【刷题】DFS
DFS
递归:
1.判断是否失败终止
2.判断是否成功终止,如果成功的,记录一个成果
3.遍历各种选择,在这部分可以进行剪枝
4.在每种情况下进行DFS,并进行回退。
199. 二叉树的右视图
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
示例 1:
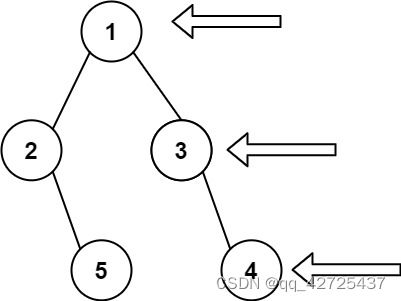
输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
示例 2:
输入: [1,null,3]
输出: [1,3]
示例 3:
输入: []
输出: []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
unordered_map<int, int> rightmostValueAtDepth;
int max_depth = -1;
stack<TreeNode*> nodeStack;
stack<int> depthStack;
nodeStack.push(root);
depthStack.push(0);
while (!nodeStack.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = nodeStack.top();nodeStack.pop();
int depth = depthStack.top();depthStack.pop();
if (node != NULL) {
// 维护二叉树的最大深度
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth);
// 如果不存在对应深度的节点我们才插入
if (rightmostValueAtDepth.find(depth) == rightmostValueAtDepth.end()) {
rightmostValueAtDepth[depth] = node -> val;
}
nodeStack.push(node -> left);
nodeStack.push(node -> right);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
}
}
vector<int> rightView;
for (int depth = 0; depth <= max_depth; ++depth) {
rightView.push_back(rightmostValueAtDepth[depth]);
}
return rightView;
}
};
39. 组合总和
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
输出:[[2,2,3],[7]]
解释:
2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。
7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。
仅有这两种组合。
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8
输出: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
示例 3:
输入: candidates = [2], target = 1
输出: []
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<int>& candidates, int target, vector<vector<int>>& ans, vector<int>& combine, int index) {
if (index >= candidates.size()) return;
if (target==0) {
ans.emplace_back(combine);
return;
}
dfs(candidates, target, ans, combine, index+1);
if (candidates[index]<=target){
combine.push_back(candidates[index]);
dfs(candidates, target-candidates[index], ans, combine, index);
combine.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> combine;
dfs(candidates, target, ans, combine, 0);
return ans;
}
};