【数据结构】顺序表---C语言版
【数据结构】顺序表
- 前言:
- 一、线性表
- 二、顺序表
-
- 1.顺序表的概念及结构:
- 2.顺序表的分类:
- 3.顺序表缺陷:
- 三、顺序表的代码实现:
-
- 1.头文件:
- 2.函数文件:
- 3.测试文件:
- 四、顺序表的相关OJ题:
-
- (1)原地移除数组中所有的元素val:
-
- 1.题目描述:
- 2.思路表述:
- 3.代码实现:
- (2)删除有序数组中的重复项
-
- 1.题目描述:
- 2.思路表述:
- 3.代码实现:
- (3)合并两个有序数组
-
- 1.题目描述:
- 2.思路表述:
- 3.代码实现:
前言:
顺序表是一种常见的数据结构,今天就让我来带领大家一起学习一下吧!
不会再休息,一分一毫了,OK,let’s go!
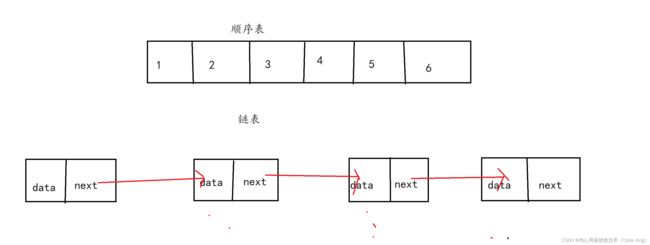
一、线性表
- 线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使
用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串… - 线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,
线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
二、顺序表
1.顺序表的概念及结构:
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存
储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
2.顺序表的分类:
顺序表一般可以分为:
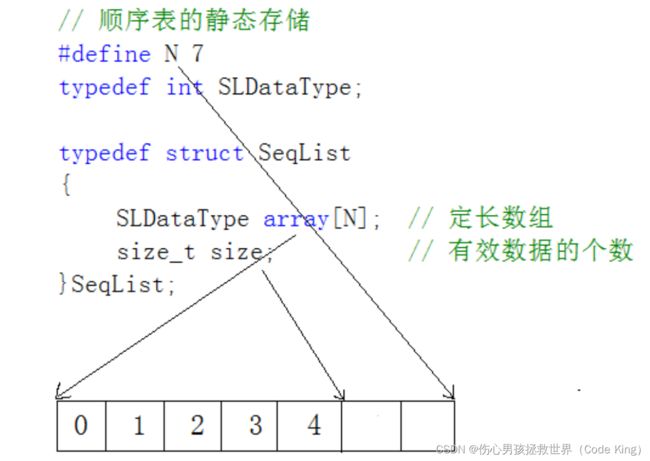
- 静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。
//顺序表的静态存储
#define N 7
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType array[N];//定长数组
size_t size;//有效数据的个数
}SeqList;
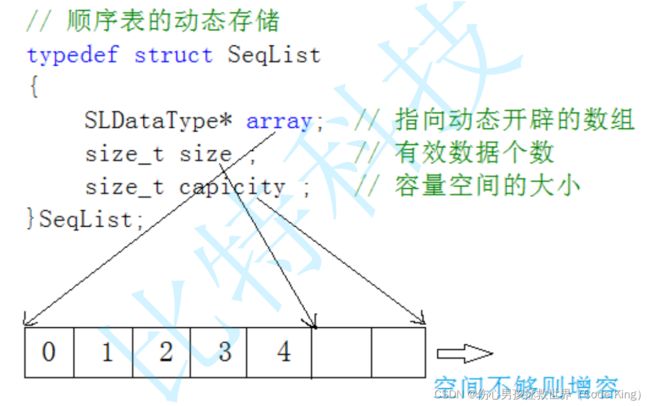
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* array;//指向动态开辟的数组
size_t size;//有效数据的个数
size_t capacity;//容量
}SeqList;
3.顺序表缺陷:
- 顺序表缺陷:
(1)动态增容有性能消耗。
(2)当头部插入数据时,需要挪动数据
三、顺序表的代码实现:
1.头文件:
#pragma once
#include 2.函数文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include 3.测试文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include 四、顺序表的相关OJ题:
(1)原地移除数组中所有的元素val:
1.题目描述:
1.原地移除数组中所有的元素val,要求时间复杂度为O(N),空间复杂度为O(1)。OJ链接:OJ链接

2.思路表述:
3.代码实现:
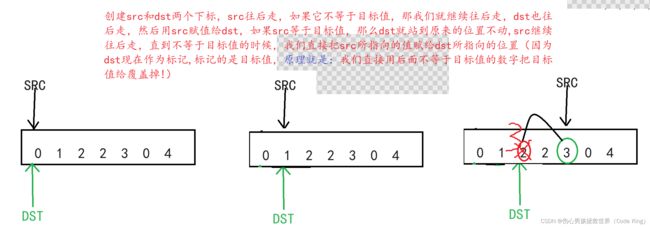
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val)
{
int src=0;
int dst=0;
while(src<numsSize)
{
if(nums[src]!=val)
{
nums[dst++]=nums[src++];
}
else
{
src++;
}
}
return dst;//返回的是:新数组的长度,因为最后一步出循环的时候,dst已经++了,所以说直接返回dst就行了
}
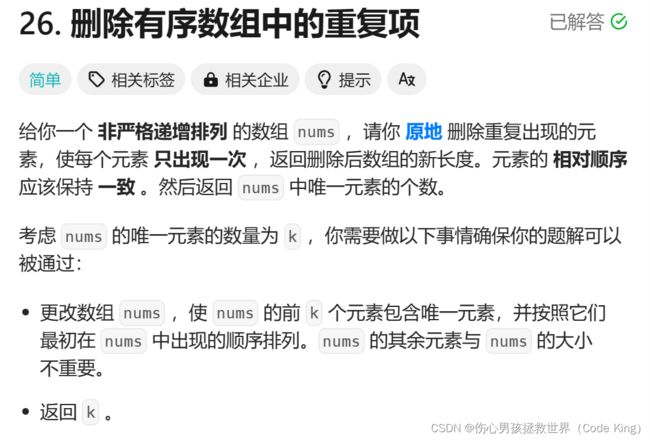
(2)删除有序数组中的重复项
1.题目描述:
2.思路表述:
3.代码实现:
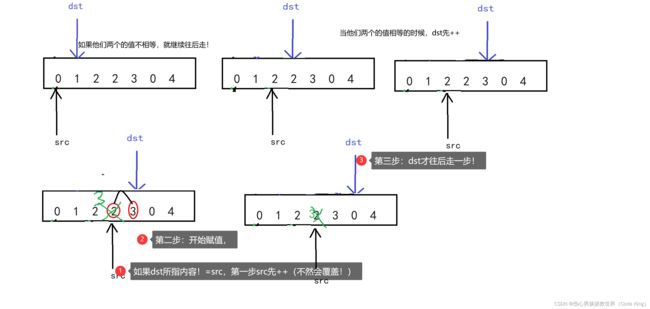
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize)
{
int dst=1;
int src=0;
while(dst<numsSize)
{
if(nums[dst]!=nums[src])
{
//nums[++src]=nums[dst++];//这里的src一定要是前置++,先++,然后再赋值。
src++;
nums[src]=nums[dst];
dst++;
}
else
{
dst++;
}
}
return src+1;
}
(3)合并两个有序数组
1.题目描述:
2.思路表述:
3.代码实现:
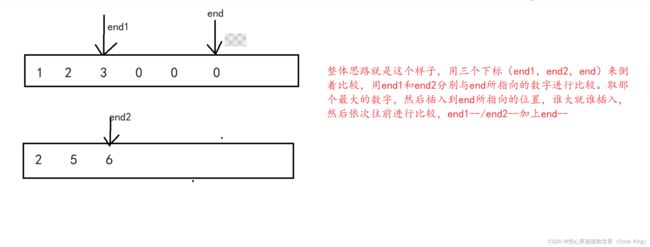
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n)
{
int end1=m-1;
int end2=n-1;
int end=m+n-1;
while(end1>=0&&end2>=0)
{
if(nums1[end1]>nums2[end2])
{
nums1[end--]=nums1[end1--];
}
else
{
nums1[end--]=nums2[end2--];
}
}
//因为用nums1的初始长度是m+n,所以不会担心数组大小不够用。
//下面这个循环是针对:比如说nums1中的所有数字都插到自己数组后面了,但是因为两个数组都是有序的,所以我只需要把nums2中的全部数字依次放到nums1前面就行了。
while(end2>=0)
{
nums1[end--]=nums2[end2--];
}
}
好了,今天的分享就到这里了
如果对你有帮助,记得点赞+关注哦!
我的主页还有其他文章,欢迎学习指点。关注我,让我们一起学习,一起成长吧!