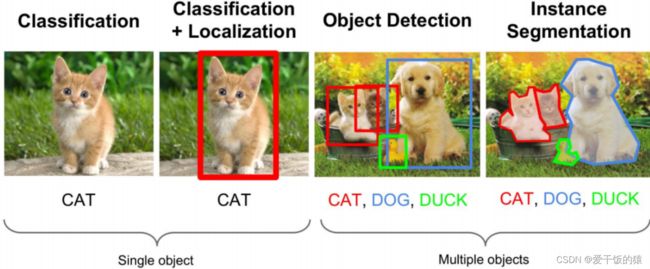
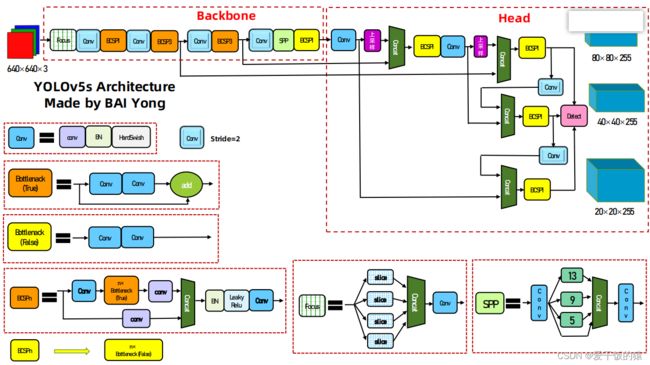
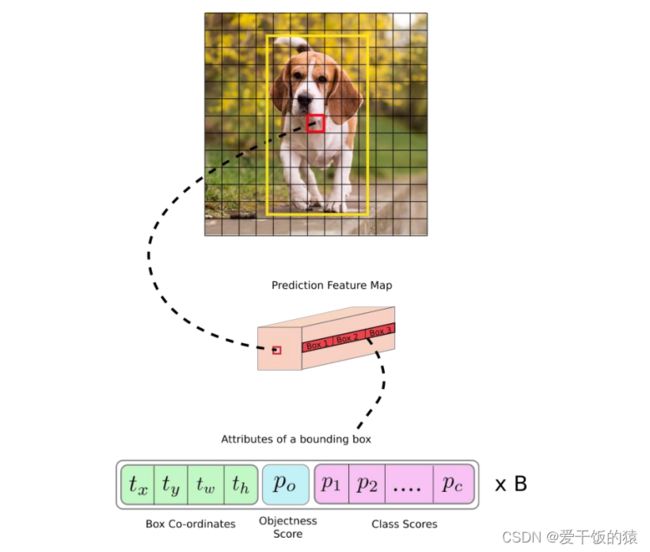
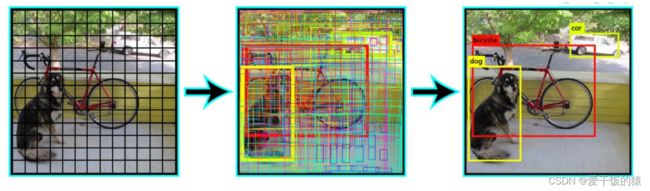
- 计算机视觉总结
Trank-Lw
计算机视觉深度学习人工智能
以下是针对上述问题的详细解答,并结合代码示例进行说明:1.改进YOLOv5人脸检测模块,复杂光照场景准确率从98.2%提升至99.5%优化具体过程:光照补偿:在数据预处理阶段,采用自适应光照补偿算法,对图像进行实时增强,以减少光照变化对人脸检测的影响。数据增强:在训练数据中增加复杂光照场景下的样本,如强光、弱光、背光等,通过数据增强提高模型对不同光照条件的适应性。模型调整:对YOLOv5模型的网络
- YOLOV11|YOLO12改进系列指南
魔鬼面具
YOLO
基于Ultralytics的YOLO11|YOLO12改进目前自带的一些改进方案(持续更新)为了感谢各位对本项目的支持,本项目的赠品是yolov5-PAGCP通道剪枝算法.具体使用教程专栏改进汇总YOLO11系列二次创新系列ultralytics/cfg/models/11/yolo11-RevCol.yaml使用(ICLR2023)ReversibleColumnNetworks对yolo11主
- 介于YOLOv5的裂缝识别系统
程序员~小强
YOLO
介于YOLOv5的裂缝识别系统在现代工业中,裂缝监测是的保障设施安全的重要环节。我们公司的新项目——基于YOLOv5的裂缝识别系统,将为您提供高效、精准的解决方案,助力各类工程项目的质量管理。系统优势我们的裂缝识别系统借助YOLOv5进行深度学习,经过精心训练,拥有强大的图像识别能力。只需简单的步骤,您就能将复杂的裂缝检测转化为轻松的操作,让分析变得更加简单、高效。核心功能图片上传与场景选择用户可
- OCR提取+识别方案
ocr
1.内容提取通过YOLO提取需要识别的区域1.1安装ultralytics创建虚拟环境(可选)#创建虚拟环境python-mvenv.venv#激活虚拟环境###激活虚拟环境将更改shell的提示以显示您正在使用的虚拟环境,并修改环境,以便运行时python可以获得特定版本和安装的Python。例如:source.venv/bin/activate#显示虚拟环境中安装的所有软件包:python-m
- 【YOLOv8】YOLOv8改进系列(9)----替换主干网络之RepViT
HABuo
YOLOv8入门+改进YOLO目标检测深度学习计算机视觉人工智能
主页:HABUO主页:HABUOYOLOv8入门+改进专栏如果再也不能见到你,祝你早安,午安,晚安【YOLOv8改进系列】:【YOLOv8】YOLOv8结构解读YOLOv8改进系列(1)----替换主干网络之EfficientViTYOLOv8改进系列(2)----替换主干网络之FasterNetYOLOv8改进系列(3)----替换主干网络之ConvNeXtV2YOLOv8改进系列(4)----
- CBNet--一种新的目标检测的复合骨干网体系结构
weixin_45963617
深度学习系列
一、Introduction一般来说,在一个典型的基于CNN的目标检测器中,使用主干网络来提取检测对象的基本特征,该网络通常是为图像分类任务而设计的,并在ImageNet上预训练。毫无疑问,更强大的主干网可以带来更好的检测性能。尽管最先进的基于深度的大骨干网络的探测器取得了很好的结果,但仍有很大改进空间。此外,通过设计一个新的更强大的主干网络并在ImageNet上预训练来获取好的检测性能是十分昂贵
- 如何使用YOLOv8在AI-TOD数据集上进行遥感目标检测,从安装依赖项、准备数据集、配置YOLOv8、训练和评估模型以及构建GUI应用程序展示检测
计算机C9硕士_算法工程师
人工智能YOLO目标检测遥感
如何使用YOLOv8在AI-TOD数据集上进行遥感目标检测,从安装依赖项、准备数据集、配置YOLOv8、训练和评估模型以及构建GUI应用程序展示检测文章目录1.安装依赖2.数据准备3.配置YOLOv83.1加载预训练模型或自定义模型4.训练模型5.评估模型6.构建GUI应用程序(可选)以下文字及代码仅供参考。遥感目标检测,AI-TOD数据集aitod,训练集11214张,测试集集14018,验证集
- YOLO算法全面改进指南(二)
niuTaylor
YOLO改进YOLO算法
以下是为YOLO系列算法设计的系统性改进框架,结合前沿技术与多领域创新,提供可支持高水平论文发表的详细改进思路。本方案整合了轻量化设计、多模态融合、动态特征优化等创新点,并给出可验证的实验方向。一、多模态提示驱动的开放场景检测系统1.核心创新三模态提示机制:文本提示编码器:基于RepRTA(可重参数化区域文本对齐)构建轻量级文本编码网络,将自然语言描述映射为128维语义向量。视觉提示编码器:采用S
- Yolo系列之Yolo的基本理解
是十一月末
YOLOpython开发语言yolo
YOLO的基本理解目录YOLO的基本理解1YOLO1.1概念1.2算法2单、多阶段对比2.1FLOPs和FPS2.2one-stage单阶段2.3two-stage两阶段1YOLO1.1概念YOLO(YouOnlyLookOnce)是一种基于深度学习的目标检测算法,由JosephRedmon等人于2016年提出。它的核心思想是将目标检测问题转化为一个回归问题,通过一个神经网络直接预测目标的类别和位
- yolov8实战第七天——pyqt5-yolov8实现车牌识别系统(参考论文(约7000字)+环境配置+完整部署代码+代码使用说明+训练好的模型)
学术菜鸟小晨
yolov8实战100天pythonYOLOpyqt5车牌识别毕业设计论文
基于pyqt5-yolov8实现车牌识别系统,包括图片车牌识别,视频车牌识别,视频流车牌识别。效果展示(图片检测,检测到的内容添加到历史记录):效果展示(视频检测,视频车辆只会添加一条记录,下文更多实际应用中的优化策略):新增功能:批量图片检测(2024/5/7更新代码)
- 深度学习与目标检测系列(六) 本文约(4.5万字) | 全面解读复现ResNet | Pytorch |
小酒馆燃着灯
深度学习目标检测pytorch人工智能ResNet残差连接残差网络
文章目录解读Abstract—摘要翻译精读主要内容Introduction—介绍翻译精读背景RelatedWork—相关工作ResidualRepresentations—残差表达翻译精读主要内容ShortcutConnections—短路连接翻译精读主要内容DeepResidualLearning—深度残差学习ResidualLearning—残差学习翻译精读ResNet目的以前方法本文改进本质
- 深度学习与目标检测系列(三) 本文约(4万字) | 全面解读复现AlexNet | Pytorch |
小酒馆燃着灯
深度学习目标检测pytorchAlexNet人工智能
文章目录解读Abstract-摘要翻译精读主要内容1.Introduction—前言翻译精读主要内容:本文主要贡献:2.TheDataset-数据集翻译精读主要内容:ImageNet简介:图像处理方法:3.TheArchitecture—网络结构3.1ReLUNonlinearity—非线性激活函数ReLU翻译精读传统方法及不足本文改进方法本文的改进结果3.2TrainingonMultipleG
- 关于离子滤波小记
文弱_书生
乱七八糟人工智能计算机视觉算法
粒子滤波(ParticleFilter,PF)粒子滤波是一种基于蒙特卡洛方法的贝叶斯滤波算法,主要用于解决非线性、非高斯的状态估计问题。它广泛应用于机器人定位、目标跟踪、金融建模等领域。1.粒子滤波的基本概念粒子滤波的核心思想是用一组加权的**随机样本(粒子)**来近似后验概率分布,而非采用卡尔曼滤波那样的参数化分布假设(如高斯分布)。设系统的状态模型如下:xk=f(xk−1,uk,wk)x_k=
- 常见经典目标检测算法
109702008
人工智能#深度学习目标检测人工智能
ChatGPT目标检测(ObjectDetection)是计算机视觉领域的一个重要分支,其目的是识别数字图像中的不同对象,并给出它们的位置和类别。近年来,许多经典的目标检测算法被提出并广泛应用。以下是一些常见的经典目标检测算法:1.R-CNN(RegionswithCNNfeatures):R-CNN通过使用区域提议方法(如选择性搜索)首先生成潜在的边界框,然后使用卷积神经网络(CNN)提取特征,
- 目标检测中归一化的目的?
林语微光
kaggle目标检测目标跟踪人工智能
在目标检测任务中,归一化坐标和尺寸时需要除以图像的宽度和高度,主要有以下几个原因:1.统一尺度不同图像可能具有不同的宽度和高度。通过将坐标和尺寸除以图像的宽度和高度,可以将所有图像的标注信息统一到相同的尺度范围([0,1])。这使得模型在训练和推理时能够处理任意尺寸的图像,而不需要关心图像的具体像素尺寸。2.位置和尺寸的相对性归一化后的坐标和尺寸是相对于图像尺寸的,而不是绝对像素值。这种相对性使得
- YOLOv12优化:图像去噪 | AAAI2025 Transformer |一种基于Transformer的盲点网络(TBSN)架构 ,结合空间和通道自注意力层来增强网络能力
AI小怪兽
YOLOv12魔术师YOLOtransformer深度学习人工智能python
提出了一种基于Transformer的盲点网络(TBSN)架构,通过分析和重新设计Transformer运算符以满足盲点要求。TBSN遵循扩张BSN的架构原则,并结合空间和通道自注意力层来增强网络能力。如何使用:1)结合C3k2二次创新使用;2)结合A2C2f二次创新使用;亮点包括:1.提出了一种新的基于Transformer的盲点网络(TBSN)架构;2.引入了知识蒸馏策略来提高计算效率;3.在
- 【ai】mocap:conda 安装python3.8+ cuda+ pytorch+torchaudio、torchvision
等风来不如迎风去
AI入门与实战人工智能ubuntuconda
MotionCapubuntu18.04不知道为啥会依赖于ffmpeg、xorg渲染?安装pytorch就是会带上cudacudnn啥的pytorch【ai】tx2nx:安装torch、torchvisionforyolov5这里就发现pytorch和torchvision有依赖关系的,还涉及到rapidjson所以python的环境隔离很重要。核心库-cudatoolkit=11.3-pytor
- YOLO11改进-模块-引入频率谱动态聚合模块FSDA 去除噪声
一勺汤
YOLOv11模型改进系列目标检测魔改模块YOLOYOLOv11YOLOv11改进改进
在图像去雾领域,深度学习在白天图像去雾方面成果显著,但夜间雾图研究较少。夜间雾图面临诸多挑战,其中包括雾、辉光和噪声因多个低强度有源彩色光源而具有复杂特性,以及模拟与真实数据的域差异导致的亮度问题。为解决这些,我们使用FSDA模块,处理频率不一致特性。FSDA先对频谱信息聚合,再计算通道权重并应用,最后映射回空间域,以此优化频谱信息,使模型更好处理复杂干扰。本文将其与YOLOv11相结合,增强YO
- YOLO魔改之频率分割模块(FDM)
清风AI
YOLO算法魔改系列YOLO人工智能计算机视觉目标检测python深度学习
目标检测原理目标检测是一种将目标分割和识别相结合的图像处理技术,旨在从图像中定位并识别特定目标。深度学习方法,如FasterR-CNN和YOLO系列,已成为主流解决方案。这些方法通常采用两阶段或单阶段策略,通过卷积神经网络(CNN)提取特征并进行分类和定位。在小目标检测中,为克服分辨率低和特征不明显的问题,模型设计中会特别注重特征融合和多尺度处理,以增强对小目标的感知能力。YOLOv8基础YOLO
- 目标检测YOLO实战应用案例100讲-基于毫米波雷达与摄像头协同的道路目标检测与识别(续)
林聪木
目标检测YOLO人工智能
目录3.2实测数据采集与分析3.2.1回波数据处理3.2.2毫米波雷达数据采集实验3.3基于传统图像特征的目标识别算法3.3.1基于灰度共生矩阵的时频图特征提取3.3.2支持向量机分类器3.3.3实验及结果分析3.4基于卷积神经网络的目标识别算法3.4.1卷积神经网络的基本理论3.4.2卷积神经网络框架设计3.4.3实验及结果分析基于图像的目标检测算法4.1目标检测算法一般流程4.2典型目标检测算
- Python 的 ultralytics 库详解
白.夜
人工智能
ultralytics是一个专注于计算机视觉任务的Python库,尤其以YOLO(YouOnlyLookOnce)系列模型为核心,提供了简单易用的接口,支持目标检测、实例分割、姿态估计等任务。本文将详细介绍ultralytics库的功能、安装方法、核心模块以及使用示例。1.ultralytics库简介ultralytics库由Ultralytics团队开发,旨在为YOLO系列模型提供高效、灵活且易
- 智慧城市道路防护栏破损缺陷检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式6939张3类别
FL1623863129
数据集YOLO深度学习机器学习
数据集格式:PascalVOC格式+YOLO格式(不包含分割路径的txt文件,仅仅包含jpg图片以及对应的VOC格式xml文件和yolo格式txt文件)图片数量(jpg文件个数):6939标注数量(xml文件个数):6939标注数量(txt文件个数):6939标注类别数:3标注类别名称(注意yolo格式类别顺序不和这个对应,而以labels文件夹classes.txt为准):["body","cr
- 将 VOC 格式 XML 转换为 YOLO 格式 TXT
JeJe同学
xmlYOLO
目录1.导入必要的模块2.定义类别名称3.设置文件路径完整代码1.导入必要的模块importosimportxml.etree.ElementTreeasETos:用于文件和目录操作,例如创建目录、遍历文件等。xml.etree.ElementTree:用于解析XML文件,从中提取信息。2.定义类别名称class_names=['nest','balloon','kite','trash']这是一
- Yolov8训练自己的数据集(脱离ultralytics库)
爱吃肉的鹏
YOLO
最近在整理关于yolov8的相关内容,有个很大的问题,抛开yolov8性能不谈,yolov8代码的使用灵活性不如yolov5,尤其是对于一些新手或者对yolo框架不是很熟悉的人(这也是因人而异,有些人可能会喜欢v8代码的使用方式)。比如在使用v8的时候需要安装ultralytics库,然后再调用YOLO进行训练或者预测,那么就有这几个问题:问题1:安装了ultralytics库后如何使用YOLO呢
- 标签转换脚本 - VOC格式转COCO格式,即voc2coco,xml2json 附VOC及COCO标签格式详解
Limiiiing
YOLO训练/写作脚本YOLO计算机视觉目标检测深度学习
前言本文的脚本功能为将VOC数据集的标签文件xml转成COCO的标签文件,指定自己的VOC数据集的标签文件路径后,可一键运行转成COCO的标签文件。专栏目录:YOLO训练/写作脚本目录一览|涉及标签转换、数据扩充、热力图、感受野、精度曲线、数量统计等近百个脚本文件专栏地址:YOLO训练/写作脚本——丰富文章内容,增强实验信服力,助力发文!!!文章目录前言一、VOC数据集介绍1.1总体结构1.2各标
- 标签转换脚本 - VOC格式转YOLO格式,即voc2yolo,xml2txt 附VOC及YOLO标签格式详解
Limiiiing
YOLO训练/写作脚本YOLO深度学习计算机视觉目标检测
前言本文的脚本功能为将VOC数据集的标签文件xml转成YOLO的标签文件,指定自己的VOC数据集的标签文件路径后,可一键运行转成YOLO的标签文件。专栏目录:YOLO训练/写作脚本目录一览|涉及标签转换、数据扩充、热力图、感受野、精度曲线、数量统计等近百个脚本文件专栏地址:YOLO训练/写作脚本——丰富文章内容,增强实验信服力,助力发文!!!文章目录前言一、VOC数据集介绍1.1总体结构1.2各标
- 数据集格式转换——json2txt、xml2txt、txt2json【复制就能用】
kay_545
YOLO11改进有效涨点python人工智能机器学习
秋招面试专栏推荐:深度学习算法工程师面试问题总结【百面算法工程师】——点击即可跳转本专栏所有程序均经过测试,可成功执行专栏地址:YOLO11入门+改进涨点——点击即可跳转欢迎订阅目录json2txt脚本xml2txttxt2json
- yolo模型coco数据集详解
工头阿乐
深度学习YOLO
深度学习文章目录深度学习前言前言instances_train2017.json和instances_val2017.json文件均分为五大部分,这五部分对应的关键字分别为info、licenses、images、annotations、categories。{"info":info,"licenses":[license1,license2,license3,...],"images":[ima
- Ultralytics包引起的编码报错问题
Xylokrysen
深度学习深度学习YOLO
安装完Ultralytics包后,加载YOLO相关模型,执行报错:UnicodeEncodeError:'gbk'codeccan'tencodecharacter'\u0467'inposition3:illegalmultibytesequence这个错误是由于文件编码问题引起的,Ultralytics在初始化时会尝试创建或更新配置文件settings.yaml,而Windows系统默认使用G
- yolov4
zzh-
笔记
V4贡献:亲民政策,单GPU就能训练的非常好,接下来很多小模块都是这个出发点两大核心方法,从数据层面和网络设计层面来进行改善消融实验,感觉能做的都让他给做了,这工作量不轻全部实验都是单GPU完成,不用太担心设备了Bagoffreebies(BOF)只增加训练成本,但是能显著提高精度,并不影响推理速度数据增强:调整亮度、对比度、色调、随机缩放、剪切、翻转、旋转网络正则化的方法:Dropout、Dro
- java类加载顺序
3213213333332132
java
package com.demo;
/**
* @Description 类加载顺序
* @author FuJianyong
* 2015-2-6上午11:21:37
*/
public class ClassLoaderSequence {
String s1 = "成员属性";
static String s2 = "
- Hibernate与mybitas的比较
BlueSkator
sqlHibernate框架ibatisorm
第一章 Hibernate与MyBatis
Hibernate 是当前最流行的O/R mapping框架,它出身于sf.net,现在已经成为Jboss的一部分。 Mybatis 是另外一种优秀的O/R mapping框架。目前属于apache的一个子项目。
MyBatis 参考资料官网:http:
- php多维数组排序以及实际工作中的应用
dcj3sjt126com
PHPusortuasort
自定义排序函数返回false或负数意味着第一个参数应该排在第二个参数的前面, 正数或true反之, 0相等usort不保存键名uasort 键名会保存下来uksort 排序是对键名进行的
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8&q
- DOM改变字体大小
周华华
前端
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml&q
- c3p0的配置
g21121
c3p0
c3p0是一个开源的JDBC连接池,它实现了数据源和JNDI绑定,支持JDBC3规范和JDBC2的标准扩展。c3p0的下载地址是:http://sourceforge.net/projects/c3p0/这里可以下载到c3p0最新版本。
以在spring中配置dataSource为例:
<!-- spring加载资源文件 -->
<bean name="prope
- Java获取工程路径的几种方法
510888780
java
第一种:
File f = new File(this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath());
System.out.println(f);
结果:
C:\Documents%20and%20Settings\Administrator\workspace\projectName\bin
获取当前类的所在工程路径;
如果不加“
- 在类Unix系统下实现SSH免密码登录服务器
Harry642
免密ssh
1.客户机
(1)执行ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "
[email protected]"生成公钥,xxx为自定义大email地址
(2)执行scp ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@xxxxxxxxx:/tmp将公钥拷贝到服务器上,xxx为服务器地址
(3)执行cat
- Java新手入门的30个基本概念一
aijuans
javajava 入门新手
在我们学习Java的过程中,掌握其中的基本概念对我们的学习无论是J2SE,J2EE,J2ME都是很重要的,J2SE是Java的基础,所以有必要对其中的基本概念做以归纳,以便大家在以后的学习过程中更好的理解java的精髓,在此我总结了30条基本的概念。 Java概述: 目前Java主要应用于中间件的开发(middleware)---处理客户机于服务器之间的通信技术,早期的实践证明,Java不适合
- Memcached for windows 简单介绍
antlove
javaWebwindowscachememcached
1. 安装memcached server
a. 下载memcached-1.2.6-win32-bin.zip
b. 解压缩,dos 窗口切换到 memcached.exe所在目录,运行memcached.exe -d install
c.启动memcached Server,直接在dos窗口键入 net start "memcached Server&quo
- 数据库对象的视图和索引
百合不是茶
索引oeacle数据库视图
视图
视图是从一个表或视图导出的表,也可以是从多个表或视图导出的表。视图是一个虚表,数据库不对视图所对应的数据进行实际存储,只存储视图的定义,对视图的数据进行操作时,只能将字段定义为视图,不能将具体的数据定义为视图
为什么oracle需要视图;
&
- Mockito(一) --入门篇
bijian1013
持续集成mockito单元测试
Mockito是一个针对Java的mocking框架,它与EasyMock和jMock很相似,但是通过在执行后校验什么已经被调用,它消除了对期望 行为(expectations)的需要。其它的mocking库需要你在执行前记录期望行为(expectations),而这导致了丑陋的初始化代码。
&nb
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(5)SQL函数
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
* SQL函数
*/
--数字函数
--ABS(n):返回数字n的绝对值
declare
v_abs number(6,2);
begin
v_abs:=abs(&no);
dbms_output.put_line('绝对值:'||v_abs);
end;
--ACOS(n):返回数字n的反余弦值,输入值的范围是-1~1,输出值的单位为弧度
- 【Log4j一】Log4j总体介绍
bit1129
log4j
Log4j组件:Logger、Appender、Layout
Log4j核心包含三个组件:logger、appender和layout。这三个组件协作提供日志功能:
日志的输出目标
日志的输出格式
日志的输出级别(是否抑制日志的输出)
logger继承特性
A logger is said to be an ancestor of anothe
- Java IO笔记
白糖_
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//输入流
InputStream in = Test.class.getResourceAsStream("/test");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in);
Bu
- Docker 监控
ronin47
docker监控
目前项目内部署了docker,于是涉及到关于监控的事情,参考一些经典实例以及一些自己的想法,总结一下思路。 1、关于监控的内容 监控宿主机本身
监控宿主机本身还是比较简单的,同其他服务器监控类似,对cpu、network、io、disk等做通用的检查,这里不再细说。
额外的,因为是docker的
- java-顺时针打印图形
bylijinnan
java
一个画图程序 要求打印出:
1.int i=5;
2.1 2 3 4 5
3.16 17 18 19 6
4.15 24 25 20 7
5.14 23 22 21 8
6.13 12 11 10 9
7.
8.int i=6
9.1 2 3 4 5 6
10.20 21 22 23 24 7
11.19
- 关于iReport汉化版强制使用英文的配置方法
Kai_Ge
iReport汉化英文版
对于那些具有强迫症的工程师来说,软件汉化固然好用,但是汉化不完整却极为头疼,本方法针对iReport汉化不完整的情况,强制使用英文版,方法如下:
在 iReport 安装路径下的 etc/ireport.conf 里增加红色部分启动参数,即可变为英文版。
# ${HOME} will be replaced by user home directory accordin
- [并行计算]论宇宙的可计算性
comsci
并行计算
现在我们知道,一个涡旋系统具有并行计算能力.按照自然运动理论,这个系统也同时具有存储能力,同时具备计算和存储能力的系统,在某种条件下一般都会产生意识......
那么,这种概念让我们推论出一个结论
&nb
- 用OpenGL实现无限循环的coverflow
dai_lm
androidcoverflow
网上找了很久,都是用Gallery实现的,效果不是很满意,结果发现这个用OpenGL实现的,稍微修改了一下源码,实现了无限循环功能
源码地址:
https://github.com/jackfengji/glcoverflow
public class CoverFlowOpenGL extends GLSurfaceView implements
GLSurfaceV
- JAVA数据计算的几个解决方案1
datamachine
javaHibernate计算
老大丢过来的软件跑了10天,摸到点门道,正好跟以前攒的私房有关联,整理存档。
-----------------------------华丽的分割线-------------------------------------
数据计算层是指介于数据存储和应用程序之间,负责计算数据存储层的数据,并将计算结果返回应用程序的层次。J
&nbs
- 简单的用户授权系统,利用给user表添加一个字段标识管理员的方式
dcj3sjt126com
yii
怎么创建一个简单的(非 RBAC)用户授权系统
通过查看论坛,我发现这是一个常见的问题,所以我决定写这篇文章。
本文只包括授权系统.假设你已经知道怎么创建身份验证系统(登录)。 数据库
首先在 user 表创建一个新的字段(integer 类型),字段名 'accessLevel',它定义了用户的访问权限 扩展 CWebUser 类
在配置文件(一般为 protecte
- 未选之路
dcj3sjt126com
诗
作者:罗伯特*费罗斯特
黄色的树林里分出两条路,
可惜我不能同时去涉足,
我在那路口久久伫立,
我向着一条路极目望去,
直到它消失在丛林深处.
但我却选了另外一条路,
它荒草萋萋,十分幽寂;
显得更诱人,更美丽,
虽然在这两条小路上,
都很少留下旅人的足迹.
那天清晨落叶满地,
两条路都未见脚印痕迹.
呵,留下一条路等改日再
- Java处理15位身份证变18位
蕃薯耀
18位身份证变15位15位身份证变18位身份证转换
15位身份证变18位,18位身份证变15位
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
蕃薯耀 201
- SpringMVC4零配置--应用上下文配置【AppConfig】
hanqunfeng
springmvc4
从spring3.0开始,Spring将JavaConfig整合到核心模块,普通的POJO只需要标注@Configuration注解,就可以成为spring配置类,并通过在方法上标注@Bean注解的方式注入bean。
Xml配置和Java类配置对比如下:
applicationContext-AppConfig.xml
<!-- 激活自动代理功能 参看:
- Android中webview跟JAVASCRIPT中的交互
jackyrong
JavaScripthtmlandroid脚本
在android的应用程序中,可以直接调用webview中的javascript代码,而webview中的javascript代码,也可以去调用ANDROID应用程序(也就是JAVA部分的代码).下面举例说明之:
1 JAVASCRIPT脚本调用android程序
要在webview中,调用addJavascriptInterface(OBJ,int
- 8个最佳Web开发资源推荐
lampcy
编程Web程序员
Web开发对程序员来说是一项较为复杂的工作,程序员需要快速地满足用户需求。如今很多的在线资源可以给程序员提供帮助,比如指导手册、在线课程和一些参考资料,而且这些资源基本都是免费和适合初学者的。无论你是需要选择一门新的编程语言,或是了解最新的标准,还是需要从其他地方找到一些灵感,我们这里为你整理了一些很好的Web开发资源,帮助你更成功地进行Web开发。
这里列出10个最佳Web开发资源,它们都是受
- 架构师之面试------jdk的hashMap实现
nannan408
HashMap
1.前言。
如题。
2.详述。
(1)hashMap算法就是数组链表。数组存放的元素是键值对。jdk通过移位算法(其实也就是简单的加乘算法),如下代码来生成数组下标(生成后indexFor一下就成下标了)。
static int hash(int h)
{
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>>
- html禁止清除input文本输入缓存
Rainbow702
html缓存input输入框change
多数浏览器默认会缓存input的值,只有使用ctl+F5强制刷新的才可以清除缓存记录。
如果不想让浏览器缓存input的值,有2种方法:
方法一: 在不想使用缓存的input中添加 autocomplete="off";
<input type="text" autocomplete="off" n
- POJO和JavaBean的区别和联系
tjmljw
POJOjava beans
POJO 和JavaBean是我们常见的两个关键字,一般容易混淆,POJO全称是Plain Ordinary Java Object / Pure Old Java Object,中文可以翻译成:普通Java类,具有一部分getter/setter方法的那种类就可以称作POJO,但是JavaBean则比 POJO复杂很多, Java Bean 是可复用的组件,对 Java Bean 并没有严格的规
- java中单例的五种写法
liuxiaoling
java单例
/**
* 单例模式的五种写法:
* 1、懒汉
* 2、恶汉
* 3、静态内部类
* 4、枚举
* 5、双重校验锁
*/
/**
* 五、 双重校验锁,在当前的内存模型中无效
*/
class LockSingleton
{
private volatile static LockSingleton singleton;
pri
![]()