消息中间件——RabbitMQ(六)理解Exchange交换机核心概念!
前言
来了解RabbitMQ一个重要的概念:Exchange交换机
1. Exchange概念
蓝色框:客户端发送消息至交换机,通过路由键路由至指定的队列。
黄色框:交换机和队列通过路由键有一个绑定的关系。
绿色框:消费端通过监听队列来接收消息。
2. 交换机属性
Name:交换机名称Type:交换机类型——direct、topic、fanout、headers、sharding(此篇不讲)Durability:是否需要持久化,true为持久化Auto Delete:当最后一个绑定到Exchange上的队列删除后,自动删除该ExchangeInternal:当前Exchange是否用于RabbitMQ内部使用,默认为falseArguments:扩展参数,用于扩展AMQP协议自定制化使用
3. Direct Exchange(直连)
- 所有发送到Direct Exchange的消息被转发到RouteKey中指定的Queue
注意:Direct模式可以使用RabbitMQ自带的Exchange:default Exchange,所以不需要将Exchange进行任何绑定(binding)操作,消息传递时,RouteKey必须完全匹配才会被队列接收,否则该消息会被抛弃。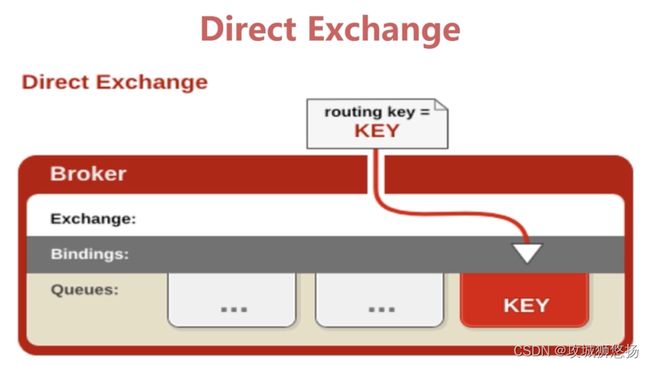
重点:routing key与队列queues 的key保持一致,即可以路由到对应的queue中。
3.1 代码演示
生产端:
public class Producer4DirectExchange {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1创建ConnectionFactory
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
//2创建Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3 声明
String exchangeName = "test_direct_exchange";
String routingKey = "test.direct";
//4 发送
String msg = "Coder编程 Hello World RabbitMQ 4 Direct Exchange Message ... ";
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey , null , msg.getBytes());
}
}
消费端:
public class Consumer4DirectExchange {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建ConnectionFactory
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明
String exchangeName = "test_direct_exchange";
String exchangeType = "direct";
String queueName = "test_direct_queue";
String routingKey = "test.direct";
//表示声明了一个交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, exchangeType, true, false, false, null);
//表示声明了一个队列
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
//建立一个绑定关系:
channel.queueBind(queueName, exchangeName, routingKey);
//durable 是否持久化消息
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//参数:队列名称、是否自动ACK、Consumer
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);
//循环获取消息
while(true){
//获取消息,如果没有消息,这一步将会一直阻塞
Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String msg = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println("收到消息:" + msg);
}
}
}
测试结果:
注意需要routingKey保持一致。可以自己尝试修改routingkey,是否能收到消息。
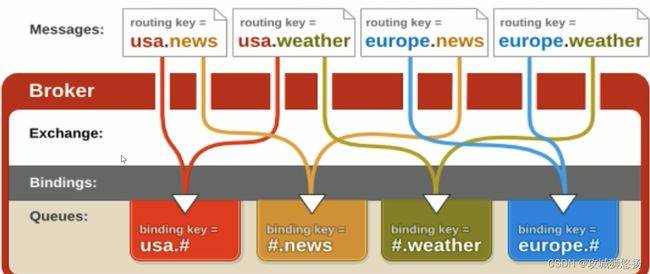
4. Topic Exchange
- 所有发送到Topic Exchange的消息被转发到所有管线RouteKey中指定Topic的Queue上
- Exchange将RouteKey和某Topic进行模糊匹配,此时队列需要绑定一个Topic
注意:可以使用通配符进行模糊匹配
符号 “#” 匹配一个或多个词
符号 “” 匹配不多不少一个词
例如:”log.#” 能够匹配到 “log.info.oa”
“log.” 只会匹配到 “log.error”
在一堆消息中,每个不同的队列只关心自己需要的消息。
4.1 代码演示
生产端:
public class Producer4TopicExchange {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1创建ConnectionFactory
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
//2创建Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3声明
String exchangeName = "test_topic_exchange";
String routingKey1 = "user.save";
String routingKey2 = "user.update";
String routingKey3 = "user.delete.abc";
//4发送
String msg = "Coder编程 Hello World RabbitMQ 4 Topic Exchange Message ...";
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey1 , null , msg.getBytes());
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey2 , null , msg.getBytes());
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey3 , null , msg.getBytes());
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费端:
public class Consumer4TopicExchange {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建ConnectionFactory
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明
String exchangeName = "test_topic_exchange";
String exchangeType = "topic";
String queueName = "test_topic_queue";
//String routingKey = "user.*";
String routingKey = "user.*";
// 1 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, exchangeType, true, false, false, null);
// 2 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
// 3 建立交换机和队列的绑定关系:
channel.queueBind(queueName, exchangeName, routingKey);
//durable 是否持久化消息
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//参数:队列名称、是否自动ACK、Consumer
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);
//循环获取消息
while(true){
//获取消息,如果没有消息,这一步将会一直阻塞
Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String msg = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println("收到消息:" + msg);
}
}
}
测试结果:
注意一个问题:需要进行解绑
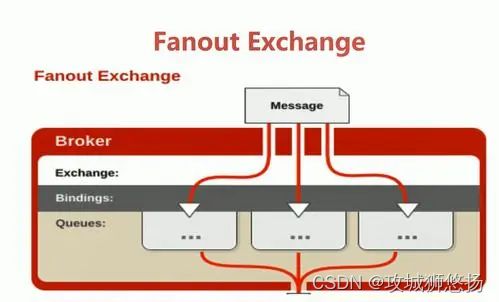
5. Fanout Exchange
- 不处理路由键,只需要简单的将队里绑定到交换机上
- 发送到交换机的消息都会被转发到与该交换机绑定的所有队列上
- Fanout交换机转发消息是最快的
5.1 代码演示
生产端:
public class Producer4FanoutExchange {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1创建ConnectionFactory
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
//2 创建Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3 声明
String exchangeName = "test_fanout_exchange";
//4 发送
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
String msg = "Coder 编程 Hello World RabbitMQ 4 FANOUT Exchange Message ...";
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, "", null , msg.getBytes());
}
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费端:
public class Consumer4FanoutExchange {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建ConnectionFactory
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明
String exchangeName = "test_fanout_exchange";
String exchangeType = "fanout";
String queueName = "test_fanout_queue";
String routingKey = ""; //不设置路由键
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, exchangeType, true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
channel.queueBind(queueName, exchangeName, routingKey);
//durable 是否持久化消息
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
//参数:队列名称、是否自动ACK、Consumer
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);
//循环获取消息
while(true){
//获取消息,如果没有消息,这一步将会一直阻塞
Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String msg = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println("收到消息:" + msg);
}
}
}
测试结果:
6. 其他
6.1 Bingding —— 绑定
- Exchange和Exchange、Queue之间的连接关系
- Bingding可以包含RoutingKey或者参数
6.2 Queue——消息队列
- 消息队列,实际存储消息数据
- Durability:是否持久化,Durable:是 ,Transient:否
- Auto delete:如选yes,代表当最后一个监听被移除之后,该Queue会自动被删除。
6.3 Message——消息
- 服务器与应用程序之间传送的数据
- 本质上就是一段数据,由Properties和Payload(Body)组成
- 常用属性:delivery mode、headers(自定义属性)
6.4 其他属性
content_type、content_encoding、priority
correlation_id、reply_to、expiration、message_id
timestamp、type、user_id、app_id、cluster_id
6.5 Virtual Host虚拟主机
- 虚拟地址,用于进行逻辑隔离,最上层的消息路由
- 一个Virtual Host里面可以有若干个Exchange和Queue
- 同一个Virtual Host里面不能有相同名称的Exchange或Queue
7. 总结
RabbitMQ的概念、安装与使用、管控台操作、结合RabbitMQ的特性、Exchange、Queue、Binding
、RoutingKey、Message进行核销API的讲解,通过本章的学习,希望大家对RabbitMQ有一个初步的认识。