- Maven
iam_leeqing
JAVA开发mavenjava
Maven是一个面向Java项目的综合性项目管理和构建工具,它通过提供标准化的项目结构、依赖管理和构建生命周期来简化开发流程。Maven使用XML格式的pom.xml文件来定义项目配置和依赖关系,支持自动化构建过程,包括编译、测试、打包和部署等阶段。此外,Maven还能自动下载所需的库文件并解决依赖冲突,同时提供了丰富的插件支持以扩展其功能。通过使用Maven,开发者可以提高构建的一致性和可重复性
- JAVA中的类与对象
A蜂蜜罐头
java开发语言
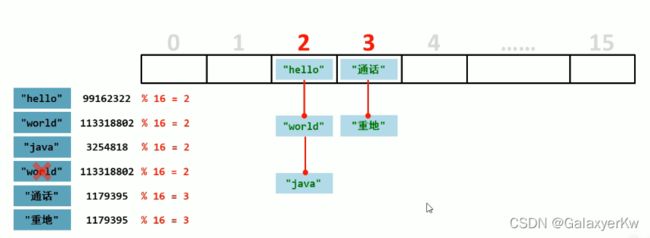
类与对象的概念什么是类?具有相同属性以及行为的一组对象叫做类。用来描述对象具体有哪些属性和功能。类是对象的模板,对象是类的实例。类只有通过对象才可以使用,而在开发之中应该先产生类,之后再产生对象。类不能直接使用,对象是可以直接使用的。举个例子:在我们的生活中,男孩女孩都是一个类,而男孩和女孩中的每一个个体就是其中的对象。所以对象就是类中的一个个成员。类与对象的定义与使用类的定义:需要使用class
- JAVA工具类AES加密,模式:CBC(开箱即用)
一行一步
没有那么多废话,我知道这是一个简单的加密工具类,但是网上的工具类很杂,我这至少保证全都是自己试验过的可以直接使用!/***AES加密工具模式:CBC补码方式:PKCS5Padding*@authorAdministrator**/publicclassAESCBCUtils{//加密publicstaticStringencrypt(StringsSrc,StringencodingFormat,
- Python爬虫实战:深入无限滚动页面抓取原理与Playwright实现
Python爬虫项目
python爬虫开发语言区块链json
一、前言:无限滚动页面的挑战在现代Web开发中,「无限滚动(InfiniteScrolling)」早已取代了传统的分页模式。以微博热搜流、知乎首页、抖音推荐页为例,用户向下滚动时会自动加载更多内容,这种体验虽提升了交互性,却让传统爬虫面临巨大挑战:页面初始只加载一部分内容剩余内容由JavaScript在滚动事件中动态加载requests类爬虫无法感知页面行为为什么传统爬虫抓不到数据?因为页面数据不
- 【Python】通过注释插桩替换代码实现开源自动化
ChrisEighteen18
pythonpython
需求提出在特定的标签注释后写上开源后的代码实现开源替换答疑解惑调用如下的代码即可实现defreplace_java_code_in_one_line_by_tag(patch_file_path,update_java_code_line_tag):"""本方法对包含update_java_code_line_tag的之前本行内所有内容进行删除操作;适用于对java文件的代码替换,即在包含upda
- java 求1_java 求1 2i
新智元
java求1
1-2求斐波拉契数求斐波拉契数斐波拉契数为,Fib(N)=Fib(N-1)+Fib(N-2)F(0)=F(1)=1用Java编写能求Fib(N)的程序输入为N,须输出Fib(N)如输入3输出:3importjava.util.Scanner;publicclassMai...文章uiiuiiu2018-07-12903浏览量求字符串的len组合数(java程序)importjava.util.Li
- 周总结5.29-6.3
Sandra_n
vuevue.js数据结构
1.混入应用的是样式?【场景】2.es6/优化==继续看3.树组件操作:数据扁平化/模糊检索{也是把数据结构改了一下复制的ant官网}/默认展开收起{中途有问题比如不默认展开:判断数据删除某一节点展开等}/只呈现查询内容适合调接口{中途研究了一下树id和内容映射[人员树专业树]数据处理}4.置空下拉框v-model设为undefined就提示placeholder了也可以在某项想要的操作后设置初始
- 2、Python 测试全攻略:自动化与驱动开发
辣条鉴定师
Python测试自动化测试测试驱动开发
Python测试全攻略:自动化与驱动开发1.测试的乐趣与收益编程过程中,测试常被视为徒劳或浪费时间的事。但实际上,测试可以变得轻松有趣且富有成效。比如回忆一下曾遇到的恼人bug,可能是数据库模式不匹配、数据结构错误等。若有一小段代码能在恰当时间捕捉到该bug并告知你,而所有代码都配有这样易执行的测试代码,那bug存活时间会大大缩短。基本思路是用简单易写的代码片段告知计算机期望结果,让计算机在编码过
- 华为OD机考2025B卷 - 表达式括号匹配(Java & Python& JS & C++ & C )
算法大师
最新华为OD机试真题华为OD机试真题(Java/JS/Py/C)华为odjavapythonjavascriptc++
最新华为OD机试真题目录:点击查看目录华为OD面试真题精选:点击立即查看2025华为od机试2025B卷-华为机考OD2025年B卷题目描述(1+(2+3)*(3+(8+0))+1-2)这是一个简单的数学表达式,今天不是计算它的值,而是比较它的括号匹配是否正确。前面这个式子可以简化为(()(()))这样的括号我们认为它是匹配正确的,而((())这样的我们就说他是错误的。注意括号里面的表达式可能是错
- SpringBoot单元测试全攻略:MockMVC+Testcontainers+覆盖率分析
fanxbl957
Webspringboot单元测试后端
博主介绍:Java、Python、js全栈开发“多面手”,精通多种编程语言和技术,痴迷于人工智能领域。秉持着对技术的热爱与执着,持续探索创新,愿在此分享交流和学习,与大家共进步。DeepSeek-行业融合之万象视界(附实战案例详解100+)全栈开发环境搭建运行攻略:多语言一站式指南(环境搭建+运行+调试+发布+保姆级详解)感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,希望帮助更多的人SpringBoot单元测试全攻略:
- 【算法-贪心算法-python】柠檬水找零
檀越@新空间
P1算法与数据结构s1Python算法贪心算法python
欢迎来到我的博客,很高兴能够在这里和您见面!希望您在这里可以感受到一份轻松愉快的氛围,不仅可以获得有趣的内容和知识,也可以畅所欲言、分享您的想法和见解。推荐:kuan的首页,持续学习,不断总结,共同进步,活到老学到老导航檀越剑指大厂系列:全面总结java核心技术点,如集合,jvm,并发编程redis,kafka,Spring,微服务,Netty等常用开发工具系列:罗列常用的开发工具,如IDEA,M
- 伪数组转换为真正的数组
会飞的鱼先生
javascript前端vue.js
在JavaScript中,**伪数组(类数组对象)**是指具有数字索引和length属性,但不具备数组原生方法的对象。常见的伪数组包括函数的arguments对象、DOM集合(如document.querySelectorAll的返回值)等。要将伪数组转换为真正的数组,可以使用以下几种方法:1.使用Array.from()Array.from()是一种简洁且高效的方法,可以将伪数组转换为真正的数组
- sqoop从mysql导数据到hdfs,出现java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: Class QueryResult not found
无级程序员
大数据sqoopmysqlhdfs
运行sqoop从postgresql/mysql导入数据到hdfs,结果出现如下错误:2025-07-1816:59:13,624INFOorm.CompilationManager:HADOOP_MAPRED_HOMEis/opt/datasophon/hadoop-3.3.3Note:/opt/sqoop/bin/QueryResult.javausesoroverridesadeprecat
- datasophon下dolphinscheduler执行脚本出错
无级程序员
大数据hive硬件架构hadoop
执行hive脚本出错:错误消息:FAILED:RuntimeExceptionErrorloadinghooks(hive.exec.post.hooks):java.lang.ClassNotFoundException:org.apache.atlas.hive.hook.HiveHookatjava.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.ja
- python pywebview + vue3 做桌面端
妃衣
python开发语言
pythonpywebview+vue3做桌面端Api.py#传给前端的api对象,定义了一个可以通过js调用退出当前应用的函数classApi:def__init__(self)->None:self._window=None#java运行的线程self.process=Nonedefset_process(self,_process):self.process=_processdefset_w
- python的pywebview库结合Flask和waitress开发桌面应用程序简介
czliutz
python笔记pythonflask开发语言
pywebview的用途与特点用途pywebview是一个轻量级Python库,用于创建桌面应用程序(GUI)。它通过嵌入Web浏览器组件(如Windows的Edge/IE、macOS的WebKit、Linux的GTKWebKit),允许开发者使用HTML/CSS/JavaScript构建界面,并用Python处理后端逻辑。这种方式结合了Web技术的灵活性和Python的强大功能,适合快速开发跨平
- [Java实战]Spring Boot 3实战:使用QQ邮箱发送精美HTML邮件(四十三)
曼岛_
Java实战javaspringboot邮件
[Java实战]SpringBoot3实战:使用QQ邮箱发送精美HTML邮件(四十三)本文将详细介绍如何在SpringBoot3中配置QQ邮箱发送专业的HTML格式邮件,解决实际开发中的邮件发送问题。一、结果验证1.1接口调用1.2邮箱查收二、QQ邮箱配置关键点2.1QQ邮箱特殊配置要求QQ邮箱与其他邮箱服务不同,需要特别注意:必须使用授权码而非登录密码需要启用SSL加密连接端口使用465(SSL
- 【031】2020.12.13 周日 Java类文件结构
算法成瘾者
Java类文件结构1.无关性基石虚拟机和字节码存储格式2.Class类文件的结构2.1)定义Class文件是一组以8字节为基础单位的二进制流2.2)Class文件格式:类似于C语言结构体的伪结构存储两种数据类型无符号数u1,u2,u4,u8表_info结尾某一类型的“集合”2.3)魔数与Class文件的版本魔数定义:每个Class文件的头4个字节被称为“魔数”(magicnumber)作用:确定是
- DDD深度解析
我是廖志伟,一名Java开发工程师、《Java项目实战——深入理解大型互联网企业通用技术》(基础篇)、(进阶篇)、(架构篇)清华大学出版社签约作家、Java领域优质创作者、CSDN博客专家、阿里云专家博主、51CTO专家博主、产品软文专业写手、技术文章评审老师、技术类问卷调查设计师、幕后大佬社区创始人、开源项目贡献者。拥有多年一线研发和团队管理经验,研究过主流框架的底层源码(Spring、Spri
- 领域驱动设计核心解析
Java开发廖志伟
Java场景面试宝典Domain-DrivenDesignSoftwareArchitectureStrategicandTacticalDesign
我是廖志伟,一名Java开发工程师、《Java项目实战——深入理解大型互联网企业通用技术》(基础篇)、(进阶篇)、(架构篇)清华大学出版社签约作家、Java领域优质创作者、CSDN博客专家、阿里云专家博主、51CTO专家博主、产品软文专业写手、技术文章评审老师、技术类问卷调查设计师、幕后大佬社区创始人、开源项目贡献者。拥有多年一线研发和团队管理经验,研究过主流框架的底层源码(Spring、Spri
- ShardingSphere技术解析
我是廖志伟,一名Java开发工程师、《Java项目实战——深入理解大型互联网企业通用技术》(基础篇)、(进阶篇)、(架构篇)清华大学出版社签约作家、Java领域优质创作者、CSDN博客专家、阿里云专家博主、51CTO专家博主、产品软文专业写手、技术文章评审老师、技术类问卷调查设计师、幕后大佬社区创始人、开源项目贡献者。拥有多年一线研发和团队管理经验,研究过主流框架的底层源码(Spring、Spri
- 微服务架构核心技术解析
Java开发廖志伟
Java场景面试宝典MicroservicesServiceDiscoveryAPIGateway
我是廖志伟,一名Java开发工程师、《Java项目实战——深入理解大型互联网企业通用技术》(基础篇)、(进阶篇)、(架构篇)清华大学出版社签约作家、Java领域优质创作者、CSDN博客专家、阿里云专家博主、51CTO专家博主、产品软文专业写手、技术文章评审老师、技术类问卷调查设计师、幕后大佬社区创始人、开源项目贡献者。拥有多年一线研发和团队管理经验,研究过主流框架的底层源码(Spring、Spri
- 前端——HTML
哪里不会点哪里.
前端html前端
目录HTML简介HTML基本框架JavaScript内嵌JavaScript外引JavaScriptCSS内部样式外部样式HTML简介HTML的全称为超文本标记语言,是一种标记语言。它包括一系列标签,通过这些标签可以将网络上的文档格式统一,使分散的Internet资源连接为一个逻辑整体。HTML文本是由HTML命令组成的描述性文本,HTML命令可以说明文字,图形、动画、声音、表格、链接等。超文本是
- 数据库管理-第349期 Oracle DB 23.9新特性一览(20250717)
胖头鱼的鱼缸(尹海文)
Oracle数据库oracle
数据库管理349期2025-07-17数据库管理-第349期OracleDB23.9新特性一览(20250717)1JavaScript过程和函数的编译时语法检查2不再需要JAVASCRIPT上的EXECUTE权限3GROUPBYALL4使用SQL创建并测试UUID5IVF索引在线重组6JSON到二元性迁移器:使用JSONschema进行模式推理7数据库认证的多因素认证8多语言引擎支持数据库驻留连
- (九)set结构
我拥抱着我的未来
set结构map,set结构都可以用foreach循环出来。set不允许插入重复的值,map键值对没有限制/*数据结构:set*集合:可以存储任何数据类型,并且唯一(不重复的值)*/constset2=newSet([1,true,'string']);console.log(set2);constset1=newSet();//往set1中添加数据set1.add(100);set1.add("
- Spring Cloud架构解析
Java开发廖志伟
Java场景面试宝典SpringCloudServiceGovernanceDistributedSystems
我是廖志伟,一名Java开发工程师、《Java项目实战——深入理解大型互联网企业通用技术》(基础篇)、(进阶篇)、(架构篇)清华大学出版社签约作家、Java领域优质创作者、CSDN博客专家、阿里云专家博主、51CTO专家博主、产品软文专业写手、技术文章评审老师、技术类问卷调查设计师、幕后大佬社区创始人、开源项目贡献者。拥有多年一线研发和团队管理经验,研究过主流框架的底层源码(Spring、Spri
- javaweb学习开发代码_HTML-CSS-JS
HTML学习标题(h1~h6)-段落p-换行brDocument当代文学之夜:2024年度长篇五佳作品及文学拉力赛颁奖当代文学之夜:2024年度长篇五佳作品及文学拉力赛颁奖当代文学之夜:2024年度长篇五佳作品及文学拉力赛颁奖当代文学之夜:2024年度长篇五佳作品及文学拉力赛颁奖当代文学之夜:2024年度长篇五佳作品及文学拉力赛颁奖当代文学之夜:2024年度长篇五佳作品及文学拉力赛颁奖《当代》作为
- Java 进阶之路:探索更强大的编程世界
七七&556
面试学习路线阿里巴巴java开发语言
在编程的浩瀚海洋中,Java如同一艘坚固的巨轮,引领着开发者们驶向创新与高效的彼岸。当我们掌握了Java的基础知识后,进阶之旅便悄然开启。一、面向对象的深入理解封装、继承与多态封装不仅仅是将数据隐藏起来,更是一种对代码的保护和组织方式。通过合理的封装,可以提高代码的可维护性和安全性。继承是代码复用的重要手段,但要避免过度继承带来的复杂性。理解继承的层次结构和正确使用继承,可以使代码更加清晰和易于扩
- Vue3 - 实现一个雨水滴落的动画效果
程序员的成长之路
Vue3html5javascriptvue
在Vue3中实现一个雨水滴落的动画效果,可以使用HTML5的元素和JavaScript来绘制和控制动画。以下是一个实现雨水滴落效果的示例:创建一个Vue3项目首先,确保你已经创建了一个Vue3项目。如果还没有,可以使用VueCLI来创建:vuecreaterain-animationcdrain-animation添加Canvas组件创建一个新的Vue组件来包含我们的元素和动画逻辑。创建一个名为R
- 飞算JavaAI:力臻开发之本真,破 AI 代码之繁琐,传统项目一键生成
微学AI
人工智能javajavaAI
飞算JavaAI:力臻开发之本真,破AI代码之繁琐,传统项目一键生成文章目录飞算JavaAI:力臻开发之本真,破AI代码之繁琐,传统项目一键生成一、前言二、飞算JavaAI是什么?2.1背景与实力2.2飞算JavaAI的“独门绝技”三、飞算JavaAI实战体验3.1IDEA插件安装配置3.2Main中写一个简单的梯度下降算法3.3main函数搭建一个卷积神经网络网络3.4飞算JavaAI:需求分析
- Java实现的基于模板的网页结构化信息精准抽取组件:HtmlExtractor
yangshangchuan
信息抽取HtmlExtractor精准抽取信息采集
HtmlExtractor是一个Java实现的基于模板的网页结构化信息精准抽取组件,本身并不包含爬虫功能,但可被爬虫或其他程序调用以便更精准地对网页结构化信息进行抽取。
HtmlExtractor是为大规模分布式环境设计的,采用主从架构,主节点负责维护抽取规则,从节点向主节点请求抽取规则,当抽取规则发生变化,主节点主动通知从节点,从而能实现抽取规则变化之后的实时动态生效。
如
- java编程思想 -- 多态
百合不是茶
java多态详解
一: 向上转型和向下转型
面向对象中的转型只会发生在有继承关系的子类和父类中(接口的实现也包括在这里)。父类:人 子类:男人向上转型: Person p = new Man() ; //向上转型不需要强制类型转化向下转型: Man man =
- [自动数据处理]稳扎稳打,逐步形成自有ADP系统体系
comsci
dp
对于国内的IT行业来讲,虽然我们已经有了"两弹一星",在局部领域形成了自己独有的技术特征,并初步摆脱了国外的控制...但是前面的路还很长....
首先是我们的自动数据处理系统还无法处理很多高级工程...中等规模的拓扑分析系统也没有完成,更加复杂的
- storm 自定义 日志文件
商人shang
stormclusterlogback
Storm中的日志级级别默认为INFO,并且,日志文件是根据worker号来进行区分的,这样,同一个log文件中的信息不一定是一个业务的,这样就会有以下两个需求出现:
1. 想要进行一些调试信息的输出
2. 调试信息或者业务日志信息想要输出到一些固定的文件中
不要怕,不要烦恼,其实Storm已经提供了这样的支持,可以通过自定义logback 下的 cluster.xml 来输
- Extjs3 SpringMVC使用 @RequestBody 标签问题记录
21jhf
springMVC使用 @RequestBody(required = false) UserVO userInfo
传递json对象数据,往往会出现http 415,400,500等错误,总结一下需要使用ajax提交json数据才行,ajax提交使用proxy,参数为jsonData,不能为params;另外,需要设置Content-type属性为json,代码如下:
(由于使用了父类aaa
- 一些排错方法
文强chu
方法
1、java.lang.IllegalStateException: Class invariant violation
at org.apache.log4j.LogManager.getLoggerRepository(LogManager.java:199)at org.apache.log4j.LogManager.getLogger(LogManager.java:228)
at o
- Swing中文件恢复我觉得很难
小桔子
swing
我那个草了!老大怎么回事,怎么做项目评估的?只会说相信你可以做的,试一下,有的是时间!
用java开发一个图文处理工具,类似word,任意位置插入、拖动、删除图片以及文本等。文本框、流程图等,数据保存数据库,其余可保存pdf格式。ok,姐姐千辛万苦,
- php 文件操作
aichenglong
PHP读取文件写入文件
1 写入文件
@$fp=fopen("$DOCUMENT_ROOT/order.txt", "ab");
if(!$fp){
echo "open file error" ;
exit;
}
$outputstring="date:"." \t tire:".$tire."
- MySQL的btree索引和hash索引的区别
AILIKES
数据结构mysql算法
Hash 索引结构的特殊性,其 检索效率非常高,索引的检索可以一次定位,不像B-Tree 索引需要从根节点到枝节点,最后才能访问到页节点这样多次的IO访问,所以 Hash 索引的查询效率要远高于 B-Tree 索引。
可能很多人又有疑问了,既然 Hash 索引的效率要比 B-Tree 高很多,为什么大家不都用 Hash 索引而还要使用 B-Tree 索引呢
- JAVA的抽象--- 接口 --实现
百合不是茶
抽象 接口 实现接口
//抽象 类 ,方法
//定义一个公共抽象的类 ,并在类中定义一个抽象的方法体
抽象的定义使用abstract
abstract class A 定义一个抽象类 例如:
//定义一个基类
public abstract class A{
//抽象类不能用来实例化,只能用来继承
//
- JS变量作用域实例
bijian1013
作用域
<script>
var scope='hello';
function a(){
console.log(scope); //undefined
var scope='world';
console.log(scope); //world
console.log(b);
- TDD实践(二)
bijian1013
javaTDD
实践题目:分解质因数
Step1:
单元测试:
package com.bijian.study.factor.test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import junit.framework.Assert;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.bijian.
- [MongoDB学习笔记一]MongoDB主从复制
bit1129
mongodb
MongoDB称为分布式数据库,主要原因是1.基于副本集的数据备份, 2.基于切片的数据扩容。副本集解决数据的读写性能问题,切片解决了MongoDB的数据扩容问题。
事实上,MongoDB提供了主从复制和副本复制两种备份方式,在MongoDB的主从复制和副本复制集群环境中,只有一台作为主服务器,另外一台或者多台服务器作为从服务器。 本文介绍MongoDB的主从复制模式,需要指明
- 【HBase五】Java API操作HBase
bit1129
hbase
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HColumnDescriptor;
import org.apache.ha
- python调用zabbix api接口实时展示数据
ronin47
zabbix api接口来进行展示。经过思考之后,计划获取如下内容: 1、 获得认证密钥 2、 获取zabbix所有的主机组 3、 获取单个组下的所有主机 4、 获取某个主机下的所有监控项
- jsp取得绝对路径
byalias
绝对路径
在JavaWeb开发中,常使用绝对路径的方式来引入JavaScript和CSS文件,这样可以避免因为目录变动导致引入文件找不到的情况,常用的做法如下:
一、使用${pageContext.request.contextPath}
代码” ${pageContext.request.contextPath}”的作用是取出部署的应用程序名,这样不管如何部署,所用路径都是正确的。
- Java定时任务调度:用ExecutorService取代Timer
bylijinnan
java
《Java并发编程实战》一书提到的用ExecutorService取代Java Timer有几个理由,我认为其中最重要的理由是:
如果TimerTask抛出未检查的异常,Timer将会产生无法预料的行为。Timer线程并不捕获异常,所以 TimerTask抛出的未检查的异常会终止timer线程。这种情况下,Timer也不会再重新恢复线程的执行了;它错误的认为整个Timer都被取消了。此时,已经被
- SQL 优化原则
chicony
sql
一、问题的提出
在应用系统开发初期,由于开发数据库数据比较少,对于查询SQL语句,复杂视图的的编写等体会不出SQL语句各种写法的性能优劣,但是如果将应用系统提交实际应用后,随着数据库中数据的增加,系统的响应速度就成为目前系统需要解决的最主要的问题之一。系统优化中一个很重要的方面就是SQL语句的优化。对于海量数据,劣质SQL语句和优质SQL语句之间的速度差别可以达到上百倍,可见对于一个系统
- java 线程弹球小游戏
CrazyMizzz
java游戏
最近java学到线程,于是做了一个线程弹球的小游戏,不过还没完善
这里是提纲
1.线程弹球游戏实现
1.实现界面需要使用哪些API类
JFrame
JPanel
JButton
FlowLayout
Graphics2D
Thread
Color
ActionListener
ActionEvent
MouseListener
Mouse
- hadoop jps出现process information unavailable提示解决办法
daizj
hadoopjps
hadoop jps出现process information unavailable提示解决办法
jps时出现如下信息:
3019 -- process information unavailable3053 -- process information unavailable2985 -- process information unavailable2917 --
- PHP图片水印缩放类实现
dcj3sjt126com
PHP
<?php
class Image{
private $path;
function __construct($path='./'){
$this->path=rtrim($path,'/').'/';
}
//水印函数,参数:背景图,水印图,位置,前缀,TMD透明度
public function water($b,$l,$pos
- IOS控件学习:UILabel常用属性与用法
dcj3sjt126com
iosUILabel
参考网站:
http://shijue.me/show_text/521c396a8ddf876566000007
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/zquENb
http://blog.csdn.net/a451493485/article/details/9454695
http://wiki.eoe.cn/page/iOS_pptl_artile_281
- 完全手动建立maven骨架
eksliang
javaeclipseWeb
建一个 JAVA 项目 :
mvn archetype:create
-DgroupId=com.demo
-DartifactId=App
[-Dversion=0.0.1-SNAPSHOT]
[-Dpackaging=jar]
建一个 web 项目 :
mvn archetype:create
-DgroupId=com.demo
-DartifactId=web-a
- 配置清单
gengzg
配置
1、修改grub启动的内核版本
vi /boot/grub/grub.conf
将default 0改为1
拷贝mt7601Usta.ko到/lib文件夹
拷贝RT2870STA.dat到 /etc/Wireless/RT2870STA/文件夹
拷贝wifiscan到bin文件夹,chmod 775 /bin/wifiscan
拷贝wifiget.sh到bin文件夹,chm
- Windows端口被占用处理方法
huqiji
windows
以下文章主要以80端口号为例,如果想知道其他的端口号也可以使用该方法..........................1、在windows下如何查看80端口占用情况?是被哪个进程占用?如何终止等. 这里主要是用到windows下的DOS工具,点击"开始"--"运行",输入&
- 开源ckplayer 网页播放器, 跨平台(html5, mobile),flv, f4v, mp4, rtmp协议. webm, ogg, m3u8 !
天梯梦
mobile
CKplayer,其全称为超酷flv播放器,它是一款用于网页上播放视频的软件,支持的格式有:http协议上的flv,f4v,mp4格式,同时支持rtmp视频流格 式播放,此播放器的特点在于用户可以自己定义播放器的风格,诸如播放/暂停按钮,静音按钮,全屏按钮都是以外部图片接口形式调用,用户根据自己的需要制作 出播放器风格所需要使用的各个按钮图片然后替换掉原始风格里相应的图片就可以制作出自己的风格了,
- 简单工厂设计模式
hm4123660
java工厂设计模式简单工厂模式
简单工厂模式(Simple Factory Pattern)属于类的创新型模式,又叫静态工厂方法模式。是通过专门定义一个类来负责创建其他类的实例,被创建的实例通常都具有共同的父类。简单工厂模式是由一个工厂对象决定创建出哪一种产品类的实例。简单工厂模式是工厂模式家族中最简单实用的模式,可以理解为是不同工厂模式的一个特殊实现。
- maven笔记
zhb8015
maven
跳过测试阶段:
mvn package -DskipTests
临时性跳过测试代码的编译:
mvn package -Dmaven.test.skip=true
maven.test.skip同时控制maven-compiler-plugin和maven-surefire-plugin两个插件的行为,即跳过编译,又跳过测试。
指定测试类
mvn test
- 非mapreduce生成Hfile,然后导入hbase当中
Stark_Summer
maphbasereduceHfilepath实例
最近一个群友的boss让研究hbase,让hbase的入库速度达到5w+/s,这可愁死了,4台个人电脑组成的集群,多线程入库调了好久,速度也才1w左右,都没有达到理想的那种速度,然后就想到了这种方式,但是网上多是用mapreduce来实现入库,而现在的需求是实时入库,不生成文件了,所以就只能自己用代码实现了,但是网上查了很多资料都没有查到,最后在一个网友的指引下,看了源码,最后找到了生成Hfile
- jsp web tomcat 编码问题
王新春
tomcatjsppageEncode
今天配置jsp项目在tomcat上,windows上正常,而linux上显示乱码,最后定位原因为tomcat 的server.xml 文件的配置,添加 URIEncoding 属性:
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTi