BIO、NIO、selector、Netty代码Demo示例
文章目录
-
- (一)BIO(Blocking I/O 阻塞I/O)
- (二)NIO(Non-Blocking I/O 非阻塞I/O)
- (三)IO多路复用--Selector
- (四)Netty
(一)BIO(Blocking I/O 阻塞I/O)
阻塞I/O的连接accept()方法及数据读取的read()方法都是阻塞的,也就是说没有客户端发起连接时会阻塞,客户端发起连接后不发送数据也会阻塞。
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* 阻塞IO
*/
public class BioServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9000);
while(true){
System.out.println("等待连接。。");
//阻塞方法
//可以通过控制台输入命令进行连接:telnet localhost 9000,CTRL+]进入Telnet指令
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("有客户端连接了。。");
//虽然采用多线程可以支持多个线程同时访问,但是会引发C10K问题
//C10K->connection=1w,C10M->connection=1000w,就是连接数很多的意思
//new Thread(new Runnable() {
// @Override
// public void run() {
// try {
handler(clientSocket);
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
//}).start();
}
}
private static void handler(Socket clientSocket) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("准备read。。");
//接收客户端的数据,阻塞方法,客户端没有发送数据,服务端就会没有数据可读时就阻塞
int read = clientSocket.getInputStream().read(bytes);
System.out.println("read完毕。。");
if (read !=-1){
System.out.println("接收客户端的数据:"+new String(bytes,0,read));
}
//clientSocket.getOutputStream().write("HelloClint".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//clientSocket.getOutputStream().flush();
}
}
(二)NIO(Non-Blocking I/O 非阻塞I/O)
非阻塞I/O在客户端连接方法accept()和read()方法中都不会阻塞,我们可以通过返回值判断是否有客户端发起连接或者发送数据,进行相应的处理。
简单的NIO因为是通过遍历的方式,会有大量的空循环
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
/**
*初版- NIO(非阻塞)编程
*/
public class NioServer {
static List<SocketChannel> channelList = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9000));
//这里可选非阻塞和阻塞,如果选择阻塞true,下面的accept()方法会阻塞线程
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("服务启动成功");
while (true){
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if(socketChannel!=null){
System.out.println("连接成功");
//这里可选非阻塞和阻塞,如果选择阻塞true,下面的read()方法会阻塞线程
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将所有连接channel交给一个集合进行管理
channelList.add(socketChannel);
}
//问题点: 空循环时间耗时太久
Iterator<SocketChannel> iterator = channelList.iterator();
//遍历访问所有channel集合获取客户端发送的数据,如果有任何一个连接客户端发送了数据,那么就处理当前channel里的数据
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SocketChannel sc = iterator.next();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
int len = sc.read(byteBuffer);
if (len>0){
System.out.println("接收到消息:"+new String(byteBuffer.array()));
}else if(len ==-1){
iterator.remove();
System.out.println("客户端断开连接");
}
}
}
}
}
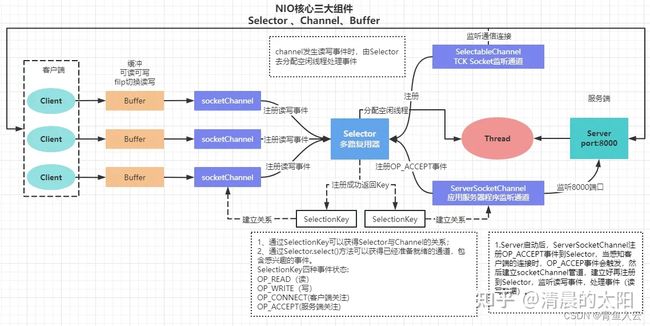
(三)IO多路复用–Selector
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
*进阶版- NIO(非阻塞)编程
* 这是netty和Redis的雏形
*/
public class NioSelectorServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9000));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//启用epoll模型,这个对应epoll_create()方法
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//注册阻塞事件:创建连接,这个对应epoll模型的epoll_ctl()方法
SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务启动成功");
while (true){
//阻塞等待需要处理的事件发生,包括连接事件和数据读取事件,如果没有客户端发起连接或者客户端发送数据,这里会一直阻塞。这个对应epoll模型的epoll_wait()方法
selector.select();
//获取阻塞的事件
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
//对阻塞事件进行遍历
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
if(iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key =iterator.next();
if(key.isAcceptable()){//这里只针对连接事件,
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = server.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//连接建立后,注册阻塞事件:读取数据
SelectionKey selKey = socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(key.isReadable()){//这里只针对read事件,有需要可以针对write事件处理
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
int len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if(len >0 ){
System.out.println("接收到消息:"+new String(byteBuffer.array()));
}else if(len ==-1 )
//关闭socket
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("接收完成");
}
}
//把处理完的阻塞事件移除
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
(四)Netty
Netty核心组件
- Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap:当需要连接客户端或者服务器绑定指定端口时需要使用Bootstrap,ServerBootstrap有两种类型,一种是用于客户端的Bootstrap,一种是用于服务端 的ServerBootstrap。
- Channel:相当于socket,与另一端进行通信的通道,具备bind、connect、read、write等IO操作的能力。
- EventLoop:事件循环,负责处理Channel的IO事件,一个EventLoopGroup包含多个EventLoop,一个EventLoop可被分配至多个Channel,一个Channel只能注册于一个EventLoop,一个EventLoop只能与一个Thread绑定。
- ChannelFuture:channel IO事件的异步操作结果。
- ChannelHandler:包含IO事件具体的业务逻辑。
- ChannelPipeline:ChannelHandler的管道容器。
DEMO
Netty服务端
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup parentGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup childGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//2.创建服务端启动引导/辅助类:ServerBootstrap
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//3.给引导类配置两大线程组,确定了线程模型
bootstrap.group(parentGroup, childGroup)
// (非必备)打印日志
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
// 4.指定 IO 模型
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder());
/**
* 服务端添加IdleStateHandler心跳检测处理器,添加自定义处理Handler类实现userEventTriggered()方法作为超时事件的逻辑处理.
* IdleStateHandler心跳检测每十五秒进行一次读检测,如果十五秒内ChannelRead()方法未被调用则触发一次userEventTrigger()方法
* 服务端为读IDLE
* pipeline.AddLast(new IdleStateHandler(15, 0, 0));//第一个参数为读,第二个为写,第三个为读写全部
*/
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(15, 0, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
//5.可以自定义客户端消息的业务处理逻辑
pipeline.addLast(new DemoSocketServerHandler());
}
});
// ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(8888).sync().addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
// @Override
// public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
// System.out.println("监听端口已经启动");
// }
// });
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(8888).sync().addListener( future1 -> {
if (future1.isSuccess()){
System.out.println("监听端口已经启动!");
} else {
System.out.println("监听端口还未启动!");
}
} );
System.out.println("服务器已启动。。。");
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
parentGroup.shutdownGracefully();
childGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
Netty客户端
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
pipeline.addLast(new DemoSocketClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8888).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
if(eventLoopGroup != null) {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
}
服务端处理handler
public class DemoSocketServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = (InetSocketAddress) ctx.channel().remoteAddress();
String ip = inetSocketAddress.getAddress().getHostAddress();
int port = inetSocketAddress.getPort();
super.channelActive(ctx);
System.out.println(ip+":"+port+" 上线了");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg);
System.out.println("Client Address ====== " + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("from server:" + UUID.randomUUID());
ctx.fireChannelActive();
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
IdleStateEvent idleStateEvent = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
if (idleStateEvent.state() == IdleState.READER_IDLE) {
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = (InetSocketAddress) ctx.channel().remoteAddress();
String ip = inetSocketAddress.getAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println((ip + ":" + inetSocketAddress.getPort() + "close"));
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
客户端处理handler
public class DemoSocketClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg);
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("from client: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(5000);
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("from client:begin talking");
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
//超时则关闭链路
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
IdleStateEvent idleStateEvent = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
if (idleStateEvent.state() == IdleState.READER_IDLE) {
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = (InetSocketAddress) ctx.channel().remoteAddress();
String ip = inetSocketAddress.getAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println((ip + ":" + inetSocketAddress.getPort() + "close"));
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
}
}