java面试:你重写过 hashcode 和 equals 么,为什么重写 equals时必须重写 hashCode 方法?
首先,我们要知道equals()方法和hashcode()方法都属于Object类,这就意味着 Java 中的任何类都可调用Object类的方法;
下面我们看下源码:
equals()方法:
可以看出,在Object的源码,底层是用的"=="来比较的,也就是判断俩个的地址是不是一样的,这让这个equals方法在我们实际开发过程中没有了太大的实用价值,我们不是要地址的相等性,我们一般需要是逻辑上的相等,比如两个对象属性完全一样,我们就可以认为他一样(可参考下面的例子)。这时候我们就得重写equals方法了。
hashCode()方法:
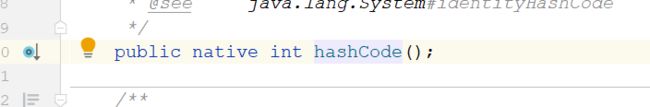
hashCode() 的作用是获取哈希码,也称为散列码;实际上是返回一个 int 整数。这个哈希码的作用是确定该对象在哈希表中的索引位置。源码可以看出,hashCode()是一个native方法,哈希值的计算利用的是内存地址。
我们来看下Object类中关于hashCode()方法的注释,原文:
/**
* Returns a hash code value for the object. This method is
* supported for the benefit of hash tables such as those provided by
* {@link java.util.HashMap}.
*
* The general contract of {@code hashCode} is:
*
* - Whenever it is invoked on the same object more than once during
* an execution of a Java application, the {@code hashCode} method
* must consistently return the same integer, provided no information
* used in {@code equals} comparisons on the object is modified.
* This integer need not remain consistent from one execution of an
* application to another execution of the same application.
*
- If two objects are equal according to the {@code equals(Object)}
* method, then calling the {@code hashCode} method on each of
* the two objects must produce the same integer result.
*
- It is not required that if two objects are unequal
* according to the {@link java.lang.Object#equals(java.lang.Object)}
* method, then calling the {@code hashCode} method on each of the
* two objects must produce distinct integer results. However, the
* programmer should be aware that producing distinct integer results
* for unequal objects may improve the performance of hash tables.
*
*
* As much as is reasonably practical, the hashCode method defined by
* class {@code Object} does return distinct integers for distinct
* objects. (This is typically implemented by converting the internal
* address of the object into an integer, but this implementation
* technique is not required by the
* Java™ programming language.)
*
* @return a hash code value for this object.
* @see java.lang.Object#equals(java.lang.Object)
* @see java.lang.System#identityHashCode
*/
public native int hashCode();
翻译一下,差不多这么个意思:
1.在执行过程中对同一对象多次调用hashCode方法时,必须始终返回相同的整数,但前提是equals方法比较时使用的对象没有被修改。同一个应用程序的一个执行与另一个执行,这个整数不需要保持一致。
2.如果equals(Object)}两个对象相等,那么两个对象必须产生相同的整数结果。即equals为true,则hashcode相等。
3.如果根据 equals(Object) 方法,两个对象不相等,不要求hashCode 方法一定生成不同的整数结果,但是,程序员应该意识到,为不相等的对象生成不同整数结果可以提高哈希表的性能。
总结一下:
A:如果两个对象相等,则 hashcode 一定也是相同的
B:两个对象有相同的 hashcode 值,它们也不一定是相等的
C:hashCode是为了提高性能
对于C,举个例子,HashSet 如何检查重复:
当你把对象加入 HashSet 时,HashSet 会先计算对象的 hashcode 值来判断对象加入的位置,同时也会与其他已经加入的对象的 hashcode 值作比较,如果没有相符的 hashcode,HashSet 会假设对象没有重复出现。但是如果发现有相同 hashcode 值的对象,这时会调用 equals()方法来检查 hashcode 相等的对象是否真的相同。如果两者相同,HashSet 就不会让其加入操作成功。
如果不同的话,就会重新散列到其他位置。这样我们就大大减少了 equals 的次数,相应就大大提高了执行速度。
好了,只是用文字来表示太空洞,我们上代码----》
新建一个测试user类(此时未重写equals和hashCode):
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}然后写个测试类
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
User u1=new User("张飒",123);
User u2=new User("张飒",123);
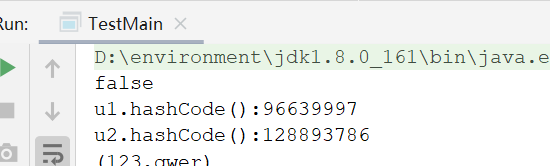
System.out.println(u1.equals(u2));
System.out.println("u1.hashCode():"+u1.hashCode());
System.out.println("u2.hashCode():"+u2.hashCode());
//Pair和Triple的使用,返回两个三个值的时候可用
Pair pair=new ImmutablePair(123,"qwer");
Triple triple=new ImmutableTriple(1,2,3);
System.out.println(pair);
System.out.println(triple);
}运行测试类,可以看出是两个对象是不同,返回false
此时我们添加重写user的equals方法:
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
User user = (User) o;
return age == user.age &&
Objects.equals(name, user.name);
}运行我们的测试类,
可得到结果为true,hashcode不一样;
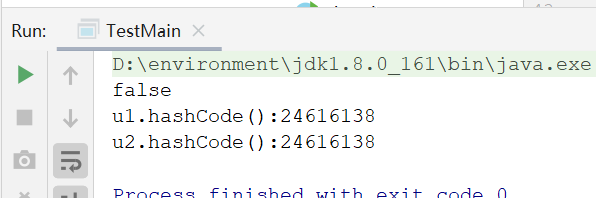
现在,将equals注释掉,重写hashCode方法:
运行测试了我们可以看出,hashcode一样,结果为false
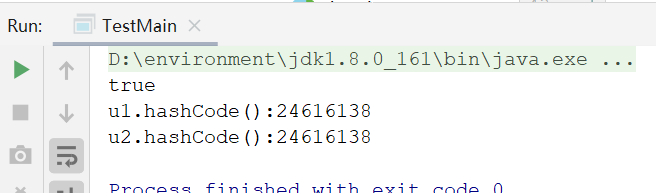
最后,我们同时重写equals和hashCode方法,可以看到返回值是true,hashcode值也是相等的。
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
User user = (User) o;
return age == user.age &&
Objects.equals(name, user.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
最后总结下为什么重写了equals要重写hashCode:
- 使用hashcode方法进行提前校验,可以避免每一次比对都调用equals方法,提高性能;
- 保证同一个对象。如果重写了equals方法,而没有重写hashcode方法,会出现equals相等的对象,hashcode不相等的情况,重写hashcode方法就是为了避免这种情况的出现。
关注公众号,回复 面试 获取初级中级高级面试题。