PostgreSQL之日期时间小结
PostgreSQL关于时间日期的语法及注意事项
- sql时间用法
-
- 获取当前日期的函数&&获取当前时间的函数
-
- 获取当前日期的函数
- 获取当前时间的函数
- 获取当前日期加时间的函数
-
- 函数: current_timestamp
- 函数: transaction_timestamp()
- 函数: statement_timestamp()
- 函数: clock_timestamp()
- 函数: timeofday()
- 函数: now()
- 延迟执行
-
- 函数: pg_sleep()
- 函数: pg_sleep_for ()
- 函数: pg_sleep_until()
- 时间和日期函数
-
-
- to_char(timestamp, text)
- to_char(int, text)
- to_char(double precision, text)
- to_date(text, text)
- to_number(text, text)
- to_timestamp(text, text)
- date - date
- date_part(text, timestamp)
- date_trunc(text, timestamp)
- extract(field from timestamp)
- make_date(year int, month int, day int)
- 使用timestamp来比较时间
- 使用interval添加时间
-
- 致谢
sql时间用法
PostgreSQL 提供了大量用于获取系统当前日期和时间的函数,例如 current_date、current_time、
current_timestamp、clock_timestamp()、localtimestamp、now()、statement_timestamp()等;同时还
支持延迟语句执行的 pg_sleep()等函数
数据库有很多,mysql、sqlserver等存在存储过程,所需要用到的函数各不相同,本文列举一下PostgreSQL的语法。
日期和时间函数主要用来处理日期和时间值,一般的日期函数除了使用date类型的参数外,也可以使用datetime或者timestamp类型,但会忽略这些值的时间部分。相同的以time类型值为参数的函数,可以接受timestamp类型的参数,但会忽略日期部分。
获取当前日期的函数&&获取当前时间的函数
1、获取当前日期的函数和获取当前时间的函数:current_date和current_time
2、调用该函数时不需要在函数名后加括号。该日期是服务器的日期,不是客户端的日期。
注意:
上面所有的函数,包括 CURRENT_DATE,返回的都是当前事务开始的时间。在同一个事务期间,多次调用相同的函数将会返回相同的值,结果不会随着时间增加。这一点与其他数据库的实现可能不同。
获取当前日期的函数
current_date函数:的作用是将当前日期按照“YYYY-MM-DD”格式的值返回,具体格式根据函数用在字符串或是数字语境中而定的。
select current_date;
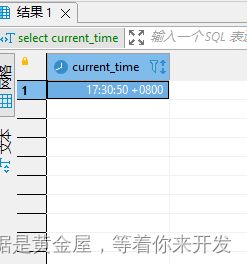
获取当前时间的函数
current_time函数:的作用是将当前时间以“HH:MM:SS”的格式返回,具体格式根据函数用在字符串或是数字语境中而定的。
select current_time;;
localtime函数:的作用是将当前时间以“HH:MM:SS”的格式返回并且localtime没有时区。
select localtime;
获取当前日期加时间的函数
基本上current_timestamp,transaction_timestamp()和now()完全相同。current_timestamp是一个函数的语法奇怪,没有尾对括号,这是根据sql标准。
如果未在sql语句中声明函数调用的列别名(需要一个),则别名默认为函数的名称。在内部,标准sql current_timestamp使用now()实现,并在您查看默认列别名时显示。
函数: current_timestamp
select current_timestamp;
函数: transaction_timestamp()
transaction_timestamp() 等价于 current_timestamp,但是作用更加明确。
select transaction_timestamp();
函数: statement_timestamp()
statement_timestamp()返回当前语句的开始时间,更准确地说,应该是接收到客户端最新命令的时间。与transaction_timestamp相比,对于事务中的第一个命令返回的结果相同,但随后再执行 statement_timestamp() 将会返回不同的值。
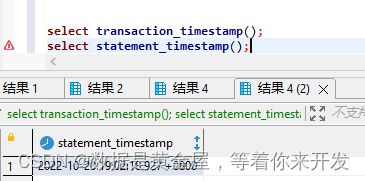
select transaction_timestamp();
select statement_timestamp();
BEGIN;
BEGIN
SELECT statement_timestamp();
SELECT pg_sleep(3);
SELECT statement_timestamp();
COMMIT;
COMMIT
两次执行结果之间相差了 3 秒左右。
当我们在存储过程(Stored Procedure)中进行调试时,通常需要打印不同语句消耗的时间;此时就需要使用 statement_timestamp(),而不能使用 CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 或者 transaction_timestamp():
CREATE OR REPLACE sp_test
...
DECLARE
lts_systimestamp timestamp;
BEGIN;
lts_systimestamp := statement_timestamp();
...
RAISE NOTICE 'Step 1 take time: %', statement_timestamp() - lts_systimestamp;
...
END;
函数: clock_timestamp()
clock_timestamp()与statement_timestamp()相比,后者是接收到客户端信息的时候更新时间,而clock_timestamp()接受到信息以后每次调用这个函数打印的时间戳都不一样。返回的是实际时间。
SELECT clock_timestamp();
SELECT clock_timestamp() FROM generate_series(1,10);

clock_timestamp() 返回当前实际的时间,即使在同一个 SQL 语句中也可能返回不同的值:
因为我使用的是Dbeaver客户端,所以返回的精度不高。正常来说,查询语句在 1 秒钟内返回了 10 条记录,但是每条记录产生的时间都不相同。
函数: timeofday()
timeofday()与clock_timestamp()一样返回的是实际的时间,不过timeofday()函数返回类型是一个格式化的字符串,而不是 timestamp with time zone:
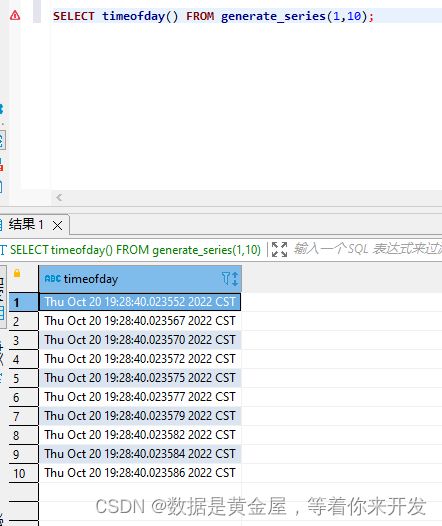
SELECT timeofday();
SELECT timeofday() FROM generate_series(1,10);
函数: now()
now()与transaction_timestamp() 一样
select now() ;

注意: now() 是 PostgreSQL 中与 transaction_timestamp() 等价的一个传统函数,同一个事务中的结果不会改变。
另外,所有的日期/时间数据类型都支持使用字面值’now’指定当前日期和时间(当前事务开始时间)。因此,以下语句效果相同:
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
SELECT now();
SELECT TIMESTAMP 'now';

另外,PostgreSQL 还提供了其他几个特殊的日期和时间字面值:

以上函数分别返回 UTC 1970 年 1 月 1 日零点、今天午夜、明天午夜、昨天午夜以及 UTC 零点。
延迟执行
以下函数可以用于延迟服务器进行的操作:
pg_sleep(seconds)
pg_sleep_for(interval)
pg_sleep_until(timestamp with time zone)
函数: pg_sleep()
pg_sleep 将当前会话的进行暂停指定的秒数。seconds 的类型为 double precision,所以支持小数秒。我们在面前使用了该函数。
select pg_sleep(10);
函数: pg_sleep_for ()
pg_sleep_for 执行一个延迟的时间间隔,通常用于指定一个较大的延迟。
select pg_sleep_for('2 minutes');
函数: pg_sleep_until()
pg_sleep_until 可以用于指定一个进程的唤醒时间。
select pg_sleep_until('tomorrow 05:00');
以上示例分别暂停 1.5 秒、5 分钟以及直到明天 5 点,在特定的存储过程里面,可以满足一些需求。
==注意:==使用这些延迟函数时,确保当前会话没有锁定过多的资源;否则,其他会话将会一直等待,导致系统性能的下降。
时间和日期函数
to_char(timestamp, text)
to_char(timestamp, text)
将时间戳转换为字符串。
SELECT to_char(current_timestamp, 'HH:MI:SS')
to_char(int, text)
to_char(int, text)
将整数转换为字符串。
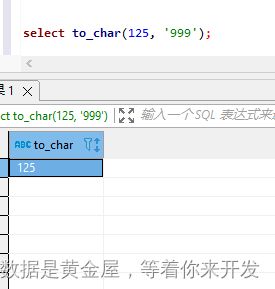
select to_char(125, '999');
to_char(double precision, text)
to_char(double precision, text)
将实数或双精度数转换为字符串。
select to_char(125.8::real, '999D9');
to_date(text, text)
to_date(text, text)
将字符串转换为日期。
select to_date('22 Oct 2022', 'DD Mon YYYY');
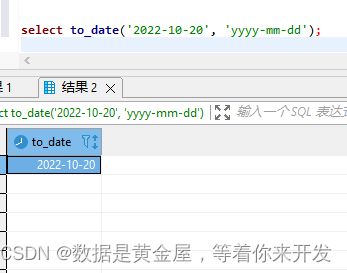
select to_date('2022-10-20', 'yyyy-mm-dd');
to_number(text, text)
to_number(text, text)
将字符串转换为数字。
select to_number('12,454.8-', '99G999D9S');
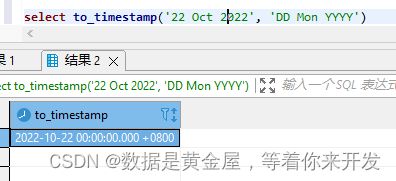
to_timestamp(text, text)
to_timestamp(text, text)
将字符串转换为时间戳。
select to_timestamp('05 Dec 2000', 'DD Mon YYYY')
date - date
date - date
日期的减法运算。
select date '2020-01-01' - date '2020-01-05'
date_part(text, timestamp)
date_part(text, timestamp)
从时间戳中获取子字段。
select date_part('hour', timestamp '2001-02-16 20:38:40')
date_trunc(text, timestamp)
date_trunc(text, timestamp)
截断时间戳到指定精度。
select date_trunc('hour', timestamp '2001-02-16 20:38:40')
extract(field from timestamp)
extract(field from timestamp)
从时间戳中获取子字段。
select extract(hour from timestamp '2001-02-16 20:38:40')
make_date(year int, month int, day int)
make_date(year int, month int, day int)
使用年月日创建日期。
select make_date(2013, 7, 15);
使用timestamp来比较时间
使用timestamp来比较时间
select '2020-01-01' < '2019-01-01'::timestamp+ '360 day'
使用interval添加时间
INTERVAL ‘3’ DAY 时间间隔为3天
INTERVAL ‘2’ HOUR 时间间隔为2小时
致谢
感谢两位作者的分享,尝试一下,确实好用。