C++ STL的基本使用及注意事项
string
头文件:#include
当string对象和字符串字面值混合连接操作时,+操作符的左右操作数至少有一个是string类型的,如
std::string strValue = "abc";
std::string strValue2 = strValue + "def"; //正确
std::string strValue3 = "abc" + "def"; //错误
vector
头文件:#include
- 下标操作
下标操作不添加元素,因此vector为空时,使用vec[index] = value会失败,需要使用push_back(value)
std::vector<int> iVec;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
//iVec[i] = i; //编译成功,运行失败
iVec.push_back(i); //正确
}
- erase
1、iVec.erase(p) 删除迭代器p所指向的元素,返回一个迭代器,指向被删除元素后面的元素。如果p是最后一个元素,则返回超出末端的下一个位置。如果p本身就是末端的下一个位置,则异常
2、iVec.erase(b,e) 删除迭代器b和e所指向的范围内元素(不包括e指向的元素),返回一个迭代器,指向被删除元素后面的元素。如果e是最后一个元素,则返回超出末端的下一个位置。如果e本身就是末端的下一个位置,则还是返回超出末端的下一个位置。
std::vector<int> iVec = { 1,2,3,4 }; //正确 C++11下支持
std::vector<int>::iterator iter2 = iVec.erase(iVec.begin());
std::cout << *iter2 << endl; //输出2
//std::vector::iterator iter3 = iVec.erase(iVec.end()); //异常
//std::vector::iterator iter4 = iVec.erase(iVec.begin(),iVec.end());
//std::cout << *iter4 << endl; //异常
std::vector<int>::iterator iter5 = iVec.erase(iVec.begin(), iVec.begin()+1);
std::cout << *iter5 << endl; //输出3
list
头文件:#include
头部与尾部都可以插入数据
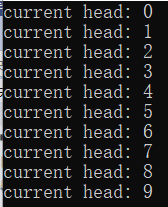
void TestList()
{
list<int> myList;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
myList.push_back(i);
}
list<int>::iterator iter = myList.begin();
while (!myList.empty())
{
cout << "current head: " << *iter << endl;
iter = myList.erase(iter);
}
}
stack
栈:后进先出
头文件:#include
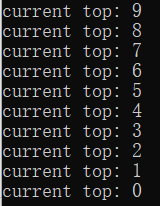
void TestStack()
{
stack<int> myStack;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
myStack.push(i);
}
while (!myStack.empty())
{
cout << "current top: " << myStack.top() << endl;
myStack.pop();
}
}
queue
队列:先进先出
头文件:#include
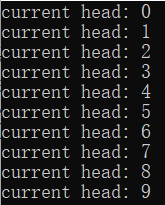
void TestQueue()
{
queue<int> myQueue;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
myQueue.push(i);
}
while (!myQueue.empty())
{
cout << "current head: " << myQueue.front() << endl;
myQueue.pop();
}
}
pair
对map的迭代器解引用将获得一个pair对象
map
关联数组:key-value
头文件:#include
class CPerson
{
public:
string m_strName;
int m_nAge;
CPerson(string strName, int nAge) {
m_strName = strName;
m_nAge = nAge;
}
//自定义类需要重载<,才可以作为map的key
bool operator<(const CPerson& p) const //注意这里的两个const
{
return (m_nAge < p.m_nAge) || (m_nAge == p.m_nAge && m_strName < p.m_strName);
}
};
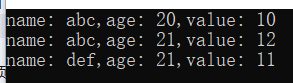
void TestMap()
{
map<CPerson, int> mapPerson;
mapPerson[CPerson("abc",20)] = 10;
mapPerson[CPerson("def", 21)] = 11;
mapPerson[CPerson("abc", 21)] = 12;
map<CPerson, int>::iterator iter = mapPerson.begin();
for (; iter != mapPerson.end(); ++iter)
{
cout << "name: " << iter->first.m_strName << ",age: " << iter->first.m_nAge << ",value: " << iter->second<< endl;
}
}
multimap
允许key重复,不支持下标操作
头文件:#include\
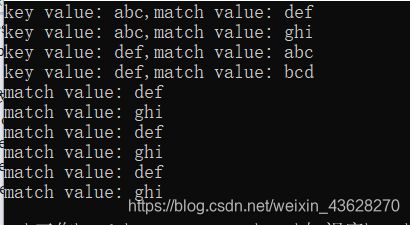
void TestMultmap()
{
multimap<string, string> mapAuthors;
mapAuthors.insert(make_pair("abc", "def"));
mapAuthors.insert(make_pair("abc", "ghi"));
mapAuthors.insert(make_pair("def", "abc"));
mapAuthors.insert(make_pair("def", "bcd"));
multimap<string, string>::iterator iter1 = mapAuthors.begin();
while (iter1 != mapAuthors.end())
{
cout << "key value: " << iter1->first << ",match value: " << iter1->second << endl;
++iter1;
}
//方式1:遍历时需要先获取查找键值个数,再循环迭代find获得的指向第一个该键所关联的元素的迭代器
string strKey = "abc";
multimap<string, string>::size_type nCount = mapAuthors.count(strKey);
multimap<string, string>::iterator iter = mapAuthors.find(strKey);
for (size_t i = 0; i < nCount; ++i,++iter)
{
cout << "match value: " << iter->second << endl;
}
//方式2:通过lower_bound与upper_bound获取
multimap<string, string>::iterator iterStart = mapAuthors.lower_bound(strKey);
multimap<string, string>::iterator iterEnd = mapAuthors.upper_bound(strKey);
while (iterStart != iterEnd)
{
cout << "match value: " << iterStart->second << endl;
++iterStart;
}
//方式3:通过equal_range返回一对迭代器pair对象。第一个迭代器指向该键关联的第一个实例,第二个迭代器指向该键关联的最后一个实例的下一个位置
typedef multimap<string, string>::iterator authors_iter;
pair<authors_iter, authors_iter> pos = mapAuthors.equal_range(strKey);
while (pos.first != pos.second)
{
cout << "match value: " << pos.first->second << endl;
++pos.first;
}
}
set
集合与map类似,只有key没有value
头文件:#include
class CPerson2
{
public:
string m_strName;
int m_nAge;
CPerson2(string strName, int nAge) {
m_strName = strName;
m_nAge = nAge;
}
//自定义类需要重载<,才可以作为set的key
bool operator<(const CPerson2& p) const //注意这里的两个const
{
return (m_nAge < p.m_nAge) || (m_nAge == p.m_nAge && m_strName < p.m_strName);
}
};
void TestSet()
{
set<CPerson2> setPerson;
setPerson.insert(CPerson2("abc", 20));
setPerson.insert(CPerson2("def", 21));
setPerson.insert(CPerson2("abc", 21));
set<CPerson2>::iterator iter = setPerson.begin();
for (; iter != setPerson.end(); ++iter)
{
cout << "name: " << iter->m_strName << ",age: " << iter->m_nAge << endl;
}
}
multiset
允许key重复,与multimap使用类似
头文件:#include
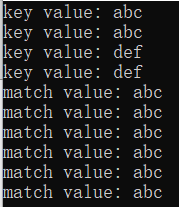
void TestMultset()
{
multiset<string> setAuthors;
setAuthors.insert("abc");
setAuthors.insert("abc");
setAuthors.insert("def");
setAuthors.insert("def");
multiset<string>::iterator iter1 = setAuthors.begin();
while (iter1 != setAuthors.end())
{
cout << "key value: " << *iter1 << endl;
++iter1;
}
//方式1:遍历时需要先获取查找键值个数,再循环迭代find获得的指向第一个该键所关联的元素的迭代器
string strKey = "abc";
multiset<string>::size_type nCount = setAuthors.count(strKey);
multiset<string>::iterator iter = setAuthors.find(strKey);
for (size_t i = 0; i < nCount; ++i, ++iter)
{
cout << "match value: " << *iter << endl;
}
//方式2:通过lower_bound与upper_bound获取
multiset<string>::iterator iterStart = setAuthors.lower_bound(strKey);
multiset<string>::iterator iterEnd = setAuthors.upper_bound(strKey);
while (iterStart != iterEnd)
{
cout << "match value: " << *iterStart << endl;
++iterStart;
}
//方式3:通过equal_range返回一对迭代器pair对象。第一个迭代器指向该键关联的第一个实例,第二个迭代器指向该键关联的最后一个实例的下一个位置
typedef multiset<string>::iterator authors_iter;
pair<authors_iter, authors_iter> pos = setAuthors.equal_range(strKey);
while (pos.first != pos.second)
{
cout << "match value: " << *pos.first << endl;
++pos.first;
}
}