kubernetes集群搭建Zabbix监控平台的详细过程
文章目录
-
- 一、框架图
- 二、环境
- 三、监控指标
- 四、zabbix模板
-
- 4.1 **K8S集群以及组件模板**
- 4.2 **K8S节点基础信息指标模板**
- 五、主要监控方式
-
- 5.1 **Agent**
- 5.2 **Agentless**
- 六、部署MySql8
-
- 6.1、软件包下载
- 6.2、卸载MariaDB
- 6.3、MySQL二进制安装
-
- 6.3.1 创建mysql工作目录:
- 6.3.2、上传软件,并解压并改名为app
- 6.3.3、修改环境变量
- 6.3.4、建立mysql用户和组(如果有可忽略)
- 6.3.5、创建mysql 数据目录,日志目录;并修改权限
- 6.3.6、初始化数据
- 6.4、配置mysql配置文件
- 6.5、使用systemd管理mysql
- 6.6、创建root用户密码,并创建zabbix数据库,定义zabbix用户
- 七、K8S部署zabbix-server&zabbix-web
-
- 7.1 创建存储,需提前搭建好nfs环境
- 7.2 **创建动态PV**
- 7.3 **创建zabbix-server.yaml**
- 7.4 **创建zabbix-web.yaml**
- 7.5 **登录zabbix-dashboard**
- 八、K8S部署zabbix-proxy&zabbix-agent
-
- 8.1 **安装Helm工具**
- 8.2 **添加Helm Chart Repository**
- 8.3 **下载Zabbix Helm Chart,并解压**
- 8.4 **配置Chart.yaml**
- 8.5 **配置values.yaml**
-
- 8.5.1 **Zabbix Proxy 与 Agent参数配置**
- 8.5.2 **kube-state-metrics 依赖Chart参数配置**
- 8.5.3 **Helm 安装Zabbix Chart**
- 8.6 **登录Zabbix页面创建Zabbix Proxy**
- 8.6 **创建K8S主机群组**
- 8.7 **创建k8s-node主机,用于自动发现K8S节点主机**
-
- 8.7.1 查看K8S服务endpoint信息
- 8.7.2 创建主机
- 8.7.3 定义宏变量
- 8.8 **创建k8s-cluster主机,用于自动发现服务组件**
-
- 8.8.1 创建主机
- 8.8.2 定义宏变量
- 九、**样例效果**
-
- 9.1 **自动发现的节点主机**
- 9.2 **自动发现的集群服务组件主机**
- 十、**参考**
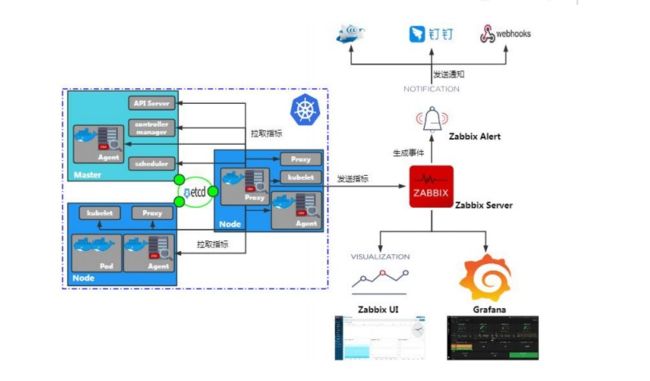
一、框架图
二、环境
| 名称 | 版本 | 操作系统 | IP | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K8S 集群 | 1.24.1 | centos7.9 | 172.16.201.30,172.16.201.31,172.16.201.32 | k8s-master01,k8s-node1, k8s-node2 |
| zabbix | 6.2.6 | centos7.9 | zabbix-server,zabbix-proxy,zabbix-agent 【部署在K8s集群zabbix命名空间内】 | |
| mysql8 | 8.0.31 | centos7.9 | 172.16.201.123 | K8S集群外部单独部署的二进制mysql8 |
| NFS | centos7.9 | 172.16.201.112 | 共享目录 /nfs |
三、监控指标
| 监控名称 | 监控对象 |
|---|---|
| 节点基础信息 | CPU,内存,磁盘 ,IO ,网络,system info … |
| 集群指标【组件】 | Api Server ,ControllerManage,SchedulerServer,kubelet … |
| 资源对象指标 | Daemonset , Deployment , Replicaset, Endpoint, Pod … |
| Pod容器指标 | Container: Menory max usage , Pod CPU: User seconds … |
四、zabbix模板
4.1 K8S集群以及组件模板
| 模板名称 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes API server by HTTP | K8S ApiServer组件指标模板 |
| Kubernetes cluster state by HTTP | K8S 集群指标模板 |
| Kubernetes Controller manager by HTTP | K8S ControllerManager组件指标模板 |
| Kubernetes Scheduler by HTTP | K8S Scheduler组件指标模板 |
| Kubernetes kubelet by HTTP | K8S Kubelet组件指标模板 |
| Kubernetes nodes by HTTP | K8S 集群节点发现以及状态指标模板 |
4.2 K8S节点基础信息指标模板
| 模板名称 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| Linux by Zabbix agent | OS Linux系统监控模板 |
五、主要监控方式
5.1 Agent
通过zabbix agent客户端,采集集群节点的CPU、内存、磁盘等基础信息指标。
5.2 Agentless
通过Zabbix内置的“HTTP agent”,“Script”两种类型的监控项,无需安装客户端,通过访问被监控端的API接口即可采集监控指标数据,主要用于K8S集群、服务组件、pod容器状态及性能指标的采集。
六、部署MySql8
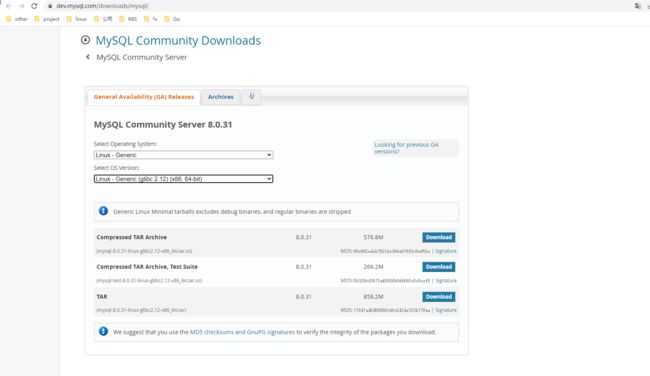
6.1、软件包下载
通用二进制版本: 本文档采用此方式安装 https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/community/
选择版本,再选择Operating System: Linux - Generic
6.2、卸载MariaDB
在CentOS中默认安装有MariaDB,是MySQL的一个分支,主要由开源社区维护。CentOS 7及以上版本已经不再使用MySQL数据库,而是使用MariaDB数据库。如果直接安装MySQL,会和MariaDB的文件冲突。因此,需要先卸载自带的MariaDB,再安装MySQL。
#查看是否存在MariaDB
rpm -qa|grep mariadb
#卸载mariadb
yum remove mariadb*
6.3、MySQL二进制安装
6.3.1 创建mysql工作目录:
root@db01 ~]# mkdir -p /home/application/mysql
6.3.2、上传软件,并解压并改名为app
[root@db01 app]# tar -xf /root/mysql-8.0.31-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.xz
[root@db01 app]# mv mysql-8.0.31-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 /home/application/mysql/app
[root@db01 app]# ls -l /home/application/mysql/app
total 36
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Mar 4 14:55 bin
-rw-r--r-- 1 7161 31415 17987 Sep 13 2017 COPYING
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 55 Mar 4 14:55 docs
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Mar 4 14:55 include
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 229 Mar 4 14:55 lib
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 30 Mar 4 14:55 man
-rw-r--r-- 1 7161 31415 2478 Sep 13 2017 README
drwxr-xr-x 28 root root 4096 Mar 4 14:55 share
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 90 Mar 4 14:55 support-files
6.3.3、修改环境变量
[root@db01 app]# vim /etc/profile
#加入一行
export PATH=$PATH:/home/application/mysql/app/bin
[root@db01 app]# source /etc/profile
6.3.4、建立mysql用户和组(如果有可忽略)
useradd -s /sbin/nologin mysql -M
6.3.5、创建mysql 数据目录,日志目录;并修改权限
mkdir -p /home/application/mysql/data
mkdir -p /home/application/mysql/data/logs
chown -Rf mysql.mysql /home/application/mysql/app
chown -Rf mysql.mysql /home/application/mysql/data
chown -Rf mysql.mysql /home/application/mysql/data/logs
6.3.6、初始化数据
[root@db01 ~]# mysqld --initialize-insecure --user=mysql --basedir=/home/application/mysql/app --datadir=/home/application/mysql/data
2022-12-05T05:42:38.231032Z 0 [System] [MY-013169] [Server] /home/application/mysql/app/bin/mysqld (mysqld 8.0.31) initializing of server in progress as process 1796
2022-12-05T05:42:38.242323Z 1 [System] [MY-013576] [InnoDB] InnoDB initialization has started.
2022-12-05T05:42:43.737861Z 1 [System] [MY-013577] [InnoDB] InnoDB initialization has ended.
2022-12-05T05:42:45.690512Z 6 [Warning] [MY-010453] [Server] root@localhost is created with an empty password ! Please consider switching off the --initialize-insecure option.
6.4、配置mysql配置文件
[mysqld]
user=mysql
basedir=/home/application/mysql/app
datadir=/home/application/mysql/data
character_set_server=utf8
collation-server=utf8mb4_bin
#只能用IP地址检查客户端的登录,不用主机名,跳过域名解析
skip-name-resolve=1
#日志时间
log_timestamps=SYSTEM
#慢日志
long_query_time=3
slow_query_log=ON
slow_query_log_file=/home/application/mysql/data/logs/slow_query.log
#通用日志
general_log=1
general_log_file=/home/application/mysql/data/logs/mysql_general.log
#错误日志
log-error=/home/application/mysql/data/logs/mysql-error.log
# 创建新表时将使用的默认存储引擎
default-storage-engine=INNODB
# 默认使用"mysql_native_password"插件认证
default_authentication_plugin=mysql_native_password
port=3306
socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
max_connections=1000
sql_mode=STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
max_allowed_packet=300M
[mysql]
socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
6.5、使用systemd管理mysql
vim /etc/systemd/system/mysqld.service
[Unit]
Description=MySQL Server
Documentation=man:mysqld(8)
Documentation=http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/en/using-systemd.html
After=network.target
After=syslog.target
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[Service]
User=mysql
Group=mysql
ExecStart=/home/application/mysql/app/bin/mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf
LimitNOFILE = 5000
#reload从新加载下systemd
[root@db01 mysql]# systemctl daemon-reload
#systemd 管理相关命令
systemctl start mysqld
6.6、创建root用户密码,并创建zabbix数据库,定义zabbix用户
[root@db01 ~]# mysqladmin -uroot -p #无密码,直接回车
#创建root用户密码
mysql> alter user 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'zabbix';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
#创建数据库
mysql> CREATE DATABASE zabbix DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
#创建用户
mysql> CREATE USER 'zabbix'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'zabbix';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
#授权用户,这里注意要给zabbix授权所有权限;不然后面创建user表中数据会失败
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'zabbix'@'%';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
#刷新权限
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
七、K8S部署zabbix-server&zabbix-web
7.1 创建存储,需提前搭建好nfs环境
使用NFS 作为后端的存储,使用动态PV 的自动供给 为zabbix持久化数据。
部署NFS 服务( 172.16.201.112主机上 )
# 创建 NFS 存储目录
mkdir -p /nfs
# 安装nfs服务
yum -y install nfs-utils rpcbind
# 修改配置文件
echo "/nfs *(rw,sync,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check)" >> /etc/exports
# 启动服务
systemctl start nfs && systemctl start rpcbind
# 设置开机启动
systemctl enable nfs-server && systemctl enable rpcbind
K8S集群所有节点都要安装nfs-utils
yum -y install nfs-utils
#注意,所有节点都要安装nfs-utils,否则无法使用pv
7.2 创建动态PV
vim StorageClass-nfs.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: managed-nfs-storage
provisioner: fuseim.pri/ifs # or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
parameters:
archiveOnDelete: "true"
---
kind: ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
---
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
image: arawak/nfs-client-provisioner
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: fuseim.pri/ifs
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 172.16.201.112 #指定nfs地址
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /nfs
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 172.16.201.112 #指定nfs地址
path: /nfs
查看StorageClass
[root@k8s-master01 zabbix-latest]# kubectl get sc
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
managed-nfs-storage fuseim.pri/ifs Delete Immediate false 2m
7.3 创建zabbix-server.yaml
vim zabbix-server.yaml
- 使用的是宿主机网络 hostNetwork: true
- 给zabbix-server pod 指定节点允许,因此需要给节点打上标签, zabbix-server: “true”
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: zabbix
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: zabbix-server
namespace: zabbix
labels:
app: zabbix-server
spec:
selector:
app: zabbix-server
ports:
- name: zabbix-server
port: 10051
nodePort: 30051
type: NodePort
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: zabbix-scripts
namespace: zabbix
spec:
storageClassName: "managed-nfs-storage"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: zabbix-server
name: zabbix-server
namespace: zabbix
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: zabbix-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: zabbix-server
spec:
nodeSelector:
zabbix-server: "true"
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- image: zabbix/zabbix-server-mysql:6.2.6-centos
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: zabbix-server-mysql
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/lib/zabbix/alertscripts
name: zabbix-scripts
env:
- name: DB_SERVER_HOST
value: 172.16.201.123
- name: DB_SERVER_PORT
value: "3306"
- name: MYSQL_DATABASE
value: zabbix
- name: MYSQL_USER
value: zabbix
- name: MYSQL_PASSWORD
value: zabbix
- name: ZBX_CACHESIZE
value: "512M"
- name: ZBX_HISTORYCACHESIZE
value: "128M"
- name: ZBX_HISTORYINDEXCACHESIZE
value: "128M"
- name: ZBX_TRENDCACHESIZE
value: "128M"
- name: ZBX_VALUECACHESIZE
value: "256M"
- name: ZBX_TIMEOUT
value: "30"
resources:
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 500Mi
limits:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 1Gi
volumes:
- name: zabbix-scripts
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: zabbix-scripts
kubectl get all -n zabbix
#给k8s-node1节点打上标签
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl label node k8s-node1 zabbix-server=true
[root@k8s-master01 zabbix-latest]# kubectl apply -f zabbix-server.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 zabbix-latest]# kubectl get all -n zabbix
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/zabbix-server-747bf9fc7-s8pqq 1/1 Running 0 2m25s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/zabbix-server NodePort 10.102.226.252 10051:30051/TCP 2m25s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/zabbix-server 1/1 1 1 2m25s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/zabbix-server-747bf9fc7 1 1 1 2m25s
7.4 创建zabbix-web.yaml
vim zabbix-web.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: zabbix-web
name: zabbix-web
namespace: zabbix
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: zabbix-web
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: zabbix-web
spec:
containers:
- image: zabbix/zabbix-web-nginx-mysql:6.2.6-centos
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: zabbix-web-nginx-mysql
env:
- name: DB_SERVER_HOST
value: 172.16.201.123
- name: MYSQL_USER
value: zabbix
- name: MYSQL_PASSWORD
value: zabbix
- name: ZBX_SERVER_HOST
value: zabbix-server
- name: PHP_TZ
value: Asia/shanghai
resources:
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 500Mi
limits:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: zabbix-web
name: zabbix-web
namespace: zabbix
spec:
ports:
- name: web
port: 8080
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
nodePort: 30008
selector:
app: zabbix-web
type: NodePort
kubectl get all -n zabbix
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/zabbix-server-747bf9fc7-s8pqq 1/1 Running 0 5m43s
pod/zabbix-web-66495bf485-hqgpg 1/1 Running 0 18m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/zabbix-server NodePort 10.102.226.252 10051:30051/TCP 5m43s
service/zabbix-web NodePort 10.108.151.52 8080:30008/TCP 18m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/zabbix-server 1/1 1 1 5m43s
deployment.apps/zabbix-web 1/1 1 1 18m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/zabbix-server-747bf9fc7 1 1 1 5m43s
replicaset.apps/zabbix-web-66495bf485 1 1 1 18m
7.5 登录zabbix-dashboard
八、K8S部署zabbix-proxy&zabbix-agent
在K8S集群中部署Zabbix Proxy 与 Zabbix Agent监控组件,这里采用官方提供的Helm Chart来安装
8.1 安装Helm工具
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.8.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# tar zxvf helm-v3.8.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# cp linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
8.2 添加Helm Chart Repository
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# helm repo add zabbix-chart-6.2 https://cdn.zabbix.com/zabbix/integrations/kubernetes-helm/6.2/
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# helm repo list
NAME URL
zabbix-chart-6.2 https://cdn.zabbix.com/zabbix/integrations/kubernetes-helm/6.2
8.3 下载Zabbix Helm Chart,并解压
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# helm pull zabbix-chart-6.2/zabbix-helm-chrt
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# ll
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 24698 Dec 8 10:38 zabbix-helm-chrt-1.1.1.tgz
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# tar -xf zabbix-helm-chrt-1.1.1.tgz
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# ls -l
total 40616
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 124 Dec 8 10:39 zabbix-helm-chrt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 24698 Dec 8 10:38 zabbix-helm-chrt-1.1.1.tgz
8.4 配置Chart.yaml
Chart.yaml主要记录的是当前Chart的基本信息,包括版本、名称、依赖
| 参数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| apiVersion | Chart API 版本 |
| name | Chart 名称 |
| description | 描述信息 |
| home | 项目home页面的URL |
| icon | 用做icon的SVG或PNG图片URL |
| type | Chart 类型 |
| version | 语义化2 版本 |
| appVersion | 包含的应用版本 |
| dependencies | 依赖的Chart列表,缓存在同级 |
[root@k8s-master01 zabbix-helm-chrt]# vim Chart.yaml
apiVersion: v2
appVersion: 6.2.0
dependencies:
- condition: kubeStateMetrics.enabled
name: kube-state-metrics
repository: https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
version: 3.5.*
description: A Helm chart for deploying Zabbix agent and proxy
home: https://www.zabbix.com/
icon: https://assets.zabbix.com/img/logo/zabbix_logo_500x131.png
name: zabbix-helm-chrt
type: application
version: 1.1.1
8.5 配置values.yaml
values.yaml主要为templates目录中定义K8S资源对象的配置文件变量值
8.5.1 Zabbix Proxy 与 Agent参数配置
只需要修改如下参数
| 参数 | 值 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| fullnameOverride | zabbix | 覆盖完全限定应用名称 |
| kubeStateMetricsEnabled | true | 部署kube-state-metrics |
| zabbixProxy.image.tag | 6.2.6-centos | ZabbixProxy Docker镜像tag,用于指定ZabbixProxy版本 |
| zabbixProxy.env.ZBX_HOSTNAME | zabbix-proxy-k8s | ZabbixProxy hostname |
| zabbixProxy.env.ZBX_SERVER_HOST | 172.16.201.31 | ZabbixServer地址 |
| zabbixAgent.image.tag | 6.2.6-centos | ZabbiAgent Docker镜像tag,用于指定 |
[root@k8s-master01 zabbix-helm-chrt]# vim values.yaml
## nameOverride -- Override name of app
nameOverride: ""
## fullnameOverride -- Override the full qualified app name
fullnameOverride: "zabbix"
## kubeStateMetricsEnabled -- If true, deploys the kube-state-metrics deployment
kubeStateMetricsEnabled: true
## Service accoun for Kubernetes API
rbac:
## rbac.create Specifies whether the RBAC resources should be created
create: true
additionalRulesForClusterRole: []
## - apiGroups: [ "" ]
## resources:
## - nodes/proxy
## verbs: [ "get", "list", "watch" ]
serviceAccount:
## serviceAccount.create Specifies whether a service account should be created
create: true
## serviceAccount.name The name of the service account to use. If not set name is generated using the fullname template
name: zabbix-service-account
## **Zabbix proxy** configurations
zabbixProxy:
## Enables use of **Zabbix proxy**
enabled: true
containerSecurityContext: {}
resources: {}
image:
## Zabbix proxy Docker image name
repository: zabbix/zabbix-proxy-sqlite3
## Tag of Docker image of Zabbix proxy
tag: 6.2.6-centos
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## List of dockerconfig secrets names to use when pulling images
pullSecrets: []
env:
## The variable allows to switch Zabbix proxy mode. Bu default, value is 0 - active proxy. Allowed values are 0 and 1.
- name: ZBX_PROXYMODE
value: 0
## Zabbix proxy hostname
- name: ZBX_HOSTNAME
value: zabbix-proxy-k8s
## Zabbix server host
## If ProxyMode is set to active mode:
## IP address or DNS name of Zabbix server to get configuration data from and send data to.
## If ProxyMode is set to passive mode:
## List of comma delimited IP addresses, optionally in CIDR notation, or DNS names of Zabbix server. Incoming connections will be accepted only from the addresses listed here. If IPv6 support is enabled then '127.0.0.1', '::127.0.0.1', '::ffff:127.0.0.1' are treated equally and '::/0' will allow any IPv4 or IPv6 address. '0.0.0.0/0' can be used to allow any IPv4 address.
## Example: Server=127.0.0.1,192.168.1.0/24,::1,2001:db8::/32,zabbix.example.com
- name: ZBX_SERVER_HOST
value: "172.16.201.31"
## Zabbix server port
- name: ZBX_SERVER_PORT
value: 10051
## The variable is used to specify debug level. By default, value is 3
- name: ZBX_DEBUGLEVEL
value: 3
## Cache size
- name: ZBX_CACHESIZE
value: 128M
## The variable enable communication with Zabbix Java Gateway to collect Java related checks
- name: ZBX_JAVAGATEWAY_ENABLE
value: false
## How often proxy retrieves configuration data from Zabbix server in seconds. Active proxy parameter. Ignored for passive proxies.
- name: ZBX_CONFIGFREQUENCY
value: 60
## List can be extended with other environment variables listed here: https://github.com/zabbix/zabbix-docker/tree/5.4/agent/alpine#other-variables
## For example:
## The variable is list of comma separated loadable Zabbix modules.
## - name: ZBX_LOADMODULE
## value : dummy1.so,dummy2.so
service:
annotations: {}
labels: {}
## Type of service for Zabbix proxy
type: ClusterIP
## Port to expose service
port: 10051
## Port of application pod
targetPort: 10051
## Zabbix proxy Ingress externalIPs with optional path
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
## Must be provided if ProxyMode is set to passive mode
externalIPs: []
## Loadbalancer IP
## Only use if service.type is "LoadBalancer"
##
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
## Node selector for Zabbix proxy
nodeSelector: {}
## Tolerations configurations for Zabbix proxy
tolerations: {}
## Affinity configurations for Zabbix proxy
affinity: {}
persistentVolume:
## If true, Zabbix proxy will create/use a Persistent Volume Claim
##
enabled: false
## Zabbix proxy data Persistent Volume access modes
## Must match those of existing PV or dynamic provisioner
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/persistent-volumes/
##
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
## Zabbix proxy data Persistent Volume Claim annotations
##
annotations: {}
## Zabbix proxy data Persistent Volume existing claim name
## Requires zabbixProxy.persistentVolume.enabled: true
## If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
existingClaim: ""
## Zabbix proxy data Persistent Volume mount root path
##
mountPath: /data
## Zabbix proxy data Persistent Volume size
##
size: 2Gi
## Zabbix proxy data Persistent Volume Storage Class
## If defined, storageClassName:
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
## set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
## GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
##
storageClass: "-"
## Zabbix proxy data Persistent Volume Binding Mode
## If defined, volumeBindingMode:
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no volumeBindingMode spec is
## set, choosing the default mode.
##
volumeBindingMode: ""
## Subdirectory of Zabbix proxy data Persistent Volume to mount
## Useful if the volume's root directory is not empty
##
subPath: ""
## **Zabbix agent** configurations
zabbixAgent:
## Enables use of Zabbix agent
enabled: true
resources: {}
## requests:
## cpu: 100m
## memory: 54Mi
## limits:
## cpu: 100m
## memory: 54Mi
securityContext: {}
# fsGroup: 65534
# runAsGroup: 65534
# runAsNonRoot: true
# runAsUser: 65534
containerSecurityContext: {}
## capabilities:
## add:
## - SYS_TIME
## Expose the service to the host network
hostNetwork: true
# Specify dns configuration options for agent containers e.g ndots
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/dns-pod-service/#pod-dns-config
dnsConfig: {}
# options:
# - name: ndots
# value: "1"
## Share the host process ID namespace
hostPID: true
## If true, agent pods mounts host / at /host/root
##
hostRootFsMount: true
extraHostVolumeMounts: []
## - name:
## hostPath:
## mountPath:
## readOnly: true|false
## mountPropagation: None|HostToContainer|Bidirectional
image:
## Zabbix agent Docker image name
repository: zabbix/zabbix-agent2
## Tag of Docker image of Zabbix agent
tag: 6.2.6-centos
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## List of dockerconfig secrets names to use when pulling images
pullSecrets: []
env:
## Zabbix server host
- name: ZBX_SERVER_HOST
value: 0.0.0.0/0
## Zabbix server port
- name: ZBX_SERVER_PORT
value: 10051
## This variable is boolean (true or false) and enables or disables feature of passive checks. By default, value is true
- name: ZBX_PASSIVE_ALLOW
value: true
## The variable is comma separated list of allowed Zabbix server or proxy hosts for connections to Zabbix agent container.
- name: ZBX_PASSIVESERVERS
value: 0.0.0.0/0
## This variable is boolean (true or false) and enables or disables feature of active checks
- name: ZBX_ACTIVE_ALLOW
value: false
## The variable is used to specify debug level, from 0 to 5
- name: ZBX_DEBUGLEVEL
value: 3
## The variable is used to specify timeout for processing checks. By default, value is 4.
- name: ZBX_TIMEOUT
value: 4
## List can be extended with other environment variables listed here: https://github.com/zabbix/zabbix-docker/tree/5.4/agent/alpine#other-variables
## For example:
## The variable is comma separated list of allowed Zabbix server or proxy hosts for connections to Zabbix agent container. You may specify port.
## - name: ZBX_ACTIVESERVERS
## value: ''
## The variable is list of comma separated loadable Zabbix modules. It works with volume /var/lib/zabbix/modules.
## - name: ZBX_LOADMODULE
## value: ''
## Node selector for Agent. Only supports Linux.
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
## Tolerations configurations
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
## Affinity configurations
affinity: {}
serviceAccount:
## Specifies whether a ServiceAccount should be created
create: true
## The name of the ServiceAccount to use.
## If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template
name: zabbix-agent-service-account
annotations: {}
imagePullSecrets: []
automountServiceAccountToken: false
service:
type: ClusterIP
port: 10050
targetPort: 10050
nodePort: 10050
portName: zabbix-agent
listenOnAllInterfaces: true
annotations:
agent.zabbix/monitor: "true"
rbac:
## If true, create & use RBAC resources
##
create: true
## If true, create & use Pod Security Policy resources
## https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/
## PodSecurityPolicies disabled by default because they are deprecated in Kubernetes 1.21 and will be removed in Kubernetes 1.25.
## If you are using PodSecurityPolicies you can enable the previous behaviour by setting `rbac.pspEnabled: true`
pspEnabled: false
pspAnnotations: {}
8.5.2 kube-state-metrics 依赖Chart参数配置
只需要修改如下参数
| 参数 | 值 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| Image.repository | bitnami/kube-state-metrics | kube-state-metrics 镜像库配置**[helm中的镜像地址国内无法下载,需要替换]** |
| Image.tag | 2.2.0 | kube-state-metrics容器镜像本版本 |
vim /root/zabbix-helm-chrt/charts/kube-state-metrics/values.yaml
# Default values for kube-state-metrics.
prometheusScrape: true
image:
repository: bitnami/kube-state-metrics
tag: 2.2.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
imagePullSecrets: []
# - name: "image-pull-secret"
# If set to true, this will deploy kube-state-metrics as a StatefulSet and the data
# will be automatically sharded across <.Values.replicas> pods using the built-in
# autodiscovery feature: https://github.com/kubernetes/kube-state-metrics#automated-sharding
# This is an experimental feature and there are no stability guarantees.
autosharding:
enabled: false
replicas: 1
# List of additional cli arguments to configure kube-state-metrics
# for example: --enable-gzip-encoding, --log-file, etc.
# all the possible args can be found here: https://github.com/kubernetes/kube-state-metrics/blob/master/docs/cli-arguments.md
extraArgs: []
service:
port: 8080
# Default to clusterIP for backward compatibility
type: ClusterIP
nodePort: 0
loadBalancerIP: ""
annotations: {}
customLabels: {}
hostNetwork: false
rbac:
# If true, create & use RBAC resources
create: true
# Set to a rolename to use existing role - skipping role creating - but still doing serviceaccount and rolebinding to it, rolename set here.
# useExistingRole: your-existing-role
# If set to false - Run without Cluteradmin privs needed - ONLY works if namespace is also set (if useExistingRole is set this name is used as ClusterRole or Role to bind to)
useClusterRole: true
serviceAccount:
# Specifies whether a ServiceAccount should be created, require rbac true
create: true
# The name of the ServiceAccount to use.
# If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template
name:
# Reference to one or more secrets to be used when pulling images
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/pull-image-private-registry/
imagePullSecrets: []
# ServiceAccount annotations.
# Use case: AWS EKS IAM roles for service accounts
# ref: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/specify-service-account-role.html
annotations: {}
prometheus:
monitor:
enabled: false
additionalLabels: {}
namespace: ""
honorLabels: false
metricRelabelings: []
relabelings: []
## Specify if a Pod Security Policy for kube-state-metrics must be created
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/
##
podSecurityPolicy:
enabled: false
annotations: {}
## Specify pod annotations
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#apparmor
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#seccomp
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#sysctl
##
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: '*'
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'docker/default'
# apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'runtime/default'
additionalVolumes: []
securityContext:
enabled: true
runAsGroup: 65534
runAsUser: 65534
fsGroup: 65534
## Specify security settings for a Container
## Allows overrides and additional options compared to (Pod) securityContext
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/#set-the-security-context-for-a-container
containerSecurityContext: {}
## Node labels for pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
nodeSelector: {}
## Affinity settings for pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
affinity: {}
## Tolerations for pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/
tolerations: []
# Annotations to be added to the pod
podAnnotations: {}
## Assign a PriorityClassName to pods if set
# priorityClassName: ""
# Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/configure-pdb/
podDisruptionBudget: {}
# Comma-separated list of metrics to be exposed.
# This list comprises of exact metric names and/or regex patterns.
# The allowlist and denylist are mutually exclusive.
metricAllowlist: []
# Comma-separated list of metrics not to be enabled.
# This list comprises of exact metric names and/or regex patterns.
# The allowlist and denylist are mutually exclusive.
metricDenylist: []
# Comma-separated list of additional Kubernetes label keys that will be used in the resource's
# labels metric. By default the metric contains only name and namespace labels.
# To include additional labels, provide a list of resource names in their plural form and Kubernetes
# label keys you would like to allow for them (Example: '=namespaces=[k8s-label-1,k8s-label-n,...],pods=[app],...)'.
# A single '*' can be provided per resource instead to allow any labels, but that has
# severe performance implications (Example: '=pods=[*]').
metricLabelsAllowlist: []
# - namespaces=[k8s-label-1,k8s-label-n]
# Comma-separated list of Kubernetes annotations keys that will be used in the resource'
# labels metric. By default the metric contains only name and namespace labels.
# To include additional annotations provide a list of resource names in their plural form and Kubernetes
# annotation keys you would like to allow for them (Example: '=namespaces=[kubernetes.io/team,...],pods=[kubernetes.io/team],...)'.
# A single '*' can be provided per resource instead to allow any annotations, but that has
# severe performance implications (Example: '=pods=[*]').
metricAnnotationsAllowList: []
# - pods=[k8s-annotation-1,k8s-annotation-n]
# Available collectors for kube-state-metrics.
# By default, all available resources are enabled, comment out to disable.
collectors:
- certificatesigningrequests
- configmaps
- cronjobs
- daemonsets
- deployments
- endpoints
- horizontalpodautoscalers
- ingresses
- jobs
- limitranges
- mutatingwebhookconfigurations
- namespaces
- networkpolicies
- nodes
- persistentvolumeclaims
- persistentvolumes
- poddisruptionbudgets
- pods
- replicasets
- replicationcontrollers
- resourcequotas
- secrets
- services
- statefulsets
- storageclasses
- validatingwebhookconfigurations
- volumeattachments
# - verticalpodautoscalers # not a default resource, see also: https://github.com/kubernetes/kube-state-metrics#enabling-verticalpodautoscalers
# Enabling kubeconfig will pass the --kubeconfig argument to the container
kubeconfig:
enabled: false
# base64 encoded kube-config file
secret:
# Comma-separated list of namespaces to be enabled for collecting resources. By default all namespaces are collected.
namespaces: ""
## Override the deployment namespace
##
namespaceOverride: ""
resources: {}
# We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as a conscious
# choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on environments with little
# resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to specify resources, uncomment the following
# lines, adjust them as necessary, and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'.
# limits:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 64Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
## Provide a k8s version to define apiGroups for podSecurityPolicy Cluster Role.
## For example: kubeTargetVersionOverride: 1.14.9
##
kubeTargetVersionOverride: ""
# Enable self metrics configuration for service and Service Monitor
# Default values for telemetry configuration can be overridden
selfMonitor:
enabled: false
# telemetryHost: 0.0.0.0
# telemetryPort: 8081
8.5.3 Helm 安装Zabbix Chart
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# cd zabbix-helm-chrt
[root@k8s-master01 zabbix-helm-chrt]# helm install zabbix . --dependency-update -n zabbix
NAME: zabbix
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Dec 8 11:43:22 2022
NAMESPACE: zabbix
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
Thank you for installing zabbix-helm-chrt.
Your release is named zabbix.
Zabbix agent installed: "zabbix/zabbix-agent2:6.2.6-centos"
Zabbix proxy installed: "zabbix/zabbix-proxy-sqlite3:6.2.6-centos"
Annotations:
app.kubernetes.io/name: zabbix
helm.sh/chart: zabbix-helm-chrt-1.1.1
app.kubernetes.io/version: "6.2.0"
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
Service account created:
zabbix-service-account
To learn more about the release, try:
$ helm status zabbix
$ helm get all zabbix
查看K8S Zabbix Pod
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get pods -n zabbix
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
zabbix-agent-c2tpt 1/1 Running 0 39m
zabbix-agent-chjlw 1/1 Running 0 39m
zabbix-agent-z7mc6 1/1 Running 0 39m
zabbix-kube-state-metrics-7649877dd4-dtrlj 1/1 Running 0 39m
zabbix-proxy-79dcdc48bd-m5kf8 1/1 Running 0 39m
zabbix-server-747bf9fc7-s8pqq 1/1 Running 0 13h
zabbix-web-66495bf485-hqgpg 1/1 Running 0 13h
获取API接口访问Token,后面配置Zabbix需要使用到
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get secret zabbix-service-account -n zabbix -o jsonpath={.data.token} | base64 -d
exxxxxxxciOiJSUzI1NiIsxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxDQifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOixxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50L3NlY3JldCxxxxxxxxxlcnZpY2UtYWNjbxxxxC9zZXJ2aWNlLWFjY291bnQudWlkIjoiMGM1ZTc3YmMtZTM3OC00NzNjLWEzNxxxxxxiwic3ViIjoixxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxJpeDp6YWJiaXgtxxxxxxxxml
8.6 登录Zabbix页面创建Zabbix Proxy
- Proxy name:zabbix-proxy-k8s
- Proxy mode: Active
如果长时间等待,Last seen (age) 这边还是爆红 ,就表示proxy 没有主动注册到zabbix-server;需要把zabbix-agent 的pod 删除重建即可
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl delete pod -n zabbix zabbix-proxy-79dcdc48bd-m5kf8
正常状态下的proxy
8.6 创建K8S主机群组
Group name: K8S Server
8.7 创建k8s-node主机,用于自动发现K8S节点主机
8.7.1 查看K8S服务endpoint信息
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get endpoints -n zabbix
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
zabbix-agent 172.16.201.30:10050,172.16.201.31:10050,172.16.201.32:10050 82m
zabbix-kube-state-metrics 10.244.36.74:8080 82m
zabbix-proxy 10.244.36.91:10051 82m
zabbix-server 172.16.201.31:10051 13h
zabbix-web 10.244.169.157:8080 14h
8.7.2 创建主机
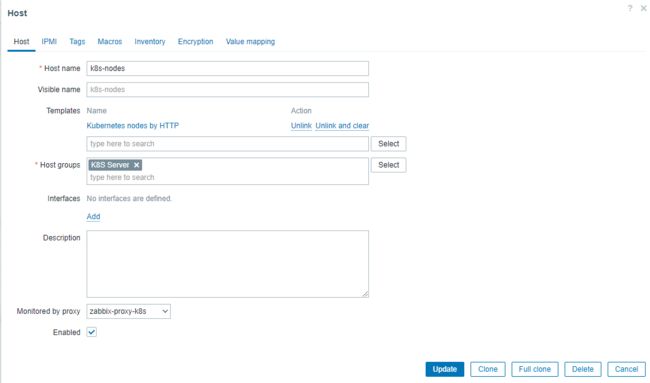
Host name: k8s-nodes
Templates: 选择Template group 中 Templates 下的 Kubernetes nodes by HTTP 模板,用于自动发现K8S节点主机
Host groups: K8S Server
Monitored by proxy: 选择 zabbix-proxy-k8s 代理节点
8.7.3 定义宏变量
- 定义三个宏变量
- {$KUBE.API.ENDPOINT.URL} : https://172.16.201.30:6443/api
- {$KUBE.API.TOKEN}: XXXXXXXX [上面获取到的token]
- {$KUBE.NODES.ENDPOINT.NAME}: zabbix-agent 【通过kubectl get ep -n zabbix 获取到】
8.8 创建k8s-cluster主机,用于自动发现服务组件
8.8.1 创建主机
Host name: k8s-cluster
Templates: 选择Template group 中 Templates 下的Kubernetes cluster state by HTTP 模板,用于自动发现K8S节点主机
Host groups: K8S Server
Monitored by proxy: 选择 zabbix-proxy-k8s 代理节点
8.8.2 定义宏变量
- 定义13个宏变量
- {$KUBE.API.HOST}: 172.16.201.30
- {$KUBE.API.PORT}:6443
- {$KUBE.API.TOKEN}: XXXXX [上面获取到的token]
- {$KUBE.API.URL} : https://172.16.201.30:6443
- {$KUBE.API_SERVER.PORT}:6443
- {$KUBE.API_SERVER.SCHEME}:https
- {$KUBE.CONTROLLER_MANAGER.PORT}:10252
- {$KUBE.CONTROLLER_MANAGER.SCHEME}:http
- {$KUBE.KUBELET.PORT}:10250
- {$KUBE.KUBELET.SCHEME}:https
- {$KUBE.SCHEDULER.PORT}:10251
- {$KUBE.SCHEDULER.SCHEME}:http
- {$KUBE.STATE.ENDPOINT.NAME}:zabbix-kube-state-metrics 【通过kubectl get ep -n zabbix 获取到】
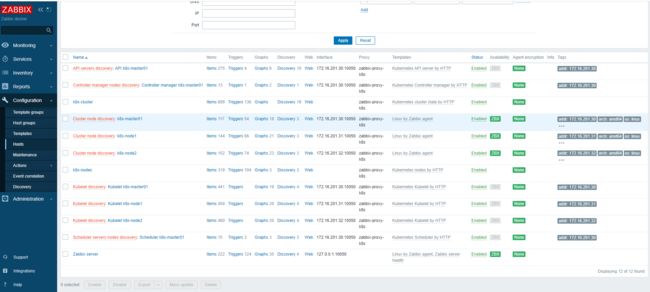
九、样例效果
9.1 自动发现的节点主机
最新数据
9.2 自动发现的集群服务组件主机
最新数据
十、参考
- https://www.cnblogs.com/likaifei/p/16709332.html
- https://git.zabbix.com/projects/ZT/repos/kubernetes-helm/browse?at=refs%2Fheads%2Frelease%2F6.2