布隆过滤器,Redis之 bitmap,场景题【如果微博某个大V发了一条消息,怎么统计有多少人看过了】
学习文档
文章目录
-
- 一、什么是 Bitmap
-
- 1-1、Bitmap 相关命令
- 二、Bitmap 和 Set 对比
-
- 2-1、数据准备
- 2-2、内存对比
- 2-3、性能对比
- 三、布隆过滤器
-
- 3-1、理论
- 3-2、代码实现
- 四、Java中的 Hash 函数
最近面试时,遇到了一个场景题,面试官问如何统计一条微博大V的消息有多少人阅读。经过老大的指点,我总结了一下。
如果微博某个大V发了一条消息,怎么统计有多少人看过了。
每一个访问记录肯定是要入库的,但页面展示的时候,我们不可能都去数据库 count 一下。最开始我说使用redis的set数据结构把用户id存进去,但这并不是一个很好的答案,因为它消耗的内存太大。
Redis有一种数据结构 Bitmap,在特定的数据场景下,它很适合来做这种统计。为什么说是特定的场景,下面我们来分析。
一、什么是 Bitmap
Bitmap是一种精简而高效的数据结构,通过二进制位存储大规模布尔值信息,常用于快速处理用户在线状态、权限管理以及行为记录等应用场景。
可以简单把它想象成是趋于无限大的数组,每个位置只能存储 1 和 0。它可以快速统计出有多少个 1,也可以快速统计某个区间内有多少个 1。
基于此我们可以创建一个 bitmap, key 就是这条消息的id,每个位置就对应一个用户,1 就表示看过。
1-1、Bitmap 相关命令
| 描述 | 命令 |
|---|---|
| 插入数据 | setbit key offset value |
| 设置为 1 | setbit bitmap001 10000 1 |
| 设置为 0 | setbit bitmap001 10000 0 |
| 查询数据 | getbit key offset (每个位置默认是 0) |
| 数据统计 | bitcount key [start end] |
| 统计全部为 1 | bitcount bitmap001 |
| 按照范围统计为 1 | bitcount bitmap001 0 1000000 |
| 获取范围内第一个 offset | bitpos key value [start] [end] |
| 获取第一个 1 | bitpos bitmap001 1 |
| 获取第一个 0 | bitpos bitmap001 0 |
| 获取 0, 100 中第一个 1 | bitpos bitmap001 1 0 100 |
二、Bitmap 和 Set 对比
如果只是想统计有多少个用户访问过,且某个用户是否访问过,其实 set类型,也可以满足我们的要求,实际上我上次也是这么回答的,但结果是不对的,下面来看分析。
看一种数据结构是否好,无非是看它消耗的存储空间和运行速率,基于此我们来对比一下 bitmap 和 set的内存消耗和运行速率。
2-1、数据准备
我们以 10w 数据为基准来进行测试。插入数据的脚本如下:
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000 * 60 * 60)
public void fun() {
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOps = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add("set10w_uuid", uuid);
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add("set10w_incr", String.valueOf(i));
valueOps.setBit("bitMap10w_hash", Murmur3.hash_x86_32(uuid.getBytes(), uuid.length(), 0),true);
valueOps.setBit("bitMap10w_hash_size", Math.abs(Murmur3.hash_x64_128(uuid.getBytes(), uuid.length(), 0)[0] % 100000),true);
valueOps.setBit("bitMap10w_incr", i,true);
System.out.println("progress " + i);
}
System.out.println("执行耗时: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
其实就是生成10w个uuid,把这个10w个uuid存入set,把这些uuid转成hash作为 bitmap的偏移量存入 bitmap,再把 i 存入另外一个set和bitmap,这样就构建了 4个数据。
另外还创建了一个特殊的 bitmap,它的生成只有一个添加语句,如下:
setbit bitMap_1_bitHash 1000000000 1
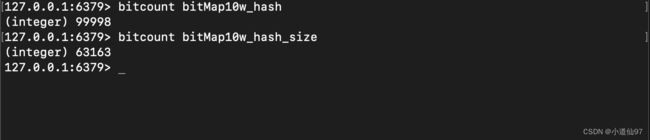
bitMap10w_hash_size 这个key展示先忽略,我们后面再说。
2-2、内存对比
使用 Redis 提供的命令查看每个 key 的内存消耗。
redis-cli memory usage keyName
上面的数据体现是不是很不可思议?为什么内存消耗会那么大? set 的数据就没什么好说了,就是按照字符串去存储的,我们主要来探讨一下 bitmap 。
bitmap是一个二进制存储结构,所以当它的偏移量越大,所占用的内存也就越大。 incr就是自增的id,所以最大偏移量也就是 100000,那它占用内存当然很小。而通过uuid转成的hashCode值是很大的。
2-3、性能对比
说实在的它们俩的类型不同,其实不太好去对比。这里只是简单的对比一下:获取数据总量和查询某个值是否存在
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000 * 60 * 60)
public void fun2() {
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOps = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
// 预热一下
Long xxxxx = redisTemplate.opsForSet().size("set10w_incr");
long one = System.currentTimeMillis();
Long set10w_uuid = redisTemplate.opsForSet().size("set10w_uuid");
redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember("set10w_uuid", "xxxxx");
long two = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("set10w_uuid = " + set10w_uuid + " " + (two - one));
Long set10wIncr = redisTemplate.opsForSet().size("set10w_incr");
redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember("set10w_incr", "1");
long three = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("set10wIncr = " + set10wIncr+ " " + (three - two));
Object bitMap10w_incr = redisTemplate.execute((RedisCallback<Long>) connection ->
connection.bitCount("bitMap10w_incr".getBytes())
);
valueOps.getBit("bitMap10w_incr", 1000);
long four = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("bitMap10w_incr = " + bitMap10w_incr+ " " + (four - three));
Object bitMap10w_hash = redisTemplate.execute((RedisCallback<Long>) connection ->
connection.bitCount("bitMap10w_hash".getBytes())
);
valueOps.getBit("bitMap10w_hash", 1000);
long five = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("bitMap10w_hash = " + bitMap10w_hash+ " " + (five - four));
}
执行结果如下
set10w_uuid = 100000 7
set10wIncr = 100000 3
bitMap10w_incr = 100000 35
bitMap10w_hash = 99998 141
看似是set好像性能更好,但术业有专攻,不应该这样对比的。
三、布隆过滤器
3-1、理论
布隆过滤器 本质就是一个bigmap,目的就是在做业务操作之前,先过滤掉一些不正当的请求
和上面的需求差不多当然也可以用set来做,但这样的内存的消耗就大了,而且容易产生大key
布隆过滤器 有两个重要的参数
- hash函数, 一个好的hash函数可以尽可能的防止冲突的发生。且我们可以设置多个hash函数
- 存储大小 size, 我们不可能设置一个无限大的空间,这样会导致数据过于分散不好统计
使用Redis的bitmap来搭建布隆过滤器的大致步骤如下,先基于业务场景定义好 size和hash函数,每一个offset的取值按照这个公式,offset = hash % size,这样计算的目的是防止hash大于 size
3-2、代码实现
下面是布隆过滤器的Java代码实现:(GPT写的,很好理解)
// Java代码示例
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import java.util.BitSet;
public class BloomFilter {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private final String filterKey;
private final int size;
private final int[] hashFunctions;
public BloomFilter(String filterKey, int size, int numHashFunctions) {
this.filterKey = filterKey;
this.size = size;
this.hashFunctions = new int[numHashFunctions];
initializeHashFunctions();
}
// 自定义多个hash函数
private void initializeHashFunctions() {
for (int i = 0; i < hashFunctions.length; i++) {
hashFunctions[i] = (int) (Math.random() * Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
public void add(String element) {
// 多次hash计算,最大程度保证可用
for (int hashFunction : hashFunctions) {
// 防止hash超出为负数
int index = Math.abs(hashFunction % size);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(filterKey, index, true);
}
}
public boolean contains(String element) {
for (int hashFunction : hashFunctions) {
int index = Math.abs(hashFunction % size);
if (!redisTemplate.opsForValue().getBit(filterKey, index)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 测试代码
public void test() {
BloomFilter bloomFilter = new BloomFilter(redisTemplate, "bloomFilter", 10000, 3);
// Add elements to the Bloom Filter
bloomFilter.add("element1");
bloomFilter.add("element2");
bloomFilter.add("element3");
// Check if an element is in the Bloom Filter
System.out.println(bloomFilter.contains("element1")); // true
System.out.println(bloomFilter.contains("element4")); // false
}
}
使用这种紧凑的bitmap(定义了size大小), 100w的空间所需要的内存也是极少的。
布隆过滤器的过滤并不是 100%,当发生hash冲突的时候就可能误杀,上面不限制大小的冲突是 0.002%,限制10w大小,生成 10w个数据的冲突是 36.84%
四、Java中的 Hash 函数
Murmur 是一个计算 hash 的工具类,使用和引入依赖如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sanguptagroupId>
<artifactId>murmurartifactId>
<version>1.0.0version>
dependency>
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 在32位机器上计算hash
long l = Murmur3.hash_x86_32(UUID.randomUUID().toString().getBytes(), 36, 0);
// 在64位机器上计算hash
long[] longs = Murmur3.hash_x64_128(UUID.randomUUID().toString().getBytes(), 36, 0);
}