《Linux C编程实战》笔记:文件属性操作函数
获取文件属性
stat函数
在shell下直接使用ls就可以获得文件属性,但是在程序里应该怎么获得呢?
#include
#include
#include
int stat(const char *file_name,struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int filedes,struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *file_name,struct stat *buf);
stat函数:
int stat(const char *file_name, struct stat *buf);
stat函数用于获取由file_name指定的文件的信息,并将其存储在由buf指向的结构体中。- 信息包括文件大小、inode号、所有者和组ID、权限、时间戳等。
fstat函数:
int fstat(int filedes, struct stat *buf);
fstat函数类似于stat,但它不是通过文件名而是通过已打开文件的文件描述符filedes来获取文件信息。- 它将文件描述符关联的文件的信息存储在由
buf指向的结构体中。- 这在你已经有一个文件描述符的情况下很有用,可以直接获取已打开文件的信息。
lstat函数:
int lstat(const char *file_name, struct stat *buf);
lstat函数类似于stat,但它不会跟随符号链接。- 如果指定的文件是符号链接,
lstat提供有关链接本身的信息,而stat则会跟随链接并提供有关链接的文件的信息。- 在你想要获取符号链接本身而不是链接指向的文件的信息时,这是很有用的。
函数失败返回-1 。
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; // 文件所在设备的ID
ino_t st_ino; // 文件的inode号
mode_t st_mode; // 文件的类型和权限
nlink_t st_nlink; // 文件的硬链接数
uid_t st_uid; // 文件所有者的用户ID
gid_t st_gid; // 文件所有者的组ID
dev_t st_rdev; // 若文件是设备文件,则为设备的ID
off_t st_size; // 文件的大小(以字节为单位)
blksize_t st_blksize; // 文件系统块大小
blkcnt_t st_blocks; // 文件占用的块数
time_t st_atime; // 最后一次访问时间
time_t st_mtime; // 最后一次修改时间
time_t st_ctime; // 最后一次状态改变时间
};
以下是一些常见的
st_mode宏:
文件类型宏:
S_ISREG(mode): 判断是否为常规文件。S_ISDIR(mode): 判断是否为目录。S_ISCHR(mode): 判断是否为字符设备。S_ISBLK(mode): 判断是否为块设备。S_ISFIFO(mode): 判断是否为FIFO(先进先出)。S_ISLNK(mode): 判断是否为符号链接。S_ISSOCK(mode): 判断是否为套接字。文件权限宏:
S_IRUSR,S_IWUSR,S_IXUSR: 用户(所有者)的读、写、执行权限。S_IRGRP,S_IWGRP,S_IXGRP: 组的读、写、执行权限。S_IROTH,S_IWOTH,S_IXOTH: 其他用户的读、写、执行权限。
示例程序1
以本代码的cpp文件为例,演示获取文件属性。注意文件名同步成自己的文件名
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
struct stat buf;
if(stat("test.cpp",&buf)==-1){
perror("stat:");
exit(1);
}
//print
printf("device is %d\n",buf.st_dev);
printf("inode is :%d\n",buf.st_ino);
printf("mode id:%o\n",buf.st_mode);
printf("number of hard links is:%d\n",buf.st_nlink);
printf("user ID of owner is:%d\n",buf.st_uid);
printf("group ID of owner is :%d\n",buf.st_gid);
printf("device type(if inode device) is :%d\n",buf.st_rdev);
printf("total size,in bytes is:%d\n",buf.st_size);
printf("blocksize for filesystem I/O is:%d\n",buf.st_blksize);
printf("number of blocks allocated is :%d\n",buf.st_blocks);
printf("time of last access is :%s",ctime(&buf.st_atime));
printf("time of last modification is :%s",ctime(&buf.st_mtime));
printf("time of last change is :%s",ctime(&buf.st_ctime));
return 0;
} 代码本身不难懂;st_mode用八进制格式输出;ctime函数可以把时间值(表示自纪元以来的秒数)转换为人类可读的ASCII字符串形式。
修改文件设置
chmod函数
修改文件的存取权限
#include
#include
int chmod(const char *path,mode_t mode);
int fchmod(int fildes,mode_t mode);
mode参数指定新的权限。mode的取值是一个八进制数字,由不同的位掩码组成。以下是一些常见的mode取值:
权限位掩码(三个八进制数字):
User (Owner) Permissions:
S_IRUSR(读权限): 00400S_IWUSR(写权限): 00200S_IXUSR(执行权限): 00100Group Permissions:
S_IRGRP(读权限): 00040S_IWGRP(写权限): 00020S_IXGRP(执行权限): 00010Others Permissions:
S_IROTH(读权限): 00004S_IWOTH(写权限): 00002S_IXOTH(执行权限): 00001特殊权限位掩码:
S_ISUID(Set User ID): 04000S_ISGID(Set Group ID): 02000S_ISVTX(Sticky Bit): 01000这些位掩码可以通过按位或操作组合在一起,形成完整的
mode参数。
修改文件的用户id和组id
#include
int chown(const char *path, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int lchown(const char *path, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int fchown(int fd, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
path: 文件或目录的路径名。owner: 新的所有者的用户ID。group: 新的组的ID。
成功返回0,失败返回-1 。
chown系统调用会清除(S_ISUID和S_ISGID)
truncate函数
用于改变文件大小
#include
#include
int truncate(const char *path,off_t length);
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length); 将指定文件大小改为length指定的大小。如果原来文件大小比参数大,超过部分会被删除;如果比参数小,文件将被拓展,和lseek类似,拓展部分将以'\0'填充。吐过文件大小被改变了,则文件 的st_mtime和st_ctime将会更新(忘了?回去看stat结构体)
执行成功返回0,发生错误返回-1 。
utime函数
用于改变文件的st_mtime和st_ctime域。
#include
#include
int utime (const char *filename,struct utimbuf *buf);
#include
int utimes (char *filename,struct timeval *tvp); struct utimbuf{
time_t actime:/*access time*/
time_t modtime; /*modification time */
};
struct timeval是表示时间的结构体,在C语言中通常用于处理微秒级别的时间。它的定义如下:
struct timeval { time_t tv_sec; // 秒数
suseconds_t tv_usec; // 微秒数
};
utime 系统调用会把由第一个参数filename指定的文件的存取时间改为第二个参数 buf 的actime域,把修改时间改为第二个参数buf 的modtime域,如果buf是一个空指针,则将存取时间和修改时间都改为当前时间。
用法如下:
const char *filename = "example.txt";
struct utimbuf new_times;
new_times.actime = 1632976800; // Example access time (in seconds since the epoch)
new_times.modtime = 1632976900; // Example modification time (in seconds since the epoch)
if (utime(filename, &new_times) == -1) {
perror("utime");
return 1;
}另一个函数用法如下:
const char *filename = "example.txt";
struct timeval new_times[2];
new_times[0].tv_sec = 1632976800; // Example access time (in seconds since the epoch)
new_times[1].tv_sec = 1632976900; // Example modification time (in seconds since the epoch)
if (utimes(filename, new_times) == -1) {
perror("utimes");
return 1;
}umask函数
#include
#include
mode_t umask(mode_t mask); 用于设置文件创建时的屏蔽字,并返回以前的值。
在创建一个新文件或目录时,新文件的实际存取权限时如open函数里mode与umask按照
(mode&~umask)的结果,可以理解为mode再去除掉umask。
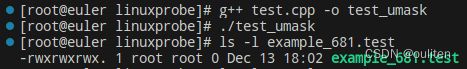
示例程序2
演示umask函数的运用
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
umask(0);//不屏蔽任何权限
if(creat("example_681.test",S_IRWXU|S_IRWXG|S_IRWXO)<0){
perror("creat");
exit(1);
}
umask(S_IRWXO);//屏蔽 其他用户的所有权限
if(creat("example_682.test",S_IRWXU|S_IRWXG|S_IRWXO)<0){
perror("creat");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
} 创建第一个文件时,不屏蔽任何权限;
创建第二个文件时,umask设置了S_IRWXO,那么S_IRWXU|S_IRWXG|S_IRWXO的组合就要去掉S_IRWXO这个权限了。
可以看到682文件其他用户的权限都消失了。