基于C#实现Prim算法
图论在数据结构中是非常有趣而复杂的,作为 Web 码农的我,在实际开发中一直没有找到它的使用场景,不像树那样的频繁使用,不过还是准备仔细的把图论全部过一遍。
一、最小生成树
图中有一个好玩的东西叫做生成树,就是用边来把所有的顶点联通起来,前提条件是最后形成的联通图中不能存在回路,所以就形成这样一个推理:假设图中的顶点有 n 个,则生成树的边有 n-1 条,多一条会存在回路,少一路则不能把所有顶点联通起来,如果非要在图中加上权重,则生成树中权重最小的叫做最小生成树。

对于上面这个带权无向图来说,它的生成树有多个,同样最小生成树也有多个,因为我们比的是权重的大小。
二、Prim 算法
求最小生成树的算法有很多,常用的是 Prim 算法和 Kruskal 算法,为了保证单一职责,我把 Kruskal 算法放到下一篇,那么 Prim 算法的思想是什么呢?很简单,贪心思想。
如上图:现有集合 M={A,B,C,D,E,F},再设集合 N={}。
- 第一步:挑选任意节点(比如 A),将其加入到 N 集合,同时剔除 M 集合的 A。
- 第二步:寻找 A 节点权值最小的邻节点(比如 F),然后将 F 加入到 N 集合,此时 N={A,F},同时剔除 M 集合中的 F。
- 第三步:寻找{A,F}中的权值最小的邻节点(比如 E),然后将 E 加入到 N 集合,此时 N={A,F,E},同时剔除 M 集合的 E。
- 。。。
最后 M 集合为{}时,生成树就构建完毕了,是不是非常的简单,这种贪心做法我想大家都能想得到,如果算法配合一个好的数据结构,就会如虎添翼。
三、代码
1、图的存储
图的存储有很多方式,邻接矩阵,邻接表,十字链表等等,当然都有自己的适合场景,下面用邻接矩阵来玩玩,邻接矩阵需要采用两个数组,
①. 保存顶点信息的一维数组,
②. 保存边信息的二维数组。
public class Graph
{
/// 2、矩阵构建
矩阵构建很简单,这里把上图中的顶点和权的信息保存在矩阵中。
#region 矩阵的构建
/// 3、Prim
要玩 Prim,我们需要两个字典。
①:保存当前节点的字典,其中包含该节点的起始边和终边以及权值,用 weight=-1 来记录当前节点已经访问过,用 weight=int.MaxValue 表示两节点没有边。
②:输出节点的字典,存放的就是我们的 N 集合。
当然这个复杂度玩高了,为 O(N2),寻找 N 集合的邻边最小权值时,我们可以玩玩 AVL 或者优先队列来降低复杂度。
#region prim算法
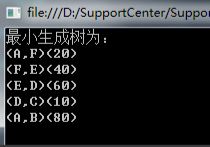
/// 4、最后我们来测试一下,看看找出的最小生成树。
public static void Main()
{
MatrixGraph martix = new MatrixGraph();
martix.Build();
var dic = martix.Prim();
Console.WriteLine("最小生成树为:");
foreach (var key in dic.Keys)
{
Console.WriteLine("({0},{1})({2})", dic[key].startEdge, dic[key].endEdge, dic[key].weight);
}
Console.Read();
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Threading;
using System.IO;
using SupportCenter.Test.ServiceReference2;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
MatrixGraph martix = new MatrixGraph();
martix.Build();
var dic = martix.Prim();
Console.WriteLine("最小生成树为:");
foreach (var key in dic.Keys)
{
Console.WriteLine("({0},{1})({2})", dic[key].startEdge, dic[key].endEdge, dic[key].weight);
}
Console.Read();
}
}
///