SpringBoot搭建个人博客系统项目2:错误处理——定制错误页面和错误数据
文章目录
- 错误处理简介
-
- 重要的类
- 错误处理步骤
- 错误处理方法
-
- 自适应方法
- 添加ErrorAttributes组件(推荐)
- 进阶:处理自己定制的异常
- 给博客系统添加错误处理
前两部分为错误处理原理,可直接跳到第三部分博客系统的错误处理部分。
错误处理简介
重要的类
- ErrorPageCustomizer:
定制错误的响应规则,发送/error请求。
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";
- BasicErrorController:
处理/error请求,通过发送请求的请求头识别是否是浏览器,决定返回页面还是json数据。
@Controller
@RequestMapping({"${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}"})
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
// 产生html类型的数据
@RequestMapping(produces = {"text/html"})
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
// 要去哪个页面,包含页面地址和页面内容
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
// 产生json类型的数据
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity(status);
} else {
Map<String, Object> body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity(body, status);
}
}
}
-
DefaultErrorViewerResolver:
返回哪个页面是由其解析得到的。如果有模板引擎,则到template文件夹下的error文件夹下找错误页面;如果模板引擎文件夹下没有error文件夹,则到静态资源文件夹下找error文件夹,但是静态资源文件夹下的错误页面不可以使用模板引擎。如果两者皆找不到则返回SpringBoot默认的错误页面。 -
DefaultErrorAttributes:
定制错误页面可以共享的信息,可以获取到的有:- timestamp:时间戳
- status:状态码
- error:错误提示
- exception:异常对象
- message:异常消息
- errors:JSR303数据校验的错误
错误处理步骤
以访问一个不存在的页面返回404为例
一旦系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误,ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则),发送/error请求;然后请求会被 BasicErrorController处理,选择返回页面还是json数据
- 定制返回页面
调用DefaultErrorViewerResolver中解析页面的方法,到模板引擎文件夹或者静态资源文件夹下找error文件夹下的错误页面解析,页面可以显示DefaultErrorAttributes共享的信息。如果找不到error文件夹则返回SpringBoot默认的错误页面。优先返回精准匹配的页面。即如果有404.html和4xx.html,如果状态码是404则返回404.html,如果是405则返回4xx.html。 - 定制返回json数据
使用@ControllerAdvice注解配置一个异常控制器,再使用@ExceptionHandler配置一个异常处理器,里面传入需要处理的异常的class文件,@ResponseBody注解设置返回的是json数据。
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Map<String, Object> handlerException(Exception e){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("message", e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}
错误处理方法
自适应方法
使用请求转发功能,出现错误后转发到/error请求,让SpringBoot决定响应页面还是json数据
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public String handlerException(Exception e){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 传入我们自己的状态码
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500);
map.put("message", e.getMessage());
return "forward:/error";
}
}
缺点是必须要传入自己的状态码,如4xx 5xx,否则服务器默认响应200状态码,不会进入定制错误页面的解析流程,无法正确返回错误页面,且无法在页面中获得自己返回的map对象,不推荐。
添加ErrorAttributes组件(推荐)
我们只关心处理/error请求时返回的数据,其它的交给SpringBoot处理。
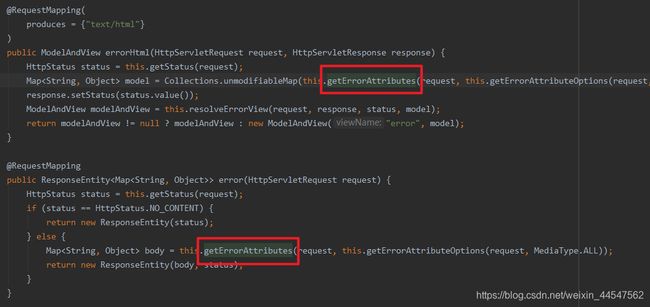
由上图可知BasicErrorController响应的页面和json数据都是由this.getErrorAttributes()方法得到的,而此方法是通过返回this.errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes()方法实现的。

而this.errorAttributes就是ErrorAttributes接口。
在ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration类中有:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ErrorAttributes.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes();
}
可知如果容器中没有我们自己配置的ErrorAttributes组件,则默认使用DefaultErrorAttributes处理数据。
因此我们可以写一个自己的ErrorAttributes类,添加到容器中,继承DefaultErrorAttributes,重写getErrorAttributes方法,在父类方法中返回的map类型的errorAttributes中添加自己想要返回的数据,再返回新的errorAttributes。
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options);
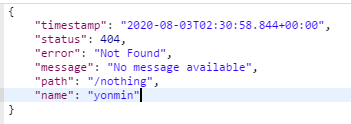
errorAttributes.put("name","yonmin");
return errorAttributes;
}
}
将name添加到了errorAttributes中,4xx.html如下
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>错误title>
head>
<body>
<h3>timestamp:[[${timestamp}]]h3>
<h3>status:[[${status}]]h3>
<h3>error:[[${error}]]h3>
<h3>exception:[[${exception}]]h3>
<h3>message:[[${message}]]h3>
<h3>errors:[[${errors}]]h3>
<h3>name:[[${name}]]h3>
body>
html>
errorAttributes中所有的键值对都在json数据中。
进阶:处理自己定制的异常
使用上面提到的自适应方法,传入自己想要定制的异常的class文件(为了方便演示我使用的Exception类,最好使用特定的异常类),在map中添加自己想要在页面或者json中返回的数据,并将其添加到request域中。
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public String handlerException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 传入我们自己的状态码
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500);
map.put("message", e.getMessage());
request.setAttribute("ext",map);
return "forward:/error";
}
}
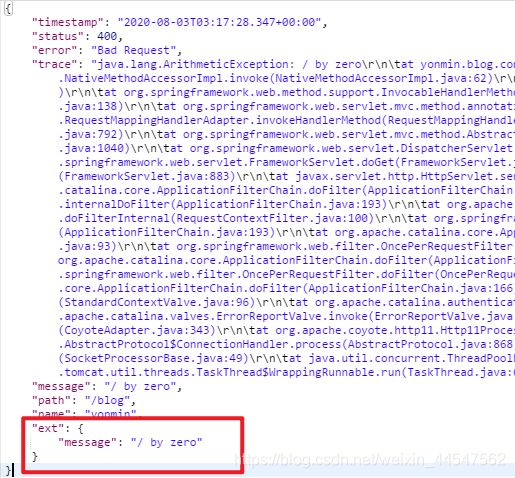
在MyErrorAttributes中使用WebRequest的getAttribute方法从request域中得到MyExceptionHandler保存的"ext",将其添加到要返回的errorAttributes中,这样浏览器和其它客户端都可以响应自己定制的异常信息。
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) {
Map<String, Object> ext = (Map<String, Object>) webRequest.getAttribute("ext", 0);
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options);
errorAttributes.put("name","yonmin");
errorAttributes.put("ext",ext);
return errorAttributes;
}
}
浏览器中可以使用[[${ext.message}]]获取到ext中的message的值

给博客系统添加错误处理
使用上面介绍的添加ErrorAttributes组件的方法进行异常处理,错误页面保存在template下的error文件夹中。
向容器中添加一个MyErrorAttributes组件
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options);
errorAttributes.put("author","yonmin");
return errorAttributes;
}
}
error文件夹下的4xx.html和5xx.html内容一样,如下:
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>错误title>
head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>[[${status}]]h1>
<p><strong>[[${error}]]strong>p>
div>
body>
html>
因为此部分不是博客系统的重点,所以不宜在前期耗费太多精力,如果想更进一步的话可以继续完善错误页面。