C语言(第二天)
C语言第二天
-
- 数据类型
-
- int
- char
- Bool
- 可移植类型
- 浮点型
- 其他类型
- 获取类型字节大小
- 小问题
- 转义字符
- 总结
数据类型
在学习编程语言,无非就是用于人机交互,那么人机交互的数据就需要区分数据类型,数据类型的出现方便了数字型数据的运算,字符型数据的合并等等。学习一门编程语言,数据类型是无法绕开的环节。
int
int用于声明整数型变量,int型的存储占用2或者4个字节。
- 声明变量
1>int p1,p2,p3;与int p1;int p2;int p3;相同 - 赋值
1>p1=123;
2>通过函数scanf()赋值
3>初始化变量 int p0=123; - 输出变量值
通过printf()函数,借助%d来进行输出。%d同时用来指出变量值打印出的位置。%d用来输出十进制,%o用来输出八进制,%x用来输出十六进制。如下给出示例:
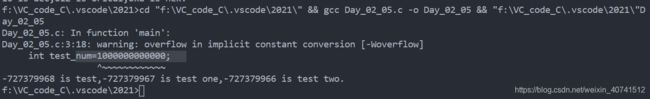
#include - 溢出现象
发生溢出时,系统不会出现错误提示,但是有的编译器会给出警告,这里给出详细示例,请大家在编写代码时注意一些。
#includechar
char类型占用一个字节,用于存储字符,但在计算机底层依然存储的是整数,在学习C的时候大家可能都会接触到ASCII码,ASCII码便体现这一原理。
#include在声明变量和赋值方面与整数型类似,但需要注意一点,便是字符需要单引号(‘’)包含,不能用其他符号引用。
Bool
Bool类型表示的是布尔值,即逻辑值为true和false。在编程式大家也会发现用1也可以表示true,0表示false。从这一点可以看出Bool实际上依然是整数类型。
可移植类型
可移植类型主要用于防止程序在不同系统运行时,有的数据类型名功能不一样。C语言主要提供了两个函数库(stdint.h和inttypes.h)用来实现可移植类型。
- 头文件:stdint.h
#include - 头文件:inttypes.h
#include 浮点型
- float
float类型必须至少能表示六位有效数字。 - double
double类型必须至少能表示十三位有效数字。 - long double
比double类型精度更高。
- 声明浮点型变量方式
float test_1,test_2;
double test_3;
float test_4=3.3e-12;(e左右不能有空格)
long double test_5; - 浮点型常量(形式如下)
-1.3e-12相当于 -1.310^(-12)
13.23
.3e12相当于0.310^12
2e12相当于2*10^12
.2相当于0.2
200 - 浮点值上溢和下溢
浮点值上溢时,C语言会输出该值为INF。例子如下:
#include - 浮点数舍入错误
当大家在用浮点数进行加减运算时,由于有效位数的限制可能出现舍入错误。下边依然是个例子:
#include其他类型
当然还有一些类型博主不在这里叙述,但C语言没有字符串类型也希望大家可以记住这一点。
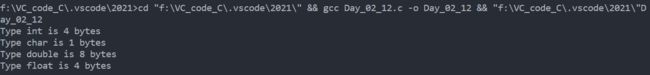
获取类型字节大小
若大家无法判定数据类型字节大小,那么大家可以根据sizeof()函数来获取相应数据类型的所占字节大小。代码示例如下:
#include 小问题
C语言在变量赋值,数据输出时等多种地方,会出现数据与类型不匹配的问题,但编译器不会出现错误,且可以正常运行。示例如下:
#include 转义字符
所有的ASCII码都可以用“\”加数字(一般是8进制数字)来表示。而C中定义了一些字母前加""来表示常见的那些不能显示的ASCII字符,如\0,\t,\n等,就称为转义字符,因为后面的字符,都不是它本来的ASCII字符意思了
转移字符,是大家在输出数据时想要添加一些特定且无法使用基本的符号来表示,就如在输出中的换行符,大家肯定不能直接按enter键来解决,这便是转移字符的功能。如下便是示例:
#include | 转义符号 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| \b | 退格,将当前位置移到前一列 |
| \n | 换行 |
| \t | tab键 |
| \r | 回车,将当前位置移到本行开头 |
总结
该篇主要用于了解C语言,总结有误的地方希望大家能够指正,有缺少的地方也希望大家指出,感觉还行的话请给个赞,给博主一点点鼓励。