Unity 常用设计模式
1.单例模式
保证一个类只有一个实例,且具有全局访问点,一般用作管理器,下面是用静态变量实现的单例
/// 其他类转换为单例,ShopMgr是商店管理器,继承Singleton就转换为单例
class ShopMgr : Singleton<ShopMgr>
{
//具体逻辑
}
Mono单例,保证GameObject唯一
using UnityEngine;
public abstract class MonoSingleton<T> : MonoBehaviour where T : MonoBehaviour
{
public bool global = true;
static T instance;
public static T Instance
{
get
{
if (instance == null)
{
instance = FindObjectOfType<T>();
}
return instance;
}
}
void Awake()
{
if (global)
{
if(instance != null && instance != this.gameObject.GetComponent<T>())
{
//已经存在一个单例,而且不是当前脚本,把这个新创建的删掉
Destroy(this.gameObject);
return;
}
DontDestroyOnLoad(this.gameObject);
//Instance是使用时创建,这里赋初始值
instance = this.gameObject.GetComponent<T>();
}
this.OnStart();
}
protected virtual void OnStart()
{
}
}
2.观察者模式
观察者模式定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并被自动更新,主要用于解耦代码
这里使用一个简单的事件管理器来演示逻辑
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class EventManager : Singleton<EventManager>
{
public delegate void EventCallBack(object param);// 事件回调函数
// 事件字典
Dictionary<int, List<EventCallBack>> mDictEvent = new Dictionary<int, List<EventCallBack>>();
/// 定义事件id
public class EventId
{
public static int OnShopDataChange = 1; //商店数据变化时触发
public static int OnGoldChange = 2; //金币变化时触发
}
以UI界面的刷新为例,打开商店UI时监听商店数据变化,关闭时移除监听
public class ShopUI
{
private void RegisterEvent()
{
EventManager.Instance.AddEvent(EventId.OnShopDataChange, OnDataChange);
EventManager.Instance.AddEvent(EventId.OnGoldChange, OnDataChange);
}
private void UnRegisterEvent()
{
EventManager.Instance.DelEvent(EventId.OnShopDataChange, OnDataChange);
EventManager.Instance.DelEvent(EventId.OnGoldChange, OnDataChange);
}
private void OnDataChange(object param)
{
//刷新UI
}
}
当商店的数据变化或者金币变化时,就会触发对应的事件,刷新商店的UI
class ShopMgr : Singleton<ShopMgr>
{
private void OnDataChange()
{
EventManager.Instance.NotifyEvent(EventId.OnShopDataChange, null);
}
}
class ItemMgr : Singleton<ItemMgr>
{
private void OnDataChange()
{
EventManager.Instance.NotifyEvent(EventId.OnGoldChange, null);
}
}
3.组合模式
把公共方法抽象成组件,组件可以添加到对象上,形成整体和部分的关系,Unity的各种组件也体现了组合模式的思想
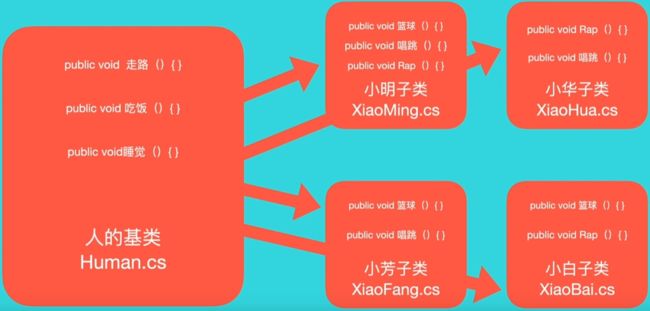
定义了基类Human,里面有三个方法,子类可以少写“走路”,“吃饭”,“睡觉”这三个方法,但是对于子类的一些特定行为还是有可能出现大量重复
我们可以把这些方法抽象成单独的组件,这里都用伪代码表示
public class 走路Component { public void 走路(){ //do something} }
public class 吃饭Component { public void 吃饭(){ //do something} }
public class 睡觉Component { public void 睡觉(){ //do something} }
public class 篮球Component { public void 篮球(){ //do something} }
public class 唱跳Component { public void 唱跳(){ //do something} }
public class RapComponent { public void Rap(){ //do something} }
创建对象时就可以根据需要添加不同的组件,这样就增加了代码的复用
小芳 xiaofang = new 小芳();
xiaofang.AddComponent<走路Component>();
xiaofang.AddComponent<吃饭Component>();
xiaofang.AddComponent<睡觉Component>();
xiaofang.AddComponent<篮球Component>();
xiaofang.AddComponent<唱跳Component>();
获取组件,参考Unity获取组件的方式,设计类似的方法获取组件,频繁使用的组件做个缓存
var c = xiaofang.GetComponent<走路Component>();
c.走路();
4.命令模式
把命令封装成对象,从而实现解耦,改变命令对象,撤销功能
这里定义了向前移动和向左移动2个命令,创建命令时传入对象,撤销就是往反方向移动,向后,向右移动命令类似,这里就不写了
using UnityEngine;
/// 命令管理器类,把命令记录到列表中,撤销时从后往前执行命令的Undo方法
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class CommandManager : MonoBehaviour
{
public static CommandManager Instance;
private readonly List<CommandBase> _commandList = new List<CommandBase>();
private void Awake()
{
if (Instance) Destroy(Instance);
else Instance = this;
}
public void AddCommands(CommandBase command)
{
_commandList.Add(command);
}
public IEnumerator UndoStart()
{
_commandList.Reverse();
foreach (CommandBase command in _commandList)
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(.2f);
command.Undo();
}
_commandList.Clear();
}
}
输入类,监听按键点击,只负责接受输入,具体的操作放在命令的Execute方法中,这样实现解耦
点击W或A键时执行命令,并把命令添加的管理器的列表中,点击B键撤销之前所有的命令
using UnityEngine;
public class InputHandler : MonoBehaviour
{
private MoveForWard _moveForward;
private MoveLeft _moveLeft;
private GameObject _playerCube;
private void Start()
{
_playerCube = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube);
}
private void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.W))
{
_moveForward = new MoveForWard(_playerCube);
_moveForward.Execute();
CommandManager.Instance.AddCommands(_moveForward);//顺序不能弄混,因为要等赋值完后再加入
}
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.A))
{
_moveLeft = new MoveLeft(_playerCube);
_moveLeft.Execute();
CommandManager.Instance.AddCommands(_moveLeft);
}
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.B))
{
StartCoroutine(CommandManager.Instance.UndoStart());
}
}
}
5.状态模式
一般使用有限状态机实现
- 将对象的行为抽象成几个独立的状态
- 某一时刻只能处于其中一种状态
- 通过管理器控制状态之间的互相切换
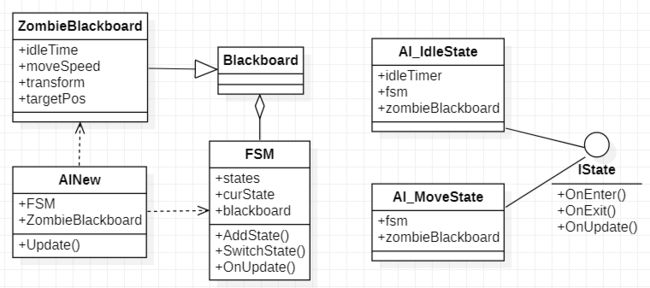
首先通过类图了解不同类之间的关系,AINew是挂在怪物身上的脚本,在Update中驱动FSM管理器的Update,通过FSM控制不同状态之间的切换,这里添加了闲置和移动两个状态,每个状态一般包含OnEnter,OnExit,OnUpdate等方法,Blackboard存储共享数据,或者向外展示的数据
代码实现
using UnityEngine;
using MY_FSM;
using System;
using Random = UnityEngine.Random;
[Serializable]
public class ZombieBlackboard : Blackboard
{
public float idleTime;
public float moveSpeed;
public Transform transform;
public Vector2 targetPos;
}
public class AI_IdleState : IState
{
private float idleTimer;
private FSM fsm;
private ZombieBlackboard blackboard;
public AI_IdleState(FSM fsm)
{
this.fsm = fsm;
this.blackboard = fsm.blackboard as ZombieBlackboard;
}
public void OnEnter()
{
idleTimer = 0;
}
public void OnExit() { }
public void OnUpdate()
{
idleTimer += Time.deltaTime;
if (idleTimer > blackboard.idleTime)
{
//超过设置的时间切换到Move状态
this.fsm.SwitchState(StateType.MOVE);
}
}
}
public class AI_MoveState : IState
{
private FSM fsm;
private ZombieBlackboard blackboard;
public AI_MoveState(FSM fsm)
{
this.fsm = fsm;
this.blackboard = fsm.blackboard as ZombieBlackboard;
}
public void OnEnter()
{
float randomX = Random.Range(-10, 10);
float randomY = Random.Range(-10, 10);
// 当前位置从黑板里拿
blackboard.targetPos = new Vector2(blackboard.transform.position.x + randomX,
blackboard.transform.position.y + randomY);
}
public void OnExit() { }
public void OnUpdate()
{
if (Vector2.Distance(blackboard.transform.position, blackboard.targetPos) < 0.1f)
{
fsm.SwitchState(StateType.Idle);
}
else
{
blackboard.transform.position = Vector2.MoveTowards(blackboard.transform.position, blackboard.targetPos, blackboard.moveSpeed * Time.deltaTime);
}
}
}
public class AINew : MonoBehaviour
{
private FSM fsm;
public ZombieBlackboard blackboard;
void Start()
{
fsm = new FSM(blackboard);
fsm.AddState(StateType.Idle, new AI_IdleState(fsm));
fsm.AddState(StateType.MOVE, new AI_MoveState(fsm));
fsm.SwitchState(StateType.Idle);
}
void Update()
{
fsm.OnCheck();
fsm.OnUpdate();
Flip();
}
void Flip()
{
if (blackboard.targetPos != Vector2.zero)
{
if (blackboard.targetPos.x > transform.position.x)
{
transform.localScale = new Vector2(-1, 1);
}
else
{
transform.localScale = new Vector2(1, 1);
}
}
}
private void FixedUpdate()
{
fsm.OnFixUpdate();
}
}
状态管理器
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using System;
namespace MY_FSM
{
public enum StateType
{
Idle,
MOVE,
Find_Enemy,
Attack,
Die,
Success,
}
public interface IState
{
void OnEnter();
void OnExit();
void OnUpdate();
// void OnCheck();
// void OnFixUpdate();
}
[Serializable]
public class Blackboard
{
// 此处存储共享数据,或者向外展示的数据,可配置的数据
}
public class FSM
{
public IState curState;
public Dictionary<StateType, IState> states;
public Blackboard blackboard;
public FSM(Blackboard blackboard)
{
this.states = new Dictionary<StateType, IState>();
this.blackboard = blackboard;
}
public void AddState(StateType stateType, IState state)
{
if (states.ContainsKey(stateType))
{
Debug.Log("[AddState] >>>>>>>>>>>>> map has contain key: " + stateType);
return;
}
states.Add(stateType, state);
}
public void SwitchState(StateType stateType)
{
if (!states.ContainsKey(stateType))
{
Debug.Log("[SwitchState] >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> not contain key: " + stateType);
return;
}
if (curState != null)
{
curState.OnExit();
}
curState = states[stateType];
curState.OnEnter();
}
public void OnUpdate()
{
curState.OnUpdate();
}
public void OnFixUpdate()
{
// curState.OnFixUpdate();
}
public void OnCheck()
{
// curState.OnCheck();
}
}
}
6.工厂模式
将对象的创建过程封装到一个类中,隐藏实现细节,降低耦合,工厂模式有三种类型
简单工厂模式
通常用于创建单一的对象类型
定义道具基类及其子类
using UnityEngine;
public abstract class ItemBase
{
protected string name;
public virtual void Use()
{
Debug.Log("使用了" + name);
}
}
public class HealthPotion : ItemBase
{
public HealthPotion()
{
name = "生命药水";
}
public override void Use()
{
base.Use();
//具体的使用逻辑
Debug.Log("恢复了100点生命");
}
}
public class ManaPotion : ItemBase
{
public ManaPotion()
{
name = "魔法药水";
}
public override void Use()
{
base.Use();
//具体的使用逻辑
Debug.Log("恢复了100点魔法");
}
}
public class SpeedBoost : ItemBase
{
public SpeedBoost()
{
name = "加速药剂";
}
public override void Use()
{
base.Use();
//具体的使用逻辑
Debug.Log("增加了移动速度");
}
}
定义创建道具的工厂
public class ItemFactory
{
public static ItemBase CreateItem(string itemName)
{
ItemBase item = null;
switch (itemName)
{
case "Health_Potion":
item = new HealthPotion();
break;
case "Mana_Potion":
item = new ManaPotion();
break;
case "Speed_Boost":
item = new SpeedBoost();
break;
}
return item;
}
}
游戏中通过ItemFactory创建并使用道具,只能创建ItemBase类型的对象
//创建并使用生命药水
ItemBase healthPotion = ItemFactory.CreateItem("Health_Potion");
healthPotion.Use();
//创建并使用加速药剂
ItemBase speedBoost = ItemFactory.CreateItem("Speed_Boost");
speedBoost.Use();
工厂方法模式
通常用于创建不同的对象类型,每个对象类型对应一个工厂方法
道具类和上面一样,定义接口IFactory,每个工厂都实现这个接口,每个工厂创建相关的道具
public interface IFactory
{
ItemBase CreateItem();
}
public class HealthPotionFactory : IFactory
{
public ItemBase CreateItem()
{
return new HealthPotion();
}
}
public class ManaPotionFactory : IFactory
{
public ItemBase CreateItem()
{
return new ManaPotion();
}
}
public class SpeedBoostFactory : IFactory
{
public ItemBase CreateItem()
{
return new SpeedBoost();
}
}
游戏中使用具体的工厂类来创建道具对象并使用
// 先创建具体的工厂,再通过工厂创建相关的道具
IFactory healthFactory = new HealthPotionFactory();
ItemBase healthPotion = healthFactory.CreateItem();
healthPotion.Use();
IFactory manaFactory = new ManaPotionFactory();
ItemBase manaPotion = manaFactory.CreateItem();
manaPotion.Use();
抽象工厂模式
创建一组相关或依赖对象的工厂模式,客户端请求一个工厂,并从工厂中获取一个产品族中的一个对象,工厂不仅仅是一个单独的类,而是一个由多个工厂组成的层次结构
使用抽象工厂模式,通常涉及一组相关产品,这里定义两种类型的武器:近战武器和远程武器,近战武器中剑和斧子认为是相关产品,远程武器中,弓箭和弩认为是相关产品
using UnityEngine;
// 抽象武器接口
public interface IWeapon {}
// 近战武器接口
public interface IMeleeWeapon : IWeapon
{
void Attack();
}
public class Sword : IMeleeWeapon
{
public void Attack()
{
Debug.Log("使用剑攻击");
}
}
public class Axe : IMeleeWeapon
{
public void Attack()
{
Debug.Log("使用斧子攻击");
}
}
// 远程武器接口
public interface IRangedWeapon : IWeapon
{
void Shoot();
}
public class Bow : IRangedWeapon
{
public void Shoot()
{
Debug.Log("使用弓箭射击");
}
}
public class Crossbow : IRangedWeapon
{
public void Shoot()
{
Debug.Log("使用弩射击");
}
}
每个角色需要近战武器和远程武器,对应英雄,使用英雄武器工厂创建剑和弓箭,对于怪物,使用怪物武器工厂创建斧子和弩
// 抽象工厂接口
public interface IWeaponFactory
{
IMeleeWeapon CreateMeleeWeapon();
IRangedWeapon CreateRangedWeapon();
}
// 英雄武器工厂
public class HeroWeaponFactory : IWeaponFactory
{
public IMeleeWeapon CreateMeleeWeapon()
{
return new Sword();
}
public IRangedWeapon CreateRangedWeapon()
{
return new Bow();
}
}
// 怪物武器工厂
public class MonsterWeaponFactory : IWeaponFactory
{
public IMeleeWeapon CreateMeleeWeapon()
{
return new Axe();
}
public IRangedWeapon CreateRangedWeapon()
{
return new Crossbow();
}
}
游戏中的逻辑,使用具体的工厂类创建相关的武器实例
// 创建英雄使用的近战武器
IWeaponFactory heroWeaponFactory = new HeroWeaponFactory();
IMeleeWeapon meleeWeapon = heroWeaponFactory.CreateMeleeWeapon();
meleeWeapon.Attack();
// 创建怪物使用的远程武器
IWeaponFactory monsterWeaponFactory = new MonsterWeaponFactory();
IRangedWeapon rangedWeapon = monsterWeaponFactory.CreateRangedWeapon();
rangedWeapon.Shoot();
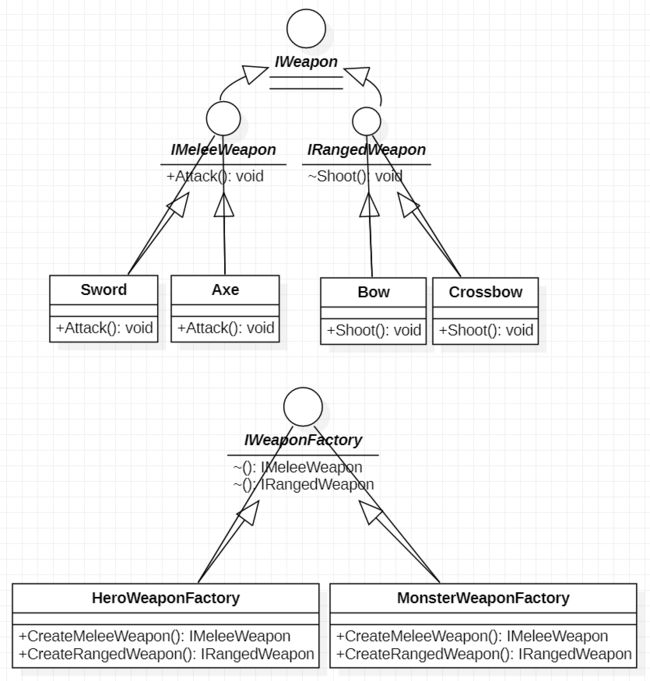
使用抽象工厂模式,将近战武器,远程武器的创建和使用代码解耦,代码类图如下
7.策略模式
首先要定义一个策略接口,然后定义几个具体的策略类实现这个接口,运行时根据需要切换不同的策略对象
// 抽象策略接口
public interface IAttackStrategy
{
void Attack();
}
//下面是具体策略类
public class MeleeStrategy : IAttackStrategy
{
public void Attack()
{
// 近战攻击
}
}
public class RangedStrategy : IAttackStrategy
{
public void Attack()
{
// 远程攻击
}
}
public class MagicStrategy : IAttackStrategy
{
public void Attack()
{
// 魔法攻击
}
}
怪物类中使用接口作为字段,可以根据和玩家的距离切换不同的策略,比如与玩家距离小于30,使用MeleeStrategy,大于使用RangedStrategy
// 怪物类
public class Monster : MonoBehaviour
{
// 攻击方式就是一个策略接口
private IAttackStrategy attackStrategy;
// 设置攻击方式
public void SetAttackStrategy(IAttackStrategy strategy)
{
attackStrategy = strategy;
}
private void Update()
{
attackStrategy?.Attack();
}
}
参考
【游戏开发设计模式】
最用心 の Unity百宝箱
