09.线程基础知识(八)----线程池
线程池
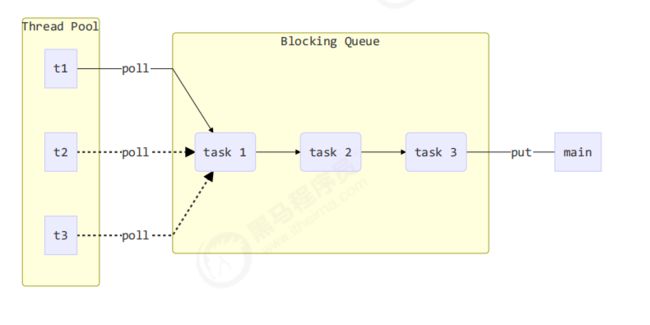
1.自定义线程池
代码实现
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @author Seven
* @create 2021-11-01 16:37
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool")
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int j=i;
threadPool.execute(()->{
log.debug("{}",j);
});
}
}
}
@Slf4j
class ThreadPool{
//任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
//线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> works =new HashSet<>();
//核心线程数
private int coreSize;
//获取任务的超时时间
private int timeout;
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, int timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit,int queueCapcity) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue=new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapcity);
}
//执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task){
//当任务数没有超过coreSize,直接交给worker对象执行
//当任务数超过了coresize,加入任务队列暂存
synchronized (works){
if(works.size()<coreSize){
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增worker{},{}",worker,task);
works.add(worker);
worker.start();
}else {
log.debug("加入任务队列{}",task);
taskQueue.put(task);
}
}
}
class Worker extends Thread{
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task=task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//执行任务
//1)当task不为空,执行任务
//2)当task执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
// while (task!=null||(task=taskQueue.take())!=null){
while (task!=null||(task=taskQueue.poll(timeout,timeUnit))!=null){
try {
log.debug("正在执行---{}",task);
task.run();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
task=null;
}
}
synchronized (works){
log.debug("worker被移除了---{}",task);
works.remove(task);
}
}
}
}
@Slf4j
class BlockingQueue<T>{
//1.任务队列
private Deque<T> queue=new ArrayDeque<>();
//2.锁
private ReentrantLock lock =new ReentrantLock();
//3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet=lock.newCondition();
//4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet=lock.newCondition();
//5.容量上限
private int capcity;
public BlockingQueue(int capcity) {
this.capcity = capcity;
}
//带超时的阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit){
lock.lock();
try {
long nanows = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()){
try {
if(nanows<=0){
return null;
}
nanows = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanows);//返回的是剩余时间
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
return t;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//阻塞获取
public T take(){
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()){
try {
emptyWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//阻塞添加
public void put(T element){
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size()==capcity){
try {
fullWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
queue.add(element);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//获取大小
public int size(){
lock.lock();
try {
return queue.size();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
2.JDK线程池----ThreadPoolExecutor
1) 线程池状态
ThreadPoolExecutor 使用 int 的高 3 位来表示线程池状态,低 29 位表示线程数量
| 状态名 | 高三位 | 接收到新任务 | 处理阻塞队列任务 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Running | 111 | Y | Y | |
| Shutdown | 000 | N | Y | 不会接收新任务,但会处理阻塞队列剩余任务 |
| Stop | 001 | N | N | 会中断正在执行的任务,并抛弃阻塞队列任务 |
| Tidying | 010 | - | - | 任务执行完毕,活动线程为0进开始进入终结 |
| Terminated | 010 | - | - | 终结状态 |
从数字上比较,TERMINATED > TIDYING > STOP > SHUTDOWN > RUNNING
这些信息存储在一个原子变量 ctl 中,目的是将线程池状态与线程个数合二为一,这样就可以用一次 cas 原子操作
进行赋值
// c 为旧值, ctlOf 返回结果为新值
ctl.compareAndSet(c, ctlOf(targetState, workerCountOf(c))));
// rs 为高 3 位代表线程池状态, wc 为低 29 位代表线程个数,ctl 是合并它们
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
2)构造方法
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
- corePoolSize 核心线程数目 (最多保留的线程数)
- maximumPoolSize 最大线程数目
- keepAliveTime 生存时间 - 针对救急线程
- unit 时间单位 - 针对救急线程
- workQueue 阻塞队列
- threadFactory 线程工厂 - 可以为线程创建时起个好名字
- handler 拒绝策略
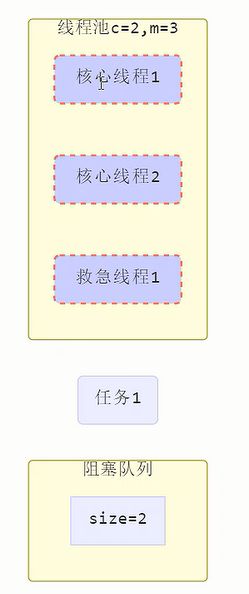
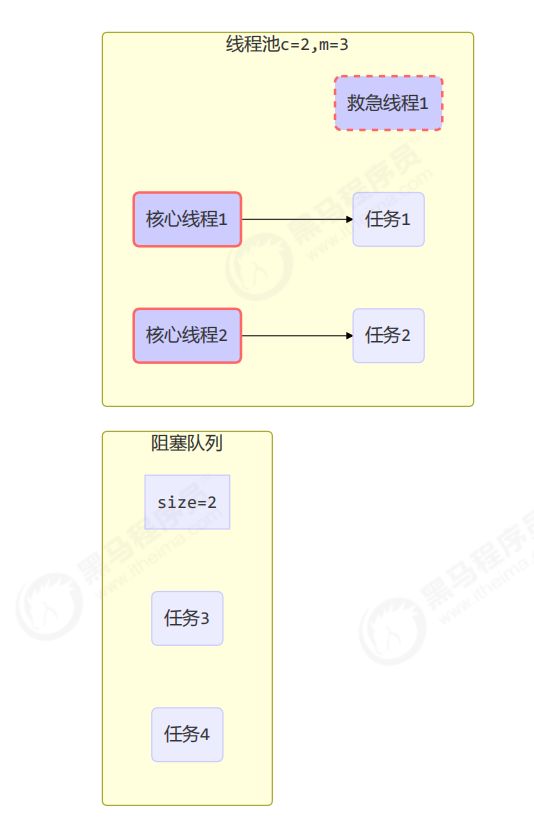
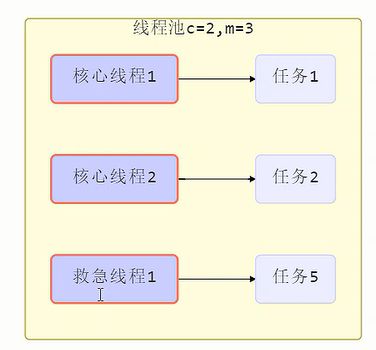
JDK中线程分两种:核心线程+救急线程=最大线程数
- 核心线程创建一直存在
- 救急线程才会有超时时间,救急线程只有在有界队列才存在。
-
线程池中刚开始没有线程,当一个任务提交给线程池后,线程池会创建一个新线程来执行任务。
-
当线程数达到 corePoolSize 并没有线程空闲,这时再加入任务,新加的任务会被加入workQueue 队列排队,直到有空闲的线程。
-
如果队列选择了有界队列,那么任务超过了队列大小时,会创建 maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize 数目的线程来救急。
-
如果线程到达 maximumPoolSize 仍然有新任务这时会执行拒绝策略。拒绝策略 jdk 提供了 4 种实现,其它著名框架也提供了实现
- AbortPolicy 让调用者抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,这是默认策略
- CallerRunsPolicy 让调用者运行任务
- DiscardPolicy 放弃本次任务
- DiscardOldestPolicy 放弃队列中最早的任务,本任务取而代之
其他框架增强
- Dubbo 的实现,在抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常之前会记录日志,并 dump 线程栈信息,方便定位问题
- Netty 的实现,是创建一个新线程来执行任务
- ActiveMQ 的实现,带超时等待(60s)尝试放入队列,类似我们之前自定义的拒绝策略
- PinPoint 的实现,它使用了一个拒绝策略链,会逐一尝试策略链中每种拒绝策略
-
当高峰过去后,超过corePoolSize 的救急线程如果一段时间没有任务做,需要结束节省资源,这个时间由keepAliveTime 和 unit 来控制。
3.JDK Executors 类—工厂方法来创建各种用途的线程池
newFixedThreadPool-----固定大小的线程池
构造方法
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
代码示例
@Slf4j
public class TestThreadPoolExecutors {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("1");
});
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("2");
});
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("3");
});
}
}
19:48:45.037 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestThreadPoolExecutors - 1
19:48:45.037 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestThreadPoolExecutors - 2
19:48:45.040 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestThreadPoolExecutors - 3
newCachedThreadPool----带缓冲线程池
构造方法
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
特点
-
核心线程数是 0, 最大线程数是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,救急线程的空闲生存时间是 60s,意味着
- 全部都是救急线程(60s 后可以回收)
- 救急线程可以无限创建
-
队列采用了 SynchronousQueue 实现特点是,它没有容量,没有线程来取是放不进去的(一手交钱、一手交货)
SynchronousQueue<Integer> integers = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("putting {} ", 1);
integers.put(1);
log.debug("{} putted...", 1);
log.debug("putting...{} ", 2);
integers.put(2);
log.debug("{} putted...", 2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t1").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("taking {}", 1);
integers.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t2").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("taking {}", 2);
integers.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t3").start();
11:48:15.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - putting 1
11:48:16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t2] - taking 1
11:48:16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - 1 putted...
11:48:16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - putting...2
11:48:17.502 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t3] - taking 2
11:48:17.503 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - 2 putted...
评价 整个线程池表现为线程数会根据任务量不断增长,没有上限,当任务执行完毕,空闲 1分钟后释放线程。 适合任务数比较密集,但每个任务执行时间较短的情况
newSingleThreadExecutor----单线程线程池
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue()));
}
使用场景:
希望多个任务排队执行。线程数固定为 1,任务数多于 1 时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这唯一的线程也不会被释放。
区别:
-
自己创建一个单线程串行执行任务,如果任务执行失败而终止那么没有任何补救措施,而线程池还会新建一个线程,保证池的正常工作
-
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() 线程个数始终为1,不能修改
- FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService 应用的是装饰器模式,只对外暴露了 ExecutorService 接口,因此不能调用 ThreadPoolExecutor 中特有的方法
-
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1) 初始时为1,以后还可以修改
- 对外暴露的是 ThreadPoolExecutor 对象,可以强转后调用 setCorePoolSize 等方法进行修改
列子—单线程失败,单线程线程池继续运行
public class TestSynchronousQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test2();
}
private static void test2() {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("1");
int i = 1 / 0;
});
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("2");
});
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("2");
});
}
}
20:09:35.801 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestSynchronousQueue - 1
20:09:35.805 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestSynchronousQueue - 2
20:09:35.805 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestSynchronousQueue - 2
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-1" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.test.TestSynchronousQueue.lambda$test2$0(TestSynchronousQueue.java:23)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1142)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:617)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
4.提交任务
// 执行任务
void execute(Runnable command);
// 提交任务 task,用返回值 Future 获得任务执行结果
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,带超时时间
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消,带超时时间
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
submit
@Slf4j
public class TestSubmit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<String> futrue = pool.submit(new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws InterruptedException {
log.debug("running");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "ok";
}
});
log.debug("{}",futrue.get());
}
}
//运用了保护性暂停模式
20:23:19.139 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - running
20:23:20.146 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - ok
invokeAll
@Slf4j
public class TestSubmit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
List<Future<String>> futures = pool.invokeAll(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "1";
}, () -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(500);
return "2";
}, () -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "3";
}
));
futures.forEach(f->{
try {
log.debug("{}",f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
20:29:04.873 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - begin
20:29:04.873 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - begin
20:29:05.376 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - begin
20:29:07.377 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - 1
20:29:07.381 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - 2
20:29:07.381 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - 3
invokeAny
@Slf4j
public class TestSubmit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
String future = pool.invokeAny(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "1";
}, () -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(500);
return "2";
}, () -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "3";
}
));
log.debug("{}",future);
}
}
20:32:34.694 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - begin
20:32:34.694 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - begin
20:32:35.198 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - begin
20:32:35.198 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestSubmit - 2
5.关闭线程池
shutdown
/*
线程池状态变为 SHUTDOWN
- 不会接收新任务
- 但已提交任务会执行完
- 此方法不会阻塞调用线程的执行
*/
void shutdown();
构造方法
public void shutdown() {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
// 修改线程池状态
advanceRunState(SHUTDOWN);
// 仅会打断空闲线程
interruptIdleWorkers();
onShutdown(); // 扩展点 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 尝试终结(没有运行的线程可以立刻终结,如果还有运行的线程也不会等)
tryTerminate();
}
shutdownNow
/*
线程池状态变为 STOP
- 不会接收新任务
- 会将队列中的任务返回
- 并用 interrupt 的方式中断正在执行的任务
*/
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
构造方法
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {
List<Runnable> tasks;
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
// 修改线程池状态
advanceRunState(STOP);
// 打断所有线程
interruptWorkers();
// 获取队列中剩余任务
tasks = drainQueue();
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 尝试终结
tryTerminate();
return tasks;
}
其它方法
// 不在 RUNNING 状态的线程池,此方法就返回 true
boolean isShutdown();
// 线程池状态是否是 TERMINATED
boolean isTerminated();
// 调用 shutdown 后,由于调用线程并不会等待所有任务运行结束,因此如果它想在线程池 TERMINATED 后做些事
情,可以利用此方法等待
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
代码演示
@Slf4j
public class TestShutDown {
public static void main(String[] args){
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<Integer> result1 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 1 running-----");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("task 1 finish---");
return 1;
});
Future<Integer> result2 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 2 running-----");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("task 2 finish---");
return 1;
});
Future<Integer> result3 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 3 running-----");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("task 3 finish---");
return 1;
});
log.debug("shutdown");
pool.shutdown();
Future<Integer> result4 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 4 running-----");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("task 4 finish---");
return 1;
});
}
}
20:45:16.198 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - shutdown
20:45:16.206 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 2 running-----
20:45:16.205 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 1 running-----
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task java.util.concurrent.FutureTask@593634ad rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@20fa23c1[Shutting down, pool size = 2, active threads = 2, queued tasks = 1, completed tasks = 0]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$AbortPolicy.rejectedExecution(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:2047)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:823)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1369)
at java.util.concurrent.AbstractExecutorService.submit(AbstractExecutorService.java:134)
at com.test.TestShutDown.main(TestShutDown.java:53)
20:45:17.206 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 1 finish---
20:45:17.206 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 2 finish---
20:45:17.206 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 3 running-----
20:45:18.206 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 3 finish---
Process finished with exit code 1
//代码可以运行完了,shutdown只会关闭之后的任务运行
@Slf4j
public class TestShutDown {
public static void main(String[] args){
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<Integer> result1 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 1 running-----");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
log.debug("task 1 finish---");
return 1;
});
Future<Integer> result2 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 2 running-----");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
log.debug("task 2 finish---");
return 1;
});
Future<Integer> result3 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task 3 running-----");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
log.debug("task 3 finish---");
return 1;
});
log.debug("shutdown");
pool.shutdownNow();
log.debug("other");
}
}
20:49:47.557 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - shutdown
20:49:47.557 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 2 running-----
20:49:47.557 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 1 running-----
20:49:47.559 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 1 finish---
20:49:47.559 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 2 finish---
20:49:47.559 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - other
Process finished with exit code 0
//shutdownNow不会等任务运行完直接打断
log.debug("task 3 running-----");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
log.debug("task 3 finish---");
return 1;
});
log.debug("shutdown");
pool.shutdownNow();
log.debug("other");
}
}
```java
20:49:47.557 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - shutdown
20:49:47.557 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 2 running-----
20:49:47.557 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 1 running-----
20:49:47.559 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 1 finish---
20:49:47.559 [pool-1-thread-2] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - task 2 finish---
20:49:47.559 [main] DEBUG com.test.TestShutDown - other
Process finished with exit code 0
//shutdownNow不会等任务运行完直接打断