Spring boot 详解
Spring boot 相关知识
微服务
微服务:架构风格(服务微化)
一个应用应该是一组小型服务,可以通过HTTP的方式进行互通。
每一个功能元素最终都是可以独立升级的软件单元。
Spring Boot Hello World
1.创建maven项目
2.导入相关Spring Boot 相关依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
3.编写主程序
package club.zw12;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication //标注一个主程序类,说明他是一个spring Boot程序
public class HelloWorldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Spring boot 应用启动起来
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldApplication.class,args);
}
}
4.编写controller、service
package club.zw12.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String HelloWorld() {
return "Hello World";
}
}
5.运行应用
6.部署应用
创建可执行的jar包、在pom.xml文件中添加plugin插件
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
选择maven->Lifecycle->package打包后的jar双击即可执行并访问
spring boot 探究
导入父项目
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
父项目依赖于
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependenciesrelativePath>
parent>
他来真正管理Spring boot 的所有依赖版本
导入启动器
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
spring-boot-starter-web
spring-boot-starter:
spring-boot,场景启动器,帮我们导入web模块正常运行所依赖的组件;
spring boot 将所有的功能场景抽取出来,做成一个个starters(启动器),只需要在项目里面引用这些starter相关的场景,所有依赖都会导入进来,要用什么功能,就导入什么场景的启动器。
spring initialize 创建spring boot 工程
相关步骤
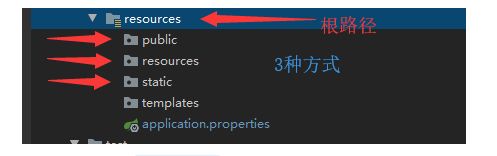
文件目录结构解析
resources文件夹下:
-
static:静态文件。eg:js、css等。
-
templates:保存所有模板页面(spring boot 默认jar使用嵌入式的tomcat,默认不支持jsp页面);但是可以使用模板引擎、如:freemarker、thymeleaf 等。
-
application.properyties:Spring Boot 应用的配置文件(可以修改一些默认设置)。
-
修改端口号
server.port=8081
-
注意事项
@RestController是==@Controller和@ResponseBody==的集合体
@ResponseBody在类上使用该注解即可实现返回的是字符串而不是页面
配置文件
- YAML
- properties
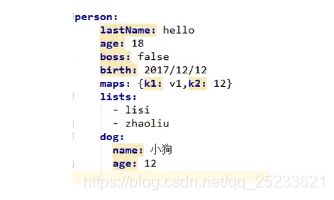
YAML
基本语法
server:
path: /home
port: 8081
属性、值大小写敏感
值得写法
-
k: v (冒号和value之间有空格)
- 字符串默认不用添加单引号或双引号
- 双引号 "”: "jwj \n comi” 输出:jwj 换行 comi
- 单引号 ‘’:‘jwj \n comi’ 输出:jwj comi
-
数组(list、set)
用 ==-==表示一个数组中的一个元素
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
- 行内语法
pets: [dog,cat,pig]
- 对象、Map(属性和值、键值对)
friends:
name: comi
age: 18
- 行内写法
friends:{name: comi,age: 18}
数据绑定
-
添加依赖(导入配置文件处理器,导入后便会有提示)
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId> <optional>trueoptional> dependency> -
创建bean
添加==@Component==注解
添加==@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="person”)==(告诉SpringBoot将本类中所有属性与配置文件中相关配置进行绑定)
-
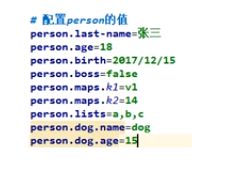
在properties中书写配置(二者选其一,若都存在,propertoes优先级高于yaml)
-
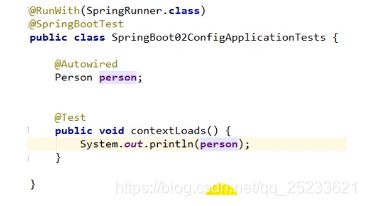
单元测试
在test类中可以进行自动注入
@value和@ConfigurationProperties的区别
@PropertySource和@ImportResource
@PropertySource
如果所有配置文件都放在application.properties文件下,会导致文件过大,为此,我们可以新建一个properties文件。
eg:person.properties,这时便可以使用注解@propertySource引入我们的配置文件
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})
public class helloController {}
@ImportResource
导入spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效。
在主应用程序上添加注解**@ImportResource(locations = {“classpath:bean.xml”})**
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:bean.xml"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Configuration
SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组建的方式:推荐使用全注解方式
@Configuration、@Bean均为spring底层知识点。
@Configuration 指明当前类是一个配置类,用来替代之前的spring配置文件。
@Bean给容器添加组件
@Configuration
public class MyConfig{
@Bean
public HelloService helloService(){
return new HelloService();
}
}
配置文件占位符
-
随机数
${random.value}、${random.int}、${random.long} ${random.int(10)、${random.int[1204,65536]} -
占位符获取之前配置的值,如果没有,使用==:==指定默认值
person.last-name = 张三${random.uuid} person.dog.name = ${person.last-name: comi's}_dog # 获取person.last_name的值,如果没有值,则默认为comi's
Profile
多个profile文件
profile是spring对不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活、指定参数等方式快速切换环境。
我们在主配置文件编写时,文件名可以是
application-{profile}.properties.xml
eg:
-
创建
application-dev.properties-
server.port=8082 -
创建
application-prod.properties-
server.port=80
-
-
默认未激活配置文件下,使用的是
application.properties-
server.port=8081 spring.profiles.active=dev # 开启端口为8082
-
-
yml 多文档块
什么是文档块?
# 默认使用
server:
port: 8081
# 激活配置文件,使用dev环境
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
--- # 文档块分界线
# 文档块一,生产环境
server:
port: 80
spring:
profiles: dev
``` # 文档块分界线
# 文档块二,开发环境
server:
port:8082
spring:
profiles: prod
激活配置文件
-
spring.profiles.active=dev方式
-
项目打包后使用命令行(cmd/Linux)方式运行
java -jar spring-boot.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev
配置文件加载位置
spring-boot启动会扫描以下位置的
application.properties或application.yml文件作为springboot的默认配置文件
- file:./congif/ : 当前项目的 ==config==文件夹下
- file: ./ : 当前项目下
- classpath: /config/ : resource文件夹即类路径下的config文件夹下
- classpath: / : 类路径下
以上文件夹优先级由高到低,高优先级配置会覆盖低优先级配置。但未配置的属性不会覆盖,而是会形成互补配置。
SLF4J使用
在开发时,日志记录方法的调用,不应该直接调用日志的实现类,而是调用日志里面的抽象方法。
系统里需导入slf4j的jar和logback的实现jar。
spring boot默认使用时slf4j和logback,能适配所有的日志,而且底层使用的slf4j+logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架时,只需要把这个框架的日志框架排除掉即可。
日志使用
Spring Boot默认帮我们配置好了日志:
package club.twzw.demo;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:bean.xml"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemoApplication.class);
//日志级别,由低到高
logger.trace("用于跟踪轨迹");
logger.debug("这是debug");
logger.info("这是info");
logger.warn("警告");
logger.error("错误");
}
}
输出结果:
未输出trance,说明spring boot的默认选项级别是debug及以上
15:30:23.094 [main] DEBUG club.twzw.demo.DemoApplication - 这是debug
15:30:23.097 [main] INFO club.twzw.demo.DemoApplication - 这是info
15:30:23.097 [main] WARN club.twzw.demo.DemoApplication - 警告
15:30:23.097 [main] ERROR club.twzw.demo.DemoApplication - 错误
可以在application.properties中配置日志级别
logging.level.club.twzw=debug
# 日志输出文件,与path不共存,都有的话是name
logging.file.name=springboot.log
# 日志输出目录,项目路径下logs文件夹中
#logging.file.path=/logs/
指定配置文件:
在classpath目录下
- 创建
logback.xml文件,即可被spring框架所识别。- 创建
logback-spring.xml:日志框架不直接加载日志的配置项,而是由spring boot解析日志配置。可以使用springboot的高级profile功能。
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<springProfile name="dev">
logging.pattern.console=$d{yyyy-mm-dd} % - dev
springProfile>
<springProfile name="!dev">
logging.pattern.console=$d{yyyy-mm-dd} % - prod
springProfile>
layout>
web开发
- 创建springBoot应用,选择模块-web,mybatis,redis等
- 在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行
- 编写业务代码
自动配置原理
-
xxxxAutoConfiguration: 给容器中添加配置组件
-
xxxProperties:配置类来封装配置文件的内容
springboot对静态资源映射规则
-
**/webjars/**路径
classpath:/Meta-INF/Resources/webjars/寻找资源所需资源只需要去 [webjars]: https://www.webjars.org/ 寻找maven,以maven的方式引用即可.- jquery
<dependency> <groupId>org.webjarsgroupId> <artifactId>jqueryartifactId> <version>3.4.1version> dependency>路由eg:
localhost:8080/webjars/jquery.js -
/**路径
路由eg:
localhost:8080/jquery.js->便会去静态资源文件夹中去找文件访问当前项目的任何资源(静态资源文件夹)。
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/" “classpath:/resources/” “classpath:/statis/” “classpath:/public/” “/”:当前项目的根路径 -
欢迎页配置,所有静态资源文件夹下的
index.html路由eg:
localhost:8080/寻找index.html文件 -
网页标签的icon
favicon.ico:都是在
**/favicon.ico都是在静态资源文件夹下寻找 -
修改默认静态资源文件夹
spring.resources.static-location=classpath:/hello/,classpath:/world/
模板引擎
图例:
spring boot 推荐thyneleaf(语法简单,功能强大)
引入thyneleaf
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
artifactId>
dependency>
指定版本号
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
<properties>
<thymeleaf.version>3.0.2.RELEASEthymeleaf.version>
<thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.1.1thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>
properties>
properties>
thyneleaf语法
待续
spring boot自动配置spring mvc
1. 默认配置:
-
ContentNegotiaingViewResolver和BeanNameViewResolver组件-
自动配置了viewResolver(视图解析器:更具返回值得到视图对象-view,视图决定如何渲染-转发/重定向)
-
ContentNegotiaingViewResolver:组合所有视图解析器
-
-
静态资源路径配置(见上面)
-
自动注册
Converter,GenericConverter,Formatter组件Converter:转换器->数据类型转换Formatter:格式化器->2017/12/17—>Date
自己添加格式化器或转换器,只需要添加到容器中即可
@Bean -
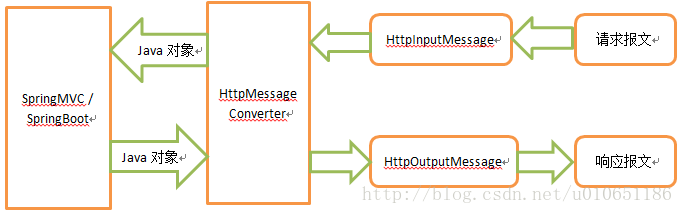
HttpMessageConverters:消息转换器,Springmvc用来转换http请求和响应的。即接收参数/返回json对象等
- `MssageCideResolver`:定义错误代码生成规则。
2.扩展springMVC(视图映射,拦截等配置)
书写配置类,该配置类只处理页面请求,并返回页面
编写一个配置类(@Configuration),该类继承WebMvcConfigureAdapter(推荐使用WebMvcConfigurer)且不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解。
//使用`WebMvcConfigureAdapter`来扩展springmvc的功能
@Configuration
public class MYViewConfig extends WebMvcConfigureAdapter{
//重写视图映射方法
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry){
registry.addViewController("/hello")
.setViewName("hello");
}
}
这样便无需书写@requestMapping("/hello”)及方法体等。
WebMvcConfigurer案例
@Configuration
public class myConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index").setViewName("index");
}
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer() {
WebMvcConfigurer configurer = new WebMvcConfigurer() {
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index").setViewName("index");
}
};
return configurer;
}
}
3.全面接管springmvc(不推荐)
Springboot对springmvc的自动配置不用了,而是所有配置都是我们自己配置,只需要在配置类(@Configuration)中添加注解@EnableWebMvc
如何修改SpringBoot的默认配置
- Springboot 在使用很多组件时,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置组件(@Bean,@Component),如果有配置,就用用户的,反之,自动配置。如果有些组件有多个组件,则将用户配置和springboot的组合起来。
- xxxxAutoConfiguration 帮助我们自动改配置
国际化
使用
在
resources文件下创建i18n文件夹
创建login文件夹
- 创建
login.properties文件- 创建
login_zh_CN.properties文件[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-FMjzFVMe-1577259586276)(D:\notes\image-20191211113503176.png)]
编写配置文件
点击properties文件,底部选择Resource Bundle,点击添加,填写要国际化的部分
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Y1Ixy37Y-1577259586277)(D:\notes\image-20191211113424415.png)]
springboot自动配置好了国际化管理的组件,所以我们需要配置
spring.messages.basename,如果不配置,就会从类路径下去寻找messages.properties文件。修改application.properties文件设置
spring.messages.basename=i18n.login页面获取国际化的值(thymeleaf模板引擎下)
<h1 th:text="#{login.username}"> h1>现在页面即可根据浏览器语言进行国际化
创建自己的区域解析器,实现点击切换locale
创建类locale实现方法
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
import org.thymeleaf.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.Locale;
public class local implements LocaleResolver {
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
String sLocale = httpServletRequest.getParameter("locale");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(sLocale)){
String[] split = sLocale.split("_");
locale = new Locale(split[0] ,split[1]);
}
return locale;
}
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Locale locale) {
}
}
在配置类中进行配置
@Bean
public local myLocaleResolver(){
return new local();
}
现在就可以通过请求携带的参数进行更改显示语言了
修改页面并实时生效
-
禁用模板引擎的缓存
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
-
ctrl + F9 重新编译文件(idea)
拦截器
- 书写类loginInterceptor实现
HandlerInterceptor类
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* 登陆检查
*/
public class loginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//目标方法执行之前
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
Object user = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser");
if (user != null) {
return true;
}
System.out.println("被拦截!!!");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/").forward(request, response);
return false;
}
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
- 在配置文件中配置拦截器,是拦截器生效
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
//拦截任意路径下的任意请求,除了登录页面的请求
// 无需处理静态资源
registry.addInterceptor(new loginInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/login","/");
}
CRUD-restful
| 普通CRUD | RestFul-crud | |
|---|---|---|
| 查询 | getEmp | Emp—GET |
| 添加 | AddEmp | Emp—-POST |
| 修改 | updateEmp | Emp—PUT |
| 删除 | deleteEmp | Emp—DELETE |
springboot 错误处理机制及定制错误信息
原理:
给容器中添加了以下组件
- DefaultErrorAttributes:
- 帮我们在页面共享信息
- BasicErrorController:
- 处理默认
/error请求- ErrorPageCustomlizer
- 系统出现错误以后,来到
/error进行处理- DefaultErrorViewResolver:
- 默认错误解析器
步骤:
一但系统出现4xx,5xx(404,500)一系列错误,ErrorPageCustomlizer(定制错误相应规则)就会生效;随后便会请求
/error,被BasicErrorController处理:
- 响应页面:去哪个页面是由
DefaultErrorViewResolver解析处理
定制错误响应:
如何定制错误响应页面?
有模板引擎的情况下:error/状态码
将错误页面命名为错误状态码.html,放在error文件夹下(resources/templates/error/404.html),发生此状态码的错误就会跳转到对应页面。
同样可以使用4xx或5xx作为错误页面的文件名来匹配这种类型的所有错误,精确有限(优先寻找精确的状态买.html)
页面能获取的信息:
- timestamp:时间戳
- status:状态码
- error :错误提示
- exception:异常对象
- message :异常消息
- errors :JSR303数据校验都在这里
没有模板引擎,就会在静态资源文件夹下找相应文件。
以上都没有错误,默认来到springboot的页面。
如何定制json数据?
自定义exceptionHandler
- 创建类
exception继承RuntimeExceptionpublic class exception extends RuntimeException{ public exception() { super("用户不存在"); } }
- 创建异常controller
且自适应。@ControllerAdvice //Aop增强 public class myexception { @ExceptionHandler(exception.class) public String handlerException(Exception e, WebRequest request){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",400,0); map.put("code",100); map.put("message",e.getMessage()); //在request-context存入数据 request.setAttribute("ext",map,0); return "forward:/error"; } }
- 在需要时调用即可。
throw new exception();定制页面数据显示并携带数据
DefaultErrorAttributes
@Component //添入容器 public class myErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes { @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) { Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace); Map<String, Object> ext = (Map<String, Object>) webRequest.getAttribute("ext", 0); map.put("ext", ext); Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(myErrorAttributes.class); logger.info(String.valueOf(map)); return map; } }现在就可以返回定制的json数据了
修改tomcat配置
-
直接修改配置文件
server.port=80 server.servlet.context-path=/crud # 访问路径 http://localhost/crud/ server.servlerPath=/ # server.servlerPath来修改springmvc前端控制器默认拦截的请求路径 -
嵌入式配置(太麻烦)
@Bean public WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory> factoryCustomizer(){ return new WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory>() { @Override public void customize(ConfigurableWebServerFactory factory) { factory.setPort(80); } }; }
注册fliter,listener,servlet三大组件
- servlet:ServletRegistrationBean
- fliter:FilterRegistrationBean
- listener:ServletListenerRegistrationBean
在配置文件中添加三大组件
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter()
{
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
registrationBean.setFilter(new myFilter());
//设置拦截器 拦截/hello,/abc请求
registrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/hello","/abc"));
return registrationBean;
}
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener()
{
ServletListenerRegistrationBean<myListener> registrationBean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean<>(new myListener());
return registrationBean;
}
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet()
{
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new myservelt());
return registrationBean;
}
myservelt.class
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class myservelt implements Servlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
@Override
public String getServletInfo() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
myListener.class
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
public class myListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
}
myFilter.class
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class myFilter extends FilterRegistrationBean implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
springboot 数据相关
JDBC
application.yml配置文件
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://47.xx.153.xx:3306/api
name: api
password: xxxxx
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
类路径下:直接通过sql文件建表-DataSourceInitializer:applicationListener
-
runSchemaScripts():运行建表语句
-
runDataScripts():运行插入数据的sql语句
默认只需要将文件命名为:
schema-*.sql , data-*.sql
指定schema通过sql文件建表
spring:
datasource:
schema:
- classpath: department.sql
- classpath: api.sql
整合druid
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.21version>
dependency>
切换数据源
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://47.xx.xx.41:3306/api
name: api
password: xxxxx
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://47.xx.xx.41:3306/api
spring.datasource.username=api
spring.datasource.password=xxxx
相关参数设置,与name同级,但此时无法设置参数,还需要将durid添加到容器中[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TN94PzeG-1577259586278)(D:\notes\image-20191213095125507.png)]
创建类duridConfig
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class druidConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}
配置druid监控
//配置druid监控
//1.配置一个管理后台的servlet
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean stateViewServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(),"/druid/*");
Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("loginUsername","comi");
initParams.put("loginPassword","146325");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
}
//配置web监控的filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStateFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
Map<String,String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
initParams.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));//拦截请求设置
return bean;
}
配置成功后,便可以访问 http://localhost:8080/druid/login.html 进行登录操作
整合mybatis
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.21version>
dependency>
注解
使用mapper注解即可使用mybatis语法
获取插入后的自增id
@Mapper
public class user {
@Select("select * from users");
public List<user> getAllUsers();
@Options(useGenerateKeys=true,ketProperty="id")
@Insert("insert into users(name,password)values(# {param1},#{param2})")
publc int insertUser(String name,Integer password)
}
自定义mybatis配置规则
@Configuration
public class mybatis {
@Bean
public ConfigurationCustomizer configurationCustomizer(){
return new ConfigurationCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration configuration) {
//开启驼峰命名等
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true);
}
};
}
}
开启mapper包扫描,批量扫描mapper接口
@MapperScan,就不需要再每个mapper上注解mapper@MapperScan(value="com.example.mybatis.mapper”)
xml
-
创建mybatis全局配置文件
mybatis-config.xml -
书写全局配置文件-开启驼峰命名等
<configuration> <settings> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCameCase" value="true"/> settings> configuration> -
书写sql映射
<mapper namespace="club.twzw.mapper.EmployeeMapper"> <select id="getEmpByid" resultMap="int"> select * form emps; select> mapper> -
指定全局配置文件位置和sql映射文件位置
mybatis: config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml mapper-location: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
整合JPA
地址: https://www.bilibili.com/video/av38657363?p=67
Spring Boot启动配置原理
地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av38657363?p=68
缓存
缓存作用:保存临时数据(
验证码)或高频访问数据(电商网站商品)
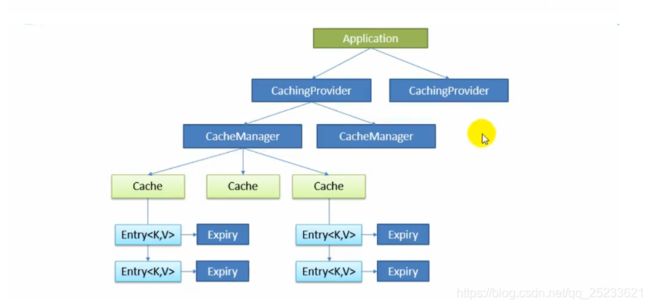
JSR107
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupid>javax.cachegroupid>
<artifactId>cache-apiartifactId>
dependency>
Spring 缓存抽象
重要概念和缓存注解
| Cache | 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现:RedisCache,EhCacheCache等 |
|---|---|
| CacheMannager | 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件 |
| keyGenerator | 缓存数据时key生成策略 |
| serialize | 缓存数据时Value序列化策略 |
| @Cacheable | 主要针对方法,能够根据方法的请求参数对方法返回结果进行缓存(若缓存中没有结果,便添加缓存,否则不添加) |
| @CacheEvict | 清空缓存(删除用户同时删除缓存) |
| @CachePut | 更新缓存(更新用户同时更新缓存) |
| @EnableCaching | 开启基于注解的缓存 |
使用注解
在主类上标注@EnableCaching
@Cacheable注解
@Cacheable(cacheName={"emp","temp"},key="#id")//可以指定一个或多个缓存中,key指的是以参数id的值为key
public Employee getEmp(Integet id){
System.out.print("查询了第"+id+"号员工");
Employee emp = empService.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
参数:
-
cacheName:指定缓存组件的名字
-
keyGenerator:key的生成器,与key二选一
- CacheMannager:指定缓存管理器
-
condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存。
condition = “#id>0”- unless:当unless指定的条件为真,方法的返回值就不会被缓存
unless="#result==null"
- unless:当unless指定的条件为真,方法的返回值就不会被缓存
-
sync:是否使用异步,如果使用,unless就不支持
原理及运行步骤:
@CachePut注解
- 即调用方法,又缓存数据
- 先调目标方法,再将目标方法的返回结果存入缓存
- 其他属性和@cacheable相同
@GetMapping("/update")
@CachePut(value = "users",key="#users.id")
public String update(users users){
return String.valueOf(mapper.updateUserInfo(users));
}
达到同步效果:存缓存的key和取缓存的key为相同的key,即
@Cacheable(cacheName="users",key="#id")
@CachePut(value = "users",key="#users.id")
#id 和 #users.id 为同一个key
@CacheEvict注解,缓存清除
- allEntries = true:清除缓存所有数据
- beforeInvocation = true :在方法执行之前清除缓存,即方法处理时出现异常,缓存中也不会有数据。
@GetMapping("/delete")
@CacheEvict(value = "users",key = "#id")
public String delete(Integer id){
System.out.println("删除用户:"+id);
return "success";
}
@Caching注解,使用多个缓存注解
-
通过多种属性去查一个员工的情况
-
@GetMapping("/byCondition") @Caching( cacheable = {@Cacheable(key = "#string")}, put = { @CachePut(key = "#result.name"), @CachePut(key = "#result.email"), } ) public String byCondition(String string){ users users = service.findBycontidition(string); return users; }
@CacheCongfig注解公共配置注解
-
在类上使用,使用后均无需再chche的注解上再去标注cache的value
-
@CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp")
整合redis作为缓存
redis 常见数据类型String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、Zset(有序集合)
引入依赖
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
配置redis
spring.redis.host=xx.xx.xx.xx
调用redis
-
StringRedisTemplate
-
redisTemplate.opsForValue().append("msg","hello"); sout(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("msg"));
-
redis序列化存入json数据或字符串而不是序列化的码
使用FASTJSON
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.62version>
dependency>
Primary注解:将某个缓存处理器作为默认的
-
bean对象实现序列化
@Component public class users implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String name; private char sexual; private String password; private Integer integral; private Integer total; private Integer user_status; private String signature; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public char getSexual() { return sexual; } public void setSexual(char sexual) { this.sexual = sexual; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Integer getIntegral() { return integral; } public void setIntegral(Integer integral) { this.integral = integral; } public Integer getTotal() { return total; } public void setTotal(Integer total) { this.total = total; } public Integer getUser_status() { return user_status; } public void setUser_status(Integer user_status) { this.user_status = user_status; } public String getSignature() { return signature; } public void setSignature(String signature) { this.signature = signature; } @Override public String toString() { return "{ id:" + id + ",name:" + name + ",sexual:" + sexual + ",password:" + password + ",integral:" + integral + ",total:" + total + ",status:" + user_status + ",signature:" + signature + "}"; } } -
书写redis的配置文件
-
@Configuration public class redisConfig { @Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); FastJsonRedisSerializer<Object> serializer = new FastJsonRedisSerializer<Object>(Object.class); // value值的序列化采用fastJsonRedisSerializer template.setValueSerializer(serializer); template.setHashValueSerializer(serializer); // key的序列化采用StringRedisSerializer template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); return template; } @Bean public RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate) { RedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory()); RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() .serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisTemplate.getValueSerializer())); return new RedisCacheManager(redisCacheWriter, redisCacheConfiguration); } } -
调用序列化器
//方法一 @Autowired private RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate1; @Test void contextLoads() { ArrayList<users> users = mapper.getAllUsers(); redisTemplate1.opsForValue().set("user",users.get(0)); } //controller调用 @RequestMapping("/getAllUsers/{id}") @Cacheable(value = "users",key = "#id") public String getAllUsers(@PathVariable(name = "id") Integer id) { ArrayList<users> allUsers = service.getAllUsers(); return JSONObject.toJSONString(allUsers); } -
out
# 方法一 { "id": 1, "name": "comiii", "sexual": "男", "password": "123456", "integral": 359, "total": 11, "user_status": -2, "signature": "原谅我一身放荡不羁爱自由!" } # 控制器调用 "{\"id\":1,\"integral\":359,\"name\":\"comiii\",\"password\":\"12xx6\",\"sexual\":\"男\",\"signature\":\"原谅我一身放荡不羁爱自由!\",\"total\":11,\"user_status\":-2}"
-
消息
应用场景
- 秒杀:10万人抢1万件商品,如果消息队列满了,则直接返回秒杀失败,随后秒杀业务才从消息队列中取出消息。
- 异步处理:应用注册场景下,一旦数据写入数据库,直接返回注册成功,而后的
身份验证等由业务逻辑去读取消息队列。- 应用节偶:订单系统添加订单到消息队列,库存系统读取消息队列。
重要概念
消息代理、目的地:当消息发送者发送消息以后,将有
消息代理(服务器)接管,消息代理保证信息传递到指定目的地(系统)。
目的地主要有两种形式的目的地:
- 队列:点对点消息通信
- 消息发送者发送消息,消息代理将其放入一个队列中,信息接收者从队列中获取消息内容,消息读取后移除队列。
- 消息只能由唯一的发送者和接收者,可以有多个接收者。
- 主题:发布/订阅消息通信
- 发送者发送消息到主题,多个接收者监听这个主题,那么就会在消息到达时同时收到消息。
RabbitMQ
概念
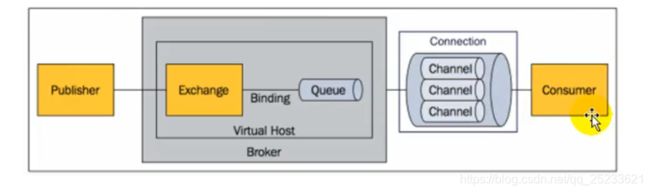
-
Messgae:由消息头和消息体组成。消息体不透明,而消息头由可选属性组成。可选属性:
- routing-key:路由键
- priority:相对于其他信息的优先权。
- delivery-mode:指出该消息可能需要持久化等。
-
publisher:消息的生产者,也是向交换器发布消息的客户端应用程序。 -
exchange:交换器,用于接收生产者的消息并将这些消息路由给服务器中的队列。四种类型:
- direct:默认,点对点模型
- fanut:发布订阅模型
- topic:发布订阅模型
- headers:发布订阅模型
-
Queue:消息队列,用来保存消息直到发送给消费者。它是消息的容器。一个消息可以投入一个或多个队列。 -
Binding:绑定,用于消息队列和交换器之间的关联。一个绑定就是介于路由键将交换器和消息队列连接起来的路由规则,所以可以将交换器理解成一个由绑定构成的路由器。- exchange和queue的绑定可以是多对多的关系。
-
connection:网络连接,TCP连接 -
Channel:信道,多路复用连接中的一条毒瘤的双向数据流通道。信道是建立在真实的TCP连接内的虚拟连接,不管是发布消息还是订阅队列还是接收消息都是通过信道完成。 -
Consumer:消息的消费者,表示一个从消息队列中取出消息的客户端应用程序。 -
Virtual Host:虚拟主机,表示一批交换器、消息队列和相关对象。本质上就是mini般的RabbitMQ服务器,拥有自己的队列,交换器,绑定和权限机制,通过指定路由访问:/、/getUsers等 -
Broker:表示消息队列的服务器实体。
运行机制
Exchange 类型
Direct:直连型,只有路由完全一样时,才会转发。
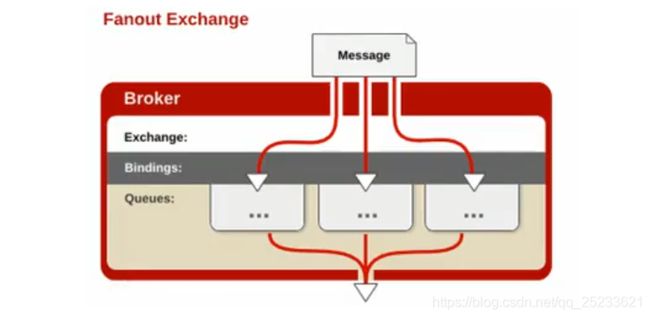
Fanout:每个发到fanout类型交换器的消息都会分到所有绑定的队列上去。类似于广播,每台子网内的主机都获得一份复制信息,该类型转发消息是最快的。
Topic:通过
模式匹配分配消息的路由键属性,将路由器和某个模式进行匹配,此时队列需要绑定到一个模式上。通配符:#、*
#:匹配0个或多个单词
*:匹配一个单词
安装RabbitMQ
- docker search rabbitmq
- docker pull rabbitmq:3-management
- docker run -d -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 --name RabbitMQ image-id
- ip:15672访问;用户名guest,密码guest
整合RabbitMQ
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqpartifactId>
dependency>
配置文件
spring.rabbitmq.host=47.xxx.xxx.xxx
spring.rabbitmq.username=guest
spring.rabbitmq.password=guest
简单案例:发送和接收消息
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("update.fanout","/","anything!");
}
@Test
void receive(){
Object receive = rabbitTemplate.receiveAndConvert("orders");
System.out.println(receive);
}
存入json消息:自定义配置
@Configuration
public class myRabbitMQ {
@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter(){
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
}
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("update.direct", "update.direct.news", "{ \"name\":\"comi\",\n \"age\":18\n }");
}
@Test
void receive() {
Object receive = rabbitTemplate.receiveAndConvert("news");
System.out.println(receive);
}
json 结合bean
-
创建bean对象、需要无参、有参、set、get方法
public class user { private String name; private Integer age; public user() { } public user(String name, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } } -
调用
@Autowired RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @Test void contextLoads() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("update.direct", "update.direct.news", new user("comi", 18)); } @Test void receive() { Object receive = rabbitTemplate.receiveAndConvert("news"); System.out.println(receive); }
消息队列监听
@RebbitListenner(queues = "news"):消息队列监听注解、只要消息队列中有内容进来,该注解下的方法便会被调用。
@Service
public class UserService {
@RabbitListener(queues = "news")
public void listener(user u){
System.out.println("收到消息:" + u.getName() +","+ u.getAge());
}
}
主程序开启支持rabbitmq支持
@EnableRabbit //开启基于注解的rabbitmq
@SpringBootApplication
public class RabbitmqApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RabbitmqApplication.class, args);
}
}
当web程序启动后,一旦消息队列收到消息,便会自动取出消息队列中的消息。
AmqpAdmin动态添加exchange交换器和queue队列
AmqpAdmin : 创建和删除Queue、exchange、Binding
@Test
public void CreateExchange() {
admin.declareExchange(new DirectExchange("amqp.exchange"));
System.out.println("创建交换器完成!");
}
@Test
public void declareQueue() {
admin.declareQueue(new Queue("amqp.queue"));
System.out.println("创建队列完成!");
}
@Test
public void declareBinding() {
Binding binding = new Binding("news", Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE, "amqp.exchange", "amqp.queue", null);
admin.declareBinding(binding);
System.out.println("创建绑定完成!");
}
@Test
public void removeBinding() {
Binding binding = new Binding("news", Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE, "amqp.exchange", "amqp.queue", null);
admin.removeBinding(binding);
System.out.println("删除绑定完成!");
}
检索
安装
> docker search elasticsearch
> docker pull docker pull docker.io/elasticsearch:6.5.0
> docker run -e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms256m -Xmx256m" -d -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 --name ELS elasticsearch:6.5.0
# 设置默认启动占用内存256M,9300端口为分布式节点端口
任务
异步任务
可以有效缓解任务处理带来的加载缓慢的体验
-
开启异步任务注解
@EnableAsync //开启异步任务注解 @SpringBootApplication public class TaskApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(TaskApplication.class, args); } } -
在需要异步任务(邮件任务)的service上进行标注开启异步任务
@Async@Service("myService") public class myService { @Async public void hello(){ try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("任务处理中。。。"); } }
定时任务
用于每月定时的
日志分析收集、客房住户分析等。
cron表达式格式
{秒数} {分钟} {小时} {日期} {月份} {星期} {年份(可为空)}
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 24 1 * ?"):每月的1号24:00启动任务
-
开启定时任务
@EnableScheduling @SpringBootApplication public class TaskApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(TaskApplication.class, args); } } -
设置启动任务时间
@Service public class scheduleService { @Scheduled(cron = "0 0 24 1 * ?") public void hello() { System.out.println("日志收集"); } }
邮件任务
-
引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mailartifactId> dependency> -
配置文件设置mail属性
[email protected] spring.mail.password=xxxxxxxxxx spring.mail.host=smtp.qq.com spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.ssl.enable=true -
简单邮件发送
@Autowired JavaMailSenderImpl javaMailSender; @Test void contextLoads() { SimpleMailMessage message = new SimpleMailMessage(); message.setSubject("今晚开会"); message.setText("今晚开会"); message.setTo("[email protected]"); message.setFrom("[email protected]"); javaMailSender.send(message); } -
复杂邮件:携带样式发送邮件
@Test void test() throws MessagingException { MimeMessage message = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage(); MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(message,true); helper.setText("今晚开会"); helper.addAttachment("11.jpg", new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop")); helper.setTo("[email protected]"); helper.setFrom("[email protected]"); javaMailSender.send(message); }
安全
身份认证、安全控制、权限控制、漏洞攻击
-
引入springboot security
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId> dependency> -
编写spring security的配置类
@EnableWebSecurity public class security extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // 定制请求的授权规则,设置访问路径 http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/").permitAll(). antMatchers("/hello/**").hasRole("manage") .antMatchers("/write/**").hasRole("user"); //开启自动配置的登录功能 /* * 1./login 登陆页面 * 2./login?error 登陆错误 */ http.formLogin(); // 开启自动配置的注销功能 /* * 访问/logout请求,清空session * 跳转到/login?logout * */ http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/"); } @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder()) .withUser("comi").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("manage", "user") .and() .withUser("siki").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("user"); } }
cookies
//cookies 开启记住我功能
http.rememberMe();
定制登录页
http.formLogin().loginPage("/login").successForwardUrl("/");