【Java】循环语句练习
文章目录
- 1. 计算5的阶乘
- 2. 计算 1! + 2! + 3! + 4! + 5!
- 3. 数字9 出现的次数
- 4. 判定素数
- 5. 求1-100之间的素数
- 6. 求2个整数的最大公约数
- 7. 计算分数的值
- 8. 模拟登陆
- 9. 输出乘法口诀表
- 10. 求出0~999之间的所有“水仙花数”并输出
- 11. 猜数字游戏
1. 计算5的阶乘
n! (阶乘),一个正整数的阶乘是所有小于及等于该数的正整数的积,并且0的阶乘为1。自然数n的阶乘写作n!,即n!=1×2×3×…×(n-1)×n。5! = 1×2×3×4x5。
- while循环实现
public class Test {
//计算5的阶乘
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1;
int ret = 1;
while(n<=5){
ret *= n;
n++;
}
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
- for循环实现
public class Test {
//计算5的阶乘
public static void main(String[] args) {
int ret = 1;
for (int n = 1;n <= 5;n++){
ret *= n;
}
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
我们上一题学习了n阶乘的计算,这一题计算阶乘的和。阶乘的求和就是在计算阶乘的基础上再加一层循环。
2. 计算 1! + 2! + 3! + 4! + 5!
- while 循环实现
public class Test {
//计算 1! + 2! + 3! + 4! + 5!
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
int sum = 0;
//外层循环负责求阶乘的和
while(i <= 5){
int n = 1;
int ret = 1;
//内层循环负责完成求阶乘的细节
while (n <= i){
ret *= n;
n++;
}
sum += ret;
i++;
}
System.out.println("sum="+sum);
}
}
- for 循环实现
public class Test {
//计算 1! + 2! + 3! + 4! + 5!
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1;i <= 5;i++){
int ret = 1;
for(int n = 1;n <= i;n++){
ret *= n;
}
sum += ret;
}
System.out.println("sum="+sum);
}
}
3. 数字9 出现的次数
编写程序数一下 1到 100 的所有整数中出现多少个数字9
个位数为9的数字有9,19,29……99;个位数判断为 i % 10 == 9;
十位数为9的数字有91,92,93……99;十位数判断为 i % 10 == 9。
其中99出现了两次
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0;i <= 100;i++){
if(i % 10 == 9){
count++;
}
if(i / 10 == 9){
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
4. 判定素数
给定一个数字,判定一个数字是否是素数。
素数是只能被 1 和它本身整除的数。也就是说能被 2 到 n-1 整除的数都不是素数。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
//判断一个数是不是素数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int i = 2;
for (i = 2;i < n ; i++) {
if(i % n == 0){
System.out.println(i+"不是素数");
}
}
if(i == n){
System.out.println(i+"是素数");
}
}
}
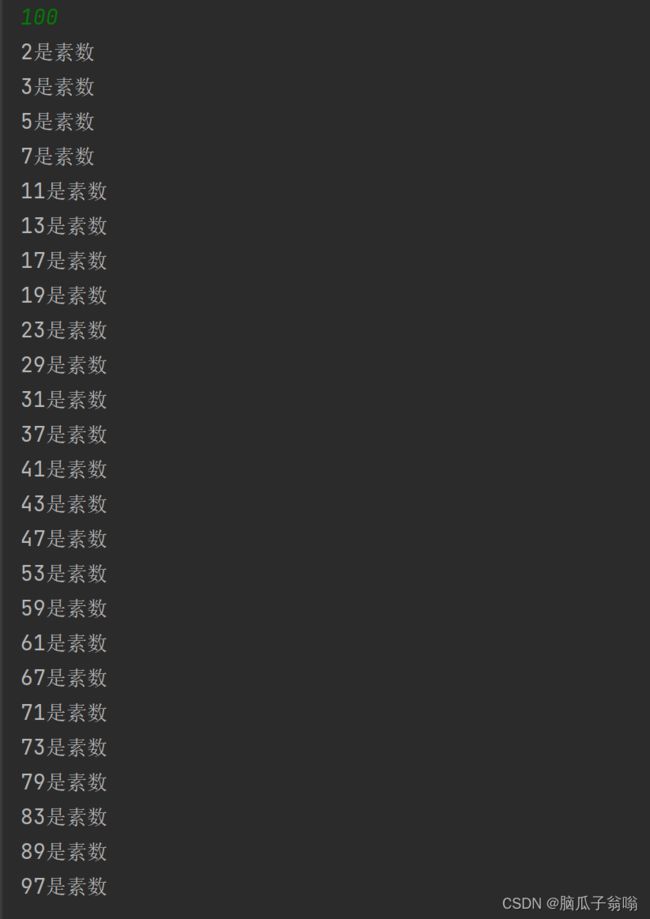
5. 求1-100之间的素数
上一题我们是从键盘输入一个数,判断是否为素数,而这一题则是在上一题的基础上从键盘输入1-100的数,判断这些数中有哪些数是素数。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印1-100之间的素数
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int k = 1;k <= n;k++){
int i = 2;
for (i = 2;i < n ; i++) {
if(k % i == 0){
break;
}
}
if(i == k){
System.out.println(k+"是素数");
}
}
}
}
- 优化1
public class Test {
//k = a * b
//16 = 1 * 16
//16 = 2 * 8
//16 = 4 * 4
//其中一定会有一个乘数小于k/2,所以我们将判断条件改为i <= k/2效率则更高
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印1-100之间的素数
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int k = 1;k <= n;k++){
int i = 2;
for (i = 2;i <= k/2 ; i++) {
if(k % i == 0){
break;
}
}
if(i >k/2){
System.out.println(k+"是素数");
}
}
}
}
- 优化2
public class Test {
//k = a * b
//16 = 1 * 16
//16 = 2 * 8
//16 = 4 * 4
//我们会发现一定会有一个值<=根号k
//根号在java中需要调用Math.sqrt(k)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印1-100之间的素数
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for(int k = 1;k <= n;k++){
int i = 2;
for (i = 2;i <= Math.sqrt(k) ; i++) {
if(k % i == 0){
break;
}
}
if(i > Math.sqrt(k)){
System.out.println(k+"是素数");
}
}
}
}
6. 求2个整数的最大公约数
给定两个数,求这两个数的最大公约数
例如:
输入:20 40
输出:20
public class Test {
//辗转相除法求最大公约数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
int tmp = a % b;
while(tmp != 0){
a = b;
b = tmp;
tmp = a % b;
}
System.out.println(b);
}
}
7. 计算分数的值
计算1/1-1/2+1/3-1/4+1/5 …… + 1/99 - 1/100 的值。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double sum = 0;
int flg = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100 ; i++) {
sum = sum + 1.0/i * flg;
flg = -flg;//正负交替
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
8. 模拟登陆
编写代码模拟三次密码输入的场景。 最多能输入三次密码,密码正确,提示“登录成功”,密码错误, 可以重新输 入,最多输入三次。三次均错,则提示退出程序 。
字符串的比较不可以使用 == 而需要使用到 equals 库方法,equals方法是由 password 点出来的,password 是一个变量能点出一个方法是因为 password 是 string 类型的。
public class Test {
//模拟登录
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int count = 3;
while (count != 0){
System.out.println("请输入你的密码,你还有 "+ count +" 次机会!");
String password = in.nextLine();
if(password.equals("1234")){
System.out.println("登录成功!");
break;
}else{
System.out.println("密码错误!");
count--;
}
}
}
}
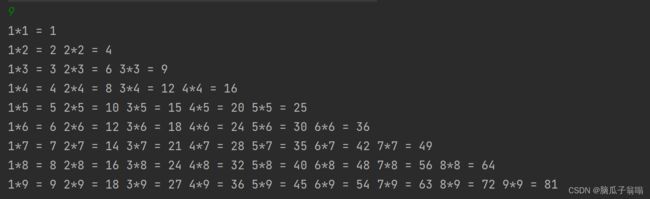
9. 输出乘法口诀表
输出n*n的乘法口诀表,n由用户输入。
public class Test {
//九九乘法表
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(j+"*"+ i +" = " +j*i+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
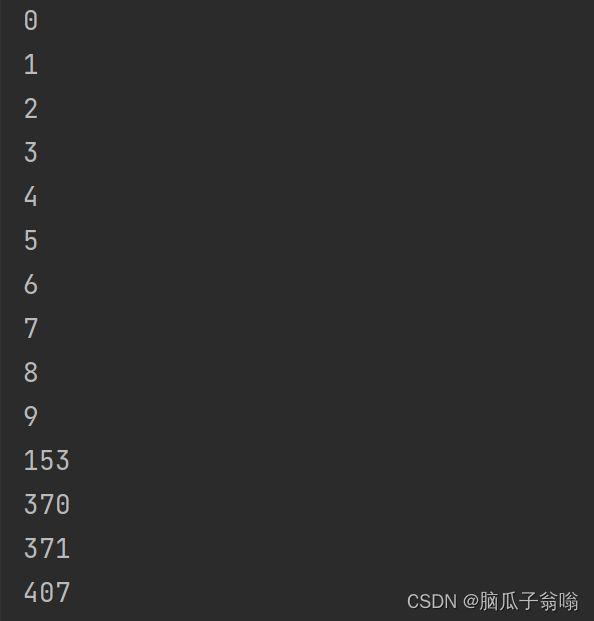
10. 求出0~999之间的所有“水仙花数”并输出
(“水仙花数”是指一个三位数,其各位数字的立方和确好等于该数
本身,如:153=1^3+5^3+3^3 ,则153是一个“水仙花数”。)
一位自幂数:独身数
三位自幂数:水仙花数
三位的水仙花数共有4个:153,370,371,407。
public class Test {
//水仙花数
//153 = 1^3 + 5^3 + 3^3
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 999; i++) {
int count = 0;//计算当前i 有几位数
int tmp = i;
while (tmp != 0) {
count++;
tmp = tmp / 10;
}
//count的值 是多少已经计算完成 i还是没有变的
//计算i[tmp]的每一位
tmp = i;
int sum = 0;
while (tmp != 0) {
sum += Math.pow(tmp%10,count);
tmp /= 10;
}
if(sum == i) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
11. 猜数字游戏
游戏规则:
系统自动生成一个随机整数(1-100), 然后由用户输入一个猜测的数字. 如果输入的数字比该随机数小, 提示 “猜小了”, 如果输入的数字比该随机数大, 提示 “猜大了” , 如果输入的数字和随机数相等, 则提示 “猜对了” 。
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
//猜数字游戏
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
int randNum = random.nextInt(100);//[0,100)
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
System.out.println("请输入你要猜的数字: ");
int num = scanner.nextInt();
if(num > randNum){
System.out.println("猜大了!");
}else if (num == randNum){
System.out.println("猜对了!");
break;
}else{
System.out.println("猜小了!");
}
}
}
}
本章到这里就结束啦,如果有哪里写的不好的地方,请指正。
如果觉得不错并且对你有帮助的话请给个三连支持一下吧!
Fighting!!!✊