JDBC连接池
文章目录
- 为什么使用连接池技术?
- 一、数据库连接池的原理
-
- (1)数据库连接池的基本介绍
- (2)数据库连接池的种类
- (3)C3P0方式
- (4)Druid(德鲁伊)连接池
- (5)Druid工具类 JDBCUtilsByDruid
- (6)Druid工具类的使用举例
- 二、查询出的结果集存在的问题-ApDBUtils工具类的引入
-
- (1)查询出的结果集存在的问题
- (2)土方法完成
- (3)ApDBUtils工具类
-
- 3.1ApDBUtils基本介绍
- 3.2ApDBUtils使用-DBUtils_USE
- 3.3ApDBUtils源码分析
- 3.4使用QueryRunner的query方法:
为什么使用连接池技术?
传统的jdbc连接有很多的弊端,比如传统的连接方式连接的个数是有限的。每次进行连接都要对连接的信息进行检查,比较耗费时间。
并且连接过多的时候,也可能导致内存泄露,MySQL崩溃。
这时,可以采用连接池(connection pool) 技术。

传统的连接,比如连接过多时,就像是1000人同时冲向一个安检口,没有任何的缓冲。就可能会出现一些意外的情况。
一、数据库连接池的原理
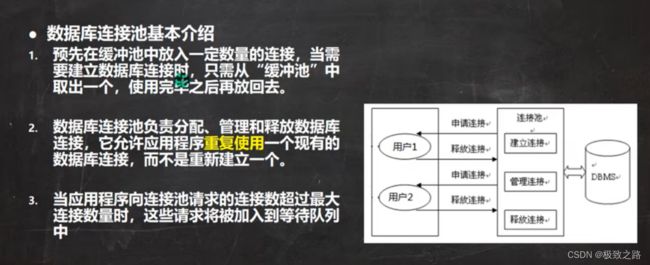
(1)数据库连接池的基本介绍
预先在缓冲池中存入一定的连接,建立连接就是从缓冲池里面取,释放连接就是放回缓冲池中。即 java程序就不再引用该连接了。
即原来 应用程序获取和释放连接 是直接对DBMS进行操作的,现在则是在 应用程序 和 DBMS 之间创建了一个媒介,即缓冲池。
(2)数据库连接池的种类

常用的是C3P0和Druid连接池。Druid连接池是目前最常用的,应用最广泛的。
Java扩展包javax里面有一个DataSource接口,是一个规范。不同的连接池技术通过实现该接口,来完成具体实现。
(3)C3P0方式
因为JDBC连接池使用的javax.sql.DataSource的DataSource只是一个接口,该接口通常由第三方具体实现【提供.jar】。
因此使用需要先引入jar包。
public class C3P0_ {
//方式1,相关参数,在程序中指定user,password,url等
@Test
public void testC3P0_01() throws IOException, PropertyVetoException, SQLException {
//引入jar包-DataSource是一个接口,不同的连接池实现的方式也不一样。这里是C3P0连接池
// 1.创建一个数据源对象
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
// 2.通过配置文件mysql.properties 获取相关连接的信息
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src//mysql.properties"));
// 3.读取相关的属性值
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
// 4.给数据源comboPooledDataSource 设置相关的参数
// 注意:连接管理是由 comboPooledDataSource来管理的
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(driver);
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(url);
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(user);
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(password);
//设置初始化连接数
comboPooledDataSource.setInitialPoolSize(10);
//最大连接数
comboPooledDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(50);
//测试连接池的效率
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {
Connection conn = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
// System.out.println("连接成功");
conn.close();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("c3p0 500000次连接mysql耗时="+(end-start));
//2026
}
// 第二种方式 使用配置文件模板来完成
// 1.将c3p0 提供的 c3p0-config.xml 拷贝到src目录下
// 2.该文件指定了连接数据库和连接池的相关参数
@Test
public void testC3p0_02() throws SQLException {
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("hsp_edu");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {
Connection conn = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
// System.out.println("连接成功");
conn.close();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("c3p0 500000次连接mysql耗时="+(end-start));
// 1923
}
}
c3p0的配置文件模板 c3p0-config.xml,引入到src目录下。
注意:配置文件的名字不能乱写。位置也不能乱放,放到src目录下面去。
<c3p0-config>
<!-- 数据源名称代表连接池-->
<named-config name="hsp_edu">
<!-- 驱动类-->
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<!-- url-->
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db03</property>
<!-- 用户名-->
<property name="user">root</property>
<!-- 密码-->
<property name="password">123456</property>
<!-- 每次增长的连接数-->
<property name="acquireIncrement">5</property>
<!-- 初始的连接数-->
<property name="initialPoolSize">10</property>
<!-- 最小连接数-->
<property name="minPoolSize">5</property>
<!-- 最大连接数-->
<property name="maxPoolSize">10</property>
<!-- 可连接的最多命令对象数-->
<property name="maxStatements">5</property>
<!-- 每个连接对象可连接的最多命令对象数-->
<property name="maxStatementsPerConnection">2</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
数据库连接池技术是连接池进行数据连接,打通的数据通道。所以连接池与数据库进行连接的时候,需要知道连接相关的信息,比如user,password,url,driver。所以需要给连接池设置相关信息。
(4)Druid(德鲁伊)连接池
Druid连接池,也是在程序开始先创建一个连接池,里面有很多连接供我们使用。只是是由阿里来实现的。DataSource接口在不同公司的底层实现机制也不一样,就意味着效率有区别。
德鲁伊数据库连接池技术是最好的,获取连接和关闭连接的速度也是极快的。
德鲁伊会在官方的网站上提供配置文件,就是个模板。
public class Druid_ {
@Test
public void testDruid() throws Exception {
// 1.加入 Druid jar包
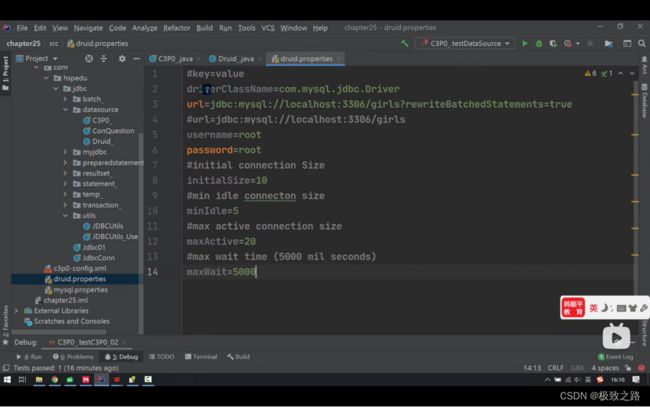
// 2.加入 配置文件 druid.properties ,将该文件拷贝到src目录下
// 3.创建Properties对象,读取配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src//druid.properties"));
// 4.创建一个指定参数的数据库连接池
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
// System.out.println("连接成功l");
conn.close();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("druid 500000次连接mysql耗时="+(end-start));
//458
}
}
连接数据库的驱动这里是由连接池中的数据源来使用的,数据源只是帮你管理数据库的连接。连接也只是做了一个包装,做成了一个缓冲池而已。
(5)Druid工具类 JDBCUtilsByDruid
在静态代码块中,数据源只会创建一次。
/**
*基于druid数据库连接池的工具类
*/
public class JDBCUtilsByDruid {
private static DataSource ds;
//静态代码块中完成ds的初始化
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src//druid.properties"));
ds= DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//编写getConnection方法
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
// 关闭连接,强调:在数据库连接池技术中,close并不是真的断掉连接
// 而是把使用的Connection对象放回连接池,相当于取消了Connection对象的引用
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement statement,Connection conn){
try {
if (rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
if (statement!=null){
statement.close();
}
if (conn!=null){
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
//将编译异常转为运行异常抛出
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
这个地方的close和原来jdbc中的close是不一样的。Connection是一个接口,不同的实现类实现的方式是不一样的。
连接池里面的close是取消连接对象的引用,就是将该连接放回到连接池中。
(6)Druid工具类的使用举例
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
*/
public class JDBCUtilsByDruid_USE {
@Test
public void testSelect() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
String sql="select * from admin2";
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pstm.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()){
String id = rs.getString("id");
String username = rs.getString("username");
String password = rs.getString("password");
System.out.println("[ "+id+"\t"+username+"\t"+password+" ]");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(rs,pstm,conn);
}
}
二、查询出的结果集存在的问题-ApDBUtils工具类的引入
(1)查询出的结果集存在的问题
比如JDBCUtilsByDruid_USE 查询的代码,查询出的结果集rs只能使用一次,不能复用,一旦关闭连接,结果集就没了。如果不及时关闭连接,其他的连接要连的时间就要推迟,就会对多并发程序造成影响。
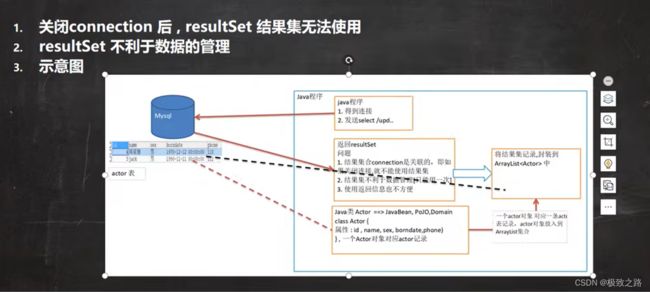
现在需要关闭连接之后,结果集还可以使用。并且结果集返回的类型很死板,只能看出是什么类型,如getString(),不能看出是具体的哪个属性,比如name,sex等。而实际开发中更希望通过方法名得知返回的是什么,如getName()。
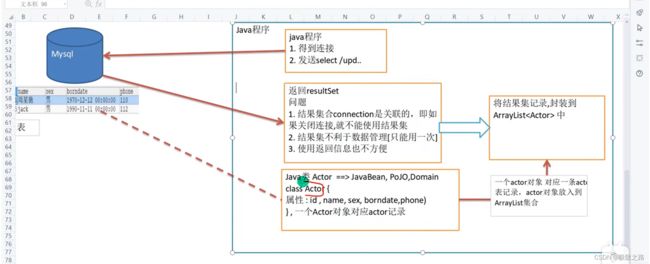
只需要当查询表时,表的记录就被中转到集合里面去了。
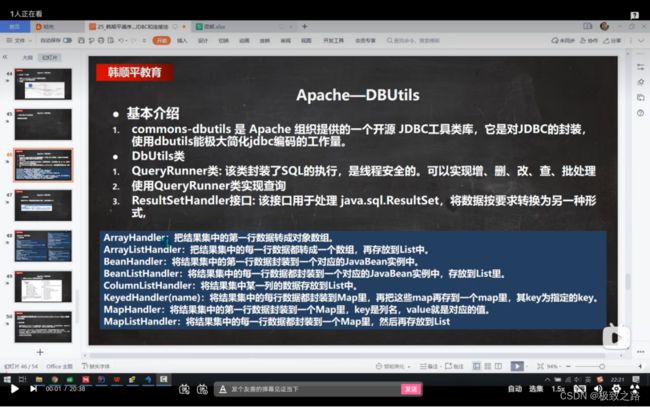
Apache-DBUtils把这个问题解决的非常完美。
(2)土方法完成
//使用土方法 来解决ResultSet =封装=>ArrayList
@Test
public void testSelectToArrayList(){
System.out.println("使用 druid方式完成");
// 1.得到连接
Connection conn=null;
// 2.组织一个Sql
String sql="select * from actor where id >=?";
PreparedStatement stmt=null;
ResultSet set=null;
List<Actor> list=new ArrayList<>();
// 3.创建PreparedStatement对象
try {
conn=JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn.getClass());
stmt=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
stmt.setInt(1,1);
// 执行,得到结果集
set=stmt.executeQuery();
// 遍历该结果集
while(set.next()){
int id = set.getInt("id");
String name = set.getString("name");
String sex = set.getString("sex");
Date borndate = set.getDate("borndate");
String phone = set.getString("phone");
list.add(new Actor(id,name,sex,borndate,phone));
}
conn.close();//这样当遍历结束后,连接即使关闭,结果集也可以用。
System.out.println("list集合数据="+list);
for (Actor actor:list){
System.out.println(actor.getName());
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(set,stmt,null);
}
}
(3)ApDBUtils工具类
3.1ApDBUtils基本介绍
3.2ApDBUtils使用-DBUtils_USE
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.ScalarHandler;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
/**
*不断的尝试 将学习和快乐联系起来
*/
public class DBUtils_USE {
// 使用apache-DBUtils工具类+ druid 完成对表的crud操作
@Test
public void testQueryMany() throws SQLException {//返回结果是多行的情况
// 1.得到连接 (druid)
Connection conn = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
// 2.使用DBUtils类和接口 ,先引入DBUtils 相关的jar ,加入到本project
// 3.创建QueryRunner
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
// 4,执行相关的方法,返回ArrayList结果集
String sql="select * from actor where id >=?";
/*
(1)query方法 执行sql语句,得到resultset -- 封装到 arraylist集合中,返回结果集封装后的集合
(2)new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class) 将Actor对象封装到arraylist
(3)Actor.class 底层使用反射机制 去获取 Actor 类的属性,然后进行封装。
后面是一个可变参数,可传多个值。
*/
List<Actor> list = queryRunner.query(conn, sql, new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class), 1);
System.out.println("输出集合的信息");
for (Actor actor:list){
System.out.println(actor);
}
// 释放资源
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null,null,conn);
}
/*
查询单行记录
*/
@Test
public void testQuerySingle() throws SQLException {
// 1.得到连接 (druid)
Connection conn = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql="select * from actor where id=?";
// 因为返回的是单行记录, -- 单个对象 使用的Handle是BeanHandler
Actor query = queryRunner.query(conn, sql, new BeanHandler<>(Actor.class), 3);
System.out.println(query);
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null,null,conn);
}
/*
查询单行单列记录 ---
*/
@Test
public void testScalar() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql="select name from actor where id = ?";
// 返回单行单列记录,即单个对象,使用的Handler就是ScalarHandler
Object query = queryRunner.query(conn, sql, new ScalarHandler(), 2);
System.out.println(query);
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null,null,conn);
}
@Test
public void testDML() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
// String sql="insert into actor values(null,?,?,now(),null)";
// String sql="update actor set name=? where id=?";
String sql="delete from actor where id=?";
// 返回的值是Int,即受影响的行数。
int update = queryRunner.update(conn,sql, 5);
System.out.println(update>0?"成功":"失败");
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null,null,conn);
}
}
通过连接池可以获取和关闭连接的。而sql语句的执行可以使用DBUtils工具类。
所以一般采用Druid+DBUtils工具类的形式。
3.3ApDBUtils源码分析
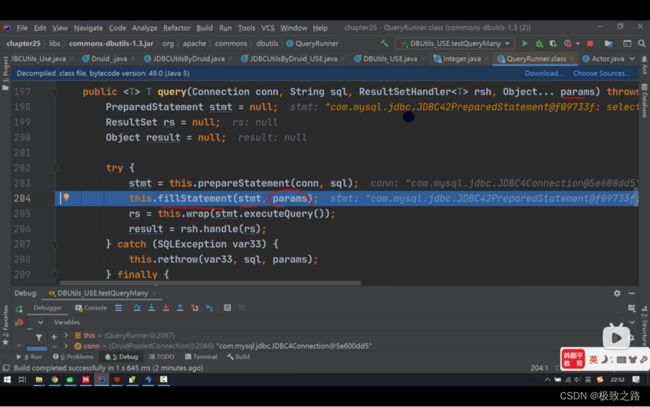
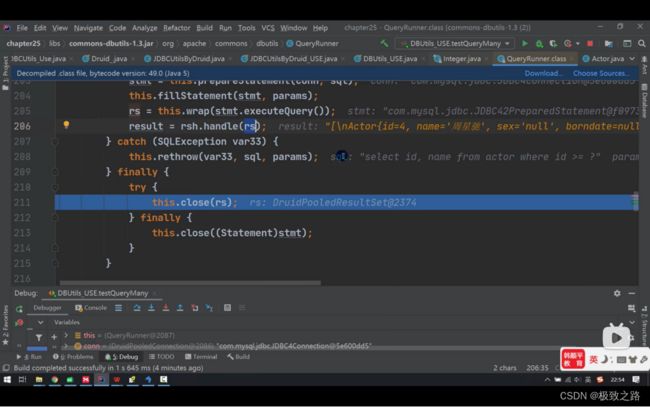
最后会自动将结果集rs和stmt关掉。所以在方法外边就不用关闭结果集和Statement了,只需要关闭连接conn即可。
即
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null,null,conn);
最后会将结果集形成的数组返回来
3.4使用QueryRunner的query方法:
返回一个集合(多行多列),所以是BeanListHandler
返回一个JavaBean对象(单行多列),所以是BeanHandler
返回一个Object对象(单行单列),所以是ScalarHandler