一个字符,寻找后面的字符串所有排列(递归);
(2)将第一个字符和后面字符串的所有字符进行交换,再进行后面的查找(递归)。
本质上是递归。
代码
参考非常易懂的版本:链接
def permutation(s):
if len(s) <= 1:
return [s]
str_list = []
for i in range(len(s)):
for j in permutation(s[0:i] + s[i+1:]): # 除开i以外的所有字符中选j
str_list.append(s[i] + j)
return str_list
permutation_repeat = permutation(input())
permutation_no_repeat = list(set(permutation_repeat ))
print('permutation with repeat: ', len(permutation_repeat), permutation_repeat )
print('permutation without repeat: ', len(permutation_no_repeat), permutation_no_repeat )
# abb
# permutation with repeat: 6 ['abb', 'abb', 'bab', 'bba', 'bab', 'bba']
# permutation without repeat: 3 ['bba', 'bab', 'abb']38-2. 字符串的组合
题目:输入一个字符串,打印出字符的所有排列。比如输入abc,返回a,b,c,ab,ac,bc, abc
输入abcd,返回a,b,c,d, ab,ac,ad,bc,bd,cd, abc,abd,acd,bcd, abcd
分析
代码
def compose_str(str_input):
li = [i for i in str_input] # 单独列出来,['a','b','c']
final_li = [] # 最后输出结果
for m in range(len(li)): # 组合的字符串长度m是从1到str_input的长度
if m == 0:
final_li.extend([i for i in li])
elif m == 1:
for n in range(len(li)):
final_li.extend([ li[n] + i for i in li[n+1:] ])
else:
final_li.extend(''.join(li[:m]) + i for i in li[m:])
return final_li
final_li = compose_str(input())
print(final_li)
39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
代码
def more_than_half_num1(numlist):
length = len(numlist)
result = numlist[0]
times = 1
for i in range(length):
if times == 0:
result = numlist[i]
times = 1
elif numlist[i] == result:
times += 1
else:
times -= 1
return result
def partition(data, s, e):
if s == e:
return s
small = s # 以第一个为计数器
pivot_index = s # 以第一个为比较标准
pivot_value = data[pivot_index]
for i in range(s, e):
if data[i] < pivot_value: # 把小值放在左边
small += 1
data[i], data[small] = data[small], data[i] #
data[small], data[s] = data[s], data[small] # 最后把这个大的标准,和小值集合最后一个做交换
return small # 返回把数据二分的标准值的index
def more_than_half_num2(numlist):
# check
length = len(numlist)
middle = length >> 1
start = 0
end = length - 1
index = partition(numlist, start, end)
while(index != middle):
if(index > middle):
end = index - 1
index = partition(numlist, start, end)
else:
start = index + 1
index = partition(numlist, start, end)
result = numlist[index]
return result
import sys
# list1 = [int(i) for i in sys.stdin.readline().strip().split()]
list2 = [5,2,4,5,2,5,5,5,9,100,5,5,5]
print(more_than_half_num1(list2))
print(more_than_half_num2(list2))
'''
超过一半,说明数组的中位数是该数字。两种方法。
(1)递归:寻找中间的index
(2)记录数字与出现次数
'''