【SpringBoot】SpringBoot——Spring Security安全框架
文章目录
- 6. Spring Boot安全框架
-
- 6.1 认识Spring Security
-
- 6.1.1 入门项目
- 6.1.2 角色访问控制
- 6.2 基于数据库的认证
-
- 6.2.1 Spring Security基于数据库认证
- 6.2.2 角色访问控制
- 6.2.3 密码加密保存
- 6.2.4 用户角色多对多关系
- 6.2.5 角色继承
6. Spring Boot安全框架
6.1 认识Spring Security
Spring Security致力于为Java应用提供核心功能认证(Authentication)和授权管理(Authorization)。
认证:主要是为了解决我是谁的问题,通过提供证据证明你是你说的那个人。
授权:主要是为了解决我能干什么的问题。
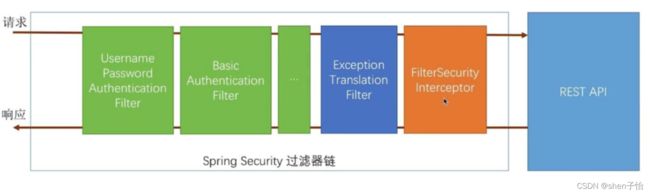
它是一个强大的、高度自定义的认证和访问控制框架。其核心就是一组过滤器链,项目启动后会自动配置。最核心就是Basic Authentication Filter用来认证用户的身份,在Spring Security中一种过滤器处理一种认证方式,如下所示:
(图源:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ef1e218f014a)
6.1.1 入门项目
-
创建项目
创建一个Spring Boot的Web项目,添加Spring Security依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId> dependency> -
控制器
新建HelloController类,添加/hello接口:
@RestController public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String home() { return "Hello ,spring security!"; } } -
测试
启动项目,在浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/login接口会自动跳转到登录页面,这是Spring Security提供的,如下所示:
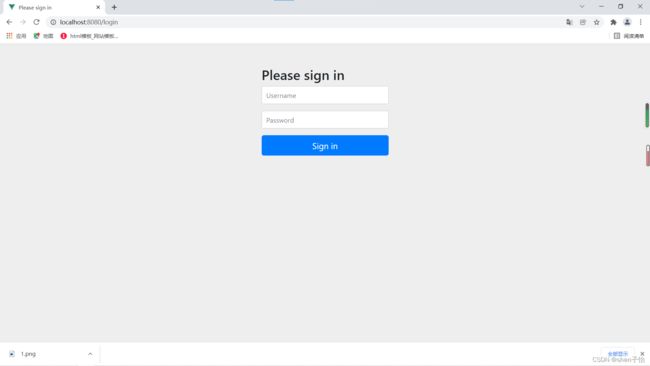
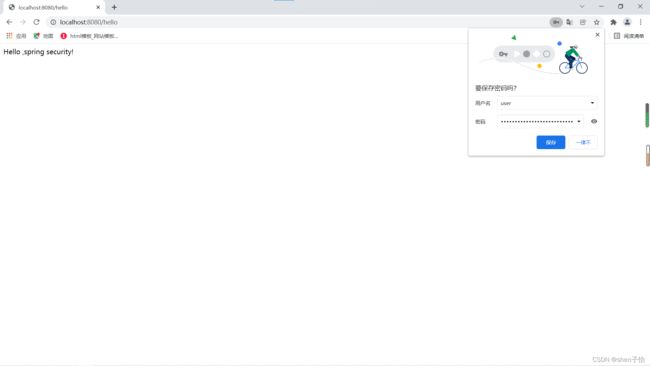
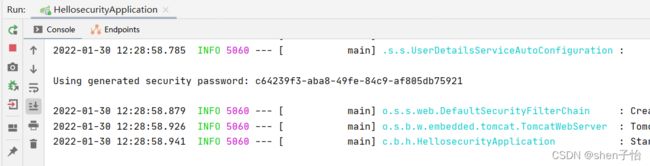
说明Spring Security已经起作用了,它会把项目里的资源保护起来。Spring Security默认用户名是user,Spring Security启动的时候会生成默认密码,在启动日志可以看到。填入用户名和密码后就可以成功访问接口了。
-
自定义用户名和密码
也可以自己设置用户名和密码,在application.yml中添加如下配置:
spring: security: user: name: admin password: 123456重启项目,访问被保护的/hello接口。自动跳转到了默认的登录页面,输入用户名和密码后成功跳转到了/hello。
6.1.2 角色访问控制
通常情况下,我们需要实现“特定资源只能由特定角色访问”的功能。假设我们的系统有以下两个角色:
- ADMIN:可以访问所有资源。
- USER:只能访问特定资源。
现在给系统增加“/user/** ”接口代表用户信息方面的资源(USER可以访问);增加“/admin/** ”接口代表管理员方面的资源(USER不能访问),代码如下:
@RestController
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/user/hello")
public String hello() {
return "user,Hello !";
}
}
@RestController
public class AdminController {
@RequestMapping("/admin/hello")
public String hello() {
return "admin,Hello !";
}
}
在实际开发中,用户和角色是保存在数据库中的,本例为了方便演示,创建两个存放于内存的用户和角色。可以自定义类并集成WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter进而实现Spring Security的更多配置:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/*不对密码进行加密*/
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
/*管理员用户 具备ADMIN和USER角色*/
.withUser("admin").password("admin").roles("ADMIN", "USER")
.and()
/*普通用户*/
.withUser("shenziyi").password("shenziyi").roles("USER");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
/*普通用户访问的url*/
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("USER")
/*管理员用户访问的url*/
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated() //其他多有路径都必须认证
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
.permitAll() //访问“/login”接口不需要进行身份认证了,防止重定向死循环
.and()
.csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf
}
}
根据上面的配置,我们知道使用“shenziyi”用户具有访问“/user/**”接口的权限,使用admin登录可以访问所有接口。
6.2 基于数据库的认证
在前面的案例中,用户登录系统的用户名、密码定义在内存中,在实际开发中,用户的基本信息及角色都是通过查询数据库进行认证和授权。
6.2.1 Spring Security基于数据库认证
Lombok的主要作用是通过注解消除实际开发中的样板式代码,如:getter、setter方法,重写toString、equals方法等,这些代码没有什么技术含量,但是常常要写,因此可以用@Data、@Setter、@Getter等注解来替换。
-
配置文件
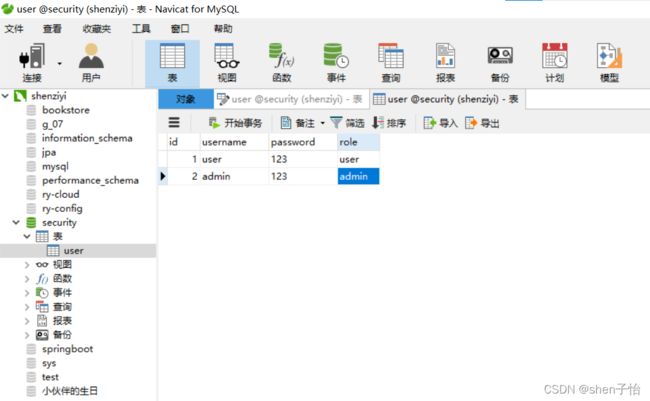
在application.yml中设置MySQL连接配置和MyBatis配置,代码如下:
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf-8 username: root password: admin123 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver logging: level: com.example.bdatabaserole.mapper: debug -
创建实体类
创建与用户表相对应的实体类并实现UserDetails:
package com.shenziyi.spring_security.entity; import lombok.Data; import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.List; @Data //lombok注解省略get/set等方法 public class UserInfo implements Serializable,UserDetails { private int id; private String username; private String password; private String role; public UserInfo(String username,String password,String role){ this.username=username; this.password=password; this.role=role; } /** * 指示用户的账户是否已过期。无法验证过期的账户。 * 如果用户的账户有效(即未过期),则返回true,如果不在有效就返回false */ @Override public boolean isAccountNonExpired() { return true; } /** * 指示用户是锁定还是解锁。无法对锁定的用户进行身份验证。 * 如果用户未被锁定,则返回true,否则返回false */ @Override public boolean isAccountNonLocked() { return true; } /** * 指示用户的凭证(密码)是否已过期。过期的凭证阻止身份验证 * 如果用户的凭证有效(即未过期),则返回true * 如果不在有效(即过期),则返回false */ @Override public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() { return true; } /** * 指示用户是启用还是禁用。无法对禁用的用户进行身份验证 * 如果启用了用户,则返回true,否则返回false */ @Override public boolean isEnabled() { return true; } @Override public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority>getAuthorities(){ Collection<GrantedAuthority>authorities=new ArrayList<>(); authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_"+this.role)); return authorities; } }UserDetails接口是提供用户信息的核心接口。该接口仅仅实现存储用户的信息。后续会将该接口提供的用户信息封装到认证对象Authentication中去。UserDetails默认提供了七个方法:
方法名 作用 getAuthorities() 用户的角色集,默认需要添加ROLE_前缀 getPassword() 获取当前用户对象密码 getUsername() 获取当前用户对象用户名 isAccountNonExpired() 账户是否过期 isAccountNonLocked() 账户是否锁定 isCredentialsNonExpired() 凭证是否过期 isEnabled() 用户是否可用 -
创建Mapper接口和Service层
创建UserMapper接口,对于简单的SQL语句可以使用注解式来替换XML式,接着创建UserInfoService业务层类:
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.shenziyi.spring_security.mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="getUserByUsername" resultType="com.shenziyi.spring_security.entity.UserInfo"> select * from user where username = #{username}; select> <select id="getRolesById" resultType="com.shenziyi.spring_security.entity.Role"> select * from role where id in(select rid from user_role where uid=#{uid}); select> mapper>package com.shenziyi.spring_security.mapper; import com.shenziyi.spring_security.entity.Role; import com.shenziyi.spring_security.entity.UserInfo; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import java.util.List; @Mapper @Repository public interface UserMapper { @Select("select * from user where username = #{username}") UserInfo getUserByUsername(String username); } -
创建Controller
接下来创建UserController
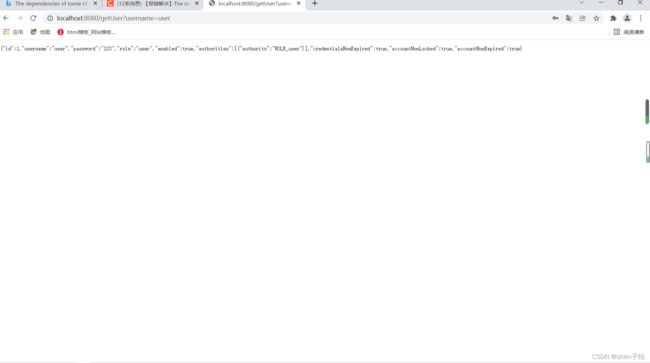
package com.shenziyi.spring_security.controller; import com.shenziyi.spring_security.entity.UserInfo; import com.shenziyi.spring_security.service.UserInfoService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController public class UserController { @Autowired private UserInfoService userInfoService; @GetMapping("/getUser") public UserInfo getUser(@RequestParam String username){ return userInfoService.getUserInfo(username); } } -
身份认证
需要从数据库读取用户信息进行身份认证,需要新建类实现UserDetailService接口并重写loadUserByUsername方法,该方法的参数是登录时的用户名,通过该用户名去数据库查找用户,如果不存在就抛出不存在的异常,如果查到了用户,就会将用户及角色信息返回。loadUserByUsername将在用户登录时自动调用:
package com.shenziyi.spring_security.service; import com.shenziyi.spring_security.entity.UserInfo; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy; import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; @Component public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { @Autowired private UserInfoService userInfoService; /** * 需新建配置类注册一个指定的加密方式Bean,或在下一步Security配置类中注册指定 */ @Autowired @Lazy private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { // 通过用户名从数据库获取用户信息 UserInfo userInfo = userInfoService.getUserInfo(username); if (userInfo == null) { throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在"); } String role=userInfo.getRole(); List<GrantedAuthority>authorities=new ArrayList<>(); authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_"+role)); return new User( userInfo.getUsername(), passwordEncoder.encode(userInfo.getPassword()), authorities ); } }(这里有个小问题,两个类相互引用对方,导致Spring在初始化bean的时候不知道先初始化哪个,会形成循环依赖,所以任选一个使用@lazy注解,延迟互相依赖的其中一个Bean的加载,从而解决Spring在初始化bean的时候不知道先初始化哪个的问题。)
-
Spring Security的配置
创建WebSecurityConfig继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,并重写configure(auth)方法:
package com.shenziyi.spring_security.config; import com.shenziyi.spring_security.service.CustomUserDetailsService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; @EnableWebSecurity //是Spring Security用于启用Web安全的注解 public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private CustomUserDetailsService userDatailService; /** * 指定加密方式 */ @Bean public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){ // 使用BCrypt加密密码 return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth // 从数据库读取的用户进行身份认证 .userDetailsService(userDatailService) .passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder()); } } -
测试
6.2.2 角色访问控制
上面设置完成后,可以使用数据库中的用户名和密码登录,并获得用户的角色。接下来要通过用户的角色,限制用户的请求访问。
-
开启访问权限
在6.1中,角色访问控制是基于URL配置的,我们也可以通过注解来灵活地配置方法安全,在WebSecurityConfig添加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注解开启方法的访问权限:
@EnableWebSecurity //是Spring Security用于启用Web安全的注解 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)//开启方法级安全验证 public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{ //... }代码解释:prePostEnabled = true会解锁@PreAuthorize和@PostAuthorize两个注解,@PreAuthorize注解会在方法执行前验证,而@PostAuthorize注解在方法执行后验证。
-
在控制层添加访问接口
在UserController类中增加方法的访问权限:
package com.shenziyi.spring_security.controller; import com.shenziyi.spring_security.entity.UserInfo; import com.shenziyi.spring_security.service.UserInfoService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController public class UserController { @Autowired private UserInfoService userInfoService; @GetMapping("/getUser") public UserInfo getUser(@RequestParam String username){ return userInfoService.getUserInfo(username); } @PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('user')") //只有user角色才能访问该方法 @GetMapping("/user") public String user(){ return "hello,user"; } @PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('admin')") //只有admin角色才能访问该方法 @GetMapping("/admin") public String admin(){ return "hello,admin"; } }代码解释:@PreAuthorize(“hasAnyRole(‘user’)”)注解表示访问该方法需要user角色。
-
测试
重新启动程序,使得角色user的用户登录,可以访问localhost:8080/user,不能访问localhost:8080/admin。如果使用角色为admin的用户登录,则可以访问所有。
6.2.3 密码加密保存
上文中的用户密码都是手动在数据库中添加的,所以在数据库中以明文显示,在实际开发中,用户密码都需要加密保存。下面模拟注册用户,并加密保存密码。
-
修改Mapper接口
在UserMapper接口中添加插入用户:
@Mapper @Repository public interface UserMapper { @Select("select * from user where username = #{username}") UserInfo getUserByUsername(String username); @Insert("insert into user(username,password,role) value(#{username},#{password},#{role})") int insertUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo); } -
修改Service类
在UserInfoService类中添加插入方法,并使密码要加密保护:
@Service public class UserInfoService { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; public UserInfo getUserInfo(String username){ return userMapper.getUserByUsername(username); } @Autowired private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; public int insertUser(UserInfo userInfo){ /*加密密码*/ userInfo.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(userInfo.getPassword())); return userMapper.insertUserInfo(userInfo); } } -
修改Controller
在UserController类中添加插入用户接口:
@PostMapping("addUser") public int addUser(@RequestBody UserInfo userInfo){ return userInfoService.insertUser(userInfo); } -
测试
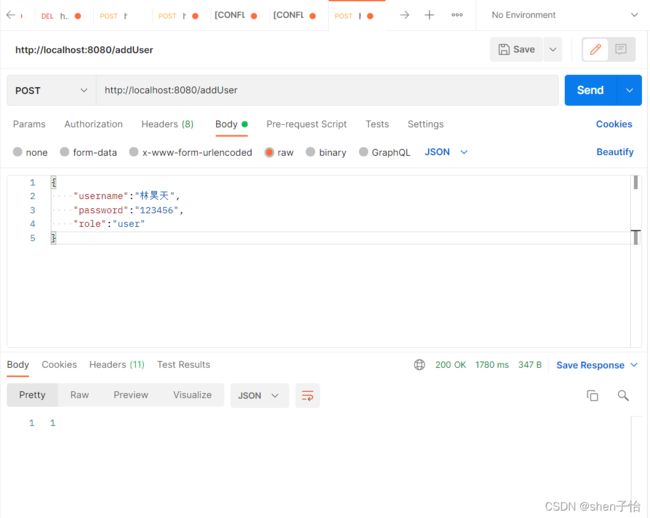
配置完成,启动服务,使用Postman发送POST请求添加用户,如下:
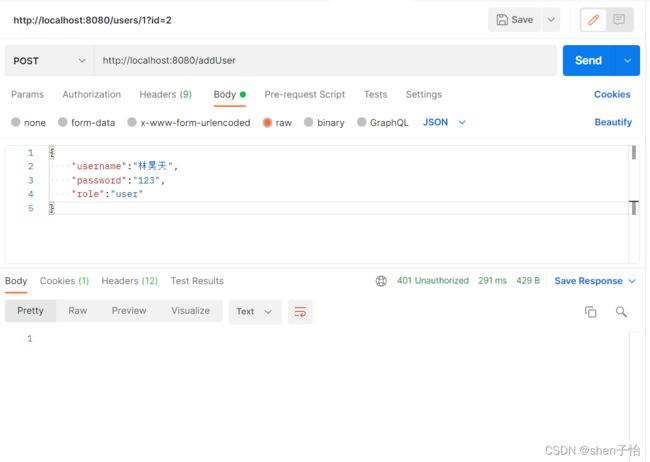
单击Send按钮后,由图看出添加失败,响应的状态码显示401 Unauthorized,说明无权限,需要登录,但注册用户是不需要登录的,所以需要给注册用户释放权限。修改WebSecurityConfig配置类,重写configure方法:
@Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http)throws Exception{ http .authorizeRequests() //允许POST请求/addUser,而无须认证 .antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST,"/addUser").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated() //所有请求都需要验证 .and() .formLogin() //使用默认的登录页面 .and() .csrf().disable(); } -
重启项目
-
使用加密密码登录
使用加密密码登录,需要修改CustomUserDetailsService类,之前从数据库获取明文密码后需要加密,就不用再加密了,代码如下:
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { // 通过用户名从数据库获取用户信息 UserInfo userInfo = userInfoService.getUserInfo(username); if (userInfo == null) { throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在"); } String role=userInfo.getRole(); List<GrantedAuthority>authorities=new ArrayList<>(); authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_"+role)); return new User( userInfo.getUsername(), //数据库密码已加密,不用再加密 userInfo.getPassword(), authorities ); }
在浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/user,输入shenziyi登录。
6.2.4 用户角色多对多关系
认证数据是多个用户对一个角色的,在实际项目中,很多时候都是多对多的情况,我们在该项目的基础上进行开发讲解。这里将介绍用户角色多对多关系的数据认证和授权。
-
创建表结构
一共三张表,分别是用户表、角色表和用户角色关联表。(角色名前要加ROLE_前缀)
-
创建实体类
根据表结构修改UserInfo实体类,创建Role类:
@Override public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() { Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>(); for (Role role : roleList) { //数据库role表字段中是以ROLE_开头的,所以此处不必再加ROLE_ authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getName())); } return authorities; } /** * 指示用户的账户是否已过期。无法验证过期的账户。 * 如果用户的账户有效(即未过期),则返回true,如果不在有效就返回false */ @Override public boolean isAccountNonExpired() { return true; } /** * 指示用户是锁定还是解锁。无法对锁定的用户进行身份验证。 * 如果用户未被锁定,则返回true,否则返回false */ @Override public boolean isAccountNonLocked() { return true; } /** * 指示用户的凭证(密码)是否已过期。过期的凭证阻止身份验证 * 如果用户的凭证有效(即未过期),则返回true * 如果不在有效(即过期),则返回false */ @Override public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() { return true; } /** * 指示用户是启用还是禁用。无法对禁用的用户进行身份验证 * 如果启用了用户,则返回true,否则返回false */ @Override public boolean isEnabled() { return true; } }@Data public class Role { private int id; private String name; private String nameZh; } -
创建UserMapper和UserMapper.xml
修改UserMapper接口中的抽象方法,代码如下:
@Mapper @Repository public interface UserMapper { // @Select("select * from user where username = #{username}") UserInfo getUserByUsername(String username); List<Role> getRolesById(int id); // 添加用户 @Insert("insert into user(username, password) value(#{username}, #{password})") int insertUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo); }接着在classpath:mappers下创建UserMapper.xml映射文件,当SQL语句比较复杂时建议使用XML式,代码如下:
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.shenziyi.mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="getUserByUsername" resultType="com.shenziyi.entity.UserInfo"> select * from user where username = #{username}; select> <select id="getRolesById" resultType="com.shenziyi.entity.Role"> select * from role where id in(select rid from user_role where uid=#{uid}); select> mapper>并在application.yml中进行配置:
mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mappers/*.xml type-aliases-package: com.shenziyi.mapper -
修改CustomUserDetailsService类
修改CustomUserDetailsService类中loadUserByUsername方法:
@Component public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { @Autowired private UserInfoService userInfoService; @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; /** * 需新建配置类注册一个指定的加密方式Bean,或在下一步Security配置类中注册指定 */ @Autowired private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { // 通过用户名从数据库获取用户信息 UserInfo userInfo = userInfoService.getUserInfo(username); if (userInfo == null) { throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在"); } userInfo.setRoleList(userMapper.getRolesById(userInfo.getId())); return userInfo; } } -
controller层
在UserController类中添加如下方法:
@RestController public class UserController { @Autowired private UserInfoService userInfoService; //添加 @PostMapping("/addUser") public int addUser(@RequestBody UserInfo userInfo){ return userInfoService.insertUser(userInfo); } @GetMapping("/getUser") public UserInfo getUser(@RequestParam String username){ return userInfoService.getUserInfo(username); } @PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('user')") // 只能user角色才能访问该方法 @GetMapping("/user") public String user(){ return "hello,user"; } @PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('dba','admin')") // dba\admin角色可以访问该方法 @GetMapping("/db") public String dba(){ return "hello,dba,admin"; } @PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('admin')") // 只能admin角色才能访问该方法 @GetMapping("/admin") public String admin(){ return "hello,admin"; } } -
配置完成后,启动项目对controller中的接口进行测试。
6.2.5 角色继承
角色继承实际上是一个很常见的继承,因为大部分公司可能采用金字塔形的治理方式,上司可能具备下属的部分甚至所有权限,这一现实场景,反映到我们的代码中,就是角色继承。
Spring Security中为开发者提供了相关的角色继承解决方案,只需开发者在配置类中提供一个RoleHierarchy,代码如下:
@Bean
RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy(){
RoleHierarchyImpl roleHierarchy=new RoleHierarchyImpl();
String hierarchy="ROLE_dba>ROLE_admin \n ROLE_admin>ROLE_user";//dba、admin、user都是user表中的角色
roleHierarchy.setHierarchy(hierarchy);
return roleHierarchy;
}
这里提供一个RoleHierarchy接口的实例,使用字符串来描述角色之间的继承关系。ROLE_dba具备ROLE_admin的所有权限,ROLE_admin具备ROLE_user的所有权限。提供了这个Bean后,以后所有具备ROLE_user角色才能访问的资源,ROLE_dba和ROLE_admin都能访问,具备ROLE_admin角色才能访问的资源,ROLE_dba也能访问。