Integral类型的跨平台使用
fundamental integral types or extended integral types
我们先通过下图,来了解可以跨平台使用的整数类型:
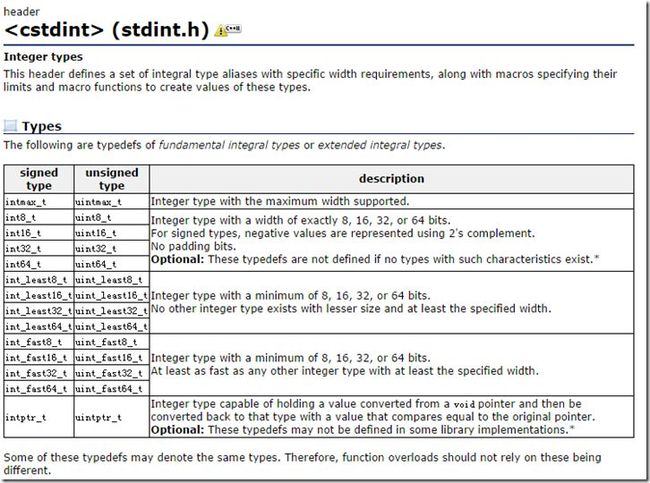
之所以我们需要以上各种明确指定宽度的int类型是因为int类型本身比较特殊,其具体的字节数同机器字长和编译器有关(标准并没有规定其具体所占的字节数)。
因此如果要保证移植性,我们应该尽量使用上图中带宽度的int类型。这种数据类型在所有平台下都分配相同的字节,因此在移植上不存在问题。
需要注意的问题
我们以整数类型int64_t为例来说明。我们都知道,int64_t用来表示64位整数,在32位系统中是long long int,在64位系统中是long int,所以打印int64_t的格式化方法如下:
printf("%ld" , value); // 64bit OS printf("%lld", value); // 32bit OS
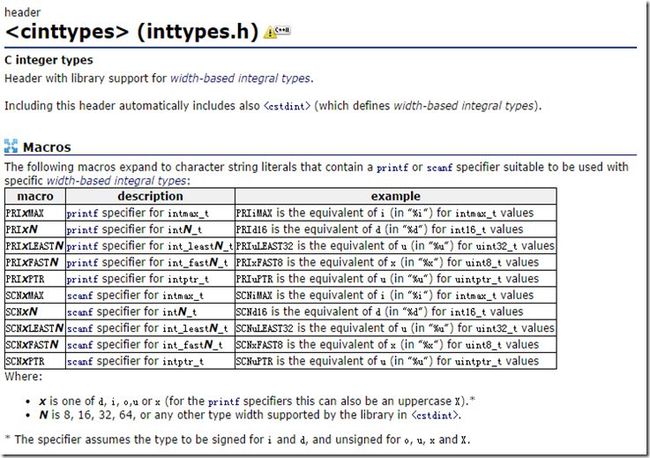
那么这样在32位系统和64位系统中,编译相同的代码,就有可能会出错。跨平台的方法是使用PRId64来格式化输出,如下:
#ifndef __STDC_FORMAT_MACROS #define __STDC_FORMAT_MACROS #endif #include <inttypes.h> printf("%" PRId64 "\n", value);
具体可以参看下图:
注意:上述宏定义针对C语言,如果C++需要使用PRId64等宏,需要定义一个__STDC_FORMAT_MACROS宏显示打开它。具体可以参见/usr/include/inttypes.h中宏__STDC_FORMAT_MACROS的定义,如下:
/* The ISO C99 standard specifies that these macros must only be defined if explicitly requested. */ #if !defined __cplusplus || defined __STDC_FORMAT_MACROS # if __WORDSIZE == 64 # define __PRI64_PREFIX "l" # define __PRIPTR_PREFIX "l" # else # define __PRI64_PREFIX "ll" # define __PRIPTR_PREFIX # endif /* Macros for printing format specifiers. */ /* Decimal notation. */ # define PRId8 "d" # define PRId16 "d" # define PRId32 "d" # define PRId64 __PRI64_PREFIX "d"
举例
MUDUO开源库中也使用了上文所提到的方式,源码如下:
#include <muduo/base/Timestamp.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <stdio.h> #ifndef __STDC_FORMAT_MACROS #define __STDC_FORMAT_MACROS #endif #include <inttypes.h> #include <boost/static_assert.hpp> using namespace muduo; BOOST_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(Timestamp) == sizeof(int64_t)); Timestamp::Timestamp(int64_t microseconds) : microSecondsSinceEpoch_(microseconds) { } string Timestamp::toString() const { char buf[32] = {0}; int64_t seconds = microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond; int64_t microseconds = microSecondsSinceEpoch_ % kMicroSecondsPerSecond; snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf)-1, "%" PRId64 ".%06" PRId64 "", seconds, microseconds); return buf; } string Timestamp::toFormattedString(bool showMicroseconds) const { char buf[32] = {0}; time_t seconds = static_cast<time_t>(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond); struct tm tm_time; gmtime_r(&seconds, &tm_time); if (showMicroseconds) { int microseconds = static_cast<int>(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ % kMicroSecondsPerSecond); snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%4d%02d%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%06d", tm_time.tm_year + 1900, tm_time.tm_mon + 1, tm_time.tm_mday, tm_time.tm_hour, tm_time.tm_min, tm_time.tm_sec, microseconds); } else { snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%4d%02d%02d %02d:%02d:%02d", tm_time.tm_year + 1900, tm_time.tm_mon + 1, tm_time.tm_mday, tm_time.tm_hour, tm_time.tm_min, tm_time.tm_sec); } return buf; } Timestamp Timestamp::now() { struct timeval tv; gettimeofday(&tv, NULL); int64_t seconds = tv.tv_sec; return Timestamp(seconds * kMicroSecondsPerSecond + tv.tv_usec); } Timestamp Timestamp::invalid() { return Timestamp(); }
说明
对于支持C++11标准的编译器,不用添加宏__STDC_FORMAT_MACROS,也可以直接编译通过。
参考文献
1. http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cinttypes/?kw=inttypes.h
2. http://www.cprogramdevelop.com/4787258/
3. https://github.com/chenshuo/muduo/blob/master/muduo/base/Timestamp.cc