CentOS7下部署Django项目
服务器
服务器的基本配置
随便购买一台服务器,使用CentOS系统并记住记住自己的公网IP
去安全组放行端口
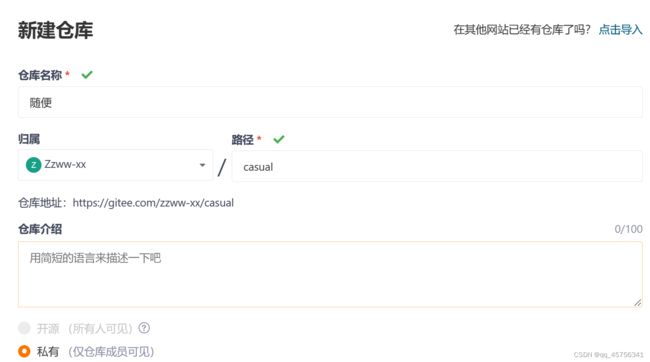
去Gitee新建一个代码仓库
Git
下载git,用来同步代码 下载地址:Git - Downloading Package (git-scm.com)
设置好安装路径一路下一步就行
安装好之后 桌面右键 Git Bash Here
全局配置 进入刚刚在Gitee新建的仓库
git config --global user.name "用户名"
git config --global user.email "邮箱"在Git输入从Gitee全局设置的两行代码
然后进入项目地址的文件夹 右键 Git Bash Here
初始化
git init配置远程地址
git remote add origin https://gitee.com/zzwxxw/xxxxx.git本地版本提交并提交至代码仓库
git add .
git commit -m '提交说明...'
git push origin master但是每次提交会输入Gitee的账号密码十分不方便,可以使用SSH
在Git里输入
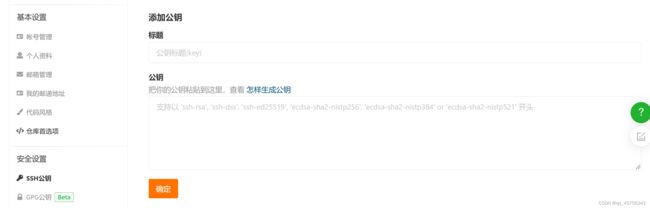
ssh-keygen -t rsa查看ssh公钥并复制下来
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub在Gitee设置找到SSH公钥,并粘贴进去,这样每次推送就不会要重复输入账号密码
在项目中创建一个 .gitignore的文件,在里面写上文件名或文件夹,可以git忽略一些文件,不要进行版本控制。
# Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files __pycache__/ *.py[cod] *$py.class # C extensions *.so # Distribution / packaging .Python build/ develop-eggs/ dist/ downloads/ eggs/ .eggs/ lib/ lib64/ parts/ sdist/ var/ wheels/ share/python-wheels/ *.egg-info/ .installed.cfg *.egg MANIFEST # PyInstaller # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it. *.manifest *.spec # Installer logs pip-log.txt pip-delete-this-directory.txt # Unit test / coverage reports htmlcov/ .tox/ .nox/ .coverage .coverage.* .cache nosetests.xml coverage.xml *.cover *.py,cover .hypothesis/ .pytest_cache/ cover/ # Translations *.mo *.pot # Django stuff: *.log local_settings.py db.sqlite3 db.sqlite3-journal # Flask stuff: instance/ .webassets-cache # Scrapy stuff: .scrapy # Sphinx documentation docs/_build/ # PyBuilder .pybuilder/ target/ # Jupyter Notebook .ipynb_checkpoints # IPython profile_default/ ipython_config.py # pyenv # For a library or package, you might want to ignore these files since the code is # intended to run in multiple environments; otherwise, check them in: # .python-version # pipenv # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control. # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not # install all needed dependencies. #Pipfile.lock # poetry # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include poetry.lock in version control. # This is especially recommended for binary packages to ensure reproducibility, and is more # commonly ignored for libraries. # https://python-poetry.org/docs/basic-usage/#commit-your-poetrylock-file-to-version-control #poetry.lock # pdm # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include pdm.lock in version control. #pdm.lock # pdm stores project-wide configurations in .pdm.toml, but it is recommended to not include it # in version control. # https://pdm.fming.dev/#use-with-ide .pdm.toml # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow and github.com/pdm-project/pdm __pypackages__/ # Celery stuff celerybeat-schedule celerybeat.pid # SageMath parsed files *.sage.py # Environments .env .venv env/ venv/ ENV/ env.bak/ venv.bak/ # Spyder project settings .spyderproject .spyproject # Rope project settings .ropeproject # mkdocs documentation /site # mypy .mypy_cache/ .dmypy.json dmypy.json # Pyre type checker .pyre/ # pytype static type analyzer .pytype/ # Cython debug symbols cython_debug/ # PyCharm # JetBrains specific template is maintained in a separate JetBrains.gitignore that can # be found at https://github.com/github/gitignore/blob/main/Global/JetBrains.gitignore # and can be added to the global gitignore or merged into this file. For a more nuclear # option (not recommended) you can uncomment the following to ignore the entire idea folder. .idea/
服务器安装git
yum install git -y进入项目克隆或拉取代码
基于用户名和密码,需要输入用户和密码
git clone https://gitee.com/wupeiqi/xxxxx.git
基于用户名和密码,直接集成用户和密码
git clone https://用户名:密码@gitee.com/wupeiqi/xxxxx.git
基于秘钥:
>>>ssh-keygen -t rsa
>>>cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
>>>拷贝公钥到代码仓库
>>>git clone [email protected]:wupeiqi/xxxxx.gitMysql
在CentOS安装Mysql
CentOS 安装 MySQL - 腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云 (tencent.com)
Python
安装Python3.9
yum install gcc -y安装Python3相关依赖
yum install zlib zlib-devel -y
yum install bzip2 bzip2-devel -y
yum install ncurses ncurses-devel -y
yum install readline readline-devel -y
yum install openssl openssl-devel -y
yum install xz lzma xz-devel -y
yum install sqlite sqlite-devel -y
yum install gdbm gdbm-devel -y
yum install tk tk-devel -y
yum install mysql-devel -y
yum install python-devel -y
yum install libffi-devel -ycd /data/
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.9.5/Python-3.9.5.tgz注意:如果没有wget,则先安装 yum install wget -y
tar -xvf Python-3.9.5.tgz进入目录并编译安装
cd Python-3.9.5
./configure
make all
make install配置豆瓣源(腾讯云服务器,默认腾讯源)
pip3.9 config set global.index-url https://pypi.douban.com/simple/虚拟环境
安装虚拟环境
pip3.9 install virtualenv创建虚拟环境目录并创建虚拟环境
mkdir /envs
virtualenv /envs/nb --python=python3.9安装项目依赖的pip包
source /envs/nb/bin/activate
pip install flask
pip install pymysql
pip install dbutilsuwsgi
激活虚拟环境并安装uwsgi
source /envs/nb/bin/activate
pip install uwsgi在本地项目根目录下创建 nb_uwsgi.ini
;添加配置选择
[uwsgi]
;配置和nginx连接的socket连接
socket=127.0.0.1:8997
;配置项目路径,项目的所在目录
chdir=/data/www/test/
;配置wsgi接口模块文件路径,也就是wsgi.py这个文件所在的目录名
wsgi-file=day01/wsgi.py
;虚拟环境地址
virtualenv = /envs/nb/
;#配置启动的进程数
processes=4
;#配置每个进程的线程数
threads=2
;#配置启动管理主进程
master=True
#配置存放主进程的进程号文件
pidfile=uwsgi.pid
;配置dump日志记录
daemonize=uwsgi.log`把本地文件上传至代码仓库
git push 仓库地址服务器更新代码
git pull 仓库地址nginx
利用nginx做反向代理和处理静态文件
yum install nginx -y修改nginx.conf配置文件: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name 127.0.0.1:80; #改为自己的域名,没域名修改为127.0.0.1:80
charset utf-8;
location / {
include uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8997; #端口要和uwsgi里配置的一样
uwsgi_param UWSGI_SCRIPT day01.wsgi; #wsgi.py所在的目录名+.wsgi
uwsgi_param UWSGI_CHDIR /data/www/test/; #项目路径
}
location /static/ {
alias /data/www/test/app01/static/; #静态资源路径
}
}
}启动
接下来就需要启动uwsgi和nginx
uwsgi
uwsgi --ini nb_uwsgi.ininginx
# 启动
systemctl start nginx
systemctl stop nginx
# 开机启动
systemctl enable nginx启动完之后就可以访问了
Shell脚本
但是每次启动停止都比较麻烦,可以写个脚本
reboot.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo -e "\033[34m--------------------wsgi process--------------------\033[0m"
ps -ef|grep nb_uwsgi.ini | grep -v grep
sleep 0.5
echo -e '\n--------------------going to close--------------------'
ps -ef |grep nb_uwsgi.ini | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9
sleep 0.5
echo -e '\n----------check if the kill action is correct----------'
/envs/nb/bin/uwsgi --ini nb_uwsgi.ini & >/dev/null
echo -e '\n\033[42;1m----------------------started...----------------------\033[0m'
sleep 1
ps -ef |grep nb_uwsgi.ini | grep -v grepstop.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo -e "\033[34m--------------------wsgi process--------------------\033[0m"
ps -ef |grep nb_uwsgi.ini | grep -v grep
sleep 0.5
echo -e '\n--------------------going to close--------------------'
ps -ef |grep nb_uwsgi.ini | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9
sleep 0.5执行需要给权限
chmod 755 reboot.sh
chmod 755 stop.sh