基于图片翘曲的后门攻击WaNet源码分析
什么是WaNet?
WaNet是一种基于图片翘曲的后门攻击手段,参考文章《基于扭曲的后门攻击》
下图分析了WaNet对于人眼的隐蔽性
下图展现了WaNet的基本原理
参考代码:github代码
一、network文件
1、blocks.py
导入pytorch库
import torch
from torch import nnConv2dBlock函数
用forward正向传播实现卷积、BN归一化、Relu激活函数
class Conv2dBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_c, out_c, ker_size=(3, 3), stride=1, padding=1, batch_norm=True, relu=True):
super(Conv2dBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_c, out_c, ker_size, stride, padding)
if batch_norm:
self.batch_norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_c, eps=1e-5, momentum=0.05, affine=True)
if relu:
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
for module in self.children():
x = module(x)
return x
ConvTranspose2dBlock
实现卷积转置(逆卷积)
卷积:A * W = B ,逆卷积: B --> A 其中W为卷积核
用forward实现逆卷积、BN归一化、Relu激活函数
class ConvTranspose2dBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_c, out_c, ker_size=(3, 3), stride=1, padding=1, batch_norm=True, relu=True):
super(ConvTranspose2dBlock, self).__init__()
self.convtranpose2d = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_c, out_c, ker_size, stride, padding)
if batch_norm:
self.batch_norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_c, eps=1e-5, momentum=0.05, affine=True)
if relu:
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
for module in self.children():
x = module(x)
return x
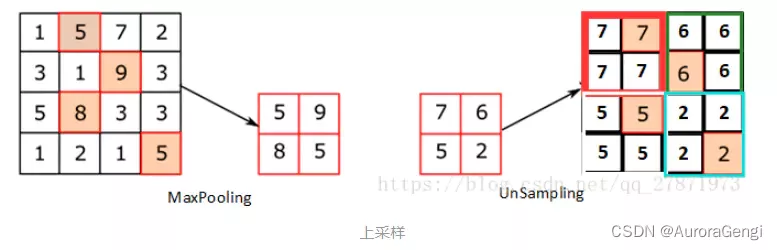
上下采样:
下采样即缩小图片,可以直接用maxpool来实现
上采样即放大图片
DownSampleBlock
进行一次最大池化,并用dropou舍弃设定的值
class DownSampleBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ker_size=(2, 2), stride=2, dilation=(1, 1), ceil_mode=False, p=0.0):
super(DownSampleBlock, self).__init__()
self.maxpooling = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=ker_size, stride=stride, dilation=dilation, ceil_mode=ceil_mode)
if p:
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p)
def forward(self, x):
for module in self.children():
x = module(x)
return xUpSampleBlock
上采样:放大图像,来使其特征更加明显
进行一次上采样、一次卷积、一次BN规范化、一次dropout
class UpSampleBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, in_c, out_c, kernel_size, stride, padding, scale_factor=(2, 2), mode="bilinear", batch_norm=True, p=0.0
):
super(UpSampleBlock, self).__init__()
self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=scale_factor, mode=mode)
self.conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_c, out_c, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding)
if batch_norm:
self.batch_norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_c, eps=1e-5, momentum=0.05, affine=True)
if p:
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p)
def forward(self, x):
for module in self.children():
x = module(x)
return x2、Models.py
导入库
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Module
from torchvision import transforms
from .blocks import *Normalize
对输入值进行规范化操作
class Normalize:
def __init__(self, opt, expected_values, variance):
self.n_channels = opt.input_channel
self.expected_values = expected_values
self.variance = variance
assert self.n_channels == len(self.expected_values)
def __call__(self, x):
x_clone = x.clone()
for channel in range(self.n_channels):
x_clone[:, channel] = (x[:, channel] - self.expected_values[channel]) / self.variance[channel]
return x_clone
对于不同类型的数据集执行不同的normalize操作
class Normalizer:
def __init__(self, opt):
self.normalizer = self._get_normalizer(opt)
def _get_normalizer(self, opt):
if opt.dataset == "cifar10":
normalizer = Normalize(opt, [0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465], [0.247, 0.243, 0.261])
elif opt.dataset == "mnist":
normalizer = Normalize(opt, [0.5], [0.5])
elif opt.dataset == "gtsrb" or opt.dataset == "celeba":
normalizer = None
else:
raise Exception("Invalid dataset")
return normalizer
def __call__(self, x):
if self.normalizer:
x = self.normalizer(x)
return x
分类器:MNISTBlock
进行BN规范化、relu激活函数、卷积
class MNISTBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1):
super(MNISTBlock, self).__init__()
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.ind = None
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv1(F.relu(self.bn1(x)))
网络搭建
class NetC_MNIST(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NetC_MNIST, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, (3, 3), 2, 1) # 14
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.layer2 = MNISTBlock(32, 64, 2) # 7
self.layer3 = MNISTBlock(64, 64, 2) # 4
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear6 = nn.Linear(64 * 4 * 4, 512)
self.relu7 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.dropout8 = nn.Dropout(0.3)
self.linear9 = nn.Linear(512, 10)
def forward(self, x):
for module in self.children():
x = module(x)
return x二、utils文件
1、dataloader.py
导入库
import csv
import kornia.augmentation as A
import random
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
ToNumpy
tensor张量和numpy之间转化
class ToNumpy:
def __call__(self, x):
x = np.array(x)
if len(x.shape) == 2:
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=2)
return x
ProbTransform
p为概率,即self.f(x)执行概率
class ProbTransform(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, f, p=1):
super(ProbTransform, self).__init__()
self.f = f
self.p = p
def forward(self, x): # , **kwargs):
if random.random() < self.p:
return self.f(x)
else:
return x
该文件作用是加载数据
utils.py
导入库
import os
import sys
import time
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.init as init
get_mean_and_std
计算平均和标准值
def get_mean_and_std(dataset):
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
mean = torch.zeros(3)
std = torch.zeros(3)
print("==> Computing mean and std..")
for inputs, targets in dataloader:
for i in range(3):
mean[i] += inputs[:, i, :, :].mean()
std[i] += inputs[:, i, :, :].std()
mean.div_(len(dataset))
std.div_(len(dataset))
return mean, stdinit_params
初始化神经层的参数
def init_params(net):
for m in net.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal(m.weight, mode="fan_out")
if m.bias:
init.constant(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant(m.weight, 1)
init.constant(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal(m.weight, std=1e-3)
if m.bias:
init.constant(m.bias, 0)改python文件主要用于计算一些值、初始化参数,通过输出实现人机交互