pybind11:实现Python调用C++代码(入门)
pybind11简介
pybind11 是一个开源的 C++ 和 Python 之间的桥接工具,它旨在使 C++ 代码能够无缝地集成到 Python 环境中。pybind11 的设计目标是简化 C++ 与 Python 的互操作性,使开发者能够更轻松地将现有的 C++ 库/代码包装为可以在 Python 中使用的模块。
pybind11 是一个非常受欢迎和有用的 Python 软件包,尤其在将现有的 C++ 代码集成到 Python 环境中时非常有用。它得到了广泛的应用,在科学计算、机器学习、计算机图形学等领域都有很多使用案例。
pybind11安装和配置(Windows)
pybind11是个C++的header-only的库。因此无需安装,只需要有头文件即可。
这是pybind11的github:https://github.com/pybind/pybind11, 可以直到github下安装,或者用git克隆:
git clone https://github.com/pybind/pybind11 --depth=1
若输入上面指令出现 “SSL certificate problem: unable to get local issuer certificate” 缺少根证书的问题则使用指令:
git -c http.sslVerify=false clone https://github.com/pybind/pybind11 --depth=1
使得Git 克隆仓库时禁用 SSL 证书验证(该操作具有一定风险,确保仓库可信)
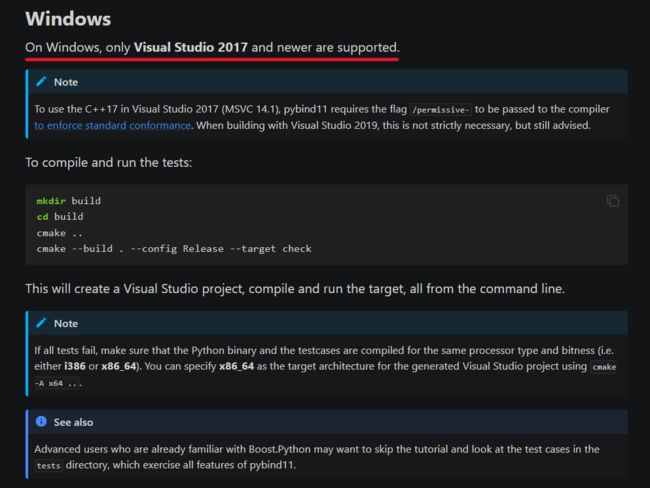
克隆后得到一个名为 “pybind11” 的文件夹,创建一个C++项目,在项目内将pybind作为一个外部库。用cmake管理,注意,官方文档中写到了 “On Windows, only Visual Studio 2017 and newer are supported.” 意思就是只有Vistual Studio 2017 或更高版本支持配置这个库
只能采用Vistual Studio的编译工具包括cmake,为了操作方便,我们在vscode中打开这个项目(vscode可以使用Vistual Studio的工具)
准备4个文件,一个是外部库Pybind11,一个是CMakeLists.txt文件,一个cpp文件,一个python文件。(先准备cmakelists文件和选择编译工具包)
CMakeLists.txt
# 版本号无关轻重
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.23)
# 项目名称
project(tryPybind)
# 指定python解释器的位置
set(PYTHON EXECUTABLE "C:/Users/27966/AppData/Local/Programs/Python/Python311/python.exe")
# 添加pybind11到项目
add_subdirectory(extern/pybind11)
# pybind11的一个cmake函数 将tryPybind.cpp编译成一个C++模块,并绑定python,生成一个python可导入的拓展模块,"tryPybind"即为模块名
Pybind11_add_module(tryPybind tryPybind.cpp)
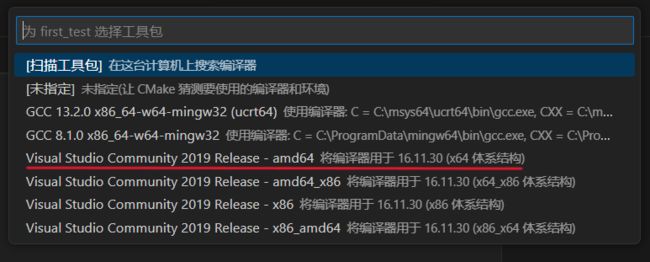
用vscode打开你准备好的项目后会提示你选择工具包
选择visual studio的第一个工具包
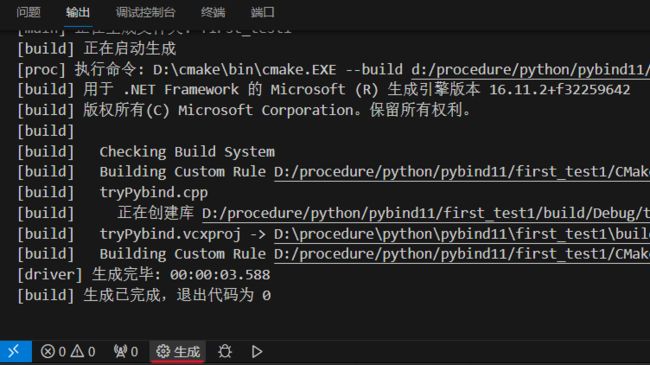
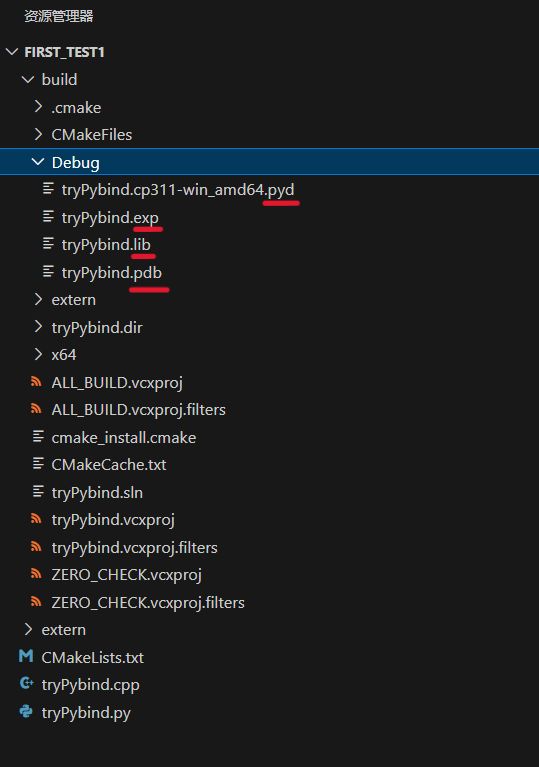
等待配置好后项目后直接点击生成即可(CMakeLists.txt文件和cpp文件(稍后介绍)没问题则能正确生成),在当前目录下就会自动生成一个build文件夹,文件夹里有个Debug文件夹 (也可能是Release 一样的用法),这里面生成了4个文件,其中:
.pyd是python的动态库
.exp是windows下面的导出库文件,它包含了导出函数和数据项的信息
.lib是windows下面的c++静态库
.pdb是Windows调试符号文件(若是release则没有这个文件)
这里面的pyd文件便能实现python代码中调用C++的代码的功能,下面是cpp文件的创建以绑定一个函数或类。
绑定一个C++函数
#include 这段的意思就是:
利用PYBIND11_MODULE这个宏,它接受两个参数。第一个tryPybind是模块名,第二个参数不用管,就m就行
m.def就是定义一个python中的函数,函数名为add,函数绑定到c++的add函数。
运行cmake生成build后,生成的pyd文件拖放到当前目录下(确保和py文件一个目录下),编写python脚本:
pyTry.py
import tryPybind
a = tryPybind.add(1, 2)
print(a)
输出:
3
这样就成功在python代码中调用了一个C++函数
绑定一个c++的类
直接把c++的源码改为:
tryPybind.cpp
#include 这段的意思和上面大体相同,多出来的部分就是:
class_定义一下类名“SomeClass”
.def定义类函数(构造函数要单独用python的init定义)
同样的操作,cmake后得到一个pyd文件,拖放到当前目录,定义python脚本:
pyTry.py
import tryPybind
print(dir(tryPybind))
a = tryPybind.SomeClass(2.1)
a.multiply(2.0)
输出:
['SomeClass', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__']
res:4.2
这样就成功在python代码中调用了一个C++类