数据结构 | 堆【图解】
数据结构 | 堆【图解】
文章目录
- 数据结构 | 堆【图解】
-
- 堆的概念及结构
- 堆的实现
-
- 堆的初始化
- 堆的插入【重点】
- 堆的删除【重点】
- 取堆顶的数据
- 堆的数据个数
- 堆的判空
- 堆的销毁
- 全部代码
堆的概念及结构
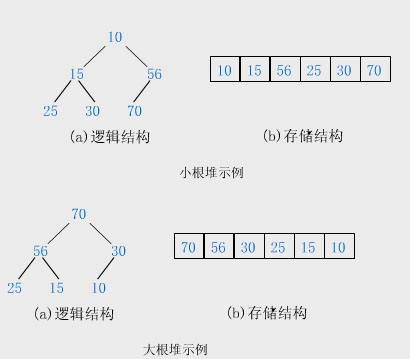
堆(heap): 一种有特殊用途的数据结构——用来在一组变化频繁(发生增删查改的频率较高)的数据集中查找最值。
堆在物理层面上:表现为一组连续的数组区间:long[] array ;将整个数组看作是堆。
堆在逻辑结构上:一般被视为是一颗完全二叉树。
满足任意结点的值都大于其子树中结点的值,叫做大堆,或者大根堆,或者最大堆;反之,则是小堆,或者小根堆,或者最小堆。当一个堆为大堆时,它的每一棵子树都是大堆。
- 堆一般是数组数据看做一颗完全二叉树
- 小堆要求:任意一个父亲<=孩子
- 大堆要求:任意一个父亲>=孩子
这里是没有中堆的!
堆的实现
Heap.h
- 需要实现堆的函数
#pragma once
#include- 接下来我们就开始实现堆~~
堆的初始化
- 这里直接初始化,不多介绍
void HeapInit(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
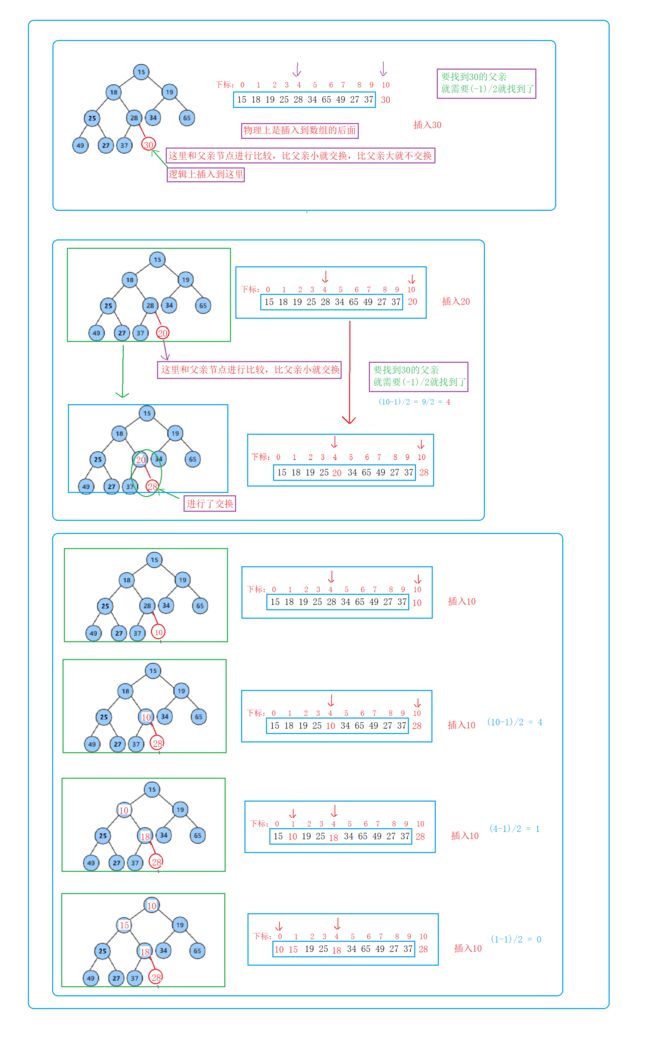
堆的插入【重点】
- 检查空间是否满了,满了就扩容
- 然后将值插入到最后
- 最后向上调整
向上调整算法,依次pk
- 这里的
size是size-1,而不是size,因为是放完数据后size++了一下,然后要取size-1的位置- 如果孩子节点小于父亲节点就交换
- 然后再将父亲节点给了孩子节点,再进行
(-1)/2- 如果大于等于父亲就跳出循环
- 跳出的条件是
child > 0- 这里的向上时间复杂度是
O(logN)
//交换
void Swap(int* p1, int* p2)
{
HPDataType tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
//向上调整
void AjustUp(HPDataType* a, HPDataType child)
{
HPDataType parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 堆的插入
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x)
{
assert(hp);
if (hp->capacity == hp->size)
{
HPDataType newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
hp->a = tmp;
hp->capacity = newcapacity;
}
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
AjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);
}
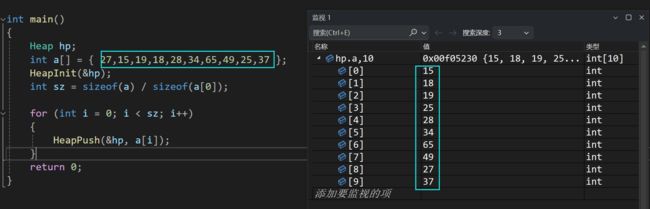
- 我们测试一下~~
int main()
{
Heap hp;
int a[] = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };
HeapInit(&hp);
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
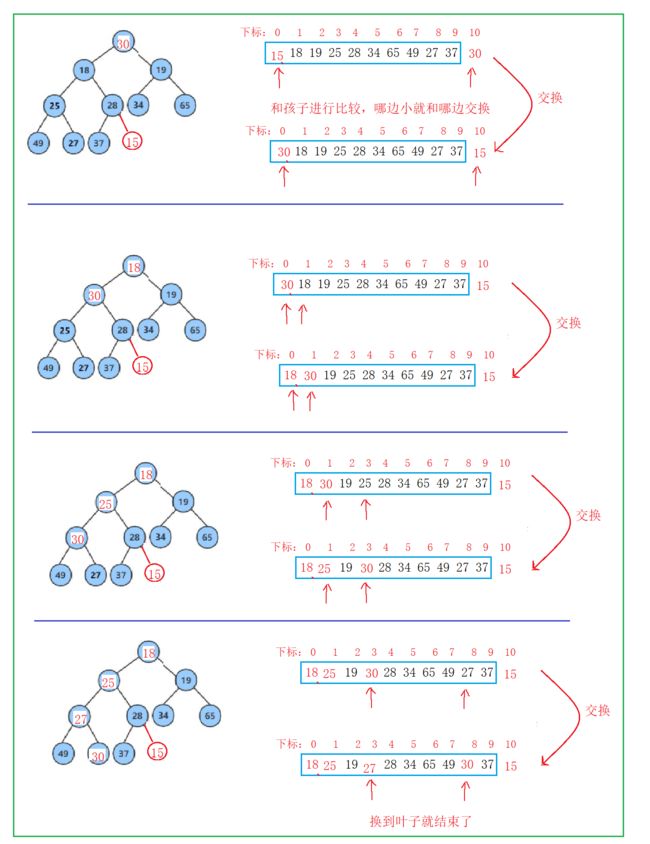
堆的删除【重点】
-
堆的删除是堆顶上的数据,而不是删除根节点,删除最下面的那个数据是没有意义的~~
-
删除后要进行调整
步骤一:
交换
步骤二:
向下调整算法
这里的向下时间复杂度是
O(logN),和向上一样,调整高度次
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(int* a, int size, int parent)
{
//假设左孩子小,假设错了就更新
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < size)
{
if (a[child + 1] < a[child])
{
++child;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 堆的删除
void HeapPop(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(hp->size > 0);
//首尾交换
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;
//从根向下调整
AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);
}
取堆顶的数据
- 这里直接取数组第一个元素就可以了
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(hp->size > 0);
return hp->a[0];
}
堆的数据个数
- 这里也一样,取size
int HeapSize(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size;
}
堆的判空
- 判断size是否为0
bool HeapEmpty(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size == 0;
}
堆的销毁
- 销毁也不多说了,很简单
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
free(hp->a);
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
全部代码
//小堆算法
// 堆的构建
void HeapInit(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
//交换
void Swap(int* p1, int* p2)
{
HPDataType tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, HPDataType child)
{
HPDataType parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 堆的插入
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x)
{
assert(hp);
if (hp->capacity == hp->size)
{
int newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
hp->a = tmp;
hp->capacity = newcapacity;
}
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);
}
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(int* a, int size, int parent)
{
//假设左孩子小,假设错了就更新
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < size)
{
if (child + 1 < size && a[child + 1] < a[child])
{
++child;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 堆的删除
void HeapPop(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(hp->size > 0);
//首尾交换
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;
//从根向下调整
AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);
}
// 取堆顶的数据
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(hp->size > 0);
return hp->a[0];
}
// 堆的数据个数
int HeapSize(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size;
}
// 堆的判空
bool HeapEmpty(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size == 0;
}
// 堆的销毁
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
free(hp->a);
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
以上是小堆的算法,大堆也是一样的,只需要改几个符号就可以了~~
堆的介绍就到这里结束了,感谢收看~~