[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)
沉淀,沉淀,再沉淀.作者:chlorine
上一篇:string标准库成员函数和非成员函数(上)
目录
构造和析构的实现
string→c类型的字符串数组
operator[]类对象元素的访问
返回字符串的长度
迭代器进行遍历访问字符串
增
❗append() 与 push_back()
❗reserve()扩容
❗operator+=()复用
删
❗erase
插
❗insert()
找
❗find()
❗获得子串substr()
改变字符串长度
流插入<<流提取>>
❗clear
比较字符串大小
字符串赋值
❗operator()
❗swap()
总代码
string.h
test.cpp
从上一篇我们了解了string标准库成员函数和非成员函数的了解,这一章我们继续学习string标准库中剩余的成员函数和非成员函数。
这一次我们模拟类实现对字符串的增删查改,在此之前我们设定一个命名空间cl,不用std命名空间。我们可以在测试的时候与std命名空间进行对比,看是否出现问题。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace cl
{
class string
{
};
} 构造和析构的实现
 我们得开一个_size大小空间的字符串,进行初始化,可以选择在函数体内赋值或者初始化列表进行初始化,为了没有顺序的思考,我们就直接在函数体内初始化吧。
我们得开一个_size大小空间的字符串,进行初始化,可以选择在函数体内赋值或者初始化列表进行初始化,为了没有顺序的思考,我们就直接在函数体内初始化吧。
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace cl
{
class string
{
public:
string(const char* str=" ")
{
_size = strlen(str);
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
memcpy(_str, str, _size + 1);
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
} string→c类型的字符串数组
c_str()就是将C++的string转化为C的字符串数组,c_str()生成一个const char *指针,指向字符串的首地址。
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}因为我们还没写流插入和流提取的函数,所以我们必须调用c_str()成员函数,c_str()函数返回一个指向正规C字符串的指针常量,内容与本string串相同。这是为了与C语言兼容,在C语言中没有string类型,故必须通过string类对象的成员函数c_str()把string对象转换成C中的字符串样式。
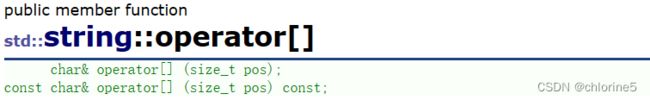
operator[]类对象元素的访问
char& operator[] (size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}返回字符串的长度
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}迭代器进行遍历访问字符串
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
大家可以通过调试深入了解一下即可。
现在我们进入类中字符串的增删查改函数的操作
增
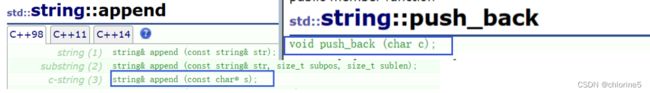
❗append() 与 push_back()
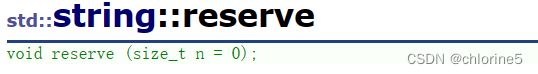
这里需要写个扩容函数reserve()
❗reserve()扩容
void reserve(size_t n = 0)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];//开辟一个n个空间
memcpy(tmp, _str, _size + 1);//将_str里面字符拷贝给tmp
delete[] _str;//销毁_str
_str = tmp;//然后将tmp字符串赋值给_str
_capacity = n;
}
}//增加字符
void push_back(char c)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
//2倍扩容
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);
}
_str[_size] = c;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
//增加字符串
void append(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
// 至少扩容到_size + len
reserve(_size + len);
}
memcpy(_str + _size, str, len + 1);
_size += len;
}❗operator+=()复用
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}删
❗erase
//删
void erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)//删除从pos开始的len长度
{
assert(pos <= _size);
//删的结束位置>=截至位置就直接给最后截至位置结束
if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';//直接给pos位置置'\0'
_size = pos;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
else
//删除的结束位置插
❗insert()
void insert(size_t pos, size_t n, char ch)//在pos位置插入n个字符
{
assert(pos <= _size);
//如果大于容量,就扩容
if (_size + n > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + n);
}
//end所在的地方在字符串位置
int end = _size;
while (end >= (int)pos)
{
_str[end + n] = _str[end];
--end;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_str[pos + i] = ch;
}
_size += n;
}找
❗find()
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0)//从pos位置找到字符ch
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == ch)
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0)//从pos位置找到字符串str
{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* ptr = strstr(_str + pos, str);
if (ptr)
{
return ptr - _str;
}
else
{
return npos;
}
}
❗获得子串substr()
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)//从pos位置开始的len个字符的字串
{
assert(pos < _size);
size_t n = len;
if (len == npos || pos + len > _size)
{
n = _size - pos;//子串长度
}
string tmp;//创建一个字串tmp
tmp.reserve(n);//字串的容量
for (size_t i = pos; i < pos + n; i++)
{
tmp += _str[i];//赋值
}
return tmp;
}我们还是用这段代码来测试。
这里涉及了拷贝构造。
string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
memcpy(_str, s._str, s._size + 1);
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}改变字符串长度
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0')
{
if (n < _size)
{
_size = n;
_str[n] = '\0';
}
else
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; i++)
{
_str[i] = c;
}
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
流插入<<流提取>>
我们在类外。
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
/*for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
out << s[i];
}*/
for (auto ch : s)
{
out << ch;
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch = in.get();
// 处理前缓冲区前面的空格或者换行
while (ch == ' ' && ch == '\n')
{
ch = in.get();//如果是空格和换行,直接跳过读下一个
}
//给定一个局部数组127.为了防止过多的开空间如果string对象的容量大
char buff[128];
int i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
//如果i=127那么就将buff[127]置'\0'
buff[127] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;//将i置0重新开始
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i != 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}❗clear
void clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}比较字符串大小
//bool operator<(const string& s)
//{
// size_t s1 = 0;
// size_t s2 = 0;
// //先判断字符对应的ascii码值是否小于
// while (s1 < _size && s2 < s._size)
// {
// if (_str[s1] < s._str[s2])
// {
// return true;
// }
// else if(_str[s1]>s._str[s2])
// {
// return false;
// }
// else
// {
// s1++;
// s2++;
// }
// }
// //结束循环之后说明有下面三种情况
//
"hello" "hello" false
"helloxx" "hello" false
"hello" "helloxx" true
// return _size < s._size;
//}
bool operator<(const string& s)const
{
//先判断字符的asscii值
int ret = memcmp(_str, s._str, _size < s._size ? _size : s._size);
//字符相等然后现在判断长度问题
//"hello" "hello" false
"helloxx" "hello" false
"hello" "helloxx" true
return ret == 0 ? _size < s._size : ret < 0;
}
bool operator==(const string& s)const
{
return _size == s._size
&& memcmp(_str, s._str, _size < s._size ? _size : s._size) == 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s)const
{
return (*this < s) || (*this == s);
}
bool operator>(const string& s)const
{
return !(*this <= s);
}
bool operator>=(const string& s)const
{
return (*this > s) || (*this == s);
}
bool operator!=(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}字符串赋值
❗operator()
传统写法:
// s1 = s3
//string& operator=(const string& s)
//{
// if (this != &s)
// {
// char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];//创建新的字符串对象
// memcpy(tmp, s._str, s._size+1);//然后拷贝
// delete[] _str;//销毁_str
// _str = tmp;//将tmp赋值给_str
// _size = s._size;//内置类型的值赋值给
// _capacity = s._capacity;
// }
// return *this;
//}
❗swap()
现代写法:
//俩个对象进行交换,要将俩个对象的内置类型成员变量都得交换
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
//string& operator=(const string& s)
//{
// if (*this != s)
// {
// string tmp(s);
// //this->swap(tmp);
// swap(tmp);
// }
// return *this;
//}
string& operator=(string& s)
{
//s1=s3
swap(s);
return *this;
}总代码
string.h
#pragma once
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace cl
{
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
//初始化//可以初始化列表
//也可以函数体内赋值(这里更推荐后者)
string(const char* str = "")
{
_size = strlen(str);
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
char& operator[] (size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
// s1 = s3
//string& operator=(const string& s)
//{
// if (this != &s)
// {
// char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];//创建新的字符串对象
// memcpy(tmp, s._str, s._size+1);//然后拷贝
// delete[] _str;//销毁_str
// _str = tmp;//将tmp赋值给_str
// _size = s._size;//内置类型的值赋值给
// _capacity = s._capacity;
// }
// return *this;
//}
//俩个对象进行交换,要将俩个对象的内置类型成员变量都得交换
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
//string& operator=(const string& s)
//{
// if (*this != s)
// {
// string tmp(s);
// //this->swap(tmp);
// swap(tmp);
// }
// return *this;
//}
string& operator=(string& s)
{
//s1=s3
swap(s);
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
void reserve(size_t n = 0)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];//开辟一个n个空间
memcpy(tmp, _str, _size + 1);//将_str拷贝给tmp
delete[] _str;//销毁_str
_str = tmp;//然后将tmp字符串赋值给_str
_capacity = n;
}
}
void push_back(char c)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
//2倍扩容
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);
}
_str[_size] = c;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void append(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
// 至少扩容到_size + len
reserve(_size + len);
}
memcpy(_str + _size, str, len + 1);
_size += len;
}
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void insert(size_t pos, size_t n, char ch)//在pos位置插入n个字符
{
assert(pos <= _size);
//如果大于容量,就扩容
if (_size + n > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + n);
}
//end所在的地方在字符串位置
int end = _size;
while (end >= (int)pos)
{
_str[end + n] = _str[end];
--end;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_str[pos + i] = ch;
}
_size += n;
}
void erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)//删除从pos开始的len长度
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';//直接给pos位置置'\0'
_size = pos;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
else
{
size_t end = pos + len;
while (end <= _size)
{
_str[pos++] = _str[end++];
}
_size -= len;
}
}
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0)//从pos位置找到字符ch
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == ch)
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0)
{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* ptr = strstr(_str + pos, str);
if (ptr)
{
return ptr - _str;
}
else
{
return npos;
}
}
string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
memcpy(_str, s._str, s._size + 1);
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)//从pos位置开始的len个字符的字串
{
assert(pos < _size);
size_t n = len;
if (len == npos || pos + len > _size)
{
n = _size - pos;//子串长度
}
string tmp;//创建一个字串tmp
tmp.reserve(n);//字串的容量
for (size_t i = pos; i < pos + n; i++)
{
tmp += _str[i];//赋值
}
return tmp;
}
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0')
{
if (n < _size)
{
_size = n;
_str[n] = '\0';
}
else
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; i++)
{
_str[i] = c;
}
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
//bool operator<(const string& s)
//{
// size_t s1 = 0;
// size_t s2 = 0;
// //先判断字符对应的ascii码值是否小于
// while (s1 < _size && s2 < s._size)
// {
// if (_str[s1] < s._str[s2])
// {
// return true;
// }
// else if(_str[s1]>s._str[s2])
// {
// return false;
// }
// else
// {
// s1++;
// s2++;
// }
// }
// //结束循环之后说明有下面三种情况
//
"hello" "hello" false
"helloxx" "hello" false
"hello" "helloxx" true
// return _size < s._size;
//}
bool operator<(const string& s)const
{
//先判断字符的asscii值
int ret = memcmp(_str, s._str, _size < s._size ? _size : s._size);
//字符相等然后现在判断长度问题
//"hello" "hello" false
"helloxx" "hello" false
"hello" "helloxx" true
return ret == 0 ? _size < s._size : ret < 0;
}
bool operator==(const string& s)const
{
return _size == s._size
&& memcmp(_str, s._str, _size < s._size ? _size : s._size) == 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s)const
{
return (*this < s) || (*this == s);
}
bool operator>(const string& s)const
{
return !(*this <= s);
}
bool operator>=(const string& s)const
{
return (*this > s) || (*this == s);
}
bool operator!=(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
const static size_t npos;
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
const size_t string::npos = -1;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
/*for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
out << s[i];
}*/
for (auto ch : s)
{
out << ch;
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch = in.get();
// 处理前缓冲区前面的空格或者换行
while (ch == ' ' && ch == '\n')
{
ch = in.get();//如果是空格和换行,直接跳过读下一个
}
//给定一个局部数组127.为了防止过多的开空间如果string对象的容量大
char buff[128];
int i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
//如果i=127那么就将buff[127]置'\0'
buff[127] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;//将i置0重新开始
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i != 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
};
test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"string.h"
#include
#include
//构造函数
void test1()
{
cl::string s1("chenle");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cl::string s2;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
}
//operator[]
void test2()
{
cl::string s1("chenle");
//调用const
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i]++;
}
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << endl;
//自动调用非const
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test3()
{
//cl::string s3("chenle");
cl::string s1("chenle");
cl::string::iterator it = s1.begin();
//auto it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
*it += 1;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//cl::string::const_iterator cit = s3.begin();
//auto cit = s3.begin();
//while (cit != s3.end())
//{
// //*cit += 1;
// cout << *cit << " ";
// ++cit;
//}
//cout << endl;
for (auto ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test4()
{
cl::string s4("chenle");
//s4.push_back(' ');
//s4.push_back('z');
//s4.append("hangyuanfei");
//cout << s4.c_str() << endl;
s4 += ' ';
s4 += 'z';
s4 += "hangyuanfei";
cout << s4.c_str() << endl;
}
void test5()
{
string s5("chenle");
//s5.insert(0, 5, 'z');
cout << s5.c_str() << endl;
s5.erase(2, 5);
cout << s5.c_str() << endl;
}
void test6()
{
cl::string url = "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/";
// 协议protocol 域名 资源名
size_t pos1 = url.find("://");
string protocol;
if (pos1 != cl::string::npos)
{
cl::string protocol = url.substr(0, pos1);
cout << protocol.c_str() << endl;
}
size_t pos2 = url.find('/', pos1 + 3);//从pos1+3位置开始找'/'
if (pos2 != string::npos)
{
cl::string domain = url.substr(pos1 + 3, pos2 - (pos1 + 3));//从pos1+3的位置,截取(pos2-(pos1+3))的长度,读到遇到第一个'/'位置
cl::string uri = url.substr(pos2 + 1);//直接从pos2+1位置后读到最后即可
cout << domain.c_str() << endl;
cout << uri.c_str() << endl;
}
}
void test7()
{
cl::string s7("chenle");
s7.resize(4);
cout << s7.c_str() << endl;
//cout << s7 << endl;
cl::string s8("chenle");
s8.resize(20, 'y');
cout << s8.c_str() << endl;
//cout << s8 << endl;
}
void test8()
{
cl::string s8("chenlelelelle");
s8 += '\0';
s8 += "zzzzzz";
cout << s8.c_str() << endl;
cout << s8 << endl;
cl::string copy(s8);
cout << s8 << endl;
cout << copy << endl;
s8 += "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
cout << s8 << endl;
}
void test9()
{
//string s1("bb");
//string s2("aaa");
//cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
cl::string s1("hello");
cl::string s2("hello");
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl << endl;
cl::string s3("hello");
cl::string s4("helloxxx");
cout << (s3 < s4) << endl;
cout << (s3 > s4) << endl;
cout << (s3 == s4) << endl << endl;
cl::string s5("helloxxx");
cl::string s6("hello");
cout << (s5 < s6) << endl;
cout << (s5 > s6) << endl;
cout << (s5 == s6) << endl << endl;
}
void test10()
{
cl::string s1("chenle");
cl::string s2(s1);//拷贝构造
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
cl::string s3("xxxxxxxxxxxxx");
s1 = s3;//赋值
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
}
void test11()
{
cl::string s1;
cin >> s1;
cout << s1;
}
int main()
{
//test1();
//test2();
//test3();
//test4();
//test5();
//test6();
//test7();
//test8();
//test9();
//test10();
test11();
return 0;
} 沉淀,沉淀,再沉淀。
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ee6361880a0a4e25bbb9b1eca5980b23.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/45930712ea89442198e79219c8870138.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/66fa4bdb476f437785cfb7f75befc78a.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/bb22a3264fab4057a30a3bbb96fd3687.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/73367a9c292a4a56a37713d2d731011d.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f4249fdd792f48008717b854ce4e536c.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e4452f255766485a8103e4bcde21fa15.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第8张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f7faf2392db44140875e24cc23b5afb8.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第9张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/4ff733322c3b414ca9b42885202a7881.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第10张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c0103501705343dab8baa6fde15f02e5.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第11张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/52b371b41f8f4d3f9ad28aff09b1780a.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第12张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/aaa95f87c5d2410993e16b04ed1e3088.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第13张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c2500fc5b9034bddb4b80da46ef2570a.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第14张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/64299ed8e47a44ec9c2c3648ba3b39aa.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第15张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ccf4e44904fb495c96da2ddbbcfef637.jpg)

![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第16张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fda9e3190b4e412a952ff562241586a9.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第17张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/a9e9cf2268de45f19accdf40427e318d.jpg)

![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第18张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fcab5a77556a4cc78f094dd4fe178b0c.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第19张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/572e0d571ba6402b94f2e73df5f88169.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第20张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/211476f7a16f438f8ee59b649f90f741.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第21张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/475bedcf19a7413ab12fc5e4e6c2ff4f.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第22张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7ebe8a7d1fd9433ba99862b358091982.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第23张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/624f5bacc2834487b516ae168ea1a434.jpg)
![[c++]—string类___深度学习string标准库底层实现(超详细)_第24张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7fafbae83401480f9c068da9dbc48c9f.jpg)
