Sentinel 实现原理——处理链
引言
从本篇文章开始,就要介绍 Sentinel 限流降级功能的核心了,前面也说过 Sentinel 使用了一套类似于责任链的模式来实现这个部分,这里我们展开一下,将责任链中的各个部分分别详细的介绍一下。更多相关文章和其他文章均收录于贝贝猫的文章目录。
源码解读
![]()
上图仅作为设计思想的展示,图中 Slot 的顺序已和最新版 Sentinel Slot Chain 顺序不一致
前面我们已解说了,Sentinel 中最核心的功能都是通过一套处理链(责任链)来实现,处理链中的每一个处理单元被称为一个 Slot。每个 Slot 执行完业务逻辑处理后,都会触发下一个节点的处理方法,如此往复直到最后一个Slot,由此就形成了sentinel的责任链。这里我们先简单地回顾一下各个 Slot 的职责:
- NodeSelectorSlot: 负责维护资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,构建不同资源在不同调用链路下的统计节点,这部分数据会用于根据调用链路来限流降级
- ClusterBuilderSlot: 负责对相同资源的不同链路流量进行耦合,构建各个资源的统计节点,此外还会根据调用源构建相应的统计节点,例如该资源在所有链路下以及资源在某一特定源下的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据
- StatistcSlot: 则用于记录,统计不同维度的 runtime 信息
- SystemSlot: 则通过系统的状态,例如 load1 等,来控制总的入口流量
- AuthoritySlot: 则根据黑白名单,来做黑白名单控制
- FlowSlot: 则用于根据预设的限流规则,以及前面 slot 统计的状态,来进行限流
- DegradeSlot: 则通过统计信息,以及预设的规则,来做熔断降级
起点
那么整个处理链是从哪开始运作起来的呢?其实 SphU#entry 就是整个处理链的入口。这里我们以最完整的两个 entry 接口为例,介绍 Sentinel 处理链的准备工作。
// SphU#entry 的下层接口 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.CtSph#entry
@Override
public Entry entry(Method method, EntryType type, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException {
MethodResourceWrapper resource = new MethodResourceWrapper(method, type);
return entry(resource, count, args);
}
@Override
public Entry entry(String name, EntryType type, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException {
StringResourceWrapper resource = new StringResourceWrapper(name, type);
return entry(resource, count, args);
}
在 CtSph#entry 这一层主要是做 Resource 的创建,最基础的就是我们前面所使用的 String 类型标识的 Resource,其中主要保存了 Resource 的 name 和该流量是流入性(EntryType#IN)还是流出行(EntryType#OUT),后续的限流降级规则中会有根据数据流入类型而做区分处理的情况。
// StringResourceWrapper 的父类 ResourceWrapper 的核心属性
protected final String name;
protected final EntryType entryType;
而 Method 类型的 Resource,在一些自适应的框架中用到的比较多,比如基于注解标识资源等。MethodResourceWrapper 和 StringResourceWrapper 一样继承自 ResourceWrapper,它会用函数的签名作为资源名。
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slotchain.MethodResourceWrapper#MethodResourceWrapper
public MethodResourceWrapper(Method method, EntryType e, int resType) {
super(MethodUtil.resolveMethodName(method), e, resType);
this.method = method;
}
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.util.MethodUtil#resolveMethodName
public static String resolveMethodName(Method method) {
if (method == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Null method");
}
String methodName = methodNameMap.get(method);
if (methodName == null) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
methodName = methodNameMap.get(method);
if (methodName == null) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
String name = method.getName();
Class<?>[] params = method.getParameterTypes();
sb.append(className).append(":").append(name);
sb.append("(");
int paramPos = 0;
for (Class<?> clazz : params) {
sb.append(clazz.getCanonicalName());
if (++paramPos < params.length) {
sb.append(",");
}
}
sb.append(")");
methodName = sb.toString();
methodNameMap.put(method, methodName);
}
}
}
return methodName;
}
对 Resource 类型进行区分之后,就到了处理链的组织和执行阶段了,这部分代码位于 CtSph#entryWithPriority 中:
- 首先,保证执行过程中有 Context 上下文
- 如果 Context 过多或者关闭了限流降级功能则不构建处理链
- 根据资源的名称查找其对应的处理链,每个资源都有一条专属于自己的处理链实例,我们后续介绍处理链的构建
- 有了处理链之后,创建当前资源的调用点 Entry,这里涉及调用链路的维护工作,我们前面已经介绍过了
- 最后,调用处理链的 entry 函数,如果抛出 BlockException 异常说明被限流或者降级,则调用 exit 函数退出调用点,退出的相关逻辑我们后续介绍
private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws BlockException {
Context context = ContextUtil.getContext();
if (context instanceof NullContext) {
// The {@link NullContext} indicates that the amount of context has exceeded the threshold,
// so here init the entry only. No rule checking will be done.
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, /*chain*/null, context);
}
if (context == null) {
// Using default context.
context = InternalContextUtil.internalEnter(Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME);
}
// Global switch is close, no rule checking will do.
if (!Constants.ON) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, /*chain*/null, context);
}
ProcessorSlot<Object> chain = lookProcessChain(resourceWrapper);
/*
* Means amount of resources (slot chain) exceeds {@link Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE},
* so no rule checking will be done.
*/
if (chain == null) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
Entry e = new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, chain, context);
try {
chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args);
} catch (BlockException e1) {
e.exit(count, args);
throw e1;
} catch (Throwable e1) {
// This should not happen, unless there are errors existing in Sentinel internal.
RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", e1);
}
return e;
}
处理链的构建同样是以 Double-Check 的方式进行的,Sentinel 中会用 Resource 的 name 作为 key 将已经构建好的处理链保存在 Map 中,方便后续使用。这里,也会限制处理链的最大数量为 6000。
ProcessorSlot<Object> lookProcessChain(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) {
ProcessorSlotChain chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
if (chain == null) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
if (chain == null) {
// Entry size limit. MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE = 6000
if (chainMap.size() >= Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE) {
return null;
}
chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain();
Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> newMap = new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>(
chainMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(chainMap);
newMap.put(resourceWrapper, chain);
chainMap = newMap;
}
}
}
return chain;
}
// Resource 对象的 equals 和 hashcode 函数
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return getName().hashCode();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof ResourceWrapper) {
ResourceWrapper rw = (ResourceWrapper)obj;
return rw.getName().equals(getName());
}
return false;
}
至于处理链的构建,Sentinel 提供了一个 SlotChainBuilder SPI,用户可以实现自己的 SlotChainBuilder,当然也能使用默认的实现。
public static ProcessorSlotChain newSlotChain() {
if (slotChainBuilder != null) {
return slotChainBuilder.build();
}
// Resolve the slot chain builder SPI.
slotChainBuilder = SpiLoader.loadFirstInstanceOrDefault(SlotChainBuilder.class, DefaultSlotChainBuilder.class);
if (slotChainBuilder == null) {
// Should not go through here.
RecordLog.warn("[SlotChainProvider] Wrong state when resolving slot chain builder, using default");
slotChainBuilder = new DefaultSlotChainBuilder();
} else {
RecordLog.info("[SlotChainProvider] Global slot chain builder resolved: "
+ slotChainBuilder.getClass().getCanonicalName());
}
return slotChainBuilder.build();
}
在默认的 SlotChainBuilder 实现 DefaultSlotChainBuilder 中会用到 Sentinel 所暴露的另一个 SPI——ProcessorSlot,DefaultSlotChainBuilder 中会将所有继承自 AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot(链式调用过程在这里实现) 的 ProcessorSlot 实现类实例化,并保存在处理链 ProcessorSlotChain 中,之所以每个 Slot 都要实例化一个新的对象是因为很多 Slot 都是有状态的。
public class DefaultSlotChainBuilder implements SlotChainBuilder {
@Override
public ProcessorSlotChain build() {
ProcessorSlotChain chain = new DefaultProcessorSlotChain();
// Note: the instances of ProcessorSlot should be different, since they are not stateless.
List<ProcessorSlot> sortedSlotList = SpiLoader.loadPrototypeInstanceListSorted(ProcessorSlot.class);
for (ProcessorSlot slot : sortedSlotList) {
if (!(slot instanceof AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot)) {
RecordLog.warn("The ProcessorSlot(" + slot.getClass().getCanonicalName() + ") is not an instance of AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot, can't be added into ProcessorSlotChain");
continue;
}
chain.addLast((AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?>) slot);
}
return chain;
}
}
Sentinel 在加载各个 ProcessorSlot 的过程中还会根据各个 Slot 实现类通过 @SpiOrder 指定的顺序进行排序,前面所说的 ProcessSlotChain 的最终顺序,就是通过这种方式确立的,只不过目前代码中所定义的顺序已经和上图中的顺序有一定的出入,Sentinel 会按照 SpiOrder 升序排列各个 Slot,如下展示的就是现阶段(v1.7.2)各个 Slot 的顺序。
- NodeSelectorSlot: @SpiOrder(-10000)
- ClusterBuilderSlot: @SpiOrder(-9000)
- LogSlot: @SpiOrder(-8000)
- StatisticSlot: @SpiOrder(-7000)
- AuthoritySlot: @SpiOrder(-6000)
- SystemSlot: @SpiOrder(-5000)
- GatewayFlowSlot: @SpiOrder(-4000)
- ParamFlowSlot: @SpiOrder(-3000)
- FlowSlot: @SpiOrder(-2000)
- DegradeSlot: @SpiOrder(-1000)
处理链
所谓处理链实际上就是一个 ProcessorSlot 实例的数组,在进入调用点时,执行 ProcessorSlot 的 entry 函数,每个 Slot 的 entry 任务都各不相同,但是每一个 Slot 在处理完自己的活之后都要通过 fireEntry 调用处理链中下一个 Slot 的 entry 函数。同理 exit 是在退出调用点的时候执行。
public interface ProcessorSlot<T> {
void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, T param, int count, boolean prioritized,
Object... args) throws Throwable;
void fireEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized,
Object... args) throws Throwable;
void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args);
void fireExit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args);
}
NodeSelectorSlot
NodeSelectorSlot 是排在最前面的 Slot,其中负责维护当前 Resource 对于不同入口(EntranceNode)的统计节点(DefaultNode)。同时它也负责维护各个节点之间的链路关系。将 DefaultNode 保存到 Context 中之后,就会调用下一 Slot。
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.nodeselector.NodeSelectorSlot#entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName());
if (node == null) {
synchronized (this) {
node = map.get(context.getName());
if (node == null) {
node = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null);
HashMap<String, DefaultNode> cacheMap = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(map.size());
cacheMap.putAll(map);
cacheMap.put(context.getName(), node);
map = cacheMap;
// Build invocation tree
((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node);
}
}
}
// 指定当前 Entry 所对应的 DefaultNode
context.setCurNode(node);
// 注意这里将 DefaultNode 作为参数传递给了下一 Slot,因为后续限流 Slot 会用这个 DefaultNode 来做链路模式的限流
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
@Override
public void fireEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
if (next != null) {
// 调用下一个 Slot
next.transformEntry(context, resourceWrapper, obj, count, prioritized, args);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
void transformEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object o, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
T t = (T)o;
// 做泛型转换
entry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}
执行完 NodeSelectSlot 之后,调用树就会变成如下形态。
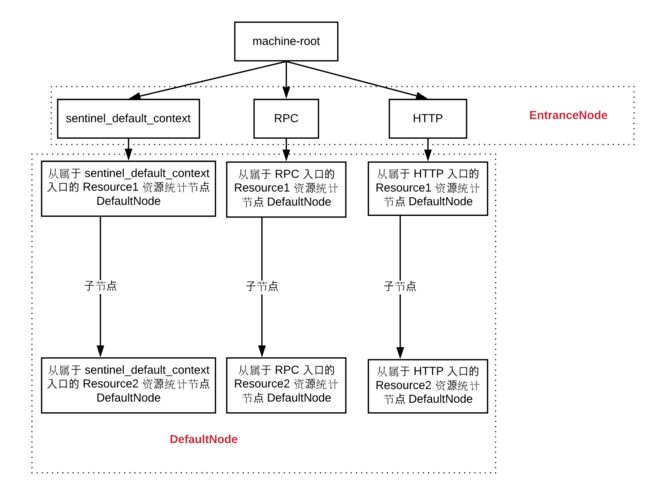
在 NodeSelectorSlot 中各个资源针对不同 Context 的统计节点会以如下方式保存。
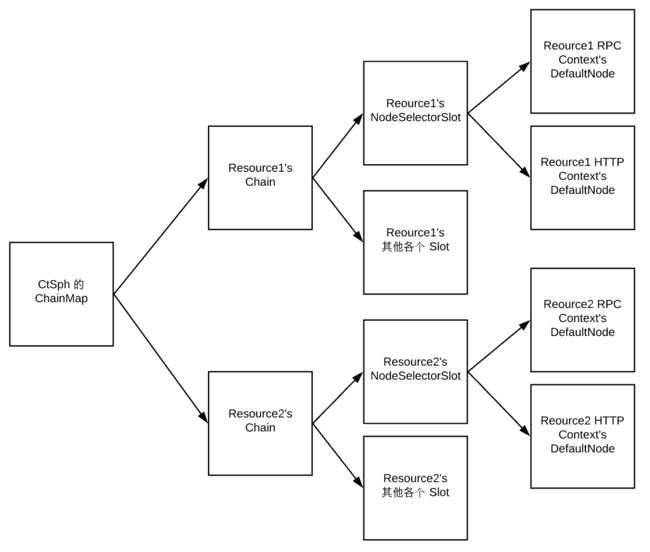
ClusterBuilderSlot
ClusterBuilderSlot 负责对某一资源在不同类型 Context 中的流量进行聚合,创建各个 Resource 的汇总统计节点(ClusterNode),同时对于指定了来源(Origin)的流量,会创建当前资源专属于各个 Origin 的流量统计节点。最后将上述两类统计节点保存在 Context 中, 并调用下一个 Slot。
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.clusterbuilder.ClusterBuilderSlot#entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
if (clusterNode == null) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (clusterNode == null) {
// Create the cluster node.
clusterNode = new ClusterNode(resourceWrapper.getName(), resourceWrapper.getResourceType());
HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(Math.max(clusterNodeMap.size(), 16));
newMap.putAll(clusterNodeMap);
newMap.put(node.getId(), clusterNode);
clusterNodeMap = newMap;
}
}
}
node.setClusterNode(clusterNode);
/*
* if context origin is set, we should get or create a new {@link Node} of
* the specific origin.
*/
if (!"".equals(context.getOrigin())) {
Node originNode = node.getClusterNode().getOrCreateOriginNode(context.getOrigin());
context.getCurEntry().setOriginNode(originNode);
}
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.node.ClusterNode#getOrCreateOriginNode
public Node getOrCreateOriginNode(String origin) {
// originCountMap 是 ClusterNode 实例的成员变量
StatisticNode statisticNode = originCountMap.get(origin);
if (statisticNode == null) {
lock.lock();
try {
statisticNode = originCountMap.get(origin);
if (statisticNode == null) {
// The node is absent, create a new node for the origin.
statisticNode = new StatisticNode();
HashMap<String, StatisticNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(originCountMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(originCountMap);
newMap.put(origin, statisticNode);
originCountMap = newMap;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
return statisticNode;
}
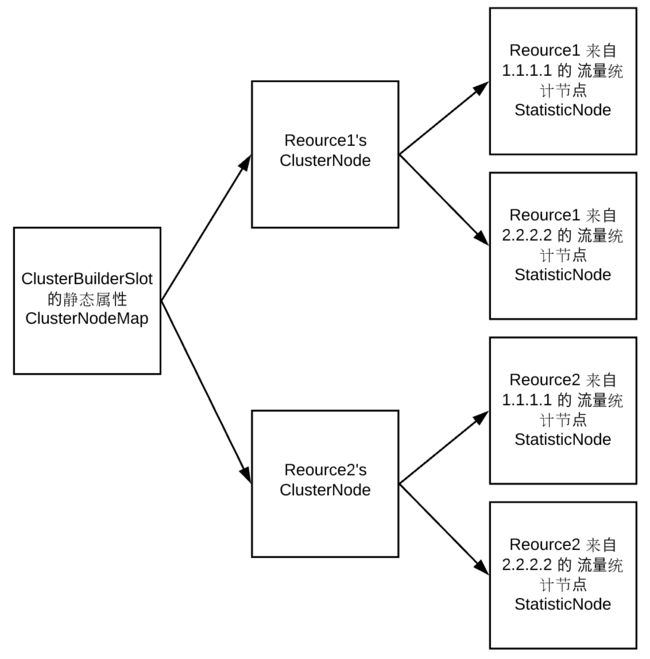
执行完 ClusterBuilderSlot 之后,调用树达到了最终形态。
![]()
在 ClusterBuilderSlot 中各个资源以及各个资源来自不同 Origin 的流量统计节点会以如下方式保存。
LogSlot
LogSlot 的工作很简单,内部直接调用下一个 Slot 的处理过程,如果发生了限流降级,就通过 EagleEyeLogUtil 进行记录(内部有线程负责周期性地将统计数据写入log),如果期间发生了异常,就记录到 Log 中。
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.logger.LogSlot#entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
try {
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, obj, count, prioritized, args);
} catch (BlockException e) {
EagleEyeLogUtil.log(resourceWrapper.getName(), e.getClass().getSimpleName(), e.getRuleLimitApp(),
context.getOrigin(), count);
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
RecordLog.warn("Unexpected entry exception", e);
}
}
StatisticSlot
StatisticSlot 是比较复杂的一个 Slot,各个维度的流量统计都是通过这个 Slot 处理的,这里 StatisticSlot 会先调用后续 Slot 的处理过程,然后根据后续 Slot 的处理结果开展不同的统计工作:
- 如果后续 Slot 都顺利通过:
- 增加 node 统计节点的线程数和 QPS 数,这里特指当前资源专属于某一 Context 的统计节点(DefaultNode),而且该 DefaultNode 中还保存了该资源的 ClusterNode(见代码下半段),也会对 ClusterNode 的线程数和 QPS 数进行增加
- 如果当前资源指明了流量的 origin(OriginNode) 不为空,则增加该统计节点的线程数和 QPS 数
- 如果当前资源是输入类型的流量的话,也会增加系统整体输入流量统计节点的线程数和 QPS 数
- 调用其他地方注入的请求通过回调函数,一些统计服务会注册这类回调,比如热点参数的统计过程就是通过这种回调机制实现的
- 如果捕获到 PriorityWaitException 异常,说明当前的限流规则是排队等待,Sentinel 内部使用虚拟队列(按照约定的 QPS 计算每个线程要 sleep 的时长)实现,所以不会出现 QPS 超标的情况,而抛出 PriorityWaitException 说明已经 sleep 完毕,可以放行流量,所以这一步只统计了线程数,没有统计 QPS 数,统计过程和上述通过的场景基本相同(除了不统计 QPS)
- 如果捕获到 BlockException 异常,可能是被限流或者降级,这时候将 BlockException 保存在 Context 中,并增加各个维度统计节点的 blocked QPS 数并抛出异常,统计过程和上述通过的场景类似
- 如果捕获到其他异常,说明出现了未知错误,如果 Sentinel 没有 BUG 并且用户引入的 CustomSlot 没有问题的话,是不是抛出这类异常的,当这类异常发生时,会将其保存在 Context 中并抛到外层
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.statistic.StatisticSlot#entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
try {
// Do some checking.
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
// Request passed, add thread count and pass count.
node.increaseThreadNum();
node.addPassRequest(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
// Add count for origin node.
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count);
}
// Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
} catch (PriorityWaitException ex) {
node.increaseThreadNum();
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
// Add count for origin node.
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
}
// Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
} catch (BlockException e) {
// Blocked, set block exception to current entry.
context.getCurEntry().setBlockError(e);
// Add block count.
node.increaseBlockQps(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseBlockQps(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseBlockQps(count);
}
// Handle block event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onBlocked(e, context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
// Unexpected internal error, set error to current entry.
context.getCurEntry().setError(e);
throw e;
}
}
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.node.DefaultNode#increaseThreadNum
@Override
public void increaseThreadNum() {
super.increaseThreadNum();
this.clusterNode.increaseThreadNum();
}
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.node.DefaultNode#addPassRequest
@Override
public void addPassRequest(int count) {
super.addPassRequest(count);
this.clusterNode.addPassRequest(count);
}
StatisticSlot 不同于之前的几个 Slot,它的 exit 函数是有实际的任务处理过程,而前面几个 Slot 的 exit 函数只是保证链式调用。
AuthoritySlot
从 AuthoritySlot 开始就到了 Sentinel 根据规则进行检查的阶段了,AuthoritySlot 是其中最简单的部分,它只做白名单和黑名单的检查。这里,首先会确认一下当前资源是否定义了授权规则,如果定义了的话,会挨个检查所有授权规则是否通过,如果发现了任意一个未通过的授权规则就抛出 AuthorityException,否则调用下一个 Slot。
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthoritySlot#entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
checkBlackWhiteAuthority(resourceWrapper, context);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthoritySlot#checkBlackWhiteAuthority
void checkBlackWhiteAuthority(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context) throws AuthorityException {
Map<String, Set<AuthorityRule>> authorityRules = AuthorityRuleManager.getAuthorityRules();
if (authorityRules == null) {
return;
}
Set<AuthorityRule> rules = authorityRules.get(resource.getName());
if (rules == null) {
return;
}
for (AuthorityRule rule : rules) {
if (!AuthorityRuleChecker.passCheck(rule, context)) {
throw new AuthorityException(context.getOrigin(), rule);
}
}
}
授权规则的检查过程也很简单,就是检查当前流量的 Origin 是否包含在设定的授权规则名单中,如果这个名单是黑名单并且当前流量的 Origin 在这个名单中,则返回不通过。另外,如果这个名单是白名单但是当前流量的 Origin 不在这个名单中,也返回不通过。
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRuleChecker#passCheck
static boolean passCheck(AuthorityRule rule, Context context) {
String requester = context.getOrigin();
// Empty origin or empty limitApp will pass.
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(requester) || StringUtil.isEmpty(rule.getLimitApp())) {
return true;
}
// Do exact match with origin name.
int pos = rule.getLimitApp().indexOf(requester);
boolean contain = pos > -1;
if (contain) {
boolean exactlyMatch = false;
String[] appArray = rule.getLimitApp().split(",");
for (String app : appArray) {
if (requester.equals(app)) {
exactlyMatch = true;
break;
}
}
contain = exactlyMatch;
}
int strategy = rule.getStrategy();
if (strategy == RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_BLACK && contain) {
return false;
}
if (strategy == RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_WHITE && !contain) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
SystemSlot
SystemSlot 是对系统规则的检查,只检查输入性流量,检查项主要包括:
- 系统总 QPS: 通过系统统计节点(Constants.ENTRY_NODE)的数据进行检查
- 总线程数: 通过系统统计节点(Constants.ENTRY_NODE)的数据进行检查
- 平均请求处理时间: 这部分数据的统计方式我们还没有介绍,这里只要知道它主要是在调用
Entry#exit是进行统计即可,后续我们会详细介绍这部分内容。这里也是通过系统统计节点(Constants.ENTRY_NODE)的数据进行检查 - CPU 使用率: Sentinel 中会有一个统计线程,每秒钟通过 OperatingSystemMXBean 获取一次当前的 CPU 使用率,SystemSlot 会根据这部分数据进行检查
- 当系统过去1分钟的负载(load1)大于某一阈值时,还会使用 BBR 算法来限制最大并发请求数,即比较当前并发的
线程数和QPS*RT的大小,如果线程数 > QPS*RT就限流
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemSlot#entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
SystemRuleManager.checkSystem(resourceWrapper);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager#checkSystem
public static void checkSystem(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) throws BlockException {
if (resourceWrapper == null) {
return;
}
// Ensure the checking switch is on.
if (!checkSystemStatus.get()) {
return;
}
// for inbound traffic only
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() != EntryType.IN) {
return;
}
// total qps
double currentQps = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0.0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.successQps();
if (currentQps > qps) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "qps");
}
// total thread
int currentThread = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.curThreadNum();
if (currentThread > maxThread) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "thread");
}
double rt = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.avgRt();
if (rt > maxRt) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "rt");
}
// load. BBR algorithm.
if (highestSystemLoadIsSet && getCurrentSystemAvgLoad() > highestSystemLoad) {
if (!checkBbr(currentThread)) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "load");
}
}
// cpu usage
if (highestCpuUsageIsSet && getCurrentCpuUsage() > highestCpuUsage) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "cpu");
}
}
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager#checkBbr
private static boolean checkBbr(int currentThread) {
if (currentThread > 1 &&
currentThread > Constants.ENTRY_NODE.maxSuccessQps() * Constants.ENTRY_NODE.minRt() / 1000) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
GatewayFlowSlot
ParamFlowSlot
FlowSlot
DegradeSlot
调用点异常
当调用点的任务执行过程中出现了异常,我们需要通过 Tracer#trace 记录异常,它本质上就是将异常保存在当前调用点 Entry 中,在保存之前还会对异常的类型进行一些检查(用户可以指定忽略一部分异常),这部分的代码如下。
// com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.Tracer
public static void trace(Throwable e) {
traceContext(e, ContextUtil.getContext());
}
public static void traceContext(Throwable e, Context context) {
if (!shouldTrace(e)) {
return;
}
if (context == null || context instanceof NullContext) {
return;
}
traceEntryInternal(e, context.getCurEntry());
}
protected static boolean shouldTrace(Throwable t) {
if (t == null || t instanceof BlockException) {
return false;
}
// 用户注入的检查器
if (exceptionPredicate != null) {
return exceptionPredicate.test(t);
}
// 用户添加的黑名单
if (ignoreClasses != null) {
for (Class<? extends Throwable> clazz : ignoreClasses) {
if (clazz != null && clazz.isAssignableFrom(t.getClass())) {
return false;
}
}
}
// 用户添加的白名单
if (traceClasses != null) {
for (Class<? extends Throwable> clazz : traceClasses) {
if (clazz != null && clazz.isAssignableFrom(t.getClass())) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
private static void traceEntryInternal(/*@NeedToTrace*/ Throwable e, Entry entry) {
if (entry == null) {
return;
}
entry.setError(e);
}
从上面的代码中可以看出 Tracer#trace 先会检查一下是否应该追踪该异常,检查依据是用户添加到 Tracer 中的检查器 exceptionPredicate、黑名单 ignoreClasses、白名单traceClasses,检查通过就将异常保存在当前调用点 Entry 中。而异常的统计工作是在调用 Entry#exit 时才会开始进行,最终在 StatisticSlot 中进行实际的统计工作。
退出调用点
退出调用点的处理流程如下:
- 检查当前 Context 保存的当前调用点是否和目前正在退出的调用点一致,如果不一致说明退出流程有问题(没有按顺序退出),这里会抛出异常。
- 检查通过后,会执行 ProcessorSlotChain 的 exit 函数
- 将 Context 中当前调用点变更为正在退出的调用点的父节点,并维护调用点父子关系
- 如果已经是最外层的调用点并且 Context 是 default Context 的话,会执行
ContextUtil#exit函数,将 Context 实例从 ThreadLocal 中清除 - 最后将 Context 的引用从已退出的 Entry 实例中清除,防止重复退出
@Override
public void exit(int count, Object... args) throws ErrorEntryFreeException {
trueExit(count, args);
}
@Override
protected Entry trueExit(int count, Object... args) throws ErrorEntryFreeException {
exitForContext(context, count, args);
return parent;
}
protected void exitForContext(Context context, int count, Object... args) throws ErrorEntryFreeException {
if (context != null) {
// Null context should exit without clean-up.
if (context instanceof NullContext) {
return;
}
if (context.getCurEntry() != this) {
String curEntryNameInContext = context.getCurEntry() == null ? null : context.getCurEntry().getResourceWrapper().getName();
// Clean previous call stack.
CtEntry e = (CtEntry)context.getCurEntry();
while (e != null) {
e.exit(count, args);
e = (CtEntry)e.parent;
}
String errorMessage = String.format("The order of entry exit can't be paired with the order of entry"
+ ", current entry in context: <%s>, but expected: <%s>", curEntryNameInContext, resourceWrapper.getName());
throw new ErrorEntryFreeException(errorMessage);
} else {
if (chain != null) {
chain.exit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
}
// Restore the call stack.
context.setCurEntry(parent);
if (parent != null) {
((CtEntry)parent).child = null;
}
if (parent == null) {
// Default context (auto entered) will be exited automatically.
if (ContextUtil.isDefaultContext(context)) {
ContextUtil.exit();
}
}
// Clean the reference of context in current entry to avoid duplicate exit.
clearEntryContext();
}
}
}
protected void clearEntryContext() {
this.context = null;
}
参考内容
[1] Sentinel GitHub 仓库
[2] Sentinel 官方 Wiki
[3] Sentinel 1.6.0 网关流控新特性介绍
[4] Sentinel 微服务流控降级实践
[5] Sentinel 1.7.0 新特性展望
[6] Sentinel 为 Dubbo 服务保驾护航
[7] 在生产环境中使用 Sentinel
[8] Sentinel 与 Hystrix 的对比
[9] 大流量下的服务质量治理 Dubbo Sentinel初涉
[10] Alibaba Sentinel RESTful 接口流控处理优化
[11] 阿里 Sentinel 源码解析
[12] Sentinel 教程 by 逅弈
[13] Sentinel 专题文章 by 一滴水的坚持
![]()