❤️详解「 A*」算法原理及其算法实现(C/C++描述)
目录
定义和概念
原理步骤
算法推演
算法源码
定义和概念
A*算法,A*(A-Star)算法是一种静态路网中求解最短路径最有效的直接搜索方法,也是解决许多搜索问题的有效算法。算法中的距离估算值与实际值越接近,最终搜索速度越快(百度百科)
百科百科将A*算法定义为求解最短路径,我认为不够严谨。
A*算法较之传统的路径规划算法,实时性更高、灵活性更强,寻路结果更加接近人工选择的路径结果. A*寻路算法 并不是找到最优路径,只是找到 相对近的路径,因为找最优要把所有可行路径都找出来进行对比,消耗性能太大, 寻路效果只要相对近路径就行了。
也因此在静态路网的寻路问题中A*算法被大量运用。
A*算法重要的三个指标 G、H、 F
G 表示从起点移动到终点的移动距离H 表示从指定的地点移动到终点的预计移动距离F = G + H ,F 即表示从起点经过此点预计到终点的总移动距离
距离有两个指标:
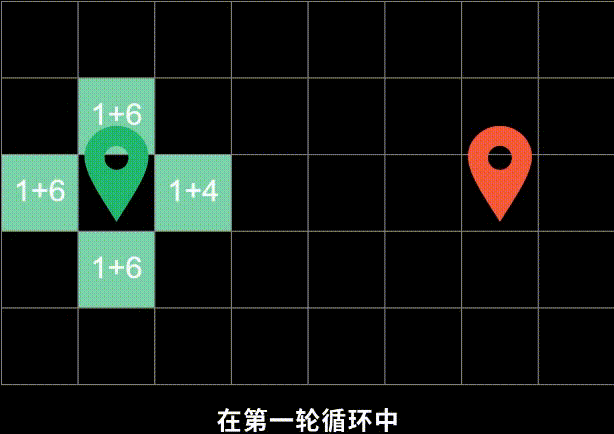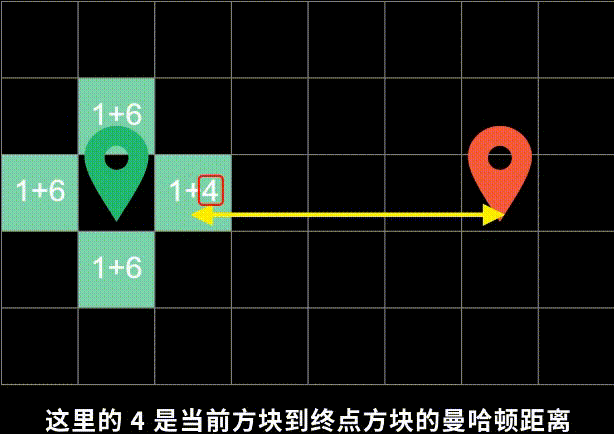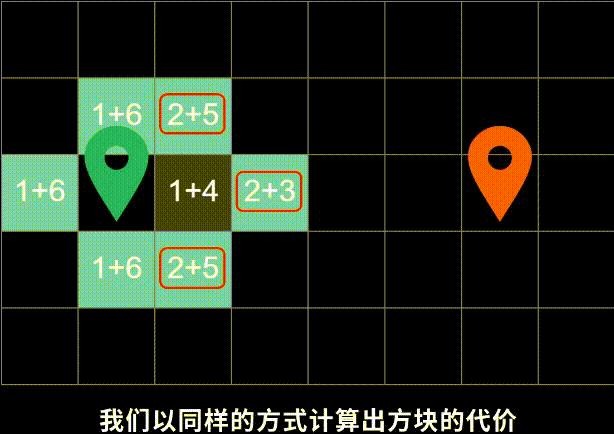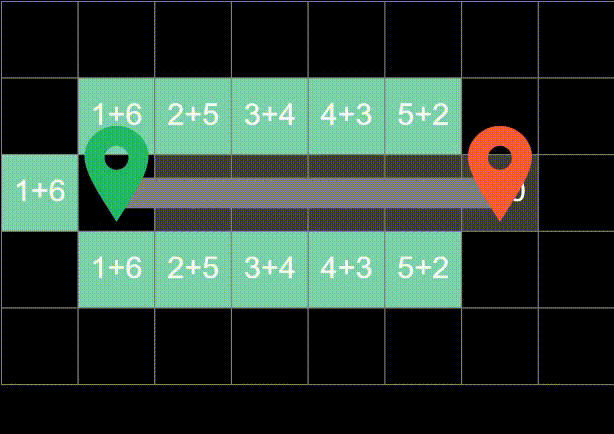
曼哈顿距离:两个点在标准坐标系上的绝对轴距总和。计算公式:|x1-x2|+|y1-y2|
原理步骤
A*算法首先定义两个重要的链表:openList、closeList
通过循环将可能到达的结点加入openList,已经走过的结点加入closeList
1)动态展示
2)静态展示
1. 从起点开始, 把它作为待处理的方格存入一个预测可达的节点列表,简称 openList, 即把起点放入“预测可达节点列表”, 可达节点列表 openList 就是一个等待检查方格的列表。2. 寻找 openList 中 F 值最小的点 min(一开始只有起点)周围可以到达的方格(可到达的意思是其不是障碍物,也不存 在关闭列表中的方格,即不是已走过的方格)。计算 min 周围可到达的方格的 F 值。将还没在 openList 中点放入其中, 并 设置它们的"父方格"为点 min,表示他们的上一步是经过 min 到达的。如果 min 下一步某个可到达的方格已经在 openList 列表那么并且经 min 点它的 F 值更优,则修改 F 值并把其"父方格"设为点 min。3. 把 2 中的点 min 从"开启列表"中删除并存入"关闭列表"closeList 中, closeList 中存放的都是不需要再次检查的方格。如 果 2 中点 min 不是终点并且开启列表的数量大于零,那么继续从第 2 步开始。如果是终点执行第 4 步,如果openList 列表数量为零,那么就是找不到有效路径。4.如果第 3 步中 min 是终点,则结束查找,直接追溯父节点到起点的路径即为所选路径。
算法推演
1)二维图中结点数据结构可定义为:
typedef struct _Point
{
int x, y;
int F, G, H;//F=G+H
struct _Point *parent;
}Point;
2)找出目标结点
static Point *FindPath(Point *startPoint, Point *endPoint)
{
openList.push_back(AllocPoint(startPoint->x,startPoint->y));
while (!openList.empty())
{
//1.第一步 取openlist中的F最小值
Point *curPoint = GetLeastPoint();
//2.将当前结点加入到closelist中
openList.remove(curPoint);
closeList.push_back(curPoint);
//3.找到当前结点周围可达的节点 并计算F值
vectorsurroundPoints = GetSurroundPoints(curPoint);
for (vector::const_iterator it= surroundPoints.begin();it!= surroundPoints.end();it++)
{
Point *target = *it;
Point *exsit = isInList(openList, target);
if (!exsit)//如果可达结点不在openList中,则直接加入openList链表
{
target->parent = curPoint;
target->G = calcDistance(curPoint, target);
target->H = calcDistance(target, endPoint);
target->F = target->G + target->H;
openList.push_back(target);
}
else
//如果可达结点已经在openList中,则重新计算F值,如果小于原F值,则改变其父节点为当前结点,G、F
//值随之改变
{
int tmpG = calcDistance(curPoint, target);
if (tmpGG)
{
exsit->parent = curPoint;
exsit->G = tmpG;
exsit->F = tmpG + exsit->H;
}
delete target;
}
}
surroundPoints.clear();
Point *resPoint = isInList(openList, endPoint);
if (resPoint)
return resPoint;
}
} 3)通过目标结点的父节遍历链表找到开始结点,以获得正确路径
/*返回正确路径*/
list GetPath(Point *startPoint, Point *endPoint)
{
Point *result = FindPath(startPoint, endPoint);
list path;
//返回路径,如果没有找到路径则返回空链表
while (result)
{
path.push_front(result);
result = result->parent;
}
return path;
}
算法源码
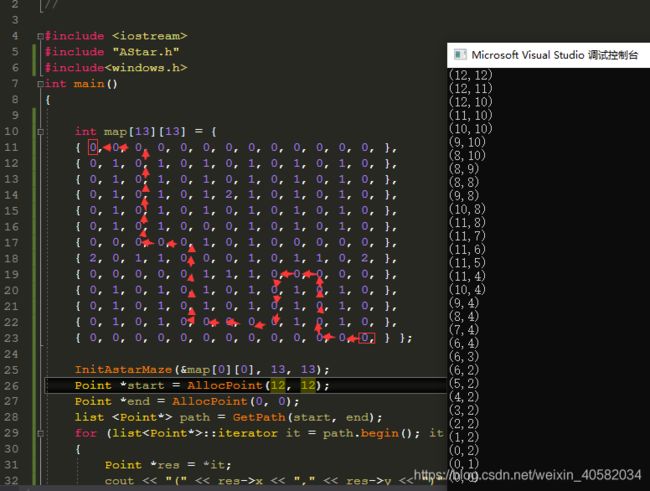
运行截图:
由此也可知,A*算法所得结果并非最短路径
AStar.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int kCost1 = 10;//直移一格消耗
const int kCost2 = 14;//斜移一格消耗
typedef struct _Point
{
int x, y;
int F, G, H;//F=G+H
struct _Point *parent;
}Point;
/*分配一个格子*/
Point *AllocPoint(int x, int y);
/*初始化地图*/
void InitAstarMaze(int *Maze, int lines, int colums);
/*A*算法寻找路径*/
list GetPath(Point *startPoint, Point *endPoint);
/*清理资源*/
void ClearAstarMaze();
AStar.cpp
#include
#include"AStar.h"
#include
#include
static int *maze;//地图
static int cols;//列数
static int lines;//行数
static listopenList;
static listcloseList;
/*A*算法寻找路径*/
Point * isInList(const list point, const Point *target);
static Point *GetLeastPoint();//找出openlist中F值最小的节点
static vector GetSurroundPoints(const Point *point);//找到当前结点周围可达的节点
bool isCanreach(const Point *point, const Point *target);//判断这两点是否可达
int calcDistance(Point *target, Point *endPoint);
static Point *FindPath(Point *startPoint, Point *endPoint)
{
openList.push_back(AllocPoint(startPoint->x,startPoint->y));
while (!openList.empty())
{
//1.第一步 取openlist中的F最小值
Point *curPoint = GetLeastPoint();
//2.将当前结点加入到closelist中
openList.remove(curPoint);
closeList.push_back(curPoint);
//3.找到当前结点周围可达的节点 并计算F值
vectorsurroundPoints = GetSurroundPoints(curPoint);
for (vector::const_iterator it= surroundPoints.begin();it!= surroundPoints.end();it++)
{
Point *target = *it;
Point *exsit = isInList(openList, target);
if (!exsit)
{
target->parent = curPoint;
target->G = calcDistance(curPoint, target);
target->H = calcDistance(target, endPoint);
target->F = target->G + target->H;
openList.push_back(target);
}
else
{
int tmpG = calcDistance(curPoint, target);
if (tmpGG)
{
exsit->parent = curPoint;
exsit->G = tmpG;
exsit->F = tmpG + exsit->H;
}
delete target;
}
}
surroundPoints.clear();
Point *resPoint = isInList(openList, endPoint);
if (resPoint)
return resPoint;
}
}
void InitAstarMaze(int *arr,int _lines, int colums)
{
maze = arr;
cols = colums;
lines = _lines;
}
Point * AllocPoint(int x, int y)
{
Point * tmp = new Point;
memset(tmp, 0, sizeof(Point));
tmp->x = x;
tmp->y = y;
return tmp;
}
/*返回正确路径*/
list GetPath(Point *startPoint, Point *endPoint)
{
Point *result = FindPath(startPoint, endPoint);
list path;
//返回路径,如果没有找到路径则返回空链表
while (result)
{
path.push_front(result);
result = result->parent;
}
return path;
}
static Point *GetLeastPoint()
{
Point *resPoint = openList.front();
if (!openList.empty())
{
for (list::const_iterator it= openList.begin();it!=openList.end();it++)
if ((*it)->F < resPoint->F)
{
resPoint = *it;
}
}
return resPoint;
}
static vector GetSurroundPoints(const Point *point)
{
vector surroundPoints;
for (int x= point->x-1;x<= point->x+1;x++)
for (int y = point->y - 1; y <= point->x+1; y++)
{
Point *tmp = AllocPoint(x, y);
if (isCanreach(point,tmp))
{
surroundPoints.push_back(tmp);
}
else
{
delete tmp;
}
}
return surroundPoints;
}
Point * isInList(const list point,const Point *target)
{
for (list::const_iterator it = point.begin(); it != point.end(); it++)
{
if ((*it)->x==target->x && (*it)->y==target->y)
{
return *it;
}
}
return NULL;
}
bool isCanreach(const Point *point, const Point *target)
{
if (target->x<0|| target->x>(lines-1)
|| target->y<0|| target->y>(cols-1)
|| maze[target->x*cols+target->y]==1//1代表无法走的格子
|| maze[target->x*cols + target->y] == 2//2代表无法走的格子
|| (target->x==point->x && target->y==point->y)
|| isInList(closeList,target)!=NULL)
{
return false;
}
if (abs(point->x - target->x) + abs(point->y - target->y) == 1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int calcDistance(Point *target, Point *endPoint)
{
return abs(target->x - endPoint->x) + abs(target->y - endPoint->y);
}
void ClearAstarMaze()
{
maze = NULL;
lines = cols = 0;
for (list::iterator it=openList.begin();it!=openList.end();)
{
delete *it;
it = openList.erase(it);
}
for (list::iterator it = closeList.begin(); it != closeList.end();)
{
delete *it;
it = closeList.erase(it);
}
} main.cpp
#include
#include "AStar.h"
#include
int main()
{
int map[13][13] = {
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, },
{ 2, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 2, },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, } };
InitAstarMaze(&map[0][0], 13, 13);
Point *start = AllocPoint(12, 12);
Point *end = AllocPoint(0, 0);
list path = GetPath(start, end);
for (list::iterator it = path.begin(); it != path.end(); it++)
{
Point *res = *it;
cout << "(" << res->x << "," << res->y << ")" << endl;
Sleep(800);
}
ClearAstarMaze();
}