数据结构与算法(七) - 二叉查找树/平衡二叉查找树/红黑树
数据结构与算法(七)-查找树
1.二叉查找树
二分查找衍生出来的树
1.1 定义与特点
定义
二叉查找树可以是一棵空树,具有如下特性:(左<根<右)
- 若根节点的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于根节点的值;
- 若根节点的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于根节点的值;
- 根节点的左右子树也都分别是二叉查查找树.
- 没有键值相等的节点
特点
对二叉排序树进行中序遍历,可以得到一个由小到大的有序序列.
1.2 结构实现
1.定义节点
public class Node {
//定义值
public int value;
//左子节点指针
public Node left;
//右子节点指针
public Node right;
public Node(Node left, int value, Node right) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
2.插入和查找操作
查找:
查找某个节点,我们必须从根节点开始查找。
①、查找值比当前节点值大,则搜索右子树;
②、查找值等于当前节点值,停止搜索(终止条件);
③、查找值小于当前节点值,则搜索左子树;
插入:
要插入节点,必须先找到插入的位置。与查找操作相似,由于二叉搜索树的特殊性,待插入的节点也需要从根节点开始进行比较,小于根节点则与根节点左子树比较,反之则与右子树比较,直到左子树为空或右子树为空,则插入到相应为空的位置。
public class BinarySearchTree {
/**
* 父节点 也就是根节点
*/
private Node parent;
/**
* 查找操作
* @param entry
* @return
*/
public Node find(int entry){
Node cur = parent;//从根节点开始找
while (cur != null){
if(cur.value > entry)//在左子树
cur = cur.left;
else if(cur.value < entry)//在右子树
cur = cur.right;
else
return cur;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 插入操作
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean put(int value){
//空树
if(parent == null) {
parent = creatNode(value);
return true;
}
Node cur = parent;
while (cur != null){
if(cur.value > value){// 当前要插入的数据 应当存储在左子树
if(cur.left == null) {//当前节点左子节点为空
cur.left = creatNode(value);
return true;
} else cur = cur.left;
} else if(cur.value < value) {// 要插入的数据存储在右子树
if(cur.right == null){
cur.right = creatNode(value);
return true;
} else cur = cur.right;
}
}
return false;
}
//删除操作
public boolean delete(int value){
//todo
return true;
}
/**
* 构建没有子节点的节点
* @param value
* @return
*/
private Node creatNode(int value){
return new Node(null,value,null);
}
/**
* 构建右左右子节点的节点
* @param left
* @param value
* @param right
* @return
*/
private Node creatNode(Node left, int value, Node right){
return new Node(left,value,right);
}
}
3.删除操作
删除操作就比较复杂一点,待删除节点分为三种情况:该节点是叶节点(没有子节点)、该节点有一个子节点、该节点有两个子节点。
1.删除没有子节点的节点
要删除叶节点,只需要改变该节点的父节点引用该节点的值,即将其引用改为 null 即可。
2.删除有一个子节点的节点
删除有一个子节点的节点,我们只需要将其父节点原本指向该节点的引用,改为指向该节点的子节点即可。
3.删除有两个子节点的节点
需要用另一个节点来代替被删除的节点。某个节点的关键字次高节点是它的中序遍历后继节点,用后继节点来代替删除的节点,显然该二叉搜索树还是有序的。
后继节点:比待删除节点大的最小节点。待删除节点的右子树中最小的节点
coding:
/**
* 删除操作
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean delete(int value){
//记录要删除的节点 从根节点开始遍历
Node del = parent;
//记录要删除节点的父节点
Node delPar = null;
//先找到要删除的元素及其父元素
while (del != null){
if(del.value > value){
delPar = del;
del = del.left;
}
else if(del.value < value) {
delPar = del;
del = del.right;
}
else {//找到要删除节点
break;
}
}
if(del == null) return false;//没有找到指定的节点
//1.待删除的节点有两个子节点
if(del.left != null && del.right != null){
Node right = del.right;
Node rPar = del;//right父节点
while (right.left != null){
rPar = right;
right = right.left;
}//找到了右子树中的最小节点 后继节点
del.value = right.value;
del = right;//此时right节点已经移动 所以right节点也是待删除节点
delPar = rPar;//同上 待删除节点父节点
}
//2.待删除的节点是叶子节点或者只有一个子节点情况
Node child = null;
if(del.right != null)
child = del.right;
else if(del.left != null)
child = del.left;
else
child = null;
//3.执行删除操作
if(delPar == null){//待删除节点的父节点为空,则待删除节点是root
parent = child;
}else if(delPar.left == del){//待删除节点是左节点
delPar.left = child;
}else {//待删除节点是右节点
delPar.right = child;
}
return true;
}
4.时间复杂度分析
二叉查找树时间复杂度为O(high):
为了解决最坏情况下的这种二叉查找树结构,就引出了平衡二叉查找树
- 最坏情况下
O(n); - 一般情况下为
O(logn),因为二叉查找树k层的节点量n不大于2^(k-1),而k的最大值为log2(n)+1.
2.平衡二叉查找树(AVL)
配合二叉查找树来理解,特比是后面的跳转、旋转等操作。思路思想很重要
2.1定义与特点
定义
- 可以是空树;
- 满足二叉查找树的性质;
- 其左右子树都是平衡二叉树;
- 左子树和右子树的高度之差的绝对值不超过
1;
特点
n个元素(节点)的AVL树的高度是log2(n);n个节点的AVL树的时间复杂度为O(logn);
2.2失衡的四种情况及其去旋转方法
有参考:https://blog.csdn.net/saasanken/article/details/80796178
插入操作后左右子树的高度之差超过1为失衡,以下操作都是插入F:
- 在节点的左子树的左子树插入元素,LL插入.单旋转,右旋转;
- 在节点的右子树的右子树插入元素,RR插入;单旋转,左旋转.
2.2代码实现
AVL树中的一系列方法的实现(每种方法实现的过程都在注释中进行描述):
public class AvlTree<T extends Comparable> {
//定义平衡二叉树的根节点
private AvlNode tree;
/**
* 计算某一个节点的高度
*
* @param node
*/
private int height(AvlNode node) {
return node == null ? 0 : node.height;
}
/**
* 计算AVL 树的高度
*
* @return
*/
private int height() {
return height(tree);
}
/**
* 计算两个高度中的最大值
* @param h1
* @param h2
* @return
*/
private int getMaxHeight(int h1, int h2) {
return h1 > h2 ? h1 : h2;
}
/**
* 中序遍历树
* @param node
*/
public void inoOrder(AvlNode node){
if(node == null)
return;
inoOrder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data+" -> ");
inoOrder(node.right);
}
/**
* LL 左旋转
* @param node
* @return
*/
public AvlNode tuneLL(AvlNode node){
AvlNode node_left = node.left;
node.left = node_left.right;
node_left.right = node;
node.height = getMaxHeight(height(node.left),height(node.right)) + 1;
node_left.height = getMaxHeight(height(node_left.left),node.height)+1;
return node_left;
}
/**
* RR 右旋转
* @param node
* @return
*/
public AvlNode tuneRR(AvlNode node){
AvlNode node_right = node.right;
node.right = node_right.left;
node_right.left = node;
node.height = getMaxHeight(height(node.left),height(node.right)) + 1;//因为
node_right.height = getMaxHeight(height(node_right.right),node.height) + 1;
return node_right;
}
/**
* LR 双旋转 先RR再LL
* @param node
* @return
*/
public AvlNode tuneLR(AvlNode node){
node.left= tuneRR(node.left);//对比图就行理解这个树操作
return tuneLL(node);
}
/**
* RL 双旋转 先LL再RR
* @param node
* @return
*/
public AvlNode tuneRL(AvlNode node){
node.right = tuneLL(node.right);
return tuneRR(node);
}
/**
* 插入
* @param data
* @param node 待出入的节点
* @return 插入后的节点
*/
public AvlNode insert(T data,AvlNode node){
if(node == null){
return new AvlNode(data);
}
int compared = data.compareTo(node.data);//>0 data大于node.data
if(compared > 0){//存储在右节点
node.right = insert(data,node.right);
//判断是否平衡
if(height(node.right) - height(node.left) > 1){//旋转
if(data.compareTo(node.right.data) > 0){
//RR
node = this.tuneRR(node);
}else {
//RL
node = this.turnRL(node);
}
}
}else if(compared < 0){//存储在左子树
node.left = insert(data,node.left);
if(height(node.left) - height(node.right) > 1){//旋转
if(data.compareTo(node.left.data) > 0){
//LR
node = this.tuneLR(node);
}else {
// LL
node = this.tuneLL(node);
}
}
}else {
//相等
return null;
}
//插入后树的高度
node.height = getMaxHeight(height(node.left),height(node.right))+1;
return node;
}
/**
* 删除操作
* @param tree 根节点
* @param del 要删除的节点
* @return
*/
public AvlNode remove(AvlNode tree,AvlNode del){
if(tree == null || del == null) return null;
int compared = del.data.compareTo(tree.data);
if(compared < 0){//del在根节点左子树上
tree.left = remove(tree.left,del);
//判断是否失去平衡 删除左节点,就高度不可能大于右节点
if(height(tree.right) - height(tree.left) > 1){
AvlNode tree_right = tree.right;
if(height(tree_right.left) > height(tree_right.right)){
//RL
tree = turnRL(tree);
}else {//RR
tree = tuneRR(tree);
}
}
}else if(compared > 0){//del在根节点左子树上
tree.right = remove(tree.right,del);
//判断是否失去平衡 删除左节点,就高度不可能大于右节点
if(height(tree.left) - height(tree.right) > 1) {
AvlNode tree_left = tree.left;
if(height(tree_left.right) > height(tree_left.left)){
//LR
tree = tuneLR(tree);
}else {
//LL
tree = tuneLL(tree);
}
}
} else {//tree是要删除的节点
//1.tree左右子树非空
if(tree.right != null && tree.left != null){
if(height(tree.left) > height(tree.right)){
//找出左子树中最大节点
AvlNode max = getMaxNode(tree.left);
tree.data = max.data;
tree.left = remove(tree.left,max);
} else {
//找出右子树中最小节点
AvlNode min = getMinNode(tree.right);
tree.data = min.data;
tree.right = remove(tree.right,min);
}
} else {//2.tree有一个子节点或没有子节点
tree = (tree.left != null) ? tree.left : tree.right;
}
}
//删除树的高度
tree.height = getMaxHeight(height(tree.left),height(tree.right)) + 1;
return tree;
}
/**
* 最大节点
* @param tree 需要查询的节点
* @return 查询的节点中的最大节点
*/
public AvlNode getMaxNode(AvlNode tree){
if(tree == null) return null;
while (tree.right != null) tree = tree.right;
return tree;
}
/**
* 最小节点
* @param tree 需要查询的节点
* @return 查询的节点中的最小节点
*/
public AvlNode getMinNode(AvlNode tree){
if(tree == null) return null;
while (tree.left != null) tree = tree.left;
return tree;
}
//AvlNode 节点
public static class AvlNode<T extends Comparable> {
//存储数据
T data;
//左右子节点
AvlNode<T> left, right;
//节点高度
int height;
public AvlNode(T data, AvlNode<T> left, AvlNode<T> right, int height) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.height = height;
}
public AvlNode(T data, AvlNode<T> left, AvlNode<T> right) {
this(data, left, right, 0);
}
public AvlNode(T data) {
this(data, null, null);
}
}
}
3.红黑树
AVL tree的调整都是即时的,频繁的插入删除操作使得AVL不断的调整,效率低下。为了解决这个问题,就产生了红黑树,又称自平衡二叉查找树。
3.1红黑树性质
- 节点是红色或黑色;
- 根接点是黑色;
- 每个叶子节点都是黑色的空节点(NIL);
- 每个红色字节点的两个子节点都是黑色;(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上,不能有两个连续的红色节点)
- 从根节点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点
- 如果一个节点存在黑子节点,那么该节点肯定有两个子节点(否则它所有路径的黑节点数不等)
红黑树不是一个完美平衡二叉查找树,满足上述条件的红黑树的这种平衡为黑色完美平衡。
3.2自平衡
红黑树能够自平衡,因为它有三种操作:左旋、右旋和变色。
- 变色:节点的颜色由红变为黑,或由黑变为红;
- 左旋:以某个节点作为支点(旋转节点),其右子节点变为旋转节点的父节点,右子节点的左子节点变为旋转节点的右子节点,左子节点保存不变;
- 右旋:以某个节点作为支点(旋转节点),其左子节点变为旋转节点的父节点,左子节点的右子节点变为旋转节点的左子节点,右子节点保存不变;
3.2.1 变色
红变黑或黑变红
3.2.2 左旋
配合动图
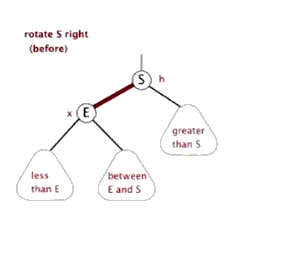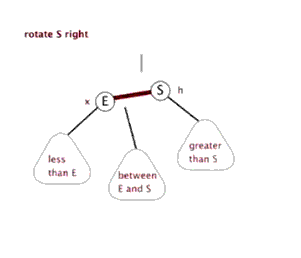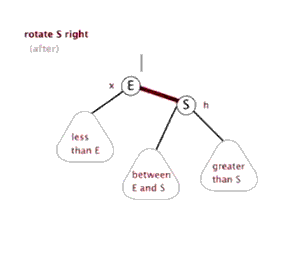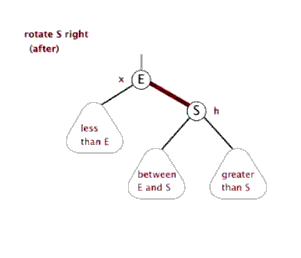
3.2.3 右旋
右旋动图
红黑树查找和二叉搜索树是一样的步骤,这里就不多说。而红黑树的插入就比较复杂。
3.3 插入
插入操作包括两部分工作:查找插入的位置、插入后自平衡。插入节点必须为红色。
插入节点必须为红色是因为:红色节点插入后红黑树的没有违背所有路径的黑色节点数相等的原则。但是有可能会导致有连续的红节点,看下面分析
约定:
红黑树插入节点情景分析
情景1:红黑树为空树
直接把插入节点作为根节点。更具红黑树性质2,还需把插入节点设为黑色。
情景2:插入节点的Key已存在
更新当前节点的值,插入节点值替换已存在节点的值。
情景3:插入节点的父节点为黑色节点
插入节点是红色的,直接插入不会影响红黑树的平衡,无需做自平衡
情景4:插入节点的父节点为红色
根据性质2,插入节点的父节点不可能是根节点,所以插入节点总是存在爷爷节点。后序旋转操作会用到的。情况分为下列两种:
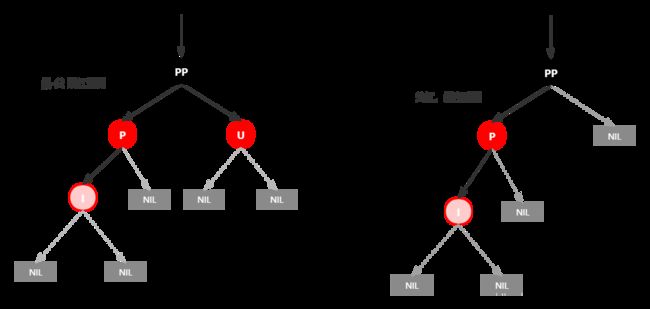
情景4.1:叔叔节点存在并且为红节点
性质4,红色节点不能相连 -> 爷爷节点肯定为黑色节点。此时插入子树的红黑树情况是 黑红红。处理方式是变色,改为 红黑红。具体步骤:
- 将P和U改为黑色;
- 将PP改为红色;
- 将PP设置为当前节点,进行后序处理(变色或旋转)
PP变为红色后,若PP父节点为黑色当然没问题,但是当PP父节点为红色节点时,就得继续处理,直到平衡为止。
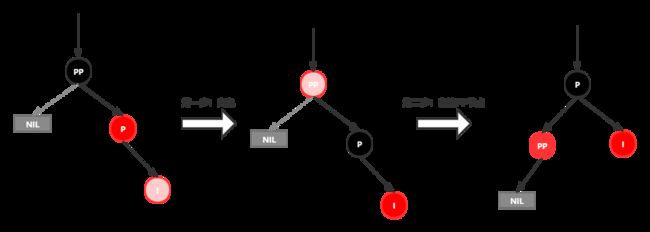
情景4.2:叔叔节点不存在或为黑节点,插入节点的父节点是爷爷节点的左子节点
从插入前来看,叔叔节点非红即空(NIL节点),否则就会破坏红黑树的性质5,此路径多一个黑色节点
4.2.1 新插入节点到父节点P的左子节点(LL红色情况)
处理方法:
- 变颜色,P变为黑色,PP变为红色;
- 对PP节点右旋;
4.2.2 新插入节点到父节点P的右子节点(LR红色情况)
处理:
- 对P左旋;
- 将P设置为当前节点,变为LL情况;
- 按照LL红色情况处理(变色,右旋PP)
情景4.3:叔叔节点不存在或为黑节点,并且插入节点的父节点是爷爷节点的右子节点
4.3.1 新插入节点到父节点P的右子节点处(RR红色情况)
处理:
变颜色,将P变为黑色,将PP变为红色;
对PP节点继续左旋
4.3.2 新插入节点到父节点P的左子节点处(RL红色情况)
处理:
对P进行右旋;
将P设置为当前节点,得到RR红色的情况;
按照RR红色情况处理(变色,左旋PP)
3.4 这里看一个实例
3.5 红黑树代码实现
步骤
- 创建RBTree,定义颜色;
- 创建RBNode;
- 辅助方法定义:parentOf(node),isRed(node),isBlack(node),setRed(node),setBlack(node),inOrderPrint();
- 左旋方法定义:leftRotate(node);
- 右旋方法定义:rightRotate(node);
- 公开插入接口方法定义:insert(K key ,V value);
- 内部插入接口方法定义:insert(RBNode node);
- 修正插入导致红黑树失衡的方法定义:insertFixUp(RBNode node);
- 测试红黑树的正确性
RNTree
/**
* step:
* 1. 创建RBTree,定义颜色;
* 2. 创建RBNode;
* 3. 辅助方法定义:parentOf(node),isRed(node),isBlack(node),setRed(node),setBlack(node),inOrderPrint();
* 4. 左旋方法定义:leftRotate(node);
* 5. 右旋方法定义:rightRotate(node);
* 6. 公开插入接口方法定义:insert(K key ,V value);
* 7. 内部插入接口方法定义:insert(RBNode node);
* 8. 修正插入导致红黑树失衡的方法定义:insertFixUp(RBNode node);
* 9. 测试红黑树的正确性
*
*/
public class RBTree<K extends Comparable<K>,V> {
private static final boolean RED = true;
private static final boolean BLACK = false;
//树根节点
private RBNode root;
public RBNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
/**
* 获取当前节点父节点
* @param node
* @return
*/
private RBNode parentOf(RBNode node){
if(node != null) return node.parent;
return null;
}
/**
* 节点是否为红色
* @param node
* @return
*/
private boolean isRed(RBNode node){
if(node != null) return node.color == RED;
return false;
}
/**
* 节点是否为黑色
* @param node
* @return
*/
private boolean isBlack(RBNode node){
if(node != null) return node.color == BLACK;
return false;
}
/**
* 设置节点为红色
* @param node
*/
private void setRed(RBNode node){
if(node != null) node.color = RED;
}
/**
* 设置节点为黑色
* @param node
*/
private void setBlack(RBNode node){
if(node != null) node.color = BLACK;
}
/**
* 中序打印红黑树
*/
public void inOrderPrint(){
inOrderPrint(this.root);
}
private void inOrderPrint(RBNode node){
if(node != null){
inOrderPrint(node.left);
System.out.println("key:"+node.key+",value:"+node.value);
inOrderPrint(node.right);
}
}
public void insert(K key,V value){
RBNode node = new RBNode();
node.setKey(key);
node.setValue(value);
//新节点一点是红色
node.setColor(RED);
insert(node);
}
private void insert(RBNode node){
//第一步:查找当前node的父节点
RBNode parent = null;
RBNode x = this.root;
while (x != null){
parent = x;//x的父节点
//cmp>0说明node.key大于x.key 需要在x的右子树插入
//cmp==0说明node.key大于于x.key 替换
//cmp<0说明node.key小于x.key 需要在x的左子树插入
int cmp = node.key.compareTo(x.key);
if(cmp > 0){
x = x.right;
} else if(cmp == 0){
x.setValue(node.getValue());
return;//结束
} else {
x = x.left;
}
}
node.parent = parent;
if(parent != null){
//判断node与parent 的key谁大
int cmp = node.key.compareTo(parent.key);
if(cmp > 0){//当前node的key比parent的key大 需要把node放入parent的右子节点
parent.right = node;
}else {//没有==0的情况,因为上面已经早==0时弹出了
//当前node.key < parent.key;
parent.left = node;
}
} else {//parent为空
this.root = node;
}
//需要调用修复红黑树平衡得到方法 todo
insertFixUp(node);
}
/**
* 插入后修复红黑树平衡的方法
* |---情景1:红黑树为空树 将根节点染色为黑色
* |---情景2:插入节点的key已经存在 不需要处理
* |---情景3:插入节点的父节点为黑色 不需要处理
*
* 情景4 需要咱们去处理
* |---情景4:插入节点的父节点为红色
* |---情景4.1:叔叔节点存在,并且为红色(父-叔 双红)
* 将叔父节点变为黑色,爷爷节点变为红色,以爷爷节点作为当前节点继续处理
* |---情景4.2:叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的左子树
* |---情景4.2.1:插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(LL情况)
* 父节点变为黑色,爷爷节点变为红色,以爷爷节点右旋
* |---情景4.2.2:插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(LR情况)
* 先以父节左旋变为LL 再作为4.2.1情景处理
* |---情景4.3:叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的右子树
* |---情景4.3.1:插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(RR情况)
* 父节点变为黑色,爷爷节点变为红色,以爷爷节点左旋
* |---情景4.3.2:插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(RL情况)
* 先以父节左旋变为RR 再作为4.3.1情景处理
*/
private void insertFixUp(RBNode node){
this.root.setColor(BLACK);
RBNode parent = parentOf(node);
RBNode grandparent = parentOf(parent);
//情景4:插入节点的父节点为红色
if(parent != null && isRed(parent)){
//如果父节点是红色,那么一点存在爷爷节点,因为根节点不可能是红色
RBNode uncle = null;
if(parent == grandparent.left){//父节点为爷爷节点左子树
uncle = grandparent.right;
//情景4.1:叔叔节点存在,并且为红色(父-叔 双红)
if(uncle != null && isRed(uncle)){
//将叔父节点变为黑色,爷爷节点变为红色,以爷爷节点作为当前节点继续处理
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(uncle);
setRed(grandparent);
insertFixUp(grandparent);
return;//结束条件
}
//情景4.2:叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的左子树
if(uncle == null || isBlack(uncle)){
//情景4.2.1:插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(LL情况)
if(node == parent.left){
//父节点变为黑色,爷爷节点变为红色,以爷爷节点右旋
setBlack(parent);
setRed(grandparent);
rightRotate(grandparent);
return;
}
//情景4.2.2:插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(LR情况)
if(node == parent.right){
//先以父节左旋变为LL 再作为4.2.1情景处理 指定父节点为当前节点做下一轮处理
leftRotate(parent);
insertFixUp(parent);
return;
}
}
/*|---情景4.3:叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的右子树
* |---情景4.3.1:插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(RR情况)
* 父节点变为黑色,爷爷节点变为红色,以爷爷节点左旋
* |---情景4.3.2:插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(RL情况)
* 先以父节左旋变为RR 再作为4.3.1情景处理*/
}else {//父节点为爷爷节点右子树
uncle = grandparent.left;
//情景4.1:叔叔节点存在,并且为红色(父-叔 双红)
if(uncle != null && isRed(uncle)){
//将叔父节点变为黑色,爷爷节点变为红色,以爷爷节点作为当前节点继续处理
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(uncle);
setRed(grandparent);
insertFixUp(grandparent);
return;//结束条件
}
//情景4.3:叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的右子树
if(uncle == null || isBlack(uncle)){
//情景4.3.1:插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(RR情况)
if(node == parent.right){
//父节点变为黑色,爷爷节点变为红色,以爷爷节点左旋
setBlack(parent);
setRed(grandparent);
leftRotate(grandparent);
return;
}
//情景4.3.2:插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(RL情况)
if(node == parent.left) {
//先以父节左旋变为RR 再作为4.3.1情景处理 然后以父节点为当前节点处理
rightRotate(parent);
insertFixUp(parent);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 左旋方法
* 左旋示意图:左旋x节点
* p p
* | |
* x y
* / \ ----> / \
* lx y x ry
* / \ / \
* ly ry lx ly
*
* 左旋做了几件事?
* 1.将y的左子节点赋值给x的右边,并且把x设置为y的左子节点的父节点
* 2.将x的父节点(非空时)指向y,更新y的父节点为x的父节点
* 3.将y的左子节点指向x,更新x的父节点为y
*/
private void leftRotate(RBNode x) {
RBNode y = x.right;
//将y的左子节点赋值给x的右边
x.right = y.left;
//并且把x设置为y的左子节点的父节点
if(y.left != null) {
y.left.parent = x;
}
//将x的父节点(非空时)指向y
if(x.parent != null) {
//如果x是parent左子树,则把y安放到parent的左边
if(x.parent.left == x) {
x.parent.left = y;
} else {//否则把y安放到parent的右边
x.parent.right = y;
}
//更新y的父节点为x的父节点
y.parent = x.parent;
} else {
this.root = y;
this.root.parent = null;
}
y.left = x;
x.parent = y;
}
/**
* 右旋方法
* 右旋示意图:右旋y节点
*
* p p
* | |
* y x
* / \ ----> / \
* x ry lx y
* / \ / \
*lx ly ly ry
*
* 右旋都做了几件事?
* 1.将x的右子节点 赋值 给了 y 的左子节点,并且更新x的右子节点的父节点为 y
* 2.将y的父节点(不为空时)指向x,更新x的父节点为y的父节点
* 3.将x的右子节点指向y,更新y的父节点为x
*/
private void rightRotate(RBNode y) {
//1.将x的右子节点赋值给y的左子节点,并将y赋值给x右子节点的父节点(x右子节点非空时)
RBNode x = y.left;
y.left = x.right;
if(x.right != null) {
x.right.parent = y;
}
//2.将y的父节点p(非空时)赋值给x的父节点,同时更新p的子节点为x(左或右)
x.parent = y.parent;
if(y.parent != null) {
if(y.parent.left == y) {
y.parent.left = x;
} else {
y.parent.right = x;
}
} else {
this.root = x;
this.root.parent = null;
}
//3.将x的右子节点赋值为y,将y的父节点设置为x
x.right = y;
y.parent = x;
}
static class RBNode <K extends Comparable<K>,V>{
private RBNode parent;
private RBNode left;
private RBNode right;
private boolean color;
private K key;
private V value;
public RBNode() {
}
public RBNode getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(RBNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public RBNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(RBNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public RBNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(RBNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
public boolean isColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(boolean color) {
this.color = color;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(K key) {
this.key = key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
public RBNode(RBNode parent, RBNode left, RBNode right, boolean color, K key, V value) {
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.color = color;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
}
查看红黑数结构
源于网络
public class TreeOperation {
/*
树的结构示例:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
*/
// 用于获得树的层数
public static int getTreeDepth(RBTree.RBNode root) {
return root == null ? 0 : (1 + Math.max(getTreeDepth(root.getLeft()), getTreeDepth(root.getRight())));
}
private static void writeArray(RBTree.RBNode currNode, int rowIndex, int columnIndex, String[][] res, int treeDepth) {
// 保证输入的树不为空
if (currNode == null) return;
// 先将当前节点保存到二维数组中
res[rowIndex][columnIndex] = String.valueOf(currNode.getKey() + "-" + (currNode.isColor() ? "R" : "B") + "");
// 计算当前位于树的第几层
int currLevel = ((rowIndex + 1) / 2);
// 若到了最后一层,则返回
if (currLevel == treeDepth) return;
// 计算当前行到下一行,每个元素之间的间隔(下一行的列索引与当前元素的列索引之间的间隔)
int gap = treeDepth - currLevel - 1;
// 对左儿子进行判断,若有左儿子,则记录相应的"/"与左儿子的值
if (currNode.getLeft() != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex - gap] = "/";
writeArray(currNode.getLeft(), rowIndex + 2, columnIndex - gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
// 对右儿子进行判断,若有右儿子,则记录相应的"\"与右儿子的值
if (currNode.getRight() != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex + gap] = "\\";
writeArray(currNode.getRight(), rowIndex + 2, columnIndex + gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
}
public static void show(RBTree.RBNode root) {
if (root == null) System.out.println("EMPTY!");
// 得到树的深度
int treeDepth = getTreeDepth(root);
// 最后一行的宽度为2的(n - 1)次方乘3,再加1
// 作为整个二维数组的宽度
int arrayHeight = treeDepth * 2 - 1;
int arrayWidth = (2 << (treeDepth - 2)) * 3 + 1;
// 用一个字符串数组来存储每个位置应显示的元素
String[][] res = new String[arrayHeight][arrayWidth];
// 对数组进行初始化,默认为一个空格
for (int i = 0; i < arrayHeight; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrayWidth; j ++) {
res[i][j] = " ";
}
}
// 从根节点开始,递归处理整个树
// res[0][(arrayWidth + 1)/ 2] = (char)(root.val + '0');
writeArray(root, 0, arrayWidth/ 2, res, treeDepth);
// 此时,已经将所有需要显示的元素储存到了二维数组中,将其拼接并打印即可
for (String[] line: res) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < line.length; i ++) {
sb.append(line[i]);
if (line[i].length() > 1 && i <= line.length - 1) {
i += line[i].length() > 4 ? 2: line[i].length() - 1;
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
}
测试类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RBTree<String, Object> rbt = new RBTree();
//测试输入:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e
while(true) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入key:");
String key = sc.next();
rbt.insert(key, null);
TreeOperation.show(rbt.getRoot());
}
}
}
到此即实现了红黑树。