kafka介绍及使用
一、MAC环境下安装启动kafka
1、安装kafka
brew install kafka复制代码安装详情
安装详情里面包含一些使用介绍,主要包括几个部分:![]()
安装kafka前默认安装了zookeeper,说明kafka依赖zookeeper,为什么依赖,下一部分会讲到。
这部分介绍了zookeeper和kafka的启动命令,要么用brew services start命令设置自启或重启(macOS 使用launchtl命令加载开机自动运行的服务,brew services是launchctl的一个子集),或者直接使用工具自带的命令启动。
2、启动kafka
启动kafka
zookeeper-server-start /usr/local/etc/kafka/zookeeper.properties & kafka-server-start /usr/local/etc/kafka/server.properties复制代码创建topic
kafka-topics --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic test复制代码查看所有topic
kafka-topics --list --zookeeper localhost:2181复制代码生产者发送消息
kafka-console-producer --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic test
>第一条消息
>第二条消息复制代码消费者消费消息
kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test --from-beginning
第一条消息二、kafka原理介绍
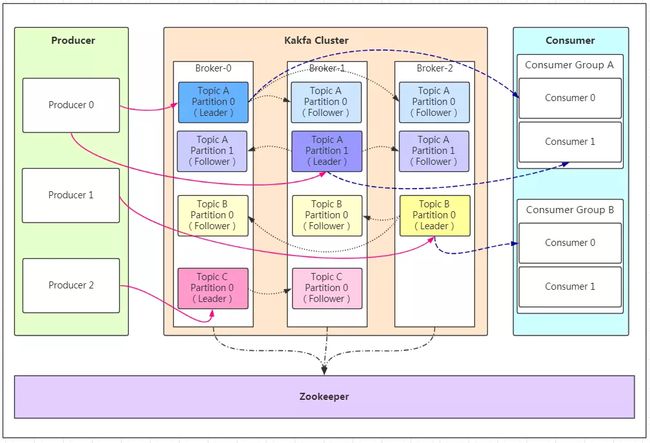
Producer:消息生产者。
Broker:kafka集群中的服务器。
Topic:消息的主题,可以理解为消息的分类,kafka的数据就保存在topic。在每个broker上都可以创建多个topic。
Partition:Topic的分区,每个topic可以有多个分区,分区的作用是做负载,提高kafka的吞吐量。
Replication:每一个分区都有多个副本,副本的作用是做备胎。当主分区(Leader)故障的时候会选择一个备胎(Follower)上位,成为Leader。在kafka中默认副本的最大数量是10个,且副本的数量不能大于Broker的数量,follower和leader绝对是在不同的机器,同一机器对同一个分区也只可能存放一个副本(包括自己)。
Consumer:消息消费者。
Consumer Group:我们可以将多个消费组组成一个消费者组,在kafka的设计中同一个分区的数据只能被消费者组中的某一个消费者消费。同一个消费者组的消费者可以消费同一个topic的不同分区的数据,这也是为了提高kafka的吞吐量!
Zookeeper:kafka集群依赖zookeeper来保存集群的的元信息,来保证系统的可用性。
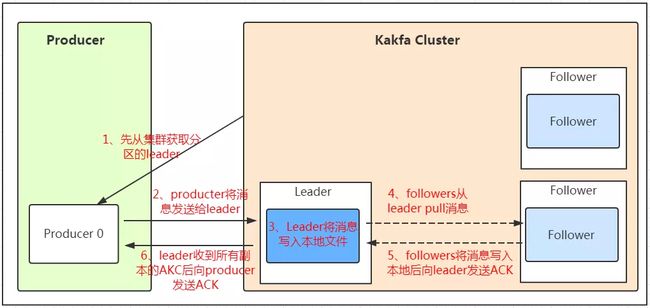
1、生产消息
kafka的数据,实际上是以文件的形式存储在文件系统的。topic下有partition,partition下有segment,segment是实际的一个个文件,topic和partition都是抽象概念。在目录/${topicName}-{$partitionid}/下,存储着实际的log文件(即segment),还有对应的索引文件。每个segment文件大小相等,文件名以这个segment中最小的offset命名,文件扩展名是.log;segment对应的索引的文件名字一样,扩展名是.index。
2、消费消息
订阅topic是以一个消费组来订阅的,一个消费组里面可以有多个消费者。同一个消费组中的两个消费者,不会同时消费一个partition。换句话来说,就是一个partition,只能被消费组里的一个消费者消费,但是可以同时被多个消费组消费。因此,如果消费组内的消费者如果比partition多的话,那么就会有个别消费者一直空闲。
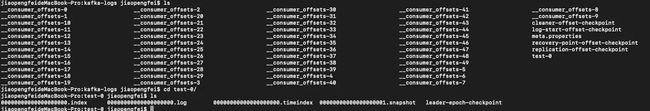
一个消费组消费partition,需要保存offset记录消费到哪,以前保存在zk中,由于zk的写性能不好,以前的解决方法都是consumer每隔一分钟上报一次。这里zk的性能严重影响了消费的速度,而且很容易出现重复消费。
在0.10版本后,kafka把这个offset的保存,从zk总剥离,保存在一个名叫__consumeroffsets topic的topic中。写进消息的key由groupid、topic、partition组成,value是偏移量offset。topic配置的清理策略是compact。总是保留最新的key,其余删掉。一般情况下,每个key的offset都是缓存在内存中,查询的时候不用遍历partition,如果没有缓存,第一次就会遍历partition建立缓存,然后查询返回。
3、kafka中消息具体是怎么被存储的
Kafka以Partition作为存储单元,一个partition是一个有序的,不变的消息队列,消息总是被追加到尾部。一个partition不能被切分成多个散落在多个broker上或者多个磁盘上。
Partition是由多个Segment组成,当Kafka要写数据到一个partition时,它会写入到状态为active的segment中。如果该segment被写满,则一个新的segment将会被新建,然后变成新的"active" segment。Segment以该segment的base offset作为自己的名称。
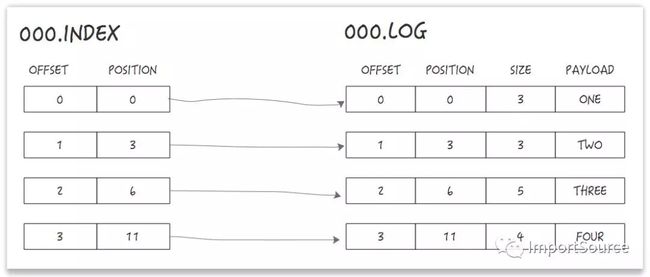
在磁盘上,一个partition就是一个目录,然后每个segment由一个index文件和一个log文件组成。如下:
![]()
Segment下的log文件就是存储消息的地方,每个消息都会包含消息体、offset、timestamp、key、size、压缩编码器、校验和、消息版本号等。在磁盘上的数据格式和producer发送到broker的数据格式一模一样,也和consumer收到的数据格式一模一样。由于磁盘格式与consumer以及producer的数据格式一模一样,这样就使得Kafka可以通过零拷贝(zero-copy)技术来提高传输效率。
Segment下的index负责映射消息offset到某个消息在log文件中的位置。如下:
索引文件是内存映射(memory mapped)的,offset查找使用二分查找来查找小于或等于目标offset的最近offset。
索引文件由8个字节的条目组成,4个字节用来存储相对于base offset的偏移量,另外4个字节用来存储position。这个偏移量由于是相对于base offset的,因此只需要4个字节来存储。比如base offset是10000000000000000000,那么接下来就不用存储为10000000000000000001 和10000000000000000002了,而是仅存储为1和2。
Kafka存储内部文件工作总结:
• Partition被分成多个segment。
• Segment包含两个文件:index和log文件。
• Index负责映射每个offset到消息的在log文件中的具体位置,主要用来查找消息。
• Indexes 保存的是当前segment的base offset的相对偏移量。
• 压缩消息批量发送是被包装一个wrapper message来发送。
• 保存在磁盘上的数据格式和broker从producer收到的以及发送给consumer的数据格式一模一样,这样就能够实现领拷贝(zero-copy)。
摘自cloud.tencent.com/developer/a…
4、kafka为什么会依赖zookeeper
1、在Kafka的设计中,选择了使用Zookeeper来进行所有Broker的管理,体现在zookeeper上会有一个专门用来进行Broker服务器列表记录的点,节点路径为/brokers/ids 每个Broker服务器在启动时,都会到Zookeeper上进行注册,即创建/brokers/ids/[0-N]的节点,然后写入IP,端口等信息,Broker创建的是临时节点,所有一旦Broker上线或者下线,对应Broker节点也就被删除了,因此我们可以通过zookeeper上Broker节点的变化来动态表征Broker服务器的可用性,Kafka的Topic也类似于这种方式。
2、生产者负载均衡。生产者需要将消息合理的发送到分布式Broker上,这就面临如何进行生产者负载均衡问题。 对于生产者的负载均衡,Kafka支持传统的4层负载均衡,zookeeper同时也支持zookeeper方式来实现负载均衡。 (1)传统的4层负载均衡 根据生产者的IP地址和端口来为其定一个相关联的Broker,通常一个生产者只会对应单个Broker,只需要维护单个TCP链接。这样的方案有很多弊端,因为在系统实际运行过程中,每个生产者生成的消息量,以及每个Broker的消息存储量都不一样,那么会导致不同的Broker接收到的消息量非常不均匀,而且生产者也无法感知Broker的新增与删除。 (2)使用zookeeper进行负载均衡很简单,生产者通过监听zookeeper上Broker节点感知Broker,Topic的状态,变更,来实现动态负载均衡机制,当然这个机制Kafka已经结合zookeeper实现了。
3、消费者的负载均衡和生产负载均衡类似
4、记录消息分区于消费者的关系,都是通过创建修改zookeeper上相应的节点实现
5、记录消息消费进度Offset记录,都是通过创建修改zookeeper上相应的节点实现 。
摘自blog.csdn.net/u011311291/…
更详细解释请参考www.jianshu.com/p/a036405f9…
三、spring-boot-kafka对接
maven依赖
org.springframework.kafka
spring-kafka
2.2.7.RELEASE
复制代码properties配置
spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers=192.168.41.140:9092
spring.kafka.consumer.bootstrap-servers=192.168.41.140:9092
spring.kafka.consumer.group-id=kafka
spring.kafka.consumer.auto-offset-reset=latest
spring.kafka.consumer.enable-auto-commit=true
spring.kafka.consumer.key-deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
spring.kafka.consumer.value-deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer复制代码1、生产消息
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.SendResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture;
/**
* kafka生产者
*
* @author blackupper
* @version $Id: KafkaProducer, v0.1
* @company
* @date 2019年08月02日 9:57 AM blackupper Exp $ */
@Component
@Slf4j
public class KafkaProducer {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate;
public void send(String topic, String msg){
log.info("send data:{}, {}", topic, msg);
ListenableFuture> future = kafkaTemplate.send(topic, msg);
future.addCallback(
success -> log.info("KafkaMessageProducer 发送消息成功!"),
fail -> log.error("KafkaMessageProducer 发送消息失败!"));
}
}复制代码
import io.swagger.annotations.*;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* 测试controller
*
* @author blackupper
* @version $Id: KafkaSendController, v0.1
* @company
* @date 2019年08月02日 10:02 AM blackupper Exp $
*/
@RestController
@Slf4j
@Api(description = "kafka测试接口")
public class KafkaSendController {
@Autowired
private KafkaProducer kafkaProducer;
@ApiOperation(value = "发送消息")
@RequestMapping(value = "/send", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public void queryBalance(
@ApiParam(value = "topic", name = "topic") @RequestParam(value = "topic") String topic,
@ApiParam(value = "消息内容", name = "msg") @RequestParam(value = "msg") String msg) {
kafkaProducer.send(topic, msg);
}
}
复制代码
2、消费消息
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.TopicPartition;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* kafka消费者
*
* @author blackupper
* @version $Id: KafKaConsumer, v0.1
* @company
* @date 2019年08月02日 10:34 AM blackupper Exp $ */
@Component
@Slf4j
public class KafKaConsumer {
@KafkaListener(id = "kafka", topicPartitions = {@TopicPartition(topic = "test1", partitions = { "0", "1" })})
public void listen (ConsumerRecord record) {
log.info("start consume");
log.info("topic-{}, offset-{}, value-{}", record.topic(), record.offset(), record.value());
}
}复制代码
3、生产者常用调用方式
ListenableFuture> sendDefault(V data);复制代码 KafkaTemplate中有defaultTopic这个属性,当调用sendDefault方法时,kafka会自动把消息发送到defaultTopic属性指定的topic中。
ListenableFuture> send(String topic, Integer partition, K key, V data);复制代码 将消息发送到指定的topic和partition中
ListenableFuture> send(String topic, Integer partition, Long timestamp, K key, V data);复制代码 将消息发送到指定的topic和partition中,并在消息上带上时间戳
ListenableFuture> send(ProducerRecord record);复制代码 将消息内容封装成ProducerRecord进行发送
其实上述几个方法,最终都是分装成ProducerRecord,调用doSend方法传递消息的,我们下面看下doSend方法的源码:
protected ListenableFuture> doSend(final ProducerRecord producerRecord) {
if (this.transactional) {
Assert.state(inTransaction(),
"No transaction is in process; "
+ "possible solutions: run the template operation within the scope of a "
+ "template.executeInTransaction() operation, start a transaction with @Transactional "
+ "before invoking the template method, "
+ "run in a transaction started by a listener container when consuming a record");
}
final Producer producer = getTheProducer();
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Sending: " + producerRecord);
}
final SettableListenableFuture> future = new SettableListenableFuture<>();
producer.send(producerRecord, buildCallback(producerRecord, producer, future));
if (this.autoFlush) {
flush();
}
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Sent: " + producerRecord);
}
return future;
}复制代码 从上述代码可以看到,doSend内部首先判断是否开启了事务,然后调用KafkaProducer的send方法发送消息,SettableListenableFuture接收返回值,SettableListenableFuture实现了ListenableFuture接口,ListenableFuture则实现了Future接口,Future是Java自带的实现异步编程的接口,支持返回值的异步。由此可见上述的几个方法都是异步发送消息的。如果想要同步获取结果,可以调用Future的get方法,该方法会阻塞直到任务返回结果。
4、@KafkaListener属性详解
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@MessageMapping
@Documented
@Repeatable(KafkaListeners.class)
public @interface KafkaListener {
/**
* The unique identifier of the container managing for this endpoint.
* If none is specified an auto-generated one is provided.
*
Note: When provided, this value will override the group id property
* in the consumer factory configuration, unless {@link #idIsGroup()}
* is set to false.
*
SpEL {@code #{...}} and property place holders {@code ${...}} are supported.
* @return the {@code id} for the container managing for this endpoint.
* @see org.springframework.kafka.config.KafkaListenerEndpointRegistry#getListenerContainer(String)
*/
String id() default "";
/**
* The bean name of the {@link org.springframework.kafka.config.KafkaListenerContainerFactory}
* to use to create the message listener container responsible to serve this endpoint.
*
If not specified, the default container factory is used, if any.
* @return the container factory bean name.
*/
String containerFactory() default "";
/**
* The topics for this listener.
* The entries can be 'topic name', 'property-placeholder keys' or 'expressions'.
* An expression must be resolved to the topic name.
*
* Mutually exclusive with {@link #topicPattern()} and {@link #topicPartitions()}.
* @return the topic names or expressions (SpEL) to listen to.
*/
String[] topics() default {};
/**
* The topic pattern for this listener. The entries can be 'topic pattern', a
* 'property-placeholder key' or an 'expression'. The framework will create a
* container that subscribes to all topics matching the specified pattern to get
* dynamically assigned partitions. The pattern matching will be performed
* periodically against topics existing at the time of check. An expression must
* be resolved to the topic pattern (String or Pattern result types are supported).
*
* Mutually exclusive with {@link #topics()} and {@link #topicPartitions()}.
* @return the topic pattern or expression (SpEL).
* @see org.apache.kafka.clients.CommonClientConfigs#METADATA_MAX_AGE_CONFIG
*/
String topicPattern() default "";
/**
* The topicPartitions for this listener.
*
* Mutually exclusive with {@link #topicPattern()} and {@link #topics()}.
* @return the topic names or expressions (SpEL) to listen to.
*/
TopicPartition[] topicPartitions() default {};
/**
* If provided, the listener container for this listener will be added to a bean
* with this value as its name, of type {@code Collection}.
* This allows, for example, iteration over the collection to start/stop a subset
* of containers.
* SpEL {@code #{...}} and property place holders {@code ${...}} are supported.
* @return the bean name for the group.
*/
String containerGroup() default "";
/**
* Set an {@link org.springframework.kafka.listener.KafkaListenerErrorHandler} bean
* name to invoke if the listener method throws an exception.
* @return the error handler.
* @since 1.3
*/
String errorHandler() default "";
/**
* Override the {@code group.id} property for the consumer factory with this value
* for this listener only.
*
SpEL {@code #{...}} and property place holders {@code ${...}} are supported.
* @return the group id.
* @since 1.3
*/
String groupId() default "";
/**
* When {@link #groupId() groupId} is not provided, use the {@link #id() id} (if
* provided) as the {@code group.id} property for the consumer. Set to false, to use
* the {@code group.id} from the consumer factory.
* @return false to disable.
* @since 1.3
*/
boolean idIsGroup() default true;
/**
* When provided, overrides the client id property in the consumer factory
* configuration. A suffix ('-n') is added for each container instance to ensure
* uniqueness when concurrency is used.
*
SpEL {@code #{...}} and property place holders {@code ${...}} are supported.
* @return the client id prefix.
* @since 2.1.1
*/
String clientIdPrefix() default "";
/**
* A pseudo bean name used in SpEL expressions within this annotation to reference
* the current bean within which this listener is defined. This allows access to
* properties and methods within the enclosing bean.
* Default '__listener'.
*
* Example: {@code topics = "#{__listener.topicList}"}.
* @return the pseudo bean name.
* @since 2.1.2
*/
String beanRef() default "__listener";
/**
* Override the container factory's {@code concurrency} setting for this listener. May
* be a property placeholder or SpEL expression that evaluates to a {@link Number}, in
* which case {@link Number#intValue()} is used to obtain the value.
*
SpEL {@code #{...}} and property place holders {@code ${...}} are supported.
* @return the concurrency.
* @since 2.2
*/
String concurrency() default "";
/**
* Set to true or false, to override the default setting in the container factory. May
* be a property placeholder or SpEL expression that evaluates to a {@link Boolean} or
* a {@link String}, in which case the {@link Boolean#parseBoolean(String)} is used to
* obtain the value.
*
SpEL {@code #{...}} and property place holders {@code ${...}} are supported.
* @return true to auto start, false to not auto start.
* @since 2.2
*/
String autoStartup() default "";
/**
* Kafka consumer properties; they will supersede any properties with the same name
* defined in the consumer factory (if the consumer factory supports property overrides).
*
Supported Syntax
* The supported syntax for key-value pairs is the same as the
* syntax defined for entries in a Java
* {@linkplain java.util.Properties#load(java.io.Reader) properties file}:
*
* - {@code key=value}
* - {@code key:value}
* - {@code key value}
*
* {@code group.id} and {@code client.id} are ignored.
* @return the properties.
* @since 2.2.4
* @see org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerConfig
* @see #groupId()
* @see #clientIdPrefix()
*/
String[] properties() default {};
}复制代码
- id:代表当前节点的唯一标识,不配置的话会自动分配一个id,主动配置的话,groupId会被设置成id的值(前提是idIsGroup这个属性值没有被设置成false)。
- containerFactory:设置监听容器工厂类。
- topics:需要监听的Topic,可监听多个。
- topicsPattern:Topic主题,支持属性占位符,或者是正则表达式。
- topicPartitions:可以设置更加详细的监听信息,包括topic、partitions和partitionOffsets。
- containerGroup:设置了这个属性,当前的监听器会被加进设置的这个容器组里面,后面你可以通过遍历这个集合来启动或终止一组监听器集合。
- errorHandler:异常处理器,如果监听器处理方法抛出异常,你可以设置一个实现了KafkaListenerErrorHandler的异常处理类来处理抛出的异常。
- groupId:设置当前消费者组id,支持SpEL表达式{@code #{...}}和属性占位符{@code ${...}}
- idIsGroup:id是否能用作groupId
- clientIdPrefix:clientId前缀,后缀会默认加上-n来保证并发时该id的唯一性,支持SpEL表达式{@code #{...}}和属性占位符{@code ${...}}
- beanRef:此注解中SpEL表达式中使用的伪bean名,用于指向此监听器的当前bean,从而允许访问封装bean中的属性和方法。
- concurrency:用于覆盖容器工厂中的并发属性,支持SpEL表达式{@code #{...}}和属性占位符{@code ${...}}
- autoStartup:是否自动启动
- properties:消费者属性,将替换在消费者工厂中定义的具有相同名称的任何属性(如果消费者工厂支持属性覆盖)。
5、ReplyingKafkaTemplate简介
在分析KafkaTemplate方法的时候,发现其实现的接口类KafkaOperations,还有另外一个实现类ReplyingKafkaTemplate,简单的描述处理流程就是:生产者通过TopicA发送消息,监听器A从TopicA中获取到消息,进行业务处理后将响应内容转发到TopicB,监听器B从TopicB获取消息再次进行处理。
通过分析源码,发现ReplyingKafkaTemplate是利用了请求响应模式,通过设置ProducerRecord.topic属性可以设置发送topic,通过设置ProducerRecord.Headers属性可以设置转发topic,当然也可以在new ReplyingKafkaTemplate()的时候,在GenericMessageListenerContainer中设置转发topic。
@Configuration
@EnableKafka
public class ReplyKafkaTemplateConfiguration {
@Value("${spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers}")
private String producer;
@Value("${spring.kafka.consumer.bootstrap-servers}")
private String consumer;
@Bean
public KafkaMessageListenerContainer replyContainer(@Autowired ConsumerFactory consumerFactory) {
ContainerProperties containerProperties = new ContainerProperties("topic.reply");
return new KafkaMessageListenerContainer<>(consumerFactory, containerProperties);
}
@Bean
public ReplyingKafkaTemplate replyingKafkaTemplate(@Autowired ProducerFactory producerFactory, KafkaMessageListenerContainer replyContainer) {
ReplyingKafkaTemplate template = new ReplyingKafkaTemplate<>(producerFactory, replyContainer);
template.setReplyTimeout(10000);
return template;
}
@Bean
public ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory kafkaListenerContainerFactory() {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory factory = new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
factory.setConsumerFactory(consumerFactory());
factory.setReplyTemplate(kafkaTemplate());
return factory;
}
@Bean
@Primary
public KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate() {
KafkaTemplate template = new KafkaTemplate<>(producerFactory());
return template;
}
@Bean
public ProducerFactory producerFactory() {
return new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory<>(senderProps());
}
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory consumerFactory() {
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(consumerProps());
}
//消费者配置参数
private Map consumerProps() {
Map props = new HashMap<>();
//连接地址
props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, consumer);
//GroupID
props.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, "replyTest");
//是否自动提交
props.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG, true);
//自动提交的频率
props.put(ConsumerConfig.AUTO_COMMIT_INTERVAL_MS_CONFIG, "100");
//Session超时设置
props.put(ConsumerConfig.SESSION_TIMEOUT_MS_CONFIG, "15000");
//键的反序列化方式
props.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, IntegerDeserializer.class);
//值的反序列化方式
props.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
return props;
}
//生产者配置
private Map senderProps (){
Map props = new HashMap<>();
//连接地址
props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, producer);
//重试,0为不启用重试机制
props.put(ProducerConfig.RETRIES_CONFIG, 1);
//控制批处理大小,单位为字节
props.put(ProducerConfig.BATCH_SIZE_CONFIG, 16384);
//批量发送,延迟为1毫秒,启用该功能能有效减少生产者发送消息次数,从而提高并发量
props.put(ProducerConfig.LINGER_MS_CONFIG, 1);
//生产者可以使用的总内存字节来缓冲等待发送到服务器的记录
props.put(ProducerConfig.BUFFER_MEMORY_CONFIG, 1024000);
//键的序列化方式
props.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, IntegerSerializer.class);
//值的序列化方式
props.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class);
return props;
}
}复制代码
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ReplyKafkaTemplateProducer {
@Autowired
private ReplyingKafkaTemplate replyingKafkaTemplate;
public void send() throws Exception {
ProducerRecord record = new ProducerRecord<>("topic.request", "request message");
record.headers().add(new RecordHeader(KafkaHeaders.REPLY_TOPIC, "topic.reply".getBytes()));
RequestReplyFuture replyFuture = replyingKafkaTemplate.sendAndReceive(record);
SendResult sendResult = replyFuture.getSendFuture().get();
log.info("send request msg result: " + sendResult.getRecordMetadata());
ConsumerRecord consumerRecord = replyFuture.get();
log.info("receive reply result: " + consumerRecord.value());
}
}复制代码
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ReplyKafkaTemplateConsumer {
@KafkaListener(id = "replyConsumer", topics = "topic.request",containerFactory = "kafkaListenerContainerFactory")
@SendTo
public String replyListen(ConsumerRecord record){
log.info("topic-{}, offset-{}, value-{}", record.topic(), record.offset(), record.value());
return "reply message";
}
}复制代码