C++初阶-list类的模拟实现
list类的模拟实现
- 一、基本框架
-
- 1.1 节点类
- 1.2 迭代器类
- 1.3 list类
- 二、构造函数和析构函数
-
- 2.1 构造函数
- 2.2 析构函数
- 三、operator=的重载和拷贝构造
-
- 3.1 operator=的重载
- 3.2 拷贝构造
- 四、迭代器的实现
-
- 4.1 迭代器类中的各种操作
- 4.1 list类中的迭代器
- 五、list的增容和删除
-
- 5.1 尾插尾删
- 5.2 头插头删
- 5.3 任意位置的插入和删除
- 六、完整代码
-
- 6.1 list.h
- 6.2 test.cpp
一、基本框架
list的底层和vector和string不同,实现也有所差别,特别是在迭代器的设计上,本文讲介绍list的简单模拟实现。
list底层是一个带头双向循环链表,在节点上变化不大。
list整体由三个类组成
1.节点类(封装一个节点)
2.迭代器类
3.list类
1.1 节点类
list节点类是一个模板类以适合于任何类型的ist对象,封装了一个节点需要的基本成员
成员变量
前驱指针 _prev
后继指针 _next
数据存储_data
成员函数
只有一个构造函数,用于初始化节点data数据和置空指针,构造函数的x参数是缺省参数,适应不同场景。
注意节点类不需要拷贝构造和析构函数,对于节点的拷贝构造在list中只需要浅拷贝即可,节点的释放也不在节点类中进行!
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
T _data;
};
1.2 迭代器类
迭代器类也是封装节点,但是迭代器类不会构造节点,只会利用现有节点构造一个迭代器,在迭代器内部通过各种运算符重载对节点的状态做修改!
其次,会涉及返回节点指针或数据data的引用,所以需要在构造对象时将list数据类型的指针和引用类型传给迭代器对象!
迭代器在不访问data的情况下返回的都是迭代器,将声明本迭代器类型self,在函数操作完成时返回self(迭代器)即可!
//1、迭代器要么就是原生指针
//2、迭代器要么就是自定义类型对原生指针的封装,模拟指针的行为
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
typedef __list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;
node* _node;
};
迭代器对象不会凭空创造节点,只会利用现有的节点(迭代器节点类型与list节点类型相同),所以不需要拷贝构造和析构函数,浅拷贝足以!
1.3 list类
list类中包含一个头节点和迭代器以及各种操作函数!
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*>const_iterator;
private:
node* _head;
};
二、构造函数和析构函数
2.1 构造函数
节点类的构造
将节点进行初始化
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
T _data;
list_node(const T& x=T())
:_next(nullptr)
,_prev(nullptr)
,_data(x)
{}
};
迭代器的构造
成员变量只有结点node,对结点进行初始化
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
typedef __list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;
node* _node;
__list_iterator(node* n)
:_node(n)
{}
};
list类的构造
因为是带头的链表,所以在实例化时必须事先申请一个头结点,所以所有的构造函数都会在操作前申请一个头结点,为了避免代码的冗余,我们将头节点的创建封装为一个函数,在构造函数初始化时调用创建头结点。
当我们需要构造空链表时,直接调用empty_init();函数即可
迭代器区间构造也是调用push_back进行尾插
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;
void empty_init()
{
_head = new node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
list()
{
/*_head = new node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;*/
empty_init();
}
template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
empty_init();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
private:
node* _head;
};
2.2 析构函数
析构函数需要释放所有结点以及头结点,在释放前需要判断当前链表是否为空,如果为空直接置空头节点
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
//it = erase(it);
erase(it++);
}
}
三、operator=的重载和拷贝构造
3.1 operator=的重载
对于赋值重载,与拷贝构造相似,但是赋值重载在传递参数时使用传值传参,这样就自动帮我们构造了一个临时对象,我们只需要swap一下临时对象的头节点即可,将我们现在的链表交给临时对象销毁,这样就完成了赋值。有时可能需要连等,所以需要返回对象的引用。
//lt1=lt3
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
3.2 拷贝构造
拷贝构造最好采用现代写法,构造临时对象使用swap交换,在此之前,因为是构造函数所以需要创造头结点,调用empty_init()函数,再进行拷贝
//lt2(lt1) 拷贝构造传统写法
/*list(const list& lt)
{
empty_init();
for (auto e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}*/
void swap(list<T>& tmp)
{
std::swap(_head, tmp._head);
}
//现代写法
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();
list<T> tmp(lt.begin(), lt.end());
swap(tmp);
}
四、迭代器的实现
4.1 迭代器类中的各种操作
const类型的对象只能使用const类型的迭代器,那么const类型的迭代器如何实现呢、需要再重新封装吗,像上面那样。可以,但是没有必要,因为那样代码的冗余度就会很高,我们只需要给模板增加两个参数就可以了。即template

//1、迭代器要么就是原生指针
//2、迭代器要么就是自定义类型对原生指针的封装,模拟指针的行为
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
typedef __list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;
node* _node;
__list_iterator(node* n)
:_node(n)
{}
Ref& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->() //it->_a1 it->->_a1 本来应该是两个->,但是为了增强可读性,省略了一个->
{
return &_node->_data;
}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};
4.1 list类中的迭代器
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;
//typedef __list_const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
//iterator it(_head->_next);
//return it;
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
//iterator it(_head->_next);
//return it;
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
//iterator it(_head);
//return it;
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
//iterator it(_head);
//return it;
return const_iterator(_head);
}
五、list的增容和删除
5.1 尾插尾删
尾插结点需要修改_head和tail的连接关系,链入新节点
1.根据参数创建一个新节点new_node
2.记录原尾结点tail
3.修改_head和tail之间的链接关系,再其中链入new_node

直接复用insert即可
void push_back(const T& x=T())
{
/*node* tail = _head->_prev;
node* new_node = new node(x);
tail->_next = new_node;
new_node->_prev = tail;
new_node->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = new_node;*/
insert(end(), x);
}
直接复用erase即可
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
5.2 头插头删
直接复用insert即可
void push_front(const T& x = T())
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
直接复用erase即可
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
5.3 任意位置的插入和删除
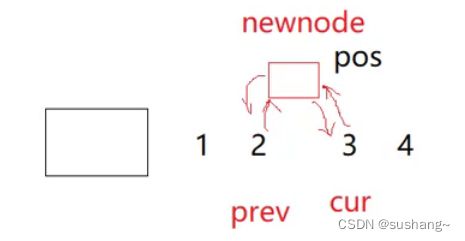
任意位置插入是在pos迭代器位置前插入一个结点,并返回这个结点的迭代器!
1.检查pos迭代器中结点但是否正常
2.获取pos位置的当前结点pos._node,获取pos位置的前驱结点cur->_prev
3.根据参数申请一个新节点new_node
4.将新节点new_node链入pos结点与pos前驱结点之间
5.链入成功后返回新插入结点的迭代器
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
assert(pos._node);
node* cur = pos._node;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
node* new_node = new node(x);
prev->_next = new_node;
new_node->_prev = prev;
new_node->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = new_node;
return iterator(new_node);
}
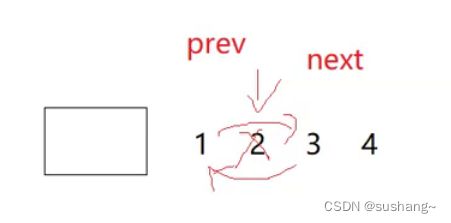
任意位置删除时删除pos迭代器位置的结点,并返回删除结点的下一个结点的迭代器
1.检查链表是否为空且pos迭代器中结点是否正常
2.获取pos结点的前驱结点pos._node->_prev
3.获取pos结点的后继结点pos._node->_next
4.链接pos._node->_prev和pos._node->_next结点,剥离pos结点
5.删除pos结点
6.返回pos._node->_next结点的迭代器(即pos的下一个结点的迭代器)
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
node* next = pos._node->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete pos._node;
return iterator(next);
}
六、完整代码
6.1 list.h
#pragma once
#include
struct __list_const_iterator
{
typedef list_node node;
typedef __list_const_iterator self;
node* _node;
__list_const_iterator(node* n)
:_node(n)
{}
const T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};*/
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;
//typedef __list_const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
//iterator it(_head->_next);
//return it;
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
//iterator it(_head->_next);
//return it;
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
//iterator it(_head);
//return it;
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
//iterator it(_head);
//return it;
return const_iterator(_head);
}
void empty_init()
{
_head = new node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
list()
{
/*_head = new node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;*/
empty_init();
}
template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
empty_init();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
//lt2(lt1) 拷贝构造传统写法
/*list(const list& lt)
{
empty_init();
for (auto e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}*/
void swap(list<T>& tmp)
{
std::swap(_head, tmp._head);
}
//现代写法
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();
list<T> tmp(lt.begin(), lt.end());
swap(tmp);
}
//lt1=lt3
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
//it = erase(it);
erase(it++);
}
}
void push_back(const T& x=T())
{
/*node* tail = _head->_prev;
node* new_node = new node(x);
tail->_next = new_node;
new_node->_prev = tail;
new_node->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = new_node;*/
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x = T())
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
void insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
node* cur = pos._node;
node* prev = cur->_prev;
node* new_node = new node(x);
prev->_next = new_node;
new_node->_prev = prev;
new_node->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = new_node;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
node* next = pos._node->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete pos._node;
return iterator(next);
}
private:
node* _head;
};
void print_list(const list<int>& lt)
{
list<int>::const_iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
//(*it) *= 2;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list1()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
print_list(lt);
}
struct AA
{
int _a1;
int _a2;
AA(int a1=0,int a2=0)
:_a1(a1)
,_a2(a2)
{}
};
void test_list2()
{
list<AA> lt;
lt.push_back(AA(1, 1));
lt.push_back(AA(2, 2));
lt.push_back(AA(3, 3));
//AA* ptr
list<AA>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
//cout << (*it)._a1 << (*it)._a2 << endl;
cout << it->_a1 << it->_a2 << endl;
//cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a1 << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list3()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
auto pos = lt.begin();
++pos;
lt.insert(pos, 20);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.push_back(100);
lt.push_front(1000);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.pop_back();
lt.pop_front();
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list4()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.clear();
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.push_back(10);
lt.push_back(20);
lt.push_back(30);
lt.push_back(40);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list5()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int> lt2(lt);
for (auto e : lt2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int> lt3;
lt3.push_back(10);
lt3.push_back(20);
lt3.push_back(30);
lt3.push_back(40);
lt3.push_back(50);
for (auto e : lt3)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt = lt3;
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
6.2 test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include
using namespace std;
#include "list.h"
int main()
{
//zl::test_list1();
//zl::test_list2();
//zl::test_list3();
//zl::test_list4();
zl::test_list5();
//std::vector::iterator it;
//cout << typeid(it).name() << endl;
return 0;
}