【精选】SpringDI依赖注入及注解实现SpringIoC
SpringDI
什么是依赖注入
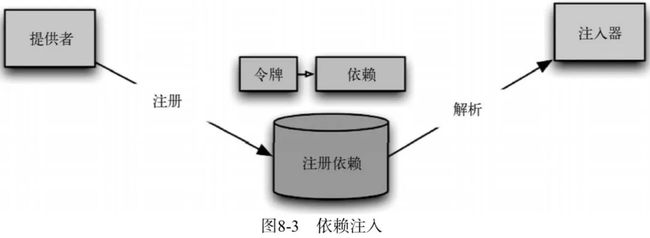
依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI),它是Spring控制反转思想的具体实现。
控制反转将对象的创建交给了Spring,但是对象中可能会依赖其他对象。比如service类中要有dao类的属性,我们称service依赖于dao。之前需要手动注入属性值,代码如下:
public interface StudentDao {
Student findById(int id);
}
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
@Override
public Student findById(int id) {
// 模拟根据id查询学生
return new Student(1,"张三","北京");
}
}
public class StudentService {
// service依赖dao,手动注入属性值,即手动维护依赖关系
private StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDaoImpl();
public Student findStudentById(int id){
return studentDao.findById(id);
}
}
此时,当StudentService的想要使用StudentDao的另一个实现类如StudentDaoImpl2时,则需要修改Java源码,造成代码的可维护性降低。
而使用Spring框架后,Spring管理Service对象与Dao对象,此时它能够为Service对象注入依赖的Dao属性值。这就是Spring的依赖注入。简单来说,控制反转是创建对象,依赖注入是为对象的属性赋值。
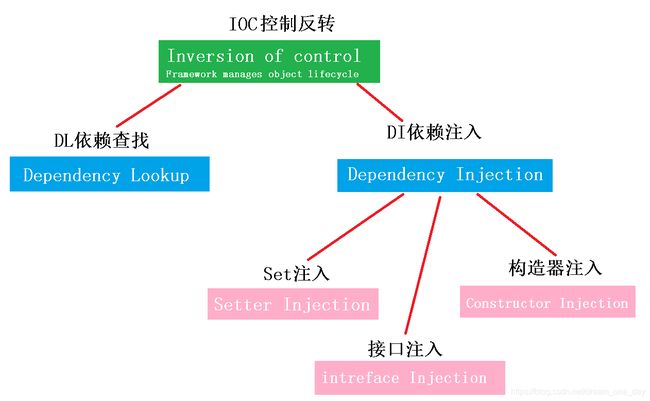
依赖注入方式
在之前开发中,可以通过setter方法或构造方法设置对象属性值:
// setter方法设置属性
StudentService studentService = new StudentService();
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
studentService.setStudentDao(studentDao);
// 构造方法设置属性
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
StudentService studentService = new StudentService(studentDao);
Spring可以通过调用setter方法或构造方法给属性赋值
Setter注入
-
被注入类编写属性的setter方法
public class StudentService { private StudentDao studentDao; public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) { this.studentDao = studentDao; } } -
配置文件中,给需要注入属性值的
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.Spring.dao.StudentDaoImpl">bean> <bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService"> <property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao">property> bean> -
测试是否注入成功
@Test public void t2(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService"); System.out.println(studentService.findStudentById(1)); }
构造方法注入
-
被注入类编写有参的构造方法
public class StudentService { private StudentDao studentDao; public StudentService(StudentDao studentDao) { this.studentDao = studentDao; } } -
给需要注入属性值的
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.Spring.dao.StudentDaoImpl">bean> <bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService"> <constructor-arg name="studentDao" ref="studentDao">constructor-arg> bean> -
测试是否注入成功
@Test public void t2(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService"); System.out.println(studentService.findStudentById(1)); }
自动注入
自动注入不需要在
自动注入有两种配置方式:
- 全局配置:在
中设置default-autowire属性可以定义所有bean对象的自动注入策略。- 局部配置:在
中设置autowire属性可以定义当前bean对象的自动注入策略。
autowire的取值如下:
- no:不会进行自动注入。
- default:全局配置default相当于no,局部配置default表示使用全局配置
- byName:在Spring容器中查找id与属性名相同的bean,并进行注入。需要提供set方法。
- byType:在Spring容器中查找类型与属性类型相同的bean,并进行注入。需要提供set方法。
- constructor:在Spring容器中查找id与属性名相同的bean,并进行注入。需要提供构造方法。
测试自动注入:
-
为依赖的对象提供setter和构造方法:
public class StudentService { // 依赖 private StudentDao studentDao; // 构造方法 public StudentService() { } public StudentService(StudentDao studentDao) { this.studentDao = studentDao; } // setter方法 public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) { this.studentDao = studentDao; } // 调用依赖的方法 public Student findStudentById(int id) { return studentDao.findById(id); } } -
配置自动注入:
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.Spring.dao.StudentDaoImpl">bean> <bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService" autowire="byName">bean><bean id="studentDao" class="com.Spring.dao.StudentDaoImpl">bean> <bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService" autowire="byType">bean><bean id="studentDao" class="com.Spring.dao.StudentDaoImpl">bean> <bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService" autowire="constructor">bean><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" default-autowire="constructor">
依赖注入类型
DI支持注入bean类型、基本数据类型和字符串、List集合、Set集合、Map集合、Properties对象类型等,他们的写法如下:
-
准备注入属性的类
public class StudentService { private StudentDao studentDao; // bean属性 private String name; //字符串类型 private int count; //基本数据类型 private List<String> names; // 字符串类型List集合 private List<Student> students1; // 对象类型List集合 private Set<Student> students2; // 对象类型Set集合 private Map<String,String> names2; // 字符串类型Map集合 private Map<String,Student> students3; // 对象类型Map集合 private Properties properties; //Properties类型 // 省略getter/setter/toString } -
准备测试方法
@Test public void t3(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService"); System.out.println(studentService); }
注入bean类型
写法一:
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.Spring.dao.StudentDaoImpl">bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService">
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao">property>
bean>
写法二:
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.Spring.dao.StudentDaoImpl">bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService">
<property name="studentDao" >
<ref bean="studentDao">ref>
property>
bean>
注入基本数据类型和字符串类型
<bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService">
<property name="name" value="李四">property>
<property name="count">
<value>10value>
property>
bean>
注入List集合
<bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService">
<property name="names">
<list>
<value>Springvalue>
<value>张三value>
list>
property>
<property name="students1">
<list>
<bean class="com.Spring.domain.Student">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="Spring"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
bean>
<bean class="com.Spring.domain.Student">
<property name="id" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="李四"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
bean>
list>
property>
bean>
注入Set集合
<bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService">
<property name="students2">
<set>
<bean class="com.Spring.domain.Student">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="Spring"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
bean>
<bean class="com.Spring.domain.Student">
<property name="id" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="李四"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
bean>
set>
property>
bean>
注入Map集合
简单数据类型Map集合:
<bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService">
<property name="names2">
<map>
<entry key="student1" value="李四"/>
<entry key="student2" value="张三"/>
map>
property>
bean>
对象类型Map集合:
<bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService">
<property name="students3">
<map>
<entry key="student1" value-ref="s1"/>
<entry key="student2" value-ref="s2"/>
map>
property>
bean>
<bean id="s1" class="com.Spring.domain.Student">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="Spring"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
bean>
<bean id="s2" class="com.Spring.domain.Student">
<property name="id" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="李四"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
bean>
注入Properties对象
<bean id="studentService" class="com.Spring.service.StudentService">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="配置1">值1prop>
<prop key="配置2">值2prop>
props>
property>
bean>
注解实现IOC
准备工作
注解配置和xml配置对于Spring的IOC要实现的功能都是一样的,只是配置的形式不一样。
准备工作
-
创建一个新的Spring项目。
-
编写pojo,dao,service类。
-
编写空的配置文件,如果想让该文件支持注解,需要添加新的约束:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> beans>
@Component
作用:用于创建对象,放入Spring容器,相当于
位置:类上方
注意:
要在配置文件中配置扫描的包,扫描到该注解才能生效。
<context:component-scan base-package="com.Spring">context:component-scan>
@Component注解配置bean的默认id是首字母小写的类名。也可以手动设置bean的id值。// 此时bean的id为studentDaoImpl @Component public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{ public Student findById(int id) { // 模拟根据id查询学生 return new Student(1,"张三","北京"); } }// 此时bean的id为studentDao
@Component(“studentDao”)
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
public Student findById(int id) {
// 模拟根据id查询学生
return new Student(1,“张三”,“北京”);
}
}
@Repository、@Service、@Controller
作用:这三个注解和@Component的作用一样,使用它们是为了区分该类属于什么层。
位置:
- @Repository用于Dao层
- @Service用于Service层
- @Controller用于Controller层
@Repository
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{}
@Service
public class StudentService {}
@Scope
作用:指定bean的创建策略
位置:类上方
取值:singleton prototype request session globalsession
@Service
@Scope("singleton")
public class StudentService {}
@Autowired
作用:从容器中查找符合属性类型的对象自动注入属性中。用于代替
位置:属性上方、setter方法上方、构造方法上方。
注意:
-
@Autowired写在属性上方进行依赖注入时,可以省略setter方法。@Component public class StudentService { @Autowired private StudentDao studentDao; public Student findStudentById(int id){ return studentDao.findById(id); } } @Test public void t2(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService"); System.out.println(studentService.findStudentById(1)); } -
容器中没有对应类型的对象会报错
// 如果StudentDaoImpl没有放到容器中会报错 //@Component("studentDao") public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{ public Student findById(int id) { // 模拟根据id查询学生 return new Student(1,"张三","北京"); } } -
容器中有多个对象匹配类型时,会找beanId等于属性名的对象,找不到会报错。
// 如果容器中都多个同类型对象,会根据id值等于属性名找对象 @Component("studentDao") public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{ public Student findById(int id) { // 模拟根据id查询学生 return new Student(1,"张三","北京"); } } @Component public class StudentDaoImpl2 implements StudentDao{ public Student findById(int id) { // 模拟根据id查询学生 return new Student(1,"张三","北京"); } }
@Qualifier
作用:在按照类型注入对象的基础上,再按照bean的id注入。
位置:属性上方
注意:@Qualifier必须和@Autowired一起使用。
@Component
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("studentDaoImpl2")
private StudentDao studentDao;
public Student findStudentById(int id){
return studentDao.findById(id);
}
}
@Value
作用:注入String类型和基本数据类型的属性值。
位置:属性上方
用法:
-
直接设置固定的属性值
@Service public class StudentService { @Value("1") private int count; @Value("hello") private String str; } -
获取配置文件中的属性值:
-
编写配置文件db.properties
jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=123456 -
spring核心配置文件扫描配置文件
<context:property-placeholder location="db.properties">context:property-placeholder> -
注入配置文件中的属性值
@Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password;
-
@Configuration
此时基于注解的IOC配置已经完成,但是我们依然离不开Spring的xml配置文件。接下来我们脱离bean.xml,使用纯注解实现IOC。
在真实开发中,我们一般还是会保留xml配置文件,很多情况下使用配置文件更加方便。
纯注解实现IOC需要一个==Java类代替xml文件。==这个Java类上方需要添加@Configuration,表示该类是一个配置类,作用是代替配置文件。
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
}
@ComponentScan
作用:指定spring在初始化容器时扫描的包。
位置:配置类上方
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.Spring")
public class SpringConfig {
}
@PropertySource
作用:代替配置文件中的
位置:配置类上方
注意:配置文件位置前要加关键字classpath
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
}
@Bean
作用:将方法的返回值对象放入Spring容器中。如果想将第三方类的对象放入容器,可以使用@Bean
位置:配置类的==方法==上方。
属性:name:给bean对象设置id
注意:@Bean修饰的方法如果有参数,spring会根据参数类型从容器中查找可用对象。
举例:如果想将jdbc连接对象放入Spring容器,我们无法修改Connection源码添加@Component,此时就需要使用将@Bean该对象放入Spring容器
-
添加驱动依赖
<dependency> <groupId>mysqlgroupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId> <version>8.0.27version> dependency> -
将Connection对象放入Spring容器
@Bean(name = "connection") public Connection getConnection(){ try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); return DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///mysql", "root", "root"); } catch (Exception exception) { return null; } } -
测试
@Test public void t5(){ ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); Connection connection = (Connection) ac.getBean("connection"); System.out.println(connection); }
@Import
作用:如果配置过多,会有多个配置类,该注解可以为主配置类导入其他配置类
位置:主配置类上方
// Jdbc配置类
@Configuration
public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean(name = "connection")
public Connection getConnection(){
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
return DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///mysql", "root", "root");
} catch (Exception exception) {
return null;
}
}
}
// 主配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.Spring")
@Import(JdbcConfig.class)
public class SpringConfig {
}