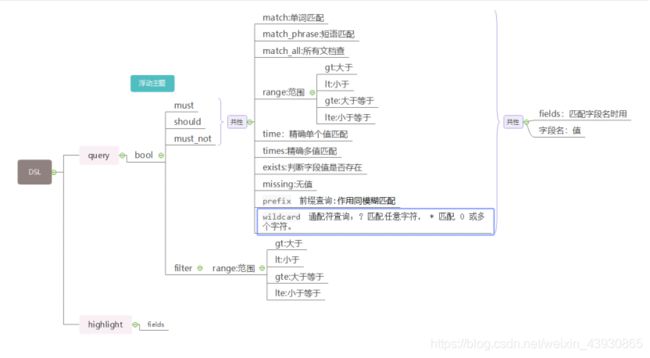
(六:3)ElasticSearch的DSL查询总结
ElasticSearch权威指南学习
文章目录
- ElasticSearch权威指南学习
- 1:基础入门
-
- 1.1:ElasticSearch交互:查询query
- 1.2:query DSL查询总结
-
- 1:示例demo
- 1.3:query DSL查询语句详解
-
- 1:match
- 2:match_all
- 3:range范围+过滤器
- 4:term精确值匹配
- 5:terms精确多值查找
- 6:exists判断
- 7:missing
- 8:分页查询from+size
- 9:高亮显示:highlight
- 10:分析聚合:aggregations
-
- 1.指标聚合
- 11:前缀模糊查询:prefix
- 12:通配符查询:windcard
- 13:正则模糊查询:regexp
- 14:排序:sort
- 15:match_phrase 短语匹配
- 15:multi_match:多字段匹配
- 1.4:ES的过滤器使用
-
- 1:bool布尔过滤器
- 2:filter过滤器
- 1.5:DSL查询原理详解
- 1.6:查询结果的显示
- 2:组合复杂查询
- 3:explain查询分析API
- 4:查询返回控制
-
-
- 1:source属性控制字段
- 2:通过docvalue_fields属性获取值
-
1:基础入门
权威指南官方文档
1.1:ElasticSearch交互:查询query
demo
curl -X '://:/?' -d ''
1.2:query DSL查询总结
下面详细解释用法,bool查询没有严格的上下级,可以嵌套使用,嵌套的多个条件是一个数组,每个条件被{}包围
1:示例demo
GET /index/type/id/_search
后续会详解查询语句
查询结果分析
get megacorp/employee/1/_search
返回结果包含了文档的一些元数据
took :值告诉我们执行整个搜索请求耗费了多少毫秒。
_shards 部分告诉我们在查询中参与分片的总数,以及这些分片成功了多少个失败了多少个
_source :原始保存的数据.
结果
{
"_index" : "megacorp",
"_type" : "employee",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "John",
"last_name" : "Smith",
"age" : 25,
"about" : "I love to go rock climbing",
"interests": [ "sports", "music" ]
}
}
1.3:query DSL查询语句详解
先准备数据
1:mapping设置
PUT test_field
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": "1",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"refresh_interval": "30s"
},
"mappings": {
"type1": {
"_all":{ "enabled": false},
"_source": {"enabled": true},
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text",
"index": true,
"store": true
},
"age":{
"type": "integer",
"index": true,
"store": true
}} }}}
插入3条数据
PUT test_field/type1/1
{
"name":"xiaoming",
"age":1
}
PUT test_field/type1/1
{
"name":"dahuang",
"age":2
}
PUT test_field/type1/3
{
"name":"xinxin",
"age":3
}
1:match
match是一个全文搜索查询,会把查询字段用分词器分词,最终转化为bool+term精确值查询,多个term间是or关系,可以设置为and关系,提高相关度。若传入字符串会分割为单词进行精确匹配,多个字符串间空格区分。
1:单层查询:
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"name": "xiaoming dahuang"
}
}
}
会分词转为term查询xiaoming dahuang为两个名字查询,也可以"operator": "and"提高相关度
GET /my_index/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{"term": { "text": "xiaoming " }},
{"term": { "text": "dahuang" }}
]
}
}
}
结果:两条结果符合
//operator参数提高精度,分词后是and关系。发现没有数据符合
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{
"match": {
"name": {
"query": "xiaoming dahuang",
"operator": "and"
}
}
2:嵌套查询:must+match
must为子条件必须全部满足
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{
"bool": {
"must":[ //多个条件是一个数组,条件间用,分割,每个条件被{}包围
{"match":{"name": "xiaoming dahuang"}}, //条件1
{ "match":{"age":2}} //条件2
] } } }
结果:只有一个满足
"_source" : {
"name" : "dahuang",
"age" : 2
}
2:match_all
没有查询条件 时默认走全文档搜索也就是match_all
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all": {}
}}
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{ }
}
3:range范围+过滤器
range范围查询,对符合条件的进行过滤,可配合filter过滤使用。range查询的字段的doc_values属性必须为true。
查询年龄>=1的
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{
"range": {
"age": { // 查询字段
"gte": 1
} } }}
结果:可发现3条都能查到
GET test_field/type1/_search //查询字段小于1580000000的
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"filter":{
"range":{
"02E0012":{
"lte":1580000000
} } }} }
}
4:term精确值匹配
精确查找年龄=1
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{
"term": {
"age": { //字段
"value": "1" //值
} }}}
5:terms精确多值查找
多值是数组的关系
查找年龄=1,=2的人
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{
"terms": {
"age": [ //多值,隔开即可
"1", "2"
}} } }
6:exists判断
用于判断文档的字段是否有值或者是否存在。没有值或者值为null或者字段不存在则不查询
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{
"exists": {
"field": "字段name"
} }}
结果:
若存在显示查询的数据,默认10条,可以配合sort进行排序
7:missing
和exists相反,判断某字段无值或者字段不存在。在7.x版本可能已经移除可以用must_not进行代替
8:分页查询from+size
解释:
size
显示应该返回的结果数量,默认是 10
from
显示应该跳过的初始结果数量,默认是 0
demo
如果每页展示 5 条结果,可以用下面方式请求得到 1 到 3 页的结果:
GET /_search?size=5&from=5
对查询结果实现分页
GET index/_search?size=5&from=5{"query":{}}
9:高亮显示:highlight
*对query的结果进行高亮显示,highlight和query同级*
也可以设置高亮显示的格式,宽度,长度等等
"highlight":{
"fields": {"name":{}}
}
GET test_field/type1/_search
{
"query":{
"bool": {
"must":[
{"match":{"name": "xiaoming dahuang"}},
{ "match":{"age":2}}
]} },
"highlight":{
"fields": {"name":{}}
}}
结果展示
"highlight" : {
"name" : [
"dahuang"
] }
10:分析聚合:aggregations
Elasticsearch 有一个功能叫聚合(aggregations),允许我们基于数据生成一些精细的分析结果。聚合与 SQL 中的 GROUP BY 类似但更强大。聚合字段必须设置doc_values属性是true才支持聚合功能
query{},
{
"aggs": {
"NAME": {# 指定结果的名称:随意起名
"AGG_TYPE": {# 指定聚合支持的具体聚合方法,比如count,max
TODO: # 聚合体内制定具体的聚合字段,field
}
}
TODO: # 该处可以嵌套聚合,对聚合结果再分析聚合
}
}
ES当中的聚合分析主要分为指标(metric)聚合和桶(bucketing)聚合。
1.指标聚合
指标聚合(也叫度量聚合),简单点来说就是对数据集中的数据进行相应的指标计算之后,得出聚合结果,如求最大值、最小值、平均值等。
指标聚合主要函数如下
max min sum avg
count 文档计数
Value count 统计某字段不同值的个数
cardinality 值去重计数
stats 统计 count max min avg sum 5个值
max函数举例使用:
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"max_agg": {
"max": {<!--指标关键词-->
"field": "score"<!--按照某个字段进行聚合-->
}
} }}
2.桶聚合(bucket)
11:前缀模糊查询:prefix
性能:prefix>windcard>regexp
GET index/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"02B0036": {
"value": "14000"
}}}
12:通配符查询:windcard
*代表任何字符
?代表任何单个字符
但是为了防止极慢的查询,应避免?和*开头
GET index/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"02B0036": {
"value": "14000*"
}}}}
13:正则模糊查询:regexp
支持标准正则表达式
14:排序:sort
对query结果再排序,字段的类型应该为long等不能是text或者keyword,否则排序的结果不一定正确。
排序字段的doc_values属性必须为true,否则不支持排序。
GET index/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"02B0036": {
"value": "14000"
}},
"sort": [{"需要排序的字段": {'order': "升序asc降序desc"}}]
}
15:match_phrase 短语匹配
和match的区别是分词后会匹配字段的先后顺序,可以通过slop参数提高相近度。
GET /my_index/my_type/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "quick brown fox"
}
}
}
//slop使用,值越高越相近。但是查询较慢,一般不用
"title": {
"query": "quick brown fox",
"slop": 100
}
15:multi_match:多字段匹配
同时查询多个字段的某个值
"multi_match": {
"query": "field value",
"type": "most_fields",
"fields": [ "field1", "field2", "field3", "field4" ]
}
1.4:ES的过滤器使用
1:bool布尔过滤器
bool 查询也可以接受 must 、 must_not 和 should 参数下的多个查询语句。比如
{
"bool" : {
"must" : [],
"should" : [],
"must_not" : [],
}
}
使用举例
GET /my_index/my_type/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "title": "quick" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "title": "lazy" }},
"should": [
{ "match": { "title": "brown" }},
{ "match": { "title": "dog" }}
]
}
}
}
must:要求所有条件都要满足(类似于&&)
should:任何一个满足就可以(类似于||)
must_not:所有条件都不能满足(类似于! (&&))
2:filter过滤器
filter和query并行度一致,等级一致,也可嵌套使用
用法1:
{
"query": {"match_all": {}},
"filter": {
"range": { "balance": { "gte":20000, "lte":30000 }
}
}
用法2:
GET test_field/type1/_search //查询字段小于1580000000的
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"filter":{
"range":{
"02E0012":{
"lte":1580000000
} } }} }
}
gte:大于等于
lte:小于等于
1.5:DSL查询原理详解
步骤分析:
1:查询语句分给各个节点
2:查询语句分给各个分片
3:各个分片执行查询,返回结果给协调节点结果汇总,返回给客户端
1.6:查询结果的显示
查询时显示的值就是source=true的属性配置的。也可以查询时通过stored_fields属性指定字段进行显示。
GET / _search { “ stored_fields” :[ “ user” ,“ postDate” ],“ query” :{ “ term” :{ “ user” :“ kimchy” } } }
2:组合复杂查询
如何写好一个查询语句,每个子结构都是一个{}包含,每个结构间是‘,’逗号分隔。包含多个条件是数组[],数组中多个结构体的话也是{}
实战1:从衬衫库里查出是古驰牌子的,然后根据颜色聚合再过滤出红色的
GET /shirts/_search
{
"query": { 1:查询体
"bool": {
"filter": {
"term": { "brand": "gucci" }
}
}
},
"aggs": { 2:聚合结构
"colors": { ## 2.1:聚合颜色
"terms": { "field": "color" }
},
"color_red": { ## 2.2:根据颜色的结果过滤出红色的再聚合
"filter": {
"term": { "color": "red" }
},
"aggs": {
"models": {
"terms": { "field": "model" }
}
}
}
},
"post_filter": { 3:过滤
"term": { "color": "red" }
}
}
3:explain查询分析API
可以通过 validate-query API 查看查询体的逻辑:?explain
GET /index/query?explain
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "field value",
"type": "most_fields",
"fields": [ "field1", "field2", "field3", "field4" ]
}
}
}
4:查询返回控制
我们可以通过控制返回结果的字段或者查看具体字段的值
1:source属性控制字段
includes:查询那些字段
excludes:排除那些字段
GET /index/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"_source": {
"includes": ["name" ,"address"],
"excludes": ["age" , "birthday" ]
}
但是如果我们在定义索引的mapping时关闭了字段source属性,如何获取到字段的内容?
2:通过docvalue_fields属性获取值
此时查询会通过字段的docvalues或者fielddata属性存储的值去查找来作为返回,此时结果会缓存到内存中
GET /index/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},"docvalue_fields":["field_name1","field_name2"]
}