linux命令目录重命名,Linux 移动或重命名文件/目录---mv命令
mv 命令是一个与cp相似的命令,可是它并不是建立文件或目录的复制品/副本。无论你在使用什么版本的Linux系统,mv 都默认安装在你的Linux系统上了。来看一下 mv 命令在平常操做中的一些例子。less
[root@localhost tmp]# mv --help
Usage: mv [OPTION]... [-T] SOURCE DEST
or: mv [OPTION]... SOURCE... DIRECTORY
or: mv [OPTION]... -t DIRECTORY SOURCE...
Rename SOURCE to DEST, or move SOURCE(s) to DIRECTORY.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
--backup[=CONTROL] make a backup of each existing destination file
-b like --backup but does not accept an argument
-f, --force do not prompt before overwriting
-i, --interactive prompt before overwrite
-n, --no-clobber do not overwrite an existing file
If you specify more than one of -i, -f, -n, only the final one takes effect.
--strip-trailing-slashes remove any trailing slashes from each SOURCE
argument
-S, --suffix=SUFFIX override the usual backup suffix
-t, --target-directory=DIRECTORY move all SOURCE arguments into DIRECTORY
-T, --no-target-directory treat DEST as a normal file
-u, --update move only when the SOURCE file is newer
than the destination file or when the
destination file is missing
-v, --verbose explain what is being done
-Z, --context set SELinux security context of destination
file to default type
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
The backup suffix is '~', unless set with --suffix or SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX.
The version control method may be selected via the --backup option or through
the VERSION_CONTROL environment variable. Here are the values:
none, off never make backups (even if --backup is given)
numbered, t make numbered backups
existing, nil numbered if numbered backups exist, simple otherwise
simple, never always make simple backups
GNU coreutils online help:
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'mv invocation'
ide
1.移动文件
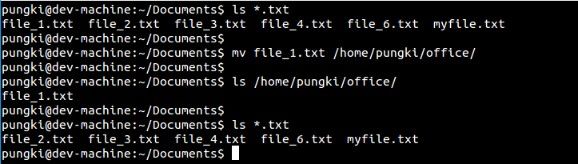
移动文件时须要注意的是文件的源地址和目标地址必须不一样。这里有个例子,想要将file_1.txt文件从当前目录移动到其它目录,以/home/pungki/为例,语法应该以下:this
$ mv file_1.txt/home/pungki/office
如咱们所见,当咱们移动 filetxt 文件时,先前目录的 file1.txt 就被删除了。spa
2.移动多个文件
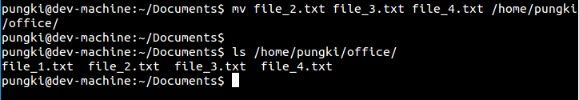
若是想一次移动多个文件,咱们能够将他们放在一行并用空格分开。3d
$ mv file_2.txt file_3.txt file_4.txt/home/pungki/office
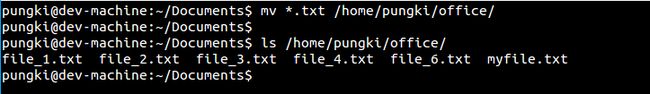
若是你的文件有规律可循的话那么你就能够使用通配符。好比,为了移除全部以.txt为扩展名的文件,咱们能够用下面的命令:orm
$ mv*.txt/home/pungki/office
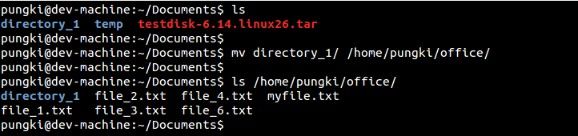
3.移动目录
不一样于复制命令,用 mv 命令移动目录至关直接。移动目录你能够使用不带选项的 mv 命令。看下面的截图就一目了然了。blog
4.重命名文件或目录
咱们也用 mv 命令来重命名文件或目录。不过目标位置和源位置必须相同才能够。而后文件名必须不一样。ip
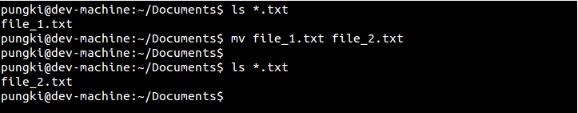
假定咱们当前所在目录为/home/pungki/Documents,而咱们想将file1.txt重命名为file2.txt。那么命令应该以下:ci
$ mv file_1.txt file_2.txt
若是是绝对路径,它应该像下面这样:rem
$ mv/home/pungki/Documents/file_1.txt/home/pungki/Documents/file_2.txt
5. 重命名目录
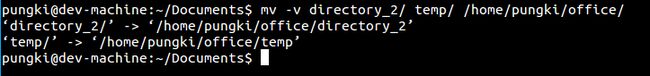
上一段的规则一样适用于目录。请看这个例子:
$ mv directory_1/directory_2/
6. 打印移动信息
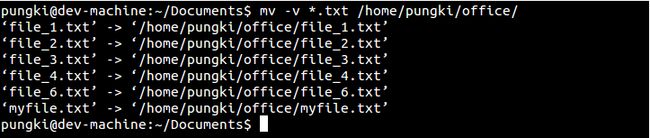
当你移动或重命名一大堆文件或目录时,你可能会想在不去目标位置去查看的状况下知道你本身的命令是否成功地执行了。这就要用到-v选项了。
$ mv-v*.txt/home/pungki/office
该方法一样适用于目录。
7. 使用交互模式
当你将文件移动到其它位置,而那个位置刚好有一样的文件,这时 mv 命令会覆盖掉原来的文件。对于mv的这一行为通常不会有什么提示。若是想产生一个关于覆盖文件的提示,咱们能够使用-i选项。(译注:一般发行版会经过alias命令,将-i做为默认选项,因此会有提示。)
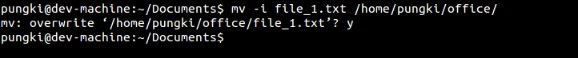
假设咱们想将 file1.txt 移动到 /home/pungki/office。同时,/home/pungki/office 目录下已经有file1.txt文件了。
$ mv-i file_1.txt/home/pungki/office
这个提示会让咱们知道目标位置处file_1.txt的存在。若是咱们按y键,那么那个文件将会被删除,不然不会。
8. 使用更新选项
-i 选项会提示咱们关于覆盖文件的提示,而 -u 则只在源文件比目标文件新时才执行更新。让咱们看一看下面的例子:
假如 file1.txt 和 file2.txt有以下特色:
File_1.txt has84bytes file sizeanditlastmodified timeis12:00
File_2.txt has0bytes file sizeanditlastmodified timeis11:59
咱们想将它们移动到 /home/pungki/office 目录下。**可是目标地址*已经有file1.txt和file2.txt了。
咱们用下面的命令将file1.txt 和file2.txt从当前目录移动到/home/pungki/office
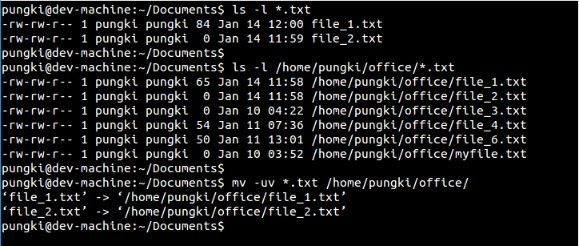
$ mv-uv*.txt/home/pungki/office
能够看到这些文件被移动了。能移动这些文件是由于它们最近的修改时间戳比 /home/pungki/office 目录中的文件新。
9.不要覆盖任何已存在的文件
若是-i选项询问咱们是否要覆盖文件,那么 -n 选项将不会容许咱们覆盖任何已存在的文件。
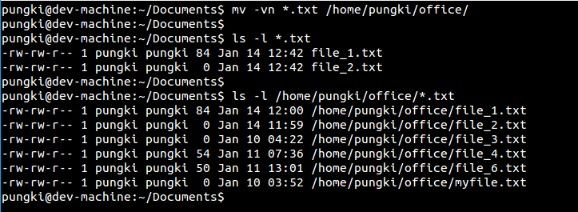
继续使用第8点中的例子,若是咱们将-u 换成 -n同时加上-v选项,那么咱们会看到没有任何文件移动到了 /home/pungki/office 目录下。
$ mv-vn*.txt/home/pungki/office
10. 复制时建立备份
默认状况下,移动文件将会覆盖已存在的目标文件。可是若是咱们移动错了文件而目标文件已经被新的文件覆盖了,这时应该怎么办才好呢?有没有一种方法能够恢复以前的文件呢?答案是确定的。咱们能够用-b选项。该选项会在新文件覆盖旧文件时将旧文件作备份。这里咱们还以第8点为例。
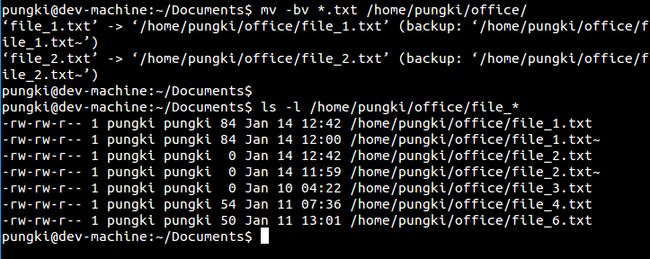
$ mv-bv*.txt/home/pungki/office
如截图中所见,在 /home/pungki/office 目录下出现了名为file1.txt~ and file2.txt~ 的文件。那个波浪符号(~)意味着这些文件是备份文件。从它们的属性中咱们能够看到,这些文件比file1.txt和file2.txt要旧。
11. 无条件覆盖已经存在的文件
(译注:这一节是译者补充的,原文遗漏了这个重要选项)
当你但愿不管如何都覆盖已经存在的文件或目录时,你能够使用 -f 选项。若是同时指定了 -f 选项和 -i 或 -n 选项,则 -f 选项会覆盖它们——即不进行任何提示而覆盖,因此,在使用此参数时,知道你在作什么。
$ mv-f*.txt/home/pungki/office
总结
移动文件和目录命令是Linux系统的基本命令。一般你能够经过man mv 或者 mv --help显示mv的手册页以了解更多详细信息。