(C语言)实验设备管理系统——源代码和解析(博主复习用)
C语言源代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include//增加Windows头文件为使界面更加美观
const char* file_name = "record2.txt";
//实验设备结构体信息
struct Information{
long int id;//仪器id
char name[200];//姓名
char type[200];//类名
double price;//价格
unsigned int number;
char company[200];//出产公司
char comment[400];//备注
};
//链表结构体——将设备放入链表(此处增添文件读取功能:将文件中信息输出到链表)
struct Info_list{
struct Information*node;
struct Info_list *next;//链接下处结点
};
//由于含有多个功能简化书写,使用枚举enum
enum InfoType{
NONE = 0,
ID =1,
NAME = 2,
TYPE = 3,
PRICE = 4,
NUMBER = 5,
COMPANY = 6,
COMMENT = 7,
ALL = 8
};
char* trimmed(char * c)
{
char* end = NULL;
if (NULL == c)
return c;
end = c + strlen(c) - 1;
while (*c && (*c == ' ' || *c == '\t' || *c == '\n')) {
c++;
}
while (*end && end >= c && end >= c && (*end == ' ' || *end == '\t' || *end == '\n')) {
*end-- = '\0';
}
return c;
}
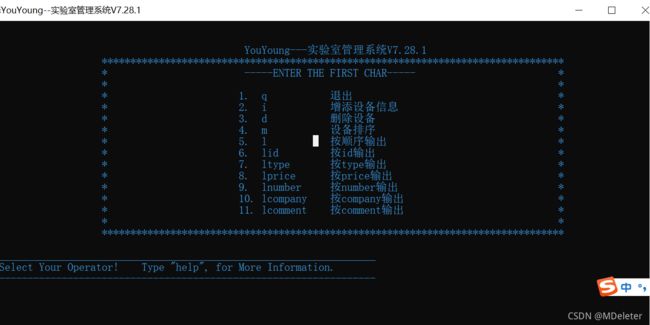
void show_help()
{
printf("\n\n");
printf("\t\t\t YouYoung---实验室管理系统V7.28.1\n");
printf("\t\t\t*********************************************************************************\n");
// printf("\t\t\t\t\t\t-----ENTER THE FIRST CHAR-----\n");
printf("\t\t\t* -----ENTER THE FIRST CHAR----- *\n");
printf("\t\t\t* *\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 1. q\t\t退出\t\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 2. i\t\t增添设备信息\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 3. d\t\t删除设备\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 4. m\t\t设备排序\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 5. l\t\t按顺序输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 6. lid\t\t按id输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 7. ltype\t按type输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 8. lprice\t按price输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 9. lnumber\t按number输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 10. lcompany\t按company输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 11. lcomment\t按comment输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t* *\n");
printf("\t\t\t*********************************************************************************\n");
}
//以下属于链表的文件操作 包含链表在文件中的保存和删除
//向文件末尾添加结构体信息
int write_info_to_file(struct Information* info){
FILE *file;
file = fopen(file_name,"a");
if(!file){
printf("\nError! Cannot Open File %s\n", file_name);
return 0;
}
fputs("\n",file);
fprintf(file, "%ld\n", info->id);
fprintf(file, "%s\n", info->name);
fprintf(file, "%s\n", info->type);
fprintf(file, "%f\n", info->price);
fprintf(file, "%d\n", info->number);
fprintf(file, "%s\n", info->company);
fprintf(file, "%s\n", info->comment);
fputs("\n",file);
fclose(file);
return 1;
}
//链表的文件保存 -wirte操作
int write_list_to_file(struct Info_list* list_head)
{
struct Info_list *list_iter = list_head->next;//类似于迭代器iterator
//文件内容的删除操作,先将原文件中内容删除再重新保存,类似于Python的w操作
FILE *file;
file = fopen(file_name,"w");
if(!file){
printf("\nError! Cannot Open File %s\n", file_name);
return 0;
}
fclose(file);
while(list_iter && list_iter->node){
write_info_to_file(list_iter->node);
list_iter = list_iter->next;
}
return 1;
}
//去除两边空白
//文件的读取操作,保存到链表
struct Info_list* read_from_file(struct Info_list* list_first)
{
FILE *file;
struct Information *info = NULL;
struct Info_list *list_next = NULL;
struct Info_list *list_temp = NULL;
char str[400];
int flag = 0;
file = fopen(file_name,"r");
if(!file){
printf("\nError! Cannot Open File %s\n",file_name);
return NULL;
}
list_temp = list_first;
while((fgets(str, 400, file))!=NULL)//从指定的流 stream 读取一行,并把它存储在 str 所指向的字符串内
{
if(strlen(str)>1){
++flag;
}
else{
continue;
}
if(flag > 7){
flag = 1;
}
switch(flag)
{
case 0:
break;
case 1:
list_next = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
info = (struct Information*)malloc(sizeof(struct Information));
if(NULL == info||NULL == list_first){
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return NULL;
}
list_next->next = NULL;
list_next->node = NULL;
list_temp->node = info;
list_temp->next = list_next;
list_temp = list_next;
info->id = atol(str);//字符串转换成长整型
break;
case 2:
strncpy(info->name,str,200);//char*strncpy(char*dest,const char*src,size_t n)把 src 所指向的字符串复制到dest,最多复制 n 个字符。
trimmed(info->name);//trim()函数用于去除字符串两端的空白字符
break;
case 3:
strncpy(info->type, str,200);
trimmed(info->type);
break;
case 4:
info->price = atof(str);
break;//将字符串转成float型
case 5:
info->number = atoi(str);//转成int型
break;
case 6:
strncpy(info->company,str,200);
trimmed(info->company);
break;
case 7:
strncpy(info->comment,str,400);
trimmed(info->comment);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
fclose(file);
return list_first;
}
//插入数据命令
void insert_information(struct Info_list *list_head)
{
char id_char[200];
char price_char[200];
char number_char[200];
struct Information *info = NULL;
struct Info_list* list_next = NULL;
struct Info_list* list_temp = NULL;
/*
if (!list_head) {
list_head = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
if (NULL == list_head) {
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return ;
}
list_head->next = NULL;
list_head->node = NULL;
}
*/
list_temp = list_head->next;
while(list_temp != NULL && list_temp->node != NULL){
list_temp = list_temp->next;
}
list_next = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
info = (struct Information*)malloc(sizeof(struct Information));
if(NULL == info || NULL == list_next){
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return;
}
list_next->next = NULL;
list_next->node = NULL;
list_temp->next=list_next;
list_temp->node = info;
printf("\nNow Insert a New Data of Devcie.\n");
printf("Please Enter ID, only numeral support, for example: \"123456\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(id_char,200,stdin);
info->id = atol(id_char);
printf("You Typed %ld\n",info->id);
printf("Please Enter Name, for example: \"Kobe Bryant\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->name, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->name);
printf("You Typed %s\n",info->name);
printf("Please Enter Type, for example: \"A\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->type, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->type);
printf("You Typed %s\n",info->type);
printf("Please Enter Price, only numeral support, example: \"123.456\"\n");
printf(">>>>");
fgets(price_char,200,stdin);
info->price = atof(price_char);
printf("You Typed %f\n", info->price);
printf("Please Enter Number, only numeral support, example: \"543210\"\n");
printf(">>>>");
fgets(number_char,200,stdin);
info->number = atof(number_char);
printf("You Typed %u\n", info->number);
printf("Please Enter Company, for example: \"Red Had\"\n");
printf(">>>>");
fgets(info->company,200,stdin);
trimmed(info->company);
printf("You Typed %s\n",info->company);
printf("Please Enter Comment,for example: \"This is Comment\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->comment, 400,stdin);
printf("You Typed %s\n",info->comment);
trimmed(info->comment);
write_info_to_file(info);
}
void list_information(struct Info_list *list_head)
{
struct Info_list *list_temp = list_head->next;
struct Information *temp = NULL;
while(list_temp !=NULL && list_temp->node !=NULL){
temp = list_temp->node;
printf("\n ID: %ld", temp->id);
printf("\t Name: %s", temp->name);
printf("\t Type %s",temp->type);
printf("\t Price: %.2f", temp->price);
printf("\t Number: %u",temp->number);
printf("\t Company: %s", temp->company);
printf("\t Comment: %s\n",temp->comment);
list_temp = list_temp->next;
}
}
//按相应的排序方法显示数据
void list_information_order(struct Info_list *list_head,const char* which)
{
struct Info_list *list_temp = list_head->next;
struct Info_list *swap_temp = NULL;
struct SortHelp
{
struct Info_list* node;
int flag;
struct SortHelp *next;
};
struct SortHelp *sort_head = NULL;
struct SortHelp *sort_iter = NULL;
struct SortHelp *sort_one = NULL;
struct SortHelp *sort_min = NULL;
struct SortHelp *sort_temp = NULL;
struct Information * info_temp = NULL;
int sort_num = 0;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
//新建链表保存原链表的信息
//copy Info_list to SortHelp
while(list_temp&&list_temp->node!=NULL){
sort_one = (struct SortHelp*)malloc(sizeof(struct SortHelp));
if(NULL == sort_one){
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
sort_iter = sort_head;
while(sort_iter) {
sort_temp = sort_iter;
sort_iter = sort_iter->next;
free(sort_temp);
}
return;
}
sort_one->node = list_temp;
sort_one->flag = 0;
sort_one->next = NULL;
if(NULL == sort_head){
sort_head = sort_one;
sort_iter = sort_head;
} else{
sort_iter->next = sort_one;
sort_iter = sort_iter->next;
}
list_temp = list_temp->next;
++sort_num;
}
//冒泡排序
for(i = sort_num; i >0; --i){
sort_iter = sort_head;
//跳过之前已经排好序的结点
for(j=0;jnext;
}
sort_temp = sort_iter;
//找到数值最小的结点
sort_min = sort_iter;
while(sort_iter) {
if (0 == sort_iter->flag) {
if (0 == strcmp(which, "id")) {
if (sort_iter->node->node->id < sort_min->node->node->id)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "name")) {
if (strcmp(sort_iter->node->node->name , sort_min->node->node->name) < 0)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "price")) {
if (sort_iter->node->node->price < sort_min->node->node->price)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "type")) {
if (strcmp(sort_iter->node->node->type , sort_min->node->node->type) < 0)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "company")) {
if (strcmp(sort_iter->node->node->company , sort_min->node->node->company) < 0)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "comment")) {
if (strcmp(sort_iter->node->node->comment , sort_min->node->node->comment) < 0)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "number")) {
if (sort_iter->node->node->number < sort_min->node->node->number)
sort_min = sort_iter;
}
}
sort_iter = sort_iter->next;
}
// (sort_min->flag)++;
swap_temp = sort_min->node;
sort_min->node = sort_temp->node;
sort_temp->node = swap_temp;
}
//将排序后的链表中得数据输出,并释放内存,防止内存泄漏
sort_iter = sort_head;
while(sort_iter){
info_temp = sort_iter->node->node;
printf("\n id: %ld",info_temp->id);
printf("\t name: %s",info_temp->name);
printf("\t type: %s", info_temp->type);
printf("\t price: %.2f", info_temp->price);
printf("\t Number: %u",info_temp->number);
printf("\n Company: %s",info_temp->company);
printf(" Comment: %s\n",info_temp->comment);
sort_temp = sort_iter;
sort_iter = sort_iter->next;
free(sort_temp);
}
}
//从链表中删除指定ID记录
void delete_id_in_list(struct Info_list *list_head, long int id)
{
struct Info_list * list_iter = list_head->next;
struct Info_list * list_pre = list_head;
struct Information * info = NULL;
while(list_iter && list_iter->node){
if(info->id == id){
free(info);
list_iter->node=NULL;
//释放当前内存,指针回退
list_pre->next = list_iter->next;
free(list_iter);
list_iter=list_pre;
}
list_pre= list_iter;//初始化
list_iter = list_iter->next;
}
}
//删除指定记录
void delete_information(struct Info_list * list_head)
{
char condition[100];
char * trimmed_condition = NULL;
long int id;
printf("Enter ID which you want delete. \n>>>> ");
fgets(condition,100,stdin);
trimmed_condition = trimmed(condition);
id = atol(trimmed_condition);
delete_id_in_list(list_head,id);
write_list_to_file(list_head);//保存
}
//查找数据
void search_information(struct Info_list * list_head,enum InfoType type)
{
enum HaveInfo{
HAVE = 1,
UNHAVE = 2
};
struct Info_list * list_iter = list_head->next;
char condition[100];
char char_id[100];
char char_price[100];
char char_number[100];
char * trimmed_condition = NULL;
struct Information * info = NULL;
enum HaveInfo is_have = UNHAVE;
if(ALL == type){
printf("Enter your condition below. (support fuzzy search) \n>>>>");
}else{
printf("Enter your condition below. \n>>>>");
}
fgets(condition, 100,stdin);
trimmed_condition = trimmed(condition);
while(list_iter && list_iter->node){
info = list_iter->node;
is_have =UNHAVE;
sprintf(char_id,"%ld",info->id);
sprintf(char_price, "%f",info->price);
sprintf(char_number,"%u",info->number);
switch(type){
case ALL:
if(strstr(char_id,trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(info->name, trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(info->type, trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(char_price, trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(info->company,trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(info->comment, trimmed_condition)
)
is_have = HAVE;
break;
case ID:
if(strstr(char_id,trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case NAME:
if(strstr(info->name,trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case TYPE:
if(strstr(info->type,trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case PRICE:
if(strstr(char_price, trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case COMPANY:
if(strstr(info->company, trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case COMMENT:
if(strstr(info->comment, trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
dafault:
is_have = UNHAVE;
break;
}
if(HAVE == is_have){
printf("\n ID: %ld", info->id);
printf("\t Name: %s", info->name);
printf("\t Type %s", info->type);
printf("\t Price: %.2f", info->price);
printf("\t Number: %u", info->number);
printf("\t Company: %s", info->company);
printf("\t Comment: %s\n", info->comment);
}
list_iter = list_iter->next;
}
}
void modify_information(struct Info_list *list_head)
{
struct Info_list * list_iter = list_head->next;
char condition[100];
char * trimmed_condition = NULL;
long int id;
struct Information * info_temp = NULL;
struct Information * info = NULL;
char id_char[200];
char price_char[200];
char number_char[200];
printf("Enter ID which you want modify. \n>>>> ");
fgets(condition, 100, stdin);
trimmed_condition = trimmed(condition);
id = atol(trimmed_condition);
while(list_iter && list_iter->node){
if(list_iter->node->id == id){
break;
}
list_iter = list_iter->next;
}
info_temp = list_iter->node;
if(!info_temp){
return;
}
printf("\n id: %ld", info_temp->id);
printf("\t name: %s", info_temp->name);
printf("\t type: %s", info_temp->type);
printf("\t price: %.2f", info_temp->price);
printf("\t Number: %u", info_temp->number);
printf("\n Company: %s", info_temp->company);
printf(" Comment: %s\n", info_temp->comment);
info = info_temp;
printf("\nNow Enter New Data of This Information.\n");
printf("Plase Enter ID, only numeral support, for example: \"123456\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(id_char, 200, stdin);
info->id = atol(id_char);
printf("You Typed %ld\n", info->id);
printf("Plase Enter Name, for example: \"Kobe Bryant\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->name, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->name);
printf("You Typed %s\n", info->name);
printf("Plase Enter Type, for example: \"A\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->type, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->type);
printf("You Typed %s\n", info->type);
printf("Plase Enter Price, only numeral support, example: \"123.456\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(price_char, 200, stdin);
info->price = atof(price_char);
printf("You Typed %f\n", info->price);
printf("Plase Enter Number, only numeral support, example: \"543210\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(number_char, 200, stdin);
info->number = atoi(number_char);
printf("You Typed %u\n", info->number);
printf("Plase Enter Company, for example: \"Red Had\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->company, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->company);
printf("You Typed %s\n", info->company);
printf("Plase Enter Comment, for example: \"This is Comment\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->comment, 400, stdin);
printf("You Typed %s\n", info->comment);
trimmed(info->comment);
//保存文件
write_list_to_file(list_head);
}
void select_operator(char operator[100],struct Info_list * list_head)
{
if( 0== strcmp(operator,"help")){
system("cls");
show_help();
}
/* 插入新数据 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "i"))
insert_information(list_head);
/* 显示数据,按插入时间输出,或按某个字段排序后输出 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "l"))
list_information(list_head);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lid"))
list_information_order(list_head, "id");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lname"))
list_information_order(list_head, "name");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lprice"))
list_information_order(list_head, "price");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lnumber"))
list_information_order(list_head, "number");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "ltype"))
list_information_order(list_head, "type");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lcompany"))
list_information_order(list_head, "company");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lcomment"))
list_information_order(list_head, "comment");
/* 删除 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "d"))
delete_information(list_head);
/* 查找数据,全文模糊查找或按字段模糊查找 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "s"))
search_information(list_head , ALL);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "sid"))
search_information(list_head, ID);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "sname"))
search_information(list_head, NAME);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "sprice"))
search_information(list_head, PRICE);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "stype"))
search_information(list_head, TYPE);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "snumber"))
search_information(list_head, NUMBER);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "scompany"))
search_information(list_head, COMPANY);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "scomment"))
search_information(list_head, COMMENT);
/* 修改 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "m"))
modify_information(list_head);
}
void freeMem(struct Info_list* list_head)
{
struct Info_list * list_temp = list_head;
struct Info_list * list_next = NULL;
while(list_temp){
if(list_temp->node){
free(list_temp->node);
}
if(list_temp->next){
list_next = list_temp->next;
free(list_temp);
list_temp = list_next;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
int main(){
system("title YouYoung--实验室管理系统V7.28.1");
system("color 3");
show_help();
char operator[100];
char * trimmed_operator = NULL;
struct Info_list * list_first = NULL;
/* 给链表的头结点分配内存,并初始化数据为NULL */
struct Info_list * list_head = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
if (NULL == list_head) {
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return 0;
}
list_head->next = NULL;
list_head->node = NULL;
/* 给链表的第一个结点分配内存,并初始化数据为NULL */
list_first = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
if (NULL == list_first) {
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return 0;
}
list_first->next = NULL;
list_first->node = NULL;
list_head->next = list_first;
/* 从保存的文件读取数据,并将数据保存到链表当中 */
read_from_file(list_first);
/* 循环执行用户输入的指令,直到输入退出指令 "q" */
do{
printf("\n________________________________________________________________________\n");
printf("Plese Select Your Operator! ");
printf("Type \"help\", for More Information.\n");
printf("------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(operator, 100, stdin);
trimmed_operator = trimmed(operator);
select_operator(trimmed_operator, list_head);
} while (strcmp(operator, "q") != 0);
/* 释放链表所申请的内存,防止内存泄露 */
freeMem(list_head);
return 0;
}
以下为解析 :
主体把握:
这类管理系统的主要功能无非是增删改查四大模块:
再者在只用C语言,C版数据结构完成的情况下,最简单,能想到的结构——顺序表、链表、双向链表、循环链表...
选取一个喜欢的(能写的出来则能称为喜欢)
在此,我选择的是单向链表。
(在此注意,由线性表分为以数组为基础的和以链表为基础的)
要是你准备从事后端工作,算法学习,参加ACM比赛(ACM用的基础算法大多是SB树,AVL树,红黑树都用的少)
链表是逃不过的基础中的基础,但是所谓的基础不代表着它简单,只是需要的预备知识很少,属于新的起点,新的概念。
明确任务
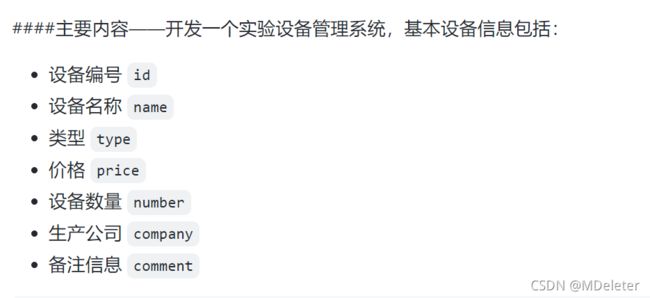
在没有思路的情况下,可以先将题目中提供的要求翻译成C语言:
在此之前可以包含万能头文件
#include
//其中包含许多基本头文件,是个头文件的集合。刷PTA,POJ,LC的同学们应该懂的 上面题目中给出的都是实验设备的需要包含的属性,也就是所有的变量。
那我可以将一个设备看成是一个结构类型。
类中包含这样的变量——(看不懂不要急,慢慢的打开C语言结构那一章)
//实验设备结构体信息
struct Information{
long int id;//仪器id
char name[200];//姓名
char type[200];//类名
double price;//价格
unsigned int number;
char company[200];//出产公司
char comment[400];//备注
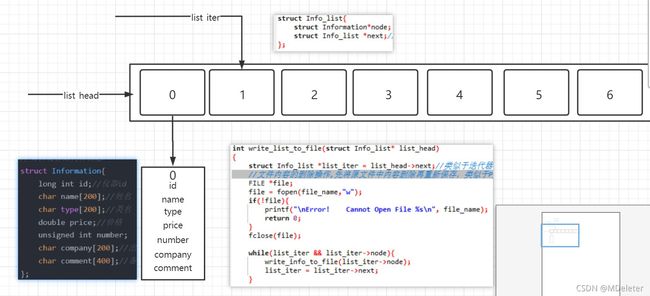
};这样我还需要写一个链表的结构体,因为我下面的增删改查是通过链表为基础的
//链表结构体——将设备放入链表(此处增添文件读取功能:将文件中信息输出到链表)
struct Info_list{
struct Information*node;
struct Info_list *next;//链接下处结点
};
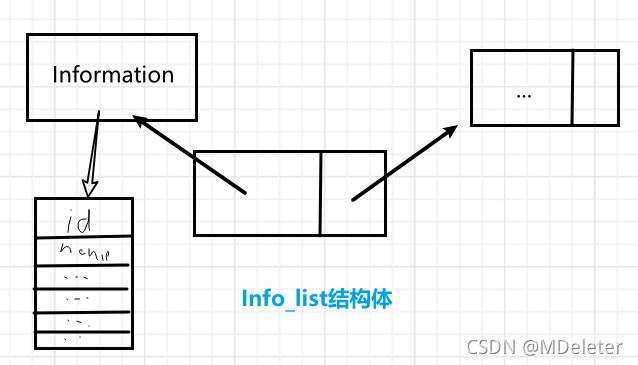
上面我定义了一个名为Info_list的结构体。每个Info_list结构体,里面都有两个结构体:一个Information结构一个Info_list结构。为了区分这些个结构体,我们起了名字,一个叫node,一个叫next,这样两个Info_list就有了区别。
其实这段是为了新手能够理解,才胡编出的,真实的结构体是由指针指向。结构体进行实例化后,每个类名为Info_list的实例化对象,都可以有一个指向Information的指针——用来访问Information中的信息,一个指向下一个Info_list的指针——用来访问下一个节点
到目前为止我们可以写出如下的代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include//增加Windows头文件为使界面更加美观
//我并未使用万能头文件,后面方便解释方法来自哪个头文件
//万能头文件#include
const char* file_name = "record2.txt";
//程序的信息最后要导入到txt文档中,因此我先定义file_name=文档名字,后面直接使用变量
//实验设备结构体信息
struct Information{
long int id;//仪器id
char name[200];//姓名
char type[200];//类名
double price;//价格
unsigned int number;
char company[200];//出产公司
char comment[400];//备注
};
//链表结构体——将设备放入链表(此处增添文件读取功能:将文件中信息输出到链表)
struct Info_list{
struct Information*node;
struct Info_list *next;//链接下处结点
};
实际编程中,经常常会遇到字符串两侧有数量不定的空格,导致难以匹配。所以去除字符串两侧的空格就显得很重要了
Qt可以使用QString中的方法
#include
str.trimmed() 可是这是C语言,不是Qt,没有trimmed()函数。
但我们完全可以凭借需求和函数功能写出一个C语言版的trimmed()函数:
现在精华来了:
如何创建一个函数?
首先我们要知道给这个函数起个名字:
就叫:trimmed v.修剪; 修整; 切去,割掉,剪下
那么定义函数需要什么?
当然是返回值和参数:
这个函数用在文本上——因此它的返回值一个也是一个文本类型
char* trimmed(???):此时,trimmed函数参数未知,但我知道它会返回一个指向char类型的指针。
为啥要返回指针,返回目标指针是便于字符串处理函数的嵌套。
假设参数为指针类型的话,我就能可以调用trimmed函数让它重复的处理已经处理过的字符串。
那trimmed函数的思路就出来了,为了让它能够嵌套的处理字符串,我最好让参数和返回值类型都为char*
于是:char* trimmed(char * c)
c为形参,而形参只起到提示的作用,叫什么都行。
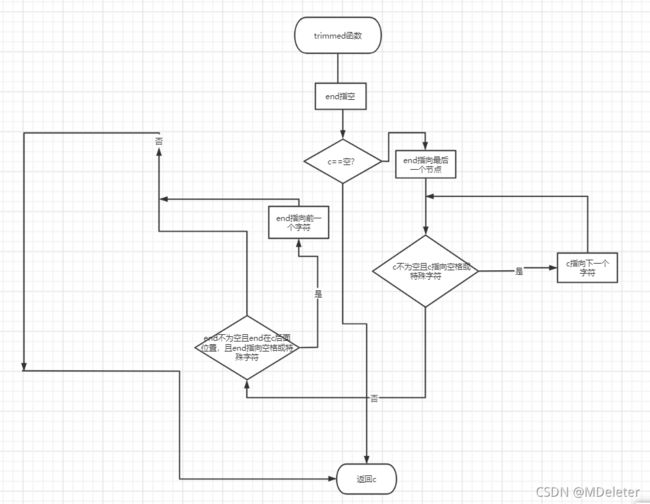
char* trimmed(char * c)的细节
- 先定义一个指向char类型的尾指针end将其赋值为空,将这个end指向字符串中最后一个字符
- 如果输入的字符为空:函数结束,返回这个空的指针;
- 当输入的字符串不为空,且字符串的首个字符为空格或制表符'\t'或换行符\n,不要它将首字符设置为下一个位置
- 当end指向的最后一个字符不为空,且end的位置比首字符位置高(说明位置存储信息无问题,涉及计算机组成原理,科班的要知道),且最后一个字符为空格或制表符'\t'或换行符\n,不要它将首字符设置为上一个位置
下面是C语言实现自定义char* trimmed(char* c)函数:
char* trimmed(char * c)
{
char* end = NULL;
if (NULL == c)
return c;
end = c + strlen(c) - 1;
while (*c && (*c == ' ' || *c == '\t' || *c == '\n')) {
c++;
}
while (*end && end >= c && end >= c && (*end == ' ' || *end == '\t' || *end == '\n')) {
*end-- = '\0';
}
return c;
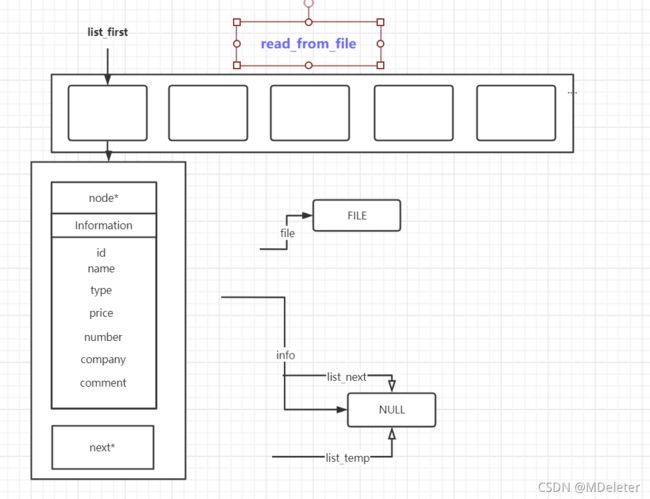
}trimmed函数流程图
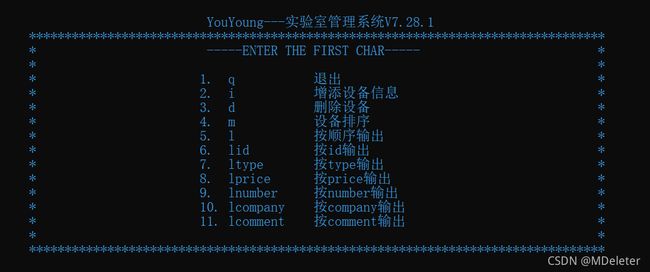
下面做的是显示页面:
void show_help()
{
printf("\n\n");
printf("\t\t\t YouYoung---实验室管理系统V7.28.1\n");
printf("\t\t\t*********************************************************************************\n");
// printf("\t\t\t\t\t\t-----ENTER THE FIRST CHAR-----\n");
printf("\t\t\t* -----ENTER THE FIRST CHAR----- *\n");
printf("\t\t\t* *\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 1. q\t\t退出\t\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 2. i\t\t增添设备信息\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 3. d\t\t删除设备\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 4. m\t\t设备排序\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 5. l\t\t按顺序输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 6. lid\t\t按id输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 7. ltype\t按type输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 8. lprice\t按price输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 9. lnumber\t按number输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 10. lcompany\t按company输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t*\t 11. lcomment\t按comment输出\t\t\t\t*\n");
printf("\t\t\t* *\n");
printf("\t\t\t*********************************************************************************\n");
}将其写成函数 show_help()方便在程序中进行调用。
提示:显示界面自己调试起来比较麻烦,如果可以,尽量从网上找个好些的模板,一个字符一个字符地码位置很耗时间。
文件操作:预备知识
1.打开文件
可以使用 fopen( ) 函数来创建一个新的文件或者打开一个已有的文件,这个调用会初始化类型 FILE 的一个对象,类型 FILE 包含了所有用来控制流的必要的信息。下面是这个函数调用的原型:
FILE *fopen( const char * filename, const char * mode );在这里,filename 是字符串,用来命名文件,访问模式 mode 的值可以是下列值中的一个:
| 模式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| r | 打开一个已有的文本文件,允许读取文件。 |
| w | 打开一个文本文件,允许写入文件。如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新文件。在这里,您的程序会从文件的开头写入内容。如果文件存在,则该会被截断为零长度,重新写入。 |
| a | 打开一个文本文件,以追加模式写入文件。如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新文件。在这里,您的程序会在已有的文件内容中追加内容。 |
| r+ | 打开一个文本文件,允许读写文件。 |
| w+ | 打开一个文本文件,允许读写文件。如果文件已存在,则文件会被截断为零长度,如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新文件。 |
| a+ | 打开一个文本文件,允许读写文件。如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新文件。读取会从文件的开头开始,写入则只能是追加模式。 |
如果处理的是二进制文件,则需使用下面的访问模式来取代上面的访问模式:
"rb", "wb", "ab", "rb+", "r+b", "wb+", "w+b", "ab+", "a+b"2.关闭文件
为了关闭文件,请使用 fclose( ) 函数。函数的原型如下:
int fclose( FILE *fp );如果成功关闭文件,fclose( ) 函数返回零,如果关闭文件时发生错误,函数返回 EOF。这个函数实际上,会清空缓冲区中的数据,关闭文件,并释放用于该文件的所有内存。EOF 是一个定义在头文件 stdio.h 中的常量。
C 标准库提供了各种函数来按字符或者以固定长度字符串的形式读写文件。
3.写入文件
下面是把字符写入到流中的最简单的函数:
int fputc( int c, FILE *fp );函数 fputc() 把参数 c 的字符值写入到 fp 所指向的输出流中。如果写入成功,它会返回写入的字符,如果发生错误,则会返回 EOF。您可以使用下面的函数来把一个以 null 结尾的字符串写入到流中:
int fputs( const char *s, FILE *fp );函数 fputs() 把字符串 s 写入到 fp 所指向的输出流中。如果写入成功,它会返回一个非负值,如果发生错误,则会返回 EOF。您也可以使用 int fprintf(FILE *fp,const char *format, ...) 函数把一个字符串写入到文件中。
注意:请确保您有可用的 tmp 目录,如果不存在该目录,则需要在您的计算机上先创建该目录。
/tmp 一般是 Linux 系统上的临时目录,如果你在 Windows 系统上运行,则需要修改为本地环境中已存在的目录,例如: C:\tmp、D:\tmp等。
管理系统一般都会需要将输入数据保存到文件中,下面是基于链表的文件操作
//向文件末尾添加结构体信息
int write_info_to_file(struct Information* info){
FILE *file;
file = fopen(file_name,"a");
if(!file){
printf("\nError! Cannot Open File %s\n", file_name);
return 0;
}
fputs("\n",file);
fprintf(file, "%ld\n", info->id);
fprintf(file, "%s\n", info->name);
fprintf(file, "%s\n", info->type);
fprintf(file, "%f\n", info->price);
fprintf(file, "%d\n", info->number);
fprintf(file, "%s\n", info->company);
fprintf(file, "%s\n", info->comment);
fputs("\n",file);
fclose(file);
return 1;
}C 库函数 int fprintf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...) 发送格式化输出到流 stream 中。
下面是 fprintf() 函数的声明。
int fprintf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...)
- stream -- 这是指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象标识了流。
- format -- 这是 C 字符串,包含了要被写入到流 stream 中的文本。它可以包含嵌入的 format 标签,format 标签可被随后的附加参数中指定的值替换,并按需求进行格式化。format 标签属性是 %[flags][width][.precision][length]specifier
·链表的文件保存
//链表的文件保存 -wirte操作
int write_list_to_file(struct Info_list* list_head)
{
struct Info_list *list_iter = list_head->next;//类似于迭代器iterator
//文件内容的删除操作,先将原文件中内容删除再重新保存,类似于Python的w操作
FILE *file;
file = fopen(file_name,"w");
if(!file){
printf("\nError! Cannot Open File %s\n", file_name);
return 0;
}
fclose(file);
while(list_iter && list_iter->node){
write_info_to_file(list_iter->node);
list_iter = list_iter->next;
}
return 1;
}·链表的文件读取
//文件的读取操作,保存到链表
struct Info_list* read_from_file(struct Info_list* list_first)
{
FILE *file;
struct Information *info = NULL;
struct Info_list *list_next = NULL;
struct Info_list *list_temp = NULL;
char str[400];
int flag = 0;
file = fopen(file_name,"r");
if(!file){
printf("\nError! Cannot Open File %s\n",file_name);
return NULL;
}
list_temp = list_first;
while((fgets(str, 400, file))!=NULL)//从指定的流 stream 读取一行,并把它存储在 str 所指向的字符串内
{
if(strlen(str)>1){
++flag;
}
else{
continue;
}
if(flag > 7){
flag = 1;
}
switch(flag)
{
case 0:
break;
case 1:
list_next = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
info = (struct Information*)malloc(sizeof(struct Information));
if(NULL == info||NULL == list_first){
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return NULL;
}
list_next->next = NULL;
list_next->node = NULL;
list_temp->node = info;
list_temp->next = list_next;
list_temp = list_next;
info->id = atol(str);//字符串转换成长整型
break;
case 2:
strncpy(info->name,str,200);//char*strncpy(char*dest,const char*src,size_t n)把 src 所指向的字符串复制到dest,最多复制 n 个字符。
trimmed(info->name);//trim()函数用于去除字符串两端的空白字符
break;
case 3:
strncpy(info->type, str,200);
trimmed(info->type);
break;
case 4:
info->price = atof(str);
break;//将字符串转成float型
case 5:
info->number = atoi(str);//转成int型
break;
case 6:
strncpy(info->company,str,200);
trimmed(info->company);
break;
case 7:
strncpy(info->comment,str,400);
trimmed(info->comment);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
fclose(file);
return list_first;
} 数据的插入操作
//插入数据命令
void insert_information(struct Info_list *list_head)
{
char id_char[200];
char price_char[200];
char number_char[200];
struct Information *info = NULL;
struct Info_list* list_next = NULL;
struct Info_list* list_temp = NULL;
/*
if (!list_head) {
list_head = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
if (NULL == list_head) {
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return ;
}
list_head->next = NULL;
list_head->node = NULL;
}
*/
list_temp = list_head->next;
while(list_temp != NULL && list_temp->node != NULL){
list_temp = list_temp->next;
}
list_next = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
info = (struct Information*)malloc(sizeof(struct Information));
if(NULL == info || NULL == list_next){
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return;
}
list_next->next = NULL;
list_next->node = NULL;
list_temp->next=list_next;
list_temp->node = info;
printf("\nNow Insert a New Data of Devcie.\n");
printf("Please Enter ID, only numeral support, for example: \"123456\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(id_char,200,stdin);
info->id = atol(id_char);
printf("You Typed %ld\n",info->id);
printf("Please Enter Name, for example: \"Kobe Bryant\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->name, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->name);
printf("You Typed %s\n",info->name);
printf("Please Enter Type, for example: \"A\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->type, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->type);
printf("You Typed %s\n",info->type);
printf("Please Enter Price, only numeral support, example: \"123.456\"\n");
printf(">>>>");
fgets(price_char,200,stdin);
info->price = atof(price_char);
printf("You Typed %f\n", info->price);
printf("Please Enter Number, only numeral support, example: \"543210\"\n");
printf(">>>>");
fgets(number_char,200,stdin);
info->number = atof(number_char);
printf("You Typed %u\n", info->number);
printf("Please Enter Company, for example: \"Red Had\"\n");
printf(">>>>");
fgets(info->company,200,stdin);
trimmed(info->company);
printf("You Typed %s\n",info->company);
printf("Please Enter Comment,for example: \"This is Comment\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->comment, 400,stdin);
printf("You Typed %s\n",info->comment);
trimmed(info->comment);
write_info_to_file(info);
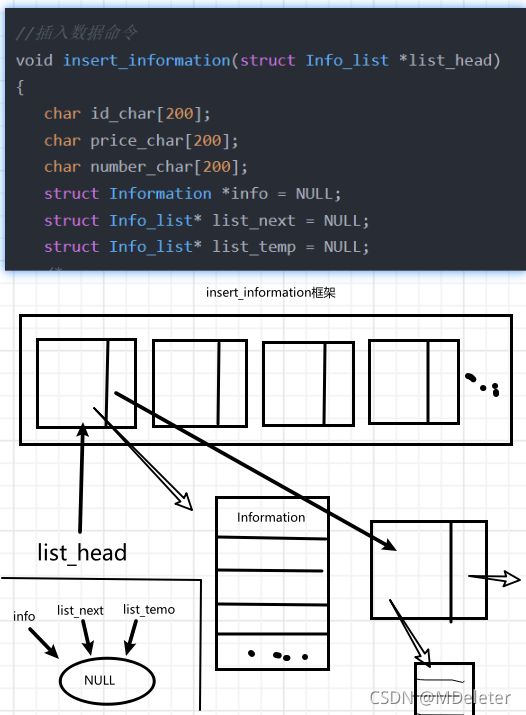
}·insert_information框架
输出用顺序表相连的设备信息
void list_information(struct Info_list *list_head)
{
struct Info_list *list_temp = list_head->next;
struct Information *temp = NULL;
while(list_temp !=NULL && list_temp->node !=NULL){
temp = list_temp->node;
printf("\n ID: %ld", temp->id);
printf("\t Name: %s", temp->name);
printf("\t Type %s",temp->type);
printf("\t Price: %.2f", temp->price);
printf("\t Number: %u",temp->number);
printf("\t Company: %s", temp->company);
printf("\t Comment: %s\n",temp->comment);
list_temp = list_temp->next;
}
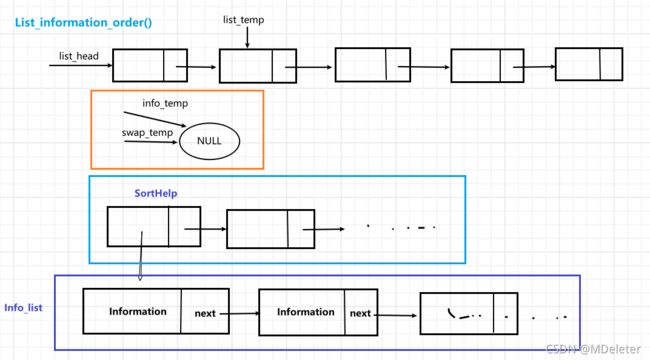
} 将数据按照要求进行排序显示:
//按相应的排序方法显示数据
void list_information_order(struct Info_list *list_head,const char* which)
{
struct Info_list *list_temp = list_head->next;
struct Info_list *swap_temp = NULL;
struct SortHelp
{
struct Info_list* node;
int flag;
struct SortHelp *next;
};
struct SortHelp *sort_head = NULL;
struct SortHelp *sort_iter = NULL;
struct SortHelp *sort_one = NULL;
struct SortHelp *sort_min = NULL;
struct SortHelp *sort_temp = NULL;
struct Information * info_temp = NULL;
int sort_num = 0;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
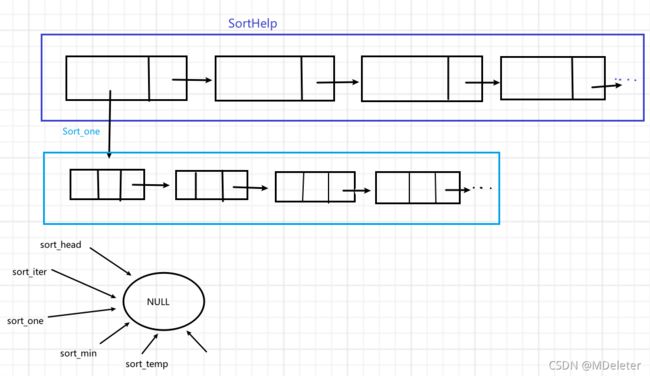
//新建链表保存原链表的信息
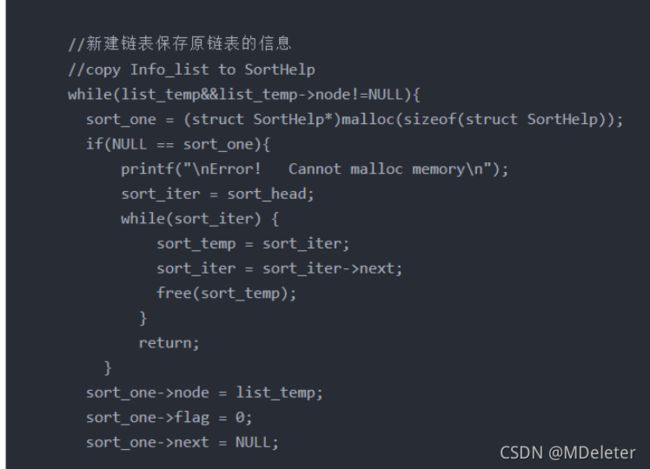
//copy Info_list to SortHelp
while(list_temp&&list_temp->node!=NULL){
sort_one = (struct SortHelp*)malloc(sizeof(struct SortHelp));
if(NULL == sort_one){
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
sort_iter = sort_head;
while(sort_iter) {
sort_temp = sort_iter;
sort_iter = sort_iter->next;
free(sort_temp);
}
return;
}
sort_one->node = list_temp;
sort_one->flag = 0;
sort_one->next = NULL;
if(NULL == sort_head){
sort_head = sort_one;
sort_iter = sort_head;
} else{
sort_iter->next = sort_one;
sort_iter = sort_iter->next;
}
list_temp = list_temp->next;
++sort_num;
}
//冒泡排序
for(i = sort_num; i >0; --i){
sort_iter = sort_head;
//跳过之前已经排好序的结点
for(j=0;jnext;
}
sort_temp = sort_iter;
//找到数值最小的结点
sort_min = sort_iter;
while(sort_iter) {
if (0 == sort_iter->flag) {
if (0 == strcmp(which, "id")) {
if (sort_iter->node->node->id < sort_min->node->node->id)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "name")) {
if (strcmp(sort_iter->node->node->name , sort_min->node->node->name) < 0)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "price")) {
if (sort_iter->node->node->price < sort_min->node->node->price)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "type")) {
if (strcmp(sort_iter->node->node->type , sort_min->node->node->type) < 0)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "company")) {
if (strcmp(sort_iter->node->node->company , sort_min->node->node->company) < 0)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "comment")) {
if (strcmp(sort_iter->node->node->comment , sort_min->node->node->comment) < 0)
sort_min = sort_iter;
} else if (0 == strcmp(which, "number")) {
if (sort_iter->node->node->number < sort_min->node->node->number)
sort_min = sort_iter;
}
}
sort_iter = sort_iter->next;
}
// (sort_min->flag)++;
swap_temp = sort_min->node;
sort_min->node = sort_temp->node;
sort_temp->node = swap_temp;
}
//将排序后的链表中得数据输出,并释放内存,防止内存泄漏
sort_iter = sort_head;
while(sort_iter){
info_temp = sort_iter->node->node;
printf("\n id: %ld",info_temp->id);
printf("\t name: %s",info_temp->name);
printf("\t type: %s", info_temp->type);
printf("\t price: %.2f", info_temp->price);
printf("\t Number: %u",info_temp->number);
printf("\n Company: %s",info_temp->company);
printf(" Comment: %s\n",info_temp->comment);
sort_temp = sort_iter;
sort_iter = sort_iter->next;
free(sort_temp);
}
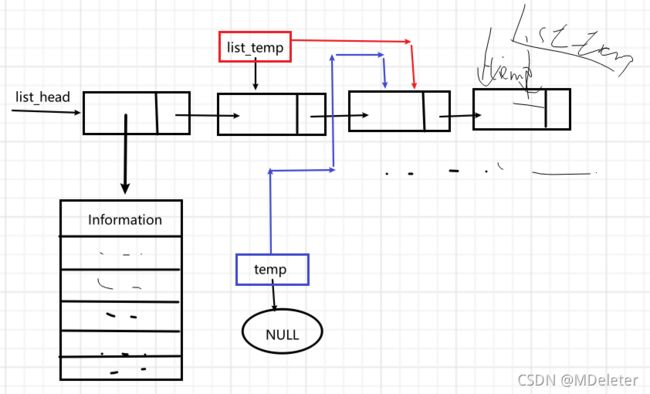
} ·按相应排序方式显示数据
·新建链表保存原链表信息
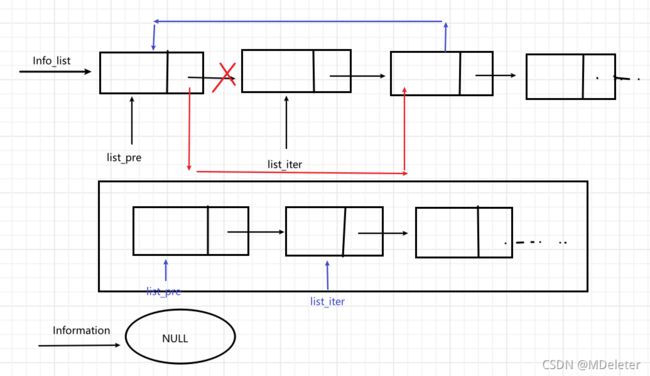
·从顺序表中删除ID记录
//从链表中删除指定ID记录
void delete_id_in_list(struct Info_list *list_head, long int id)
{
struct Info_list * list_iter = list_head->next;
struct Info_list * list_pre = list_head;
struct Information * info = NULL;
while(list_iter && list_iter->node){
if(info->id == id){
free(info);
list_iter->node=NULL;
//释放当前内存,指针回退
list_pre->next = list_iter->next;
free(list_iter);
list_iter=list_pre;
}
list_pre= list_iter;//初始化
list_iter = list_iter->next;
}
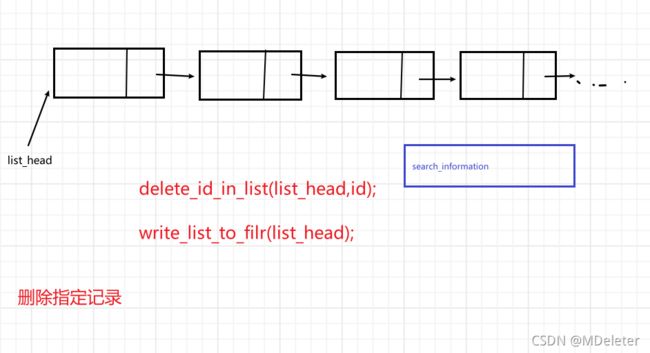
} ·删除指定记录
//删除指定记录
void delete_information(struct Info_list * list_head)
{
char condition[100];
char * trimmed_condition = NULL;
long int id;
printf("Enter ID which you want delete. \n>>>> ");
fgets(condition,100,stdin);
trimmed_condition = trimmed(condition);
id = atol(trimmed_condition);
delete_id_in_list(list_head,id);
write_list_to_file(list_head);//保存
}
//查找数据
void search_information(struct Info_list * list_head,enum InfoType type)
{
enum HaveInfo{
HAVE = 1,
UNHAVE = 2
};
struct Info_list * list_iter = list_head->next;
char condition[100];
char char_id[100];
char char_price[100];
char char_number[100];
char * trimmed_condition = NULL;
struct Information * info = NULL;
enum HaveInfo is_have = UNHAVE;
if(ALL == type){
printf("Enter your condition below. (support fuzzy search) \n>>>>");
}else{
printf("Enter your condition below. \n>>>>");
}
fgets(condition, 100,stdin);
trimmed_condition = trimmed(condition);
while(list_iter && list_iter->node){
info = list_iter->node;
is_have =UNHAVE;
sprintf(char_id,"%ld",info->id);
sprintf(char_price, "%f",info->price);
sprintf(char_number,"%u",info->number);
switch(type){
case ALL:
if(strstr(char_id,trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(info->name, trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(info->type, trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(char_price, trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(info->company,trimmed_condition)
|| strstr(info->comment, trimmed_condition)
)
is_have = HAVE;
break;
case ID:
if(strstr(char_id,trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case NAME:
if(strstr(info->name,trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case TYPE:
if(strstr(info->type,trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case PRICE:
if(strstr(char_price, trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case COMPANY:
if(strstr(info->company, trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
case COMMENT:
if(strstr(info->comment, trimmed_condition)){
is_have = HAVE;
}
break;
dafault:
is_have = UNHAVE;
break;
}
if(HAVE == is_have){
printf("\n ID: %ld", info->id);
printf("\t Name: %s", info->name);
printf("\t Type %s", info->type);
printf("\t Price: %.2f", info->price);
printf("\t Number: %u", info->number);
printf("\t Company: %s", info->company);
printf("\t Comment: %s\n", info->comment);
}
list_iter = list_iter->next;
}
}
void modify_information(struct Info_list *list_head)
{
struct Info_list * list_iter = list_head->next;
char condition[100];
char * trimmed_condition = NULL;
long int id;
struct Information * info_temp = NULL;
struct Information * info = NULL;
char id_char[200];
char price_char[200];
char number_char[200];
printf("Enter ID which you want modify. \n>>>> ");
fgets(condition, 100, stdin);
trimmed_condition = trimmed(condition);
id = atol(trimmed_condition);
while(list_iter && list_iter->node){
if(list_iter->node->id == id){
break;
}
list_iter = list_iter->next;
}
info_temp = list_iter->node;
if(!info_temp){
return;
}
printf("\n id: %ld", info_temp->id);
printf("\t name: %s", info_temp->name);
printf("\t type: %s", info_temp->type);
printf("\t price: %.2f", info_temp->price);
printf("\t Number: %u", info_temp->number);
printf("\n Company: %s", info_temp->company);
printf(" Comment: %s\n", info_temp->comment);
info = info_temp;
printf("\nNow Enter New Data of This Information.\n");
printf("Plase Enter ID, only numeral support, for example: \"123456\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(id_char, 200, stdin);
info->id = atol(id_char);
printf("You Typed %ld\n", info->id);
printf("Plase Enter Name, for example: \"Kobe Bryant\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->name, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->name);
printf("You Typed %s\n", info->name);
printf("Plase Enter Type, for example: \"A\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->type, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->type);
printf("You Typed %s\n", info->type);
printf("Plase Enter Price, only numeral support, example: \"123.456\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(price_char, 200, stdin);
info->price = atof(price_char);
printf("You Typed %f\n", info->price);
printf("Plase Enter Number, only numeral support, example: \"543210\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(number_char, 200, stdin);
info->number = atoi(number_char);
printf("You Typed %u\n", info->number);
printf("Plase Enter Company, for example: \"Red Had\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->company, 200, stdin);
trimmed(info->company);
printf("You Typed %s\n", info->company);
printf("Plase Enter Comment, for example: \"This is Comment\"\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(info->comment, 400, stdin);
printf("You Typed %s\n", info->comment);
trimmed(info->comment);
//保存文件
write_list_to_file(list_head);
}void select_operator(char operator[100],struct Info_list * list_head)
{
if( 0== strcmp(operator,"help")){
system("cls");
show_help();
}
/* 插入新数据 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "i"))
insert_information(list_head);
/* 显示数据,按插入时间输出,或按某个字段排序后输出 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "l"))
list_information(list_head);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lid"))
list_information_order(list_head, "id");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lname"))
list_information_order(list_head, "name");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lprice"))
list_information_order(list_head, "price");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lnumber"))
list_information_order(list_head, "number");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "ltype"))
list_information_order(list_head, "type");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lcompany"))
list_information_order(list_head, "company");
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "lcomment"))
list_information_order(list_head, "comment");
/* 删除 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "d"))
delete_information(list_head);
/* 查找数据,全文模糊查找或按字段模糊查找 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "s"))
search_information(list_head , ALL);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "sid"))
search_information(list_head, ID);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "sname"))
search_information(list_head, NAME);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "sprice"))
search_information(list_head, PRICE);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "stype"))
search_information(list_head, TYPE);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "snumber"))
search_information(list_head, NUMBER);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "scompany"))
search_information(list_head, COMPANY);
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "scomment"))
search_information(list_head, COMMENT);
/* 修改 */
else if (0 == strcmp(operator, "m"))
modify_information(list_head);
}void freeMem(struct Info_list* list_head)
{
struct Info_list * list_temp = list_head;
struct Info_list * list_next = NULL;
while(list_temp){
if(list_temp->node){
free(list_temp->node);
}
if(list_temp->next){
list_next = list_temp->next;
free(list_temp);
list_temp = list_next;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
int main(){
system("title YouYoung--实验室管理系统V7.28.1");
system("color 3");
show_help();
char operator[100];
char * trimmed_operator = NULL;
struct Info_list * list_first = NULL;
/* 给链表的头结点分配内存,并初始化数据为NULL */
struct Info_list * list_head = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
if (NULL == list_head) {
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return 0;
}
list_head->next = NULL;
list_head->node = NULL;
/* 给链表的第一个结点分配内存,并初始化数据为NULL */
list_first = (struct Info_list*)malloc(sizeof(struct Info_list));
if (NULL == list_first) {
printf("\nError! Cannot malloc memory\n");
return 0;
}
list_first->next = NULL;
list_first->node = NULL;
list_head->next = list_first;
/* 从保存的文件读取数据,并将数据保存到链表当中 */
read_from_file(list_first);
/* 循环执行用户输入的指令,直到输入退出指令 "q" */
do{
printf("\n________________________________________________________________________\n");
printf("Plese Select Your Operator! ");
printf("Type \"help\", for More Information.\n");
printf("------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf(">>>> ");
fgets(operator, 100, stdin);
trimmed_operator = trimmed(operator);
select_operator(trimmed_operator, list_head);
} while (strcmp(operator, "q") != 0);
/* 释放链表所申请的内存,防止内存泄露 */
freeMem(list_head);
return 0;
}
后面无非是将前面要求的功能封装成为函数,一定要注意,刚开始时,可能不熟练,看不懂,多看几遍就会了。