Java IO流(详解)
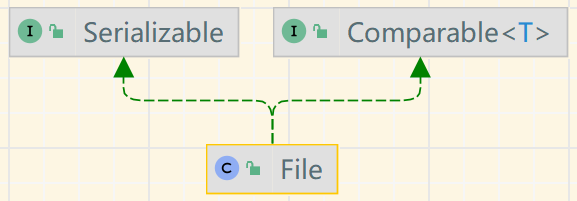
- 1. File
-
- 1. 创建
- 2. 操作
-
- 1. 获取文件信息
- 2. 目录创建/删除
- 2. IO流
-
- 1. FileInputStream
-
- 1. 简单使用
- 2. 读取中文
- 2. FileOutputStream
-
- 1. 简单使用
- 2. 追加写入
- 3. 文件拷贝
- 4. FileReader
-
- 1. 简单使用
- 2. 提高读取速度
- 5. FileWriter
-
- 1. 简单使用
- 6. 节点流和处理流简介
- 7. BufferedReader
-
- 1. 简单使用
- 8. BufferedWriter
-
- 1. 简单使用
- 9. Buffered字符流拷贝
- 10. Buffered字节流拷贝
- 11 对象流
-
- 1. 简单使用
- 2. 注意事项
- 12. 标准输入/输出流
- 13. 转换流
-
- 1. 乱码问题
- 2. InputStreamReader
- 3. OutputStreamWriter
- 14. 打印流
-
- 1. PrintStream
- 2. PrintWriter
- 15. 读写.properties 文件
1. File
1. 创建
构造器:
new File
- (String pathName) // 根据路径构建一个 File对象
- (File parent, String child) // 根据父目录文件 + 子路径构建
- (String parent, String child) // 根据父目录 + 子路径构建
创建对象:
createNewFile
(String pathName) —— 目录必须存在,才能创建文件
如果 D:\Study\file_demo\ 路径不存在,会抛出异常:java.io.IOException: 系统找不到指定的路径 。
public static File create_01(String path) {
File file = new File(path);
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return file;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\demo1.txt";
File file = create_01(path);
}
(File parent, String child)
如果 D:\Study\file_demo\ 路径不存在,会抛出异常:java.io.IOException: 系统找不到指定的路径 。
public static File create_02(File parent, String child) {
File file = new File(parent, child);
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return file;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File parent = new File("D:\\Study\\file_demo\\");
String path = "demo2.txt";
File file = create_02(parent, path);
}
(String parent, String child)
如果 D:\Study\file_demo\ 路径不存在,会抛出异常:java.io.IOException: 系统找不到指定的路径 。
public static File create_03(String parent, String child) {
File file = new File(parent, child);
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return file;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String parent = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\";
String child = "demo3.txt";
File file = create_03(parent, child);
}

注意:
- new File 只是在内存中创建了一个对象
- createNewFile 才是在磁盘上创建了一个文件
2. 操作
1. 获取文件信息
方法:
- getName
- getAbsolutePath
- getParent
- length
- exists
- isFile
- isDirectory
public static Map<String, String> getFileInfo(File file) {
Map<String, String> info = new HashMap<>();
info.put("文件名", file.getName());
info.put("文件绝对路径", file.getAbsolutePath());
info.put("文件父级目录", file.getParent());
info.put("文件大小(byte)", String.valueOf(file.length()));
info.put("文件是否存在", file.exists() + "");
info.put("是否是文件", file.isFile() + "");
info.put("是否是目录", String.valueOf(file.isDirectory()));
return info;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("D:\\Study\\file_demo\\demo1.txt");
getFileInfo(file).forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + ":" + v);
});
}
2. 目录创建/删除
方法:
- mkdir
创建一级目录 - mkdirs
创建多级目录 - delete
删除空目录/文件
注意: Java中,目录也被当做文件。
public static void create_01(String path) {
File file = new File(path);
String flagE = null;
String flagM = null;
String flagMs = null;
if (file.exists()) {
flagE = file.delete() ? "文件删除成功" : "文件删除失败";
} else {
flagE = "文件不存在";
}
System.out.println(flagE);
boolean isMk = file.mkdir();
flagM = isMk ? "一级目录创建成功" : "一级目录创建失败";
System.out.println(flagM);
if (!isMk) {
flagMs = file.mkdirs() ? "多级目录创建成功" : "多级目录创建失败";
System.out.println(flagMs);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\test";
create_01(path);
}
2. IO流
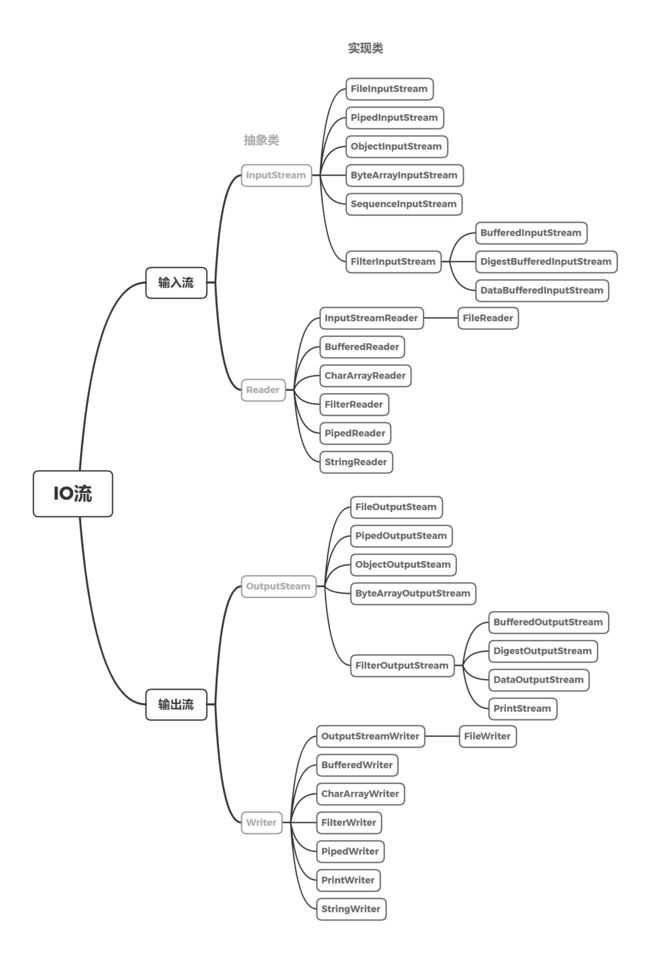
IO: Input/Output,处理数据传输的技术。
Stream: 流,Java中的数据的输入/输出都以流的方式进行。
- 分类(数据单位)
- 字节流(1 byte)—— InputStream、OutputStream
- 字符流(1 字符)—— Reader、Writer
- 分类(流向)
- 输入流
- 输出流
- 分类(角色)
- 节点流
- 处理流/包装流
1. FileInputStream
1. 简单使用
public static String readFile_01(String path) {
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int curr = 0;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(path);
while ((curr = inputStream.read()) != -1) {
// read ———— 每次读取 1byte, 读取完毕就返回 -1
sb.append((char) curr + "");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\user.txt";
System.out.println(readFile_01(path));
}
注意:
- read 每次读取 1byte,读取完毕返回 -1
- 每次使用完流,都得使用 close 关闭流,避免资源浪费
- 使用 FileInputStream 读取中文可能会出现中文乱码问题
- 原因:
FileInputStream 每次读取大小为 1byte = 8bit,在 GBK 编码模式下,每个中文为 2bit,但在 UTF-8 编码 模式下,每个中文为 3bit,显然不能刚好装进一个 byte 数组。 - 解决方案:
- 使用 FileReader
- 使用 read(byte b[]),并将 byte 数组的容量设置足够大
这个方法就是自定义每次读取的字节数组的大小
- 原因:
2. 读取中文
思路: 声明一个容量足够大的 byte 数组(能一次性吧文件读完),然后使用 public int read(byte b[]) 读取文件(会将文件内容存入 b[],并返回 b.length)。
public static String readFile_01(String path) {
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// 用一个足够大的 byte 数组来装下内容
byte [] bytes = new byte[83];
int readLen = 0;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(path);
// 返回值是读取的字节长度
while ((readLen = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
// read ———— 每次读取 1byte, 读取完毕就返回 -1
sb.append(new String(bytes, 0, readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\user.txt";
System.out.println(readFile_01(path));
}
2. FileOutputStream
1. 简单使用
write
-
write(int b)
-
write(byte b[])
-
write(byte b[], int off, int len)
public static void write_01(String path, String words) {
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(path);
//
outputStream.write(words.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String words = "在龟友百货上班,规规矩矩地纳税。";
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\user.txt";
write_01(path, words);
}
注意:
- 直接这样 write 会覆盖掉之前的内容
- 进行写操作的时候,文件可以不存在,但目录必须存在
2. 追加写入
在初始化 FileOutputStream 的时候,传入一个参数 true,表明——在文件末尾追加内容。
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(path, true);
3. 文件拷贝
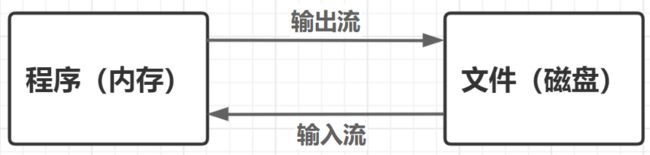
步骤: 输入流(读取到内存)→ 输出流(写入到磁盘)
读取部分数据,就写入磁盘,不能一次性读完再写(防止内存不够)。
public static void copy(String resPath, String tarPath) {
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
byte []bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024]; // 一次读 1MB
int len = 0;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(resPath);
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(tarPath);
while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
outputStream.write(bytes, 0, len); // 这里必须使用此方法,防止文件读取时没装完
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
if (outputStream != null) {
outputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String res1 = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\resource\\pic.jpg";
String res2 = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\resource\\user.txt";
String res3 = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\resource\\电锯人5.mp4";
String res4 = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\resource\\周杰伦 - 我是如此相信.mp3";
String tar1 = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\target\\pic.jpg";
String tar2 = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\target\\user.txt";
String tar3 = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\target\\电锯人5.mp4";
String tar4 = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\target\\周杰伦 - 我是如此相信.mp3";
copy(res1, tar1);
copy(res2, tar2);
copy(res3, tar3);
copy(res4, tar4);
}

4. FileReader
1. 简单使用
public static String readFile_02(String path) {
FileReader reader = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int curr = 0;
try {
reader = new FileReader(path);
while (true) {
if ((curr = reader.read()) == -1) break;
sb.append((char) curr + "");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\target\\user.txt";
System.out.println(readFile_02(path));
}

注意: 因为 FileReader 是一个字符一个字符地读取的,所以不存在中文乱码问题。
2. 提高读取速度
按照上面的写法,每次只读取一个字符,效率太低,为了提高读取效率,可以使用这个方法:public int read(char cbuf[])
public static String readFile_02(String path) {
FileReader reader = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
char []chars = new char[8]; // 一次读取 8 个字符
int len = 0;
try {
reader = new FileReader(path);
while (true) {
if ((len = reader.read(chars)) == -1) break;
sb.append(new String(chars, 0, len));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\target\\user.txt";
System.out.println(readFile_02(path));
}
5. FileWriter
常用用法:
-
FileWriter(String fileName)
覆盖写入 -
FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append)
append 为 true => 追加写入 -
write(int c)
写入单个字符 -
write(char cbuf[])
写入指定数组 -
write(char cbuf[], int off, int len)
写入指定数组的指定部分 -
write(String str)
写入整个字符串 -
write(String str, int off, int len)
写入字符串的指定部分
注意: FileWriter 使用完后,必须关闭 close 或 flush 才能向文件写入内容。
1. 简单使用
public static void write_02(String path, String words, boolean flag) {
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
try {
if (flag) {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(path, true);
} else {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(path);
}
fileWriter.write(words);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// close = flush + 关闭流
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\user.txt";
String words = "每晚八点回家却不会觉得累。";
write_02(path, words, true);
}
6. 节点流和处理流简介
节点流: 可以从一个特定的数据源 读写数据(FileReader、FileWriter、…)。
处理流/包装流: 基于已存在的流(节点流或处理流),为程序提供较为强大的读写功能(BufferedReader、BufferedWriter、…)。
处理流就是在节点流简单读写数据源的基础上,对读写功能进行扩展,比如说增加一个缓冲区。处理流的构造必须基于已存在的流。

两者关联
- 节点流是 底层流/低级流,直接跟数据源连接
- 处理流 包装节点流,可以消除不同节点流的实现差异,也可以提供更方便的方法来完成输入输出
- 处理流 包装节点流,使用了 修饰器设计模式,不会直接与数据源相连
- 处理流的优势:
- 性能提高:主要以增加缓冲的方式来提高读写的效率
- 操作便捷:提供了一系列便捷的方法来一次输入输出大批量的数据,更加灵活轻便
7. BufferedReader
1. 简单使用
public static String read_03(String path) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
BufferedReader reader = null;
String line;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\user.txt";
System.out.println(read_03(path));
}
注意: 关闭了处理流,其节点流也会自动关闭。
8. BufferedWriter
1. 简单使用
public static void write_03(String path, String words) {
BufferedWriter writer = null;
try {
writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(path, true));
writer.write("\n" + words);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\user.txt";
String words = "喝酒从来止于浅尝从不买醉。";
write_03(path, words);
}
9. Buffered字符流拷贝
public static void copy(String src, String target) {
BufferedReader reader = null;
BufferedWriter writer = null;
BufferedWriter clear = null;
String line;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));
writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(target, true));
// 清空文件内容
clear = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(target));
clear.write("");
while (true) {
if ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
// 每写一行
writer.write(line);
// 就换一行
writer.newLine();
continue;
}
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
clear.close();
reader.close();
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String src = "D:\\sedemo\\src\\main\\java\\io\\file\\FileCreate.java";
String target = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\target\\FileCreate.java";
copy(src, target);
}
注意: BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter 只用来处理文本文件,别用来处理二进制文件。
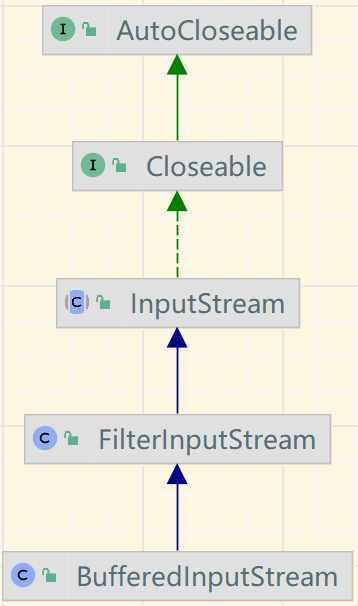
10. Buffered字节流拷贝
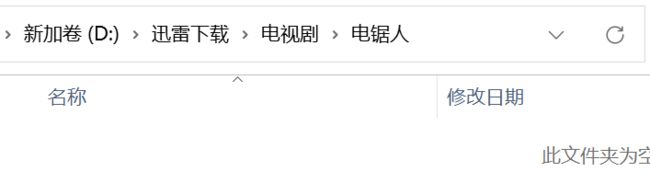
需求: 将下图中的 电锯人6 和 周杰伦 - 倒影.mp3 分别移动到指定文件夹


public static void copy(String src, String tar) {
byte []bytes = new byte[1024*1024];
int len = 0;
try (
BufferedInputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
BufferedOutputStream outputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(tar))
) {
while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
outputStream.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String mp4Src = "D:\\迅雷下载\\电锯人6.mp4";
String mp3Src = "D:\\迅雷下载\\周杰伦 - 倒影.mp3";
String mp4Tar = "D:\\迅雷下载\\电视剧\\电锯人\\电锯人6.mp4";
String mp3Tar = "D:\\迅雷下载\\音乐\\周杰伦 - 倒影.mp3";
copy(mp3Src, mp3Tar);
copy(mp4Src, mp4Tar);
}
11 对象流
对象流: 对Java对象进行序列化和反序列化操作,使对象便于持久化到本地,并从本地传到内存(ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream)。
1. 简单使用
-
定义一个 User 对象
需要实现了 Serializable 接口的对象才能序列化
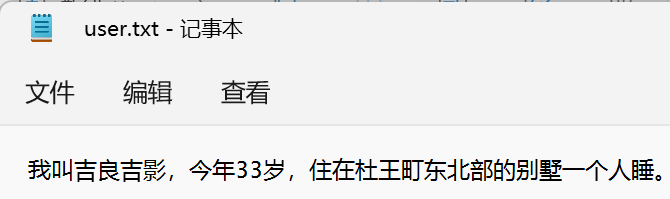
这个接口是一个标记接口,只表明该类可以序列化@Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class User implements Serializable { private String name; private Integer age; private char gend; } -
写读
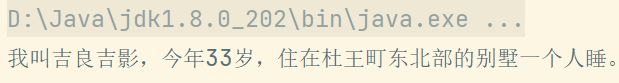
public static void writeObj(String path) { try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path))){ // 序列化数据 oos.writeInt(1); // 包装类都实现了 Serializable 接口, 可序列化 oos.write(2); oos.writeBoolean(true); oos.writeObject(new User("吉良吉影", 33, '男')); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void readObj(String path) { try (ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path))){ // 注意:读取顺序必须与保存顺序一致 System.out.println(ois.readInt()); System.out.println(ois.read()); System.out.println(ois.readBoolean()); User user = (User) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(user); System.out.println(user.getName()); } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // 序列化后保存的格式不是纯文本,这里指定后缀没啥意义 String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\obj.hehe"; writeObj(path); readObj(path); }
2. 注意事项
-
序列化写入是啥顺序,读取的时候就应该是啥顺序
-
可以被 ObjectOutputStream 序列化写入的对象,都必须实现 Serializable 接口
-
序列化的类中建议添加 serialVersionUID,提高版本的兼容性
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L虚拟机是否允许反序列化,不仅取决于类路径和功能代码是否一致,一个非常重要的一点是两个类的序列化 ID 是否一致
-
序列化对象,默认将里面所有的属性都进行序列化(除了 static、transient 修饰的成员)
-
序列化对象,要求对象的所有属性的类型也要实现 Serializable 接口
-
序列化具备可继承性,父类可以序列化,那么其子类也可以进行序列化
12. 标准输入/输出流
System.in 标准输入——默认设备:键盘
System.out 标准输出——默认设备:屏幕
public static String sys_in() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (scanner.hasNextInt()) {
int cur = scanner.nextInt();
if (cur == 0) break;
sb.append(cur + "");
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(sys_in());
}

13. 转换流
转换流: 将字节流转换为字符流,常用于解决中文乱码问题。
- InputStreamReader
- OutputStreamWriter
1. 乱码问题
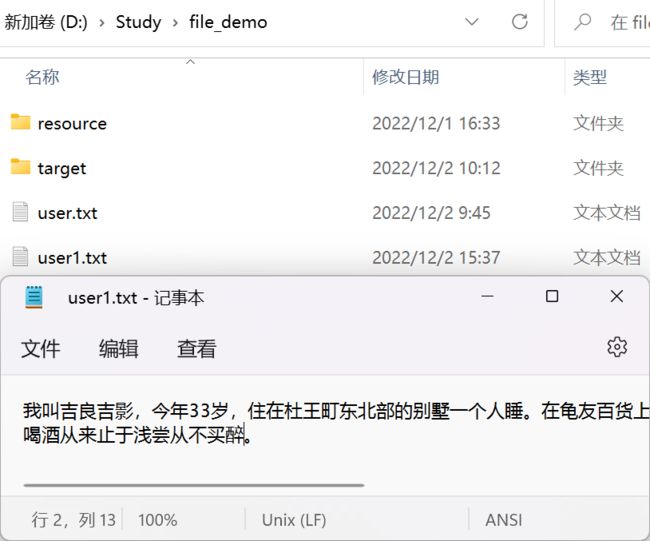
我们已经分析过:直接使用字节流,如 FileInputStream 读取含有中文的文档,就会出现乱码问题,这是因为字节流默认一次读取 8bit。
其实,使用字符流读取中文文档的时候也会出现乱码问题:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader reader = new FileReader("D:\\Study\\file_demo\\user1.txt");
int curr = 0;
while ((curr = reader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) curr);
}
reader.close();
}
那为什么读取user.txt就不会出现此类问题呢?
因为编码问题:txt默认 UTF-8,编码,这时候使用字符流去读取不会出现乱码(读取的编码方式,默认也是 UTF-8),但是修改了编码,就会出现乱码:
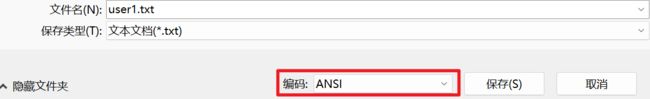
可以使用转换流来解决中文乱码——指定读取文件的编码方式。
转换流:
- 可以将一个字节流转换成字符流
- 字节流可以指定编码读取方式
解决思路:
- 先指定字节流读取的编码方式
- 先后将字节流转换为字符流
2. InputStreamReader

InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs)
当处理纯文本数据时,如果使用字符流效率更高,并且可以有效解决中文乱码问题,建议使用转换流将字节流转换为字符流。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\Study\\file_demo\\user1.txt");
InputStreamReader streamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "gbk");
int curr = 0;
while ((curr = streamReader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) curr);
}
streamReader.close();
}
3. OutputStreamWriter

public static void main(String[] args) {
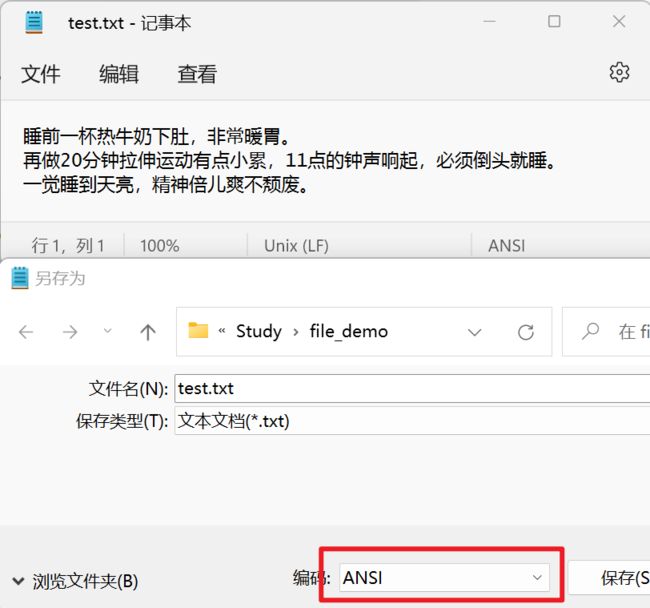
String path = "D:\\Study\\file_demo\\test.txt";
try (OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(path), "gbk")) {
osw.write("睡前一杯热牛奶下肚,非常暖胃。\n再做20分钟拉伸运动有点小累,11点的钟声响起,必须倒头就睡。\n一觉睡到天亮,精神倍儿爽不颓废。");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
14. 打印流
打印流: 字节打印流
注意: 打印流只有输出流,没有输入流。
1. PrintStream
System.out 就是打印流。
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintStream out = System.out;
out.print("The World !");
out.close();
}
因为 out.print 的底层就是 out.write
public void print(String s) {
if (s == null) {
s = "null";
}
write(s);
}
所以,可以直接使用 out.write
out.write(("The World !").getBytes());
使用 PrintStream 写入本地文件:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.setOut(new PrintStream("D:\\Study\\file_demo\\test.txt"));
System.out.println("The World !");
}
2. PrintWriter
public static void main(String[] args) {
// PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(System.out);
PrintWriter writer = null;
try {
writer = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("D:\Study\file_demo\test.txt"));
writer.print("The World !");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
writer.close();
}
}
注意: 因为是基于 PrintWriter 初始化的,所以必须要 close 才能将数据写入文件。
15. 读写.properties 文件
properties类: 对 .properties 配置文件进行读写操作。

常用方法:
- load
加载配置文件的键值对到 properties 对象 - list
将数据显示到指定设备 - getProperty(key)
根据键获取值 - setProperty(key, value)
设置键值对到 Properties 对象中 - store
将 .properties 中的键值对存储到配置文件(Idea中,保存信息到配置文件,如果包含中文,会存储为 Unicode 码)
data.properties
driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
username=root
password=admin
读取:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
// 加载配置文件
properties.load(new FileReader("D:\sedemo\io\src\main\resources\data.properties"));
// 显示
properties.list(System.out);
properties.list(new PrintStream("D:\Study\file_demo\data.txt"));
// 根据key,获取value
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("url"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
修改:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 该配置文件没有 对应的key,就是新增一对键值对,否则就是修改 value
properties.setProperty("role.name", "张三");
properties.setProperty("role.age", "17");
properties.setProperty("role.gend", "男");
properties.store(new FileOutputStream("D:\yinhai\gonghui\sedemo\clone\src\main\resources\role.properties"), "这是一段注释,可以为空");
}