axios 拦截器分析
在 Axios 中设置拦截器很简单,通过 axios.interceptors.request 和 axios.interceptors.response 对象提供的 use 方法,就可以分别设置请求拦截器和响应拦截器:
// 添加请求拦截器
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
config.headers.token = 'added by interceptor';
return config;
});
// 添加响应拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (data) {
data.data = data.data + ' - modified by interceptor';
return data;
});在看具体的代码之前,我们先来分析一下它的设计思路。Axios 的作用是用于发送 HTTP 请求,而请求拦截器和响应拦截器的本质都是一个实现特定功能的函数。
我们可以按照功能把发送 HTTP 请求拆解成不同类型的子任务,比如有用于处理请求配置对象的子任务,用于发送 HTTP 请求的子任务和用于处理响应对象的子任务。当我们按照指定的顺序来执行这些子任务时,就可以完成一次完整的 HTTP 请求。
了解完这些,接下来我们将从 「任务注册、任务编排和任务调度」 三个方面来分析 Axios 拦截器的实现。
任务注册
要搞清楚任务是如何注册的,就需要了解 axios 和 axios.interceptors 对象。
/**
* Create an instance of Axios
*
* @param {Object} defaultConfig The default config for the instance
* @return {Axios} A new instance of Axios
*/
function createInstance(defaultConfig) {
var context = new Axios(defaultConfig);
var instance = bind(Axios.prototype.request, context);
// Copy axios.prototype to instance
utils.extend(instance, Axios.prototype, context);
// Copy context to instance
utils.extend(instance, context);
return instance;
}
// Create the default instance to be exported
var axios = createInstance(defaults);
// Expose Axios class to allow class inheritance
axios.Axios = Axios;bind函数:
module.exports = function bind(fn, thisArg) {
return function wrap() {
var args = new Array(arguments.length);
for (var i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
args[i] = arguments[i];
}
return fn.apply(thisArg, args);
};
};
在 Axios 的源码中,我们找到了 axios 对象的定义,很明显默认的 axios 实例是通过 createInstance 方法创建的,该方法最终返回的是Axios.prototype.request 函数对象。同时,我们发现了 Axios的构造函数:
/**
* Create a new instance of Axios
*
* @param {Object} instanceConfig The default config for the instance
*/
function Axios(instanceConfig) {
this.defaults = instanceConfig;
this.interceptors = {
request: new InterceptorManager(),
response: new InterceptorManager()
};
}在构造函数中,我们找到了 axios.interceptors 对象的定义,也知道了 interceptors.request 和 interceptors.response 对象都是 InterceptorManager 类的实例。因此接下来,进一步分析InterceptorManager 构造函数及相关的 use 方法就可以知道任务是如何注册的:
function InterceptorManager() {
this.handlers = [];
}
/**
* Add a new interceptor to the stack
*
* @param {Function} fulfilled The function to handle `then` for a `Promise`
* @param {Function} rejected The function to handle `reject` for a `Promise`
*
* @return {Number} An ID used to remove interceptor later
*/
InterceptorManager.prototype.use = function use(fulfilled, rejected) {
this.handlers.push({
fulfilled: fulfilled,
rejected: rejected
});
return this.handlers.length - 1;
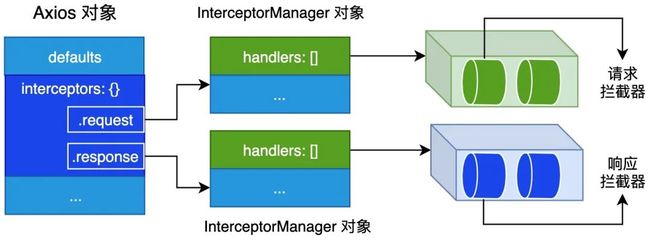
};通过观察 use 方法,我们可知注册的拦截器都会被保存到 InterceptorManager 对象的 handlers 属性中。下面我们用一张图来总结一下 Axios 对象与 InterceptorManager 对象的内部结构与关系:
任务编排
现在我们已经知道如何注册拦截器任务,但仅仅注册任务是不够,我们还需要对已注册的任务进行编排,这样才能确保任务的执行顺序。这里我们把完成一次完整的 HTTP 请求分为处理请求配置对象、发起 HTTP 请求和处理响应对象 3 个阶段。
接下来我们来看一下 Axios 如何发请求的:
axios({
url: '/hello',
method: 'get',
}).then(res =>{
console.log('axios res: ', res)
console.log('axios res.data: ', res.data)
})通过前面的分析,我们已经知道 axios 对象对应的是 Axios.prototype.request 函数对象,该函数的具体实现如下:
Axios.prototype.request = function request(config) {
/*eslint no-param-reassign:0*/
// Allow for axios('example/url'[, config]) a la fetch API
if (typeof config === 'string') {
config = arguments[1] || {};
config.url = arguments[0];
} else {
config = config || {};
}
config = mergeConfig(this.defaults, config);
// Set config.method
if (config.method) {
config.method = config.method.toLowerCase();
} else if (this.defaults.method) {
config.method = this.defaults.method.toLowerCase();
} else {
config.method = 'get';
}
// Hook up interceptors middleware
var chain = [dispatchRequest, undefined];
var promise = Promise.resolve(config);
this.interceptors.request.forEach(function unshiftRequestInterceptors(interceptor) {
chain.unshift(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
this.interceptors.response.forEach(function pushResponseInterceptors(interceptor) {
chain.push(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
while (chain.length) {
promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift());
}
return promise;
};参考资料:
Promise.resolve() - JavaScript | MDN
Promise.prototype.then() - JavaScript | MDN
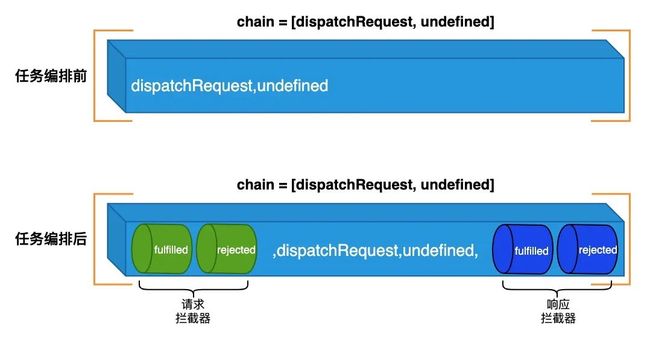
任务编排的代码比较简单,我们来看一下任务编排前和任务编排后的对比图:
任务调度
任务编排完成后,要发起 HTTP 请求,我们还需要按编排后的顺序执行任务调度。在 Axios 中具体的调度方式很简单,具体如下所示:
while (chain.length) {
promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift());
}
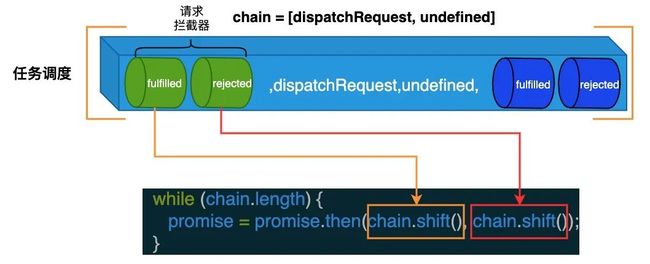
return promise;因为 chain 是数组,所以通过 while 语句我们就可以不断地取出设置的任务,然后组装成 Promise 调用链从而实现任务调度,对应的处理流程如下图所示:
下面我们来回顾一下 Axios 拦截器完整的使用流程:
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
config.headers.token = 'added by interceptor';
return config;
});
// 添加响应拦截器 —— 处理响应对象
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (data) {
data.data = data.data + ' - modified by interceptor';
return data;
});
axios({
url: '/hello',
method: 'get',
}).then(res =>{
console.log('axios res.data: ', res.data)
})介绍完 Axios 的拦截器,我们来总结一下它的优点。Axios 通过提供拦截器机制,让开发者可以很容易在请求的生命周期中自定义不同的处理逻辑。
此外,也可以通过拦截器机制来灵活地扩展 Axios 的功能,比如 Axios 生态中列举的 axios-response-logger 和 axios-debug-log 这两个库。
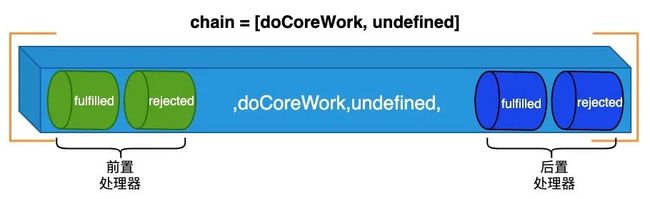
参考 Axios 拦截器的设计模型,我们就可以抽出以下通用的任务处理模型: