算法入门二:分支结构:
文章目录
- 算法入门二:分支结构:
-
- 引言:
- 分支结构
-
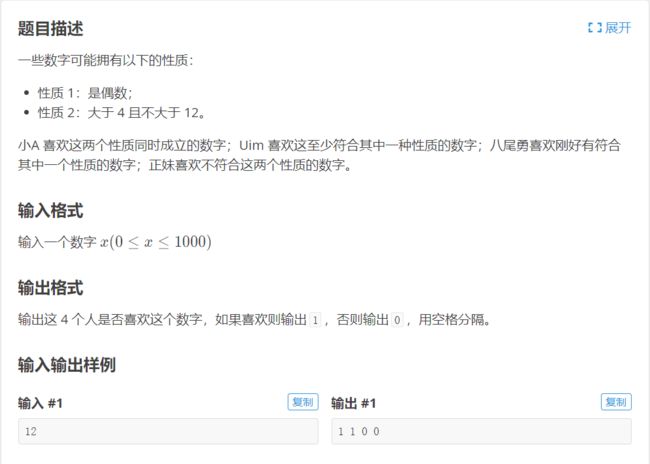
- 1.洛谷 p5710 Java 书的性质
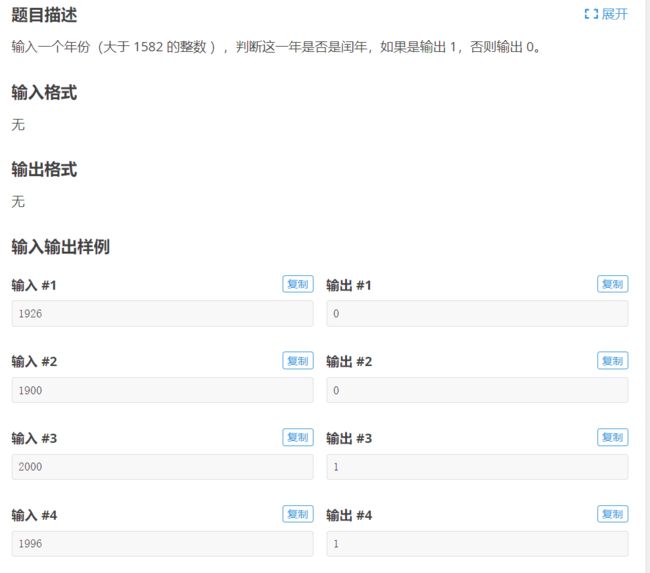
- 2.洛谷 p5711 Java 闰年判断
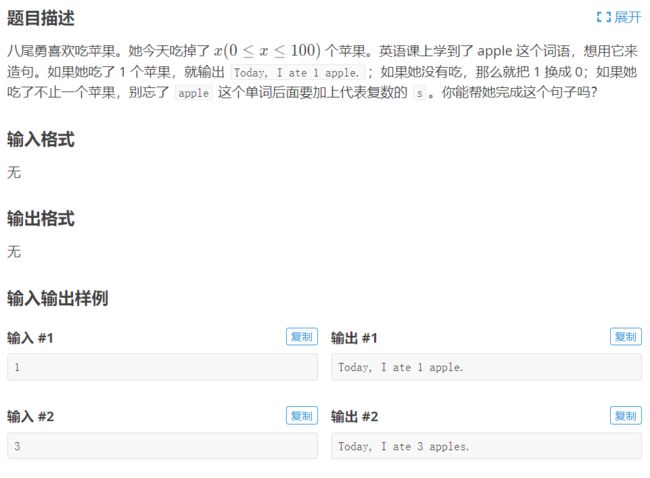
- 3.洛谷 p5712 Java Apples
- 4.洛谷 p5713 Java 洛谷团队系统
- 5.洛谷 p5714 Java 肥胖问题
- 6.洛谷 p5715 Java 三位数排序
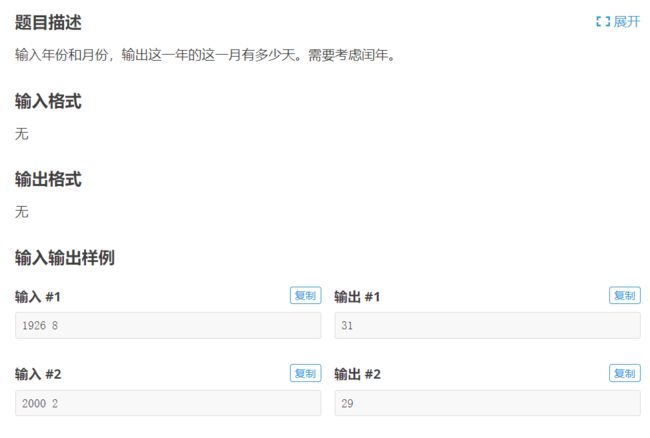
- 7.洛谷 p5716 java 月份天数
- 8.洛谷 p1085 java 不高兴地津津
- 9.洛谷 p1909 java 买铅笔
- 10.洛谷 p1422 java 小玉家的电费
- 11.洛谷 p1424 java 小鱼的航程(改进版)
- 12.洛谷 p1888 java 三角函数
- 13.洛谷 p5717 java 三角形分类
- 14.洛谷 p4414 java ABC
- 15.洛谷 p1055 java ISBN号码;普及题
算法入门二:分支结构:
引言:
在小组的安排下,这个暑假我们统一学习三个星期的算法,在这里让我感觉最大的感受是,前面有人引你入门真的好,可以少走很多的冤枉路,可以快速增长自己的能力和水平,但后续就要求自己自主的学习,因为别人的路线毕竟是别人的,不可能完全的适合自己的,但入门系列是每一个程序员或爱好算法的同学的必经之路,入门系列就是基础阶段,只有将基础打好,后面才能走的更远更好。在完成入门系列专项训练之后,我将自己做的题和做题过程中遇到的问题及解题思路总结成笔记。
记得上数据结构的时候老师说过,数据结构好比是武林高手的内功,往往刚修炼的时候内功比较的弱,但当我们持之以恒的练习,我们终将练就一身内功成就宗师。加油!
分支结构
人们在人生中需要做出许多选择,小到考虑晚上吃什么,大到决定高考志愿填报的学校。只有一次次选择后才能带来无限可能,我们要根据自己掌握的情况,做出最佳的选择。
程序的执行也不是一成不变的,往往会要求程序能够在不同的场合下有不同的动作。这时就需要在代码中使用条件语句来做出不同的选择。比如说,登录洛谷网时,网站后台会将你提交的用户名和密码在后台数据库中看看是否匹配,如果能够匹配就登陆成功,否则就登陆失败。这一章就来介绍如何让程序做出选择。
1.洛谷 p5710 Java 书的性质
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0, d = 0, m = 0;
if(x % 2 == 0){
m ++; //满足性质1
}
if(4 < x && x <= 12){
m ++; //满足性质2
}
if(m == 2){//满足两个性质
a = 1;
}
if(m>0){//至少满足一个性质
b = 1;
}
if(m == 1){//满足一个性质
c = 1;
}
if(m == 0){//一个性值都不满足
d = 1;
}
System.out.println(a + " " + b + " " + c + " " +d);
}
}
本题重点:
- 有的数字可以同时满足多个性质,本题中采用一个中间数m,当满足一个性质的时候 m++,最后通过判断m的大小来判断这个数符合几个性质。
2.洛谷 p5711 Java 闰年判断
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = sc.nextInt();
//对输入的年限进行判断
if(year % 100!=0 && year % 4 == 0 || year % 400 == 0){
System.out.println("1");
}else{
System.out.println("0");
}
}
}
本题重点
- 题中要求我们判断输入的年份是否是闰年,这个时候大家想的就是如何判断某一年是闰年,闰年:能被4整除但不能被100整除或能被400整除的年叫闰年。感觉本题最大的难点就是大家不知道闰年的判断,这也算是一个生活小常识,大家可以记一下。
3.洛谷 p5712 Java Apples
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();
if(x == 0){
System.out.println("Today, I ate 0 apple.");
}
if(x == 1){
System.out.println("Today, I ate 1 apple.");
}
if(x > 1){
System.out.println("Today, I ate "+x+" apples.");
}
}
}
本题重点:
- 本题主要是考察if语句判断,没有难度,但通过刚入门的同学那边反馈,不分同学在本道题的考察上没有问题,最后出问题的地方居然在输出语句上,大小写,字母,空格等都要符合要求,否则你就喜获 “WA”。
4.洛谷 p5713 Java 洛谷团队系统
AC代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int sum1 = a * 5;//个人电脑上
int sum2 = a * 3 + 11;//洛谷题库
if(sum1 > sum2){
System.out.println("Luogu");
}else{
System.out.println("Local");
}
}
}
本题重点:
- 分别计算两种方法在相同的时间内的所用总时长,最终进行判断。
5.洛谷 p5714 Java 肥胖问题
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double m = sc.nextDouble();
double h = sc.nextDouble();
double BMI = m/(h*h);//根据公式计算出BMI值
//当BMI小于18.5时。
if (BMI < 18.5){
System.out.println("Underweight");
}
//当BMI大于18.5小于24时。
if (18.5 < BMI && BMI < 24){
System.out.println("Normal");
}
//当BMI大于24时。
if (BMI > 24){
System.out.printf("%6.4f\n",BMI);//输入保留六位有效数字的数据
System.out.println("Overweight");
}
}
}
本题重点:
- 计算出IBM的值进行判断
- 当BMI的值大于24的时候还需要输入六位有效数字的数据。我们可以观察题意和提示说明,大于24时输出,m和n都不能超过三位数,那么最终的BMI的小数前有两位,小数后有4位,此时利用printf(%6.4f\n,BMI)即可。具体使用可以查阅相关资料。
6.洛谷 p5715 Java 三位数排序
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
// int[] arr = new int[]{a,b,c};
// Arrays.sort(arr);
int middle = 0;
//三个数进行判断
if(a > b){ //a和b判断
middle = a;
a = b;
b = middle;
}
if(a > c){ //a和c判断
middle = a;
a = c;
c = middle;
}
if(b > c){ //b和c判断
middle = b;
b = c;
c = middle;
}
System.out.println(a+" "+b+" "+c);
// System.out.println(arr[0]+" "+arr[1]+" "+arr[2]);
}
}
本题重点:
- 定义一个中间变量,让三个数据变量之间进行比较,然后通过中间变量进行置换操作。
- 我的注释部分是另外的部分,我们可以将这三个数据存到一个数组中,可以使用数组的Arrays.sort(数组名)来进行数组的升序排序。
7.洛谷 p5716 java 月份天数
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
//天数为31天的月份判断
if(n == 1 || n == 3 || n == 5 || n == 7 || n == 8 || n == 10 || n == 12){
System.out.println("31");
}
//天数为30天的月份判断
if(n == 4 || n == 6 || n == 9 || n == 11){
System.out.println("30");
}
//对二月进行单独的判断,是否是闰年
if(n == 2){
if(year % 100!=0 && year % 4 == 0 || year % 400 == 0){
System.out.println("29");//闰年
}else{
System.out.println("28");//非闰年
}
}
}
}
本题重点:
- 这道题除了考察分支语句外,还需要大家有一定的生活常识。一年中:1,3,5,7,8,10,12月是31天,4,6,9,11月是30天,闰年的二月是29天,非闰年的二月是28天。这样一说大家肯定都会做了。
8.洛谷 p1085 java 不高兴地津津
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[][] array = new int[7][2];
int temp = 0;
Integer[] arr = new Integer[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
array[i][j] = sc.nextInt(); //各个时段的时间
}
arr[i] = array[i][0]+array[i][1];//定义数组,对应某一天的总时长
}
//通过比较得到最长的时间,若有两天去前面的。
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
if (i == 0){
temp = arr[0];
}else if(arr[i] > temp){
temp = arr[i];
continue;
}else {
continue;
}
}
if (temp<=8){//当最长的时间小于8时
System.out.println(0);
}else {//当最长的时间大于8时
for (int m=0;m<arr.length;m++){
if (arr[m] == temp){//这一操作是为了得到对应的天数
System.out.println(m+1);
return;
}
}
}
}
}
本题重点:
- 先输入每天津津的在校时间和校外时间定义一个数组进行当天时间的总和
- 进行for循环,计算出时间最长的一天,然后存到数组对应的i值是上
- 判断时间最长的那一天的时间是否大于8,若不大于则输出“0”,若大于遍历arr数组得到对应的天数。
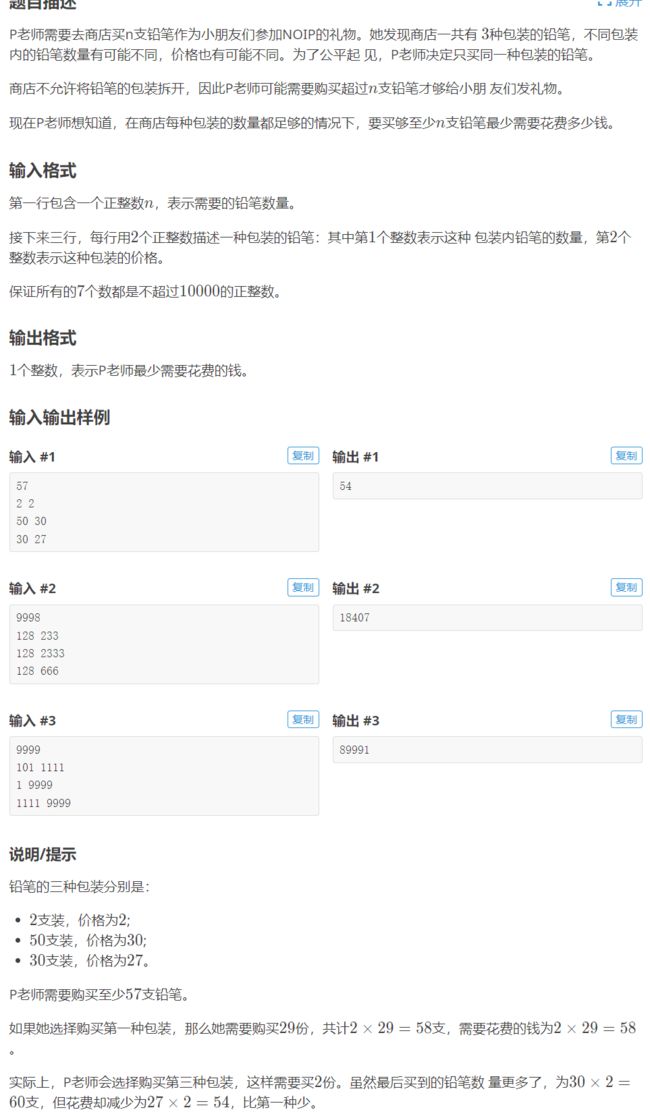
9.洛谷 p1909 java 买铅笔
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[3];
int[] b = new int[3];
int middle=0,sum,sum1,sum2;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
b[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
//第一种方案
if(n % a[0] == 0){//当需要买的笔数正好是整盒的倍数时 下同
sum = b[0] * n / a[0];
}else{
sum = b[0] * (n / a[0]+1);//当需要买的笔数不是整盒的倍数时,需要多买一盒 下同
}
//第二种方案
if(n % a[1] == 0){
sum1 = b[1] * n / a[1];
}else{
sum1 = b[1] * (n / a[1]+1);
}
//第三种方案
if(n % a[2] == 0){
sum2 = b[2] * n / a[2];
}else {
sum2 = b[2] * (n / a[2] + 1);
}
//比较哪一种比较的便宜
if(sum > sum1){
middle = sum;
sum = sum1;
sum1 = middle;
}
if(sum >sum2){
middle = sum;
sum = sum2;
sum2 = middle;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
本题重点、
-
为了公平起见,所有的笔都买同一款。
-
正确的输入数据,然后对三种方案都进行计算,比较哪一种比较的便宜就用哪一种方案。
-
这里主要注意的点就是,包装的铅笔不散卖,所以要买只能整盒的买。这里就要判断所要买的套装是否和需要购买的铅笔的数量匹配,然后进行计算。
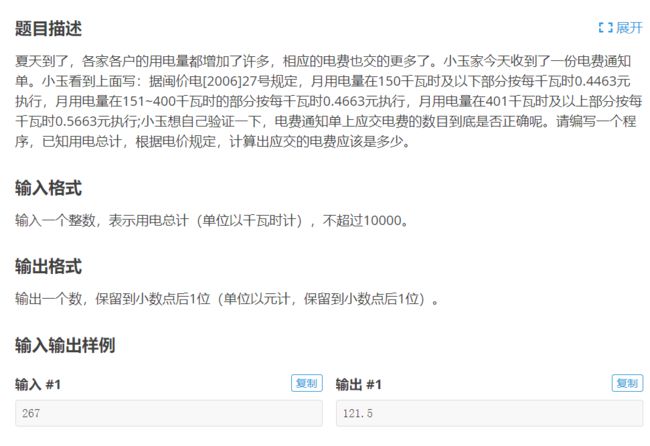
10.洛谷 p1422 java 小玉家的电费
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
double sum = 0;
if (n <= 150){
sum = n * 0.4463;
String num = String.format("%.1f",sum); //保留一位小数
System.out.println(num);
}else if (n <= 400){
sum = 150 * 0.4463 + (n - 150)*0.4663;
// String num = String.format("%.1f",sum);
System.out.printf("%.1f",sum); //保留一位小数
}else{
sum = 150 * 0.4463 + (400 - 150)*0.4663 + (n - 400)* 0.5663;
String num = String.format("%.1f",sum); //保留一位小数
System.out.println(num);
}
}
}
- 分支语句的正确使用,只使用if和使用if-else应该注意的点。
- 保留一位小数,可以使用printf,也可以使用String.format.建议大家都了解一下,虽然这两种方法在本题中的效果一样,可能printf这种较为简便,但也许在其他的算法中,这种方法就不再适用,可以使用String.format这种方法。
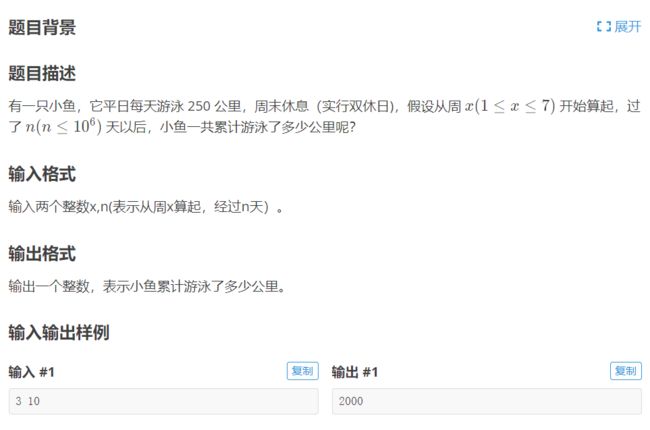
11.洛谷 p1424 java 小鱼的航程(改进版)
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();//输入周几
int n = sc.nextInt();//输入航行的天数
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++) {
if(x != 6 && x != 7){//判断是否是周六周日
sum += 250;
}
if(x == 7){//当周日的时候就将x变为1
x = 1;
}else{
x++;
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
本题重点:
- 刚拿到这道题的时候,我的第一感觉既然是找规律,找了小半小时,,,我放弃了。正好手头有点事先放放,回来的时候脑袋就清醒了,这一章节的训练主要就是分支结构,怎么会像递归,地推那种找公式呢,想的有点多。
- 这道题的思路就是进行for循环遍历,遇到非周六,周日的时候加250。就这么简单,有时候简单的问题大家不要想的太复杂。
12.洛谷 p1888 java 三角函数
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt(),b= sc.nextInt(),c= sc.nextInt();
int max=Math.max(Math.max(a,b),c);//得到最大的数
int min=Math.min(Math.min(a,b),c);//得到最小的数
int gongyinshu = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < min; i++) {//遍历得到最大的公因数
if (min % i == 0 && max % i == 0){//能同时被整除的书肯定是公因数,随着i增加,最后那个能被整除的数就是最大公因数。
gongyinshu = i;
}
}
System.out.println(min/gongyinshu+"/"+max/gongyinshu);
}
}
本题重点:
- 求得三角形最大的边和最小的边。
- 使用for循环得到最大公因数。
13.洛谷 p5717 java 三角形分类
AC代码:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
Integer[] arr = new Integer[]{a,b,c};//将三边存入数组中
Integer[] n = sort(arr);//使用sort()方法对数组进行排序。这个是自己写的,本身就有Arrays.sort()这个方法进行升序排序
//不能组成三角形
if (n[0]+n[1] <= n[2]){
System.out.println("Not triangle");
System.exit(0);//当构成不了三角形就得结束,否则将进行下面的操作,可能会符合一些要求
}
//锐角三角形
if ((n[0]*n[0]+n[1]*n[1]) > n[2]*n[2]){
System.out.println("Acute triangle");
}
//直角三角形
if ((n[0]*n[0]+n[1]*n[1]) == n[2]*n[2]){
System.out.println("Right triangle");
}
//钝角三角形
if ((n[0]*n[0]+n[1]*n[1]) < n[2]*n[2]){
System.out.println("Obtuse triangle");
}
//等腰三角形
if(n[0].equals(n[1])){
System.out.println("Isosceles triangle");
}
//等边三角形
if((n[0].equals(n[1])) && n[1].equals(n[2])){
System.out.println("Equilateral triangle");
}
}
public static Integer[] sort(Integer[] arr){
Arrays.sort(arr, 0, arr.length, new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
});
return arr;
}
}
本题重点
- 当构成不了三角形就得结束,否则将进行下面的操作,可能会符合一些要求,
- 写进数组中的sort方法可以不用自己写,直接使用Arrays.sort()即可。
14.洛谷 p4414 java ABC
AC代码:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[3];//定义一个数组
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();//输入相关的数据
}
String str = sc.next();//输入字符串
Arrays.sort(arr);//按照题意的要求进行升序排序
System.out.println(arr[str.charAt(0) - 65] +" "+ arr[str.charAt(1) - 65] +" "+ arr[str.charAt(2) - 65]);//根据输入的字符串的顺序依次输出相对应的数据
}
}
本题重点:
- 题中说输入的三个正整数ABC顺序不一定按照由大到小的顺序进行,所以要对输入的三个数据进行升序排序,这里用到的是定义数组将数组内的数据进行升序排序。
- 因为ABC的ASCALL表对应的数相连,所以使用字符串中的String.charAt()来获得每一个字符在减去A对应的SACALL数得到0,1,2.正好对应数组中的0,1,2.这样很巧妙地实现规定顺序的输出。
- 本题需要掌握:获得字符串第几个字符:使用String.charAt(); char类型转int类型;ASCALL表
15.洛谷 p1055 java ISBN号码;普及题
AC代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 接受输入,处理字符串
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String isbn = input.nextLine();// 获得输入的ISBN
// 处理数据
char isbnArray[] = isbn.toCharArray();// 将ISBN转换为char数组
int sum = (isbnArray[0] - '0') + (isbnArray[2] - '0') * 2 + (isbnArray[3] - '0') * 3
+ (isbnArray[4] - '0') * 4 + (isbnArray[6] - '0') * 5 + (isbnArray[7] - '0') * 6
+ (isbnArray[8] - '0') * 7 + (isbnArray[9] - '0') * 8 + (isbnArray[10] - '0') * 9;
int result = sum % 11;//按照题中要求对数据进行求余。模数:11;
if (result != 10) {
if ((isbnArray[12] - '0') != result) {// 如果识别码错误
isbnArray[12] = (char)(result + '0');// 改为正确的值
System.out.println(isbnArray);
} else {
System.out.println("Right");
}
} else {// 特殊情况,余数为10时
if (isbnArray[12] == 'X') {// 如果是X则正确
System.out.println("Right");
} else {
isbnArray[12] = 'X';// 改为正确的值
System.out.println(isbnArray);
}
}
}
}
- 先输入字符串,使用next() 和 nextLine都阔以。在使用toCharArray()方法,将字符串转化为对应的char类型数组。在数组中找到对应的数据,通过char类型转化为int类型,进行计算。得到最后的求余数据与字符串的第13位比较。
- 需要掌握的知识:字符串转成对应的char类型数组。char类型和int类型的相互转换。