稀疏数组举例详解(Java形式表示)
稀疏数组
- 稀疏数组的定义
- 稀疏数组的形式
- 稀疏数组的用途
- Java形式实现稀疏数组
-
- 1.创建稀疏矩阵
- 2.遍历矩阵提取有效元素个数,来确立稀疏数组创建的行数(行数=有效元素个数+1)
- 3.通过有效元素个数创建稀疏数组的个数
- 4.填入初始行(第一行)数据
- 5.填入后续行数据
- 6.将稀疏数组数据打印在控制台上
- 7.学会了压缩,当然也要学会解压缩
- 附上面所有的组成的整体代码
- Java形式表示稀疏数组并结合IO流

稀疏数组的定义
稀疏数组是一种表示稀疏矩阵的数据结构。(在编程中,我们常以二维数组来表示矩阵)
一个矩阵被称为稀疏矩阵,当其中大部分元素都是0时。
稀疏数组通过记录非零元素的行、列和值来表示一个稀疏矩阵,从而节省存储空间。

稀疏数组的形式
具体地说,稀疏数组通常以三列形式存储:第一列表示非零元素的行,第二列表示非零元素的列,第三列表示非零元素的值。
不过第一行有点特殊,具体看图
类似于这样:
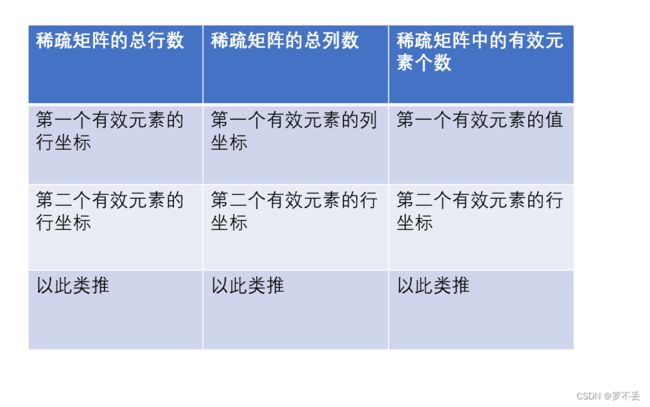
例如一个8行8列的稀疏矩阵,里面有三个有效的元素(颜色为红色的)需要我们记录:

第一行,我们知道了矩阵是8*8的,同时知道矩阵中有效元素有3个,然后剩下的三行就把有效元素的行列坐标与值依次填入就行。

稀疏数组的用途
稀疏矩阵的存储:
对于一个非常大的矩阵,如果其中大部分元素都是0,那么可以使用稀疏数组来存储这个矩阵,从而节省存储空间。
图像处理:
在图像处理中,通常需要处理大量的像素,而大部分像素的取值都是相同的。这时候可以使用稀疏数组来存储图像数据,只记录非零的像素值,从而节省存储空间和加快处理速度。
网络图:
在网络图中,通常需要记录节点之间的连接关系。如果节点之间的连接关系比较稀疏,可以使用稀疏数组来存储连接关系,只记录存在连接的节点,从而节省存储空间和加快处理速度。
后面两个比较高级,我还没真正使用过,所以我只用第一个用途为例。
Java形式实现稀疏数组
1.创建稀疏矩阵
int[][] sparseArrays=new int[8][8];
//假设里面只有3个有效数据
sparseArrays[2][3]=1;
sparseArrays[3][4]=2;
sparseArrays[6][3]=3;
2.遍历矩阵提取有效元素个数,来确立稀疏数组创建的行数(行数=有效元素个数+1)
当然也可以采用动态创建或者利用Java中的集合来动态添加,这里就不用那些复杂的了
第一步:遍历待压缩矩阵,提取有效元素个数
int value_sum=0;//有效数据的总数
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArrays.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sparseArrays[i].length; j++) {
if(sparseArrays[i][j]!=0) {
value_sum++;
}
}
}
遍历完成后就能得到有效元素的个数
3.通过有效元素个数创建稀疏数组的个数
第二步:创建压缩数组,将值写入
int[][] compressed_arrays=new int[value_sum+1][3];
4.填入初始行(第一行)数据
第三步:压缩后的数组首行对应分别是稀疏数组的行,列,有效值总数
compressed_arrays[0][0]=sparseArrays.length;
compressed_arrays[0][1]=sparseArrays[0].length;
compressed_arrays[0][2]=value_sum;
5.填入后续行数据
第四步:再次遍历矩阵,将有效元素的行列坐标和值拿到
int count=0;//临时计数器
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArrays.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sparseArrays[i].length; j++) {
if(sparseArrays[i][j]!=0) {
compressed_arrays[count+1][0]=i;
compressed_arrays[count+1][1]=j;
compressed_arrays[count+1][2]=sparseArrays[i][j];
//将具体的有效值插入到压缩中的数组中
count++;
}
}
}
6.将稀疏数组数据打印在控制台上
//展示压缩后的数组
for (int i = 0; i < compressed_arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("[\t");
for (int j = 0; j < compressed_arrays[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t",compressed_arrays[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("]");
}
7.学会了压缩,当然也要学会解压缩
恢复稀疏数组成稀疏矩阵
System.out.println("恢复成正常数组");
int[][] normalArrays=new int[compressed_arrays[0][0]][compressed_arrays[0][1]];
for (int i=1;i<compressed_arrays.length;i++){
normalArrays[compressed_arrays[i][0]][compressed_arrays[i][1]]=compressed_arrays[i][2];
}
for (int i = 0; i < normalArrays.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("[\t");
for (int j = 0; j < normalArrays[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t",normalArrays[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("]");
}
附上面所有的组成的整体代码
顺便加上了几次输出,让过程更明显
public class SparseArrays {
//自己创建一个稀疏数组
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] sparseArrays=new int[8][8];
//假设里面只有3个有效数据
sparseArrays[2][3]=1;
sparseArrays[3][4]=2;
sparseArrays[6][3]=3;
//二维数组打印遵循先行后列的嵌套循环
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArrays.length; i++) {//这里的length字段是二维数组的行数
System.out.printf("[\t");
for (int j = 0; j < sparseArrays[i].length; j++) {//这里的length字段反映的是二维数组所在行的长度
System.out.printf("%d\t",sparseArrays[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("]");
System.out.println();
}
// 第一步:遍历待压缩数组,提取有效信息。
int value_sum=0;//有效数据的总数
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArrays.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sparseArrays[i].length; j++) {
if(sparseArrays[i][j]!=0) {
value_sum++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("将其进行压缩");
//第二步:创建压缩数组,将值写入
int[][] compressed_arrays=new int[value_sum+1][3];
//压缩后的数组首行对应分别是稀疏数组的行,列,有效值总数
compressed_arrays[0][0]=sparseArrays.length;
compressed_arrays[0][1]=sparseArrays[0].length;
compressed_arrays[0][2]=value_sum;
int count=0;//临时计数器
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArrays.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sparseArrays[i].length; j++) {
if(sparseArrays[i][j]!=0) {
compressed_arrays[count+1][0]=i;
compressed_arrays[count+1][1]=j;
compressed_arrays[count+1][2]=sparseArrays[i][j];//将具体的有效值插入到压缩中的数组中
count++;
}
}
}
//展示压缩后的数组
for (int i = 0; i < compressed_arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("[\t");
for (int j = 0; j < compressed_arrays[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t",compressed_arrays[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("]");
}
//恢复压缩数组成正常数组
System.out.println("恢复成正常数组");
int[][] normalArrays=new int[compressed_arrays[0][0]][compressed_arrays[0][1]];
for (int i=1;i<compressed_arrays.length;i++){
normalArrays[compressed_arrays[i][0]][compressed_arrays[i][1]]=compressed_arrays[i][2];
}
for (int i = 0; i < normalArrays.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("[\t");
for (int j = 0; j < normalArrays[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t",normalArrays[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
}
Java形式表示稀疏数组并结合IO流
这里本质就是将读取内存里的稀疏矩阵和稀疏数组和输出,变成读取存储里的文件数据再转化为内存里的稀疏数组和稀疏矩阵的形式。不做详细介绍了,这里给个将稀疏数组存储到文件中以达到持久化的例子。
记得文件路径改成自己的。
package com.budiu;
/**
结合IO流运用稀疏数组
*/
import java.io.*;
public class SparseArrays_IO {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int[][] sparseArrays=new int[8][8];
//假设里面只有三个有效数据
sparseArrays[2][3]=1;
sparseArrays[3][4]=2;
sparseArrays[6][3]=3;
//二维数组打印遵循先行后列的嵌套循环
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArrays.length; i++) {//这里的length字段是二维数组的行数
System.out.printf("[\t");
for (int j = 0; j < sparseArrays[i].length; j++) {//这里的length字段反映的是二维数组所在行的长度
System.out.printf("%d\t",sparseArrays[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("]");
System.out.println();
}
// 第一步:遍历待压缩数组,提取有效信息。
int value_sum=0;//有效数据的总数
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArrays.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sparseArrays[i].length; j++) {
if(sparseArrays[i][j]!=0) {
value_sum++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("将其进行压缩");
//第二步:创建压缩数组,将值写入
int[][] compressed_arrays=new int[value_sum+1][3];
//压缩后的数组首行对应分别是稀疏数组的行,列,有效值总数
compressed_arrays[0][0]=sparseArrays.length;
compressed_arrays[0][1]=sparseArrays[0].length;
compressed_arrays[0][2]=value_sum;
int count=0;//临时计数器
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArrays.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sparseArrays[i].length; j++) {
if(sparseArrays[i][j]!=0) {
compressed_arrays[count+1][0]=i;
compressed_arrays[count+1][1]=j;
compressed_arrays[count+1][2]=sparseArrays[i][j];//将具体的有效值插入到压缩中的数组中
count++;
}
}
}
//展示压缩后的数组
for (int i = 0; i < compressed_arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("[\t");
for (int j = 0; j < compressed_arrays[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t",compressed_arrays[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("]");
}
//将压缩数组写入到文件中
//创建IO流
File file=new File("D:\\javaworkspace\\note\\data_structure\\src\\file\\map.data");
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
for (int i = 0; i < compressed_arrays.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < compressed_arrays[i].length; j++) {
bos.write((compressed_arrays[i][j]+"\t").getBytes());
}
bos.write("\n".getBytes());
}
bos.close();
//
FileReader fr=new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(fr);
int bytesSize=0;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
int count1=0;
String content=null;
int[][] compressed_arrays1=null;
while ((content=reader.readLine())!=null){
//将字节转化为字符
String[] tmp=content.split("\t");
int row=Integer.parseInt(tmp[0]);
int column=Integer.parseInt(tmp[1]);
int value=Integer.parseInt(tmp[2]);
count1++;
if(count1==1){
compressed_arrays1=new int[value+1][3];
}
compressed_arrays1[count1-1][0]=row;
compressed_arrays1[count1-1][1]=column;
compressed_arrays1[count1-1][2]=value;
}
//恢复压缩数组成正常数组
System.out.println("恢复成正常数组");
int[][] normalArrays=new int[compressed_arrays1[0][0]][compressed_arrays1[0][1]];
for (int i=1;i<compressed_arrays1.length;i++){
normalArrays[compressed_arrays1[i][0]][compressed_arrays1[i][1]]=compressed_arrays1[i][2];
}
for (int i = 0; i < normalArrays.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("[\t");
for (int j = 0; j < normalArrays[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t",normalArrays[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
}
