【Spring】Spring中的事务
文章目录
- 1. Spring事务简介
- 2. Spring事务的案例
-
- 案例代码
-
- 代码目录结构
- 数据库
- pom.xml
- Resource/jdbc.properties
- config/SpringConfig.java
- config/JdbcConfig.java
- config/MyBatisConfig.java
- dao/AccountDao.java
- service/AccountService.java
- service/impl/AccountServiceImpl.java
- 测试方法
- 问题分析
- 事务管理三步
-
- 第一步:在业务层接口上加上注解@Transactional
- 第二步:在JdbcConfig.java中注册事务管理器
- 第三步:在SpringConfig.java上加上开启事务管理的注解@EnableTransactionManagement
- 3. Spring事务角色
- 4. Spring事务属性
-
- 事务配置
- 案例:转账业务追加日志
-
- 案例代码
-
- 代码结构
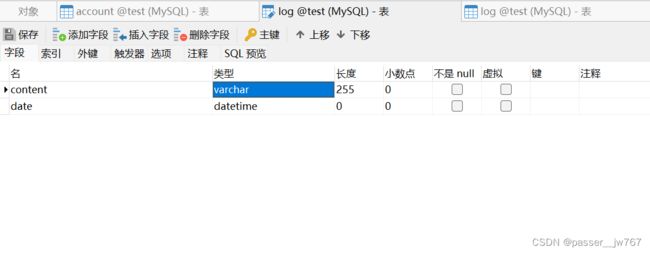
- 数据库表
- dao/LogDao.java
- service/LogService.java
- service/LogServiceImpl.java
- 修改service/impl/AccountServiceImpl.java如下
- 改进
- 事务传播行为
1. Spring事务简介
事务作用: 在数据层保障一系列的数据库操作同成功、同失败
Spring事务作用: 在数据层或业务层保障一系列的数据库操作同成功、同失败
Spring为事务提供的接口和实现类:
// 接口
public interface PlatformTransactionManager{
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
// 实现类
public class DataSourceTransactionManager{
...
}
2. Spring事务的案例
需求: 实现两个账户间的转账操作
需求微缩: A账户减钱,B账户加钱
分析:

案例代码
代码目录结构
数据库
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>3.1.5version>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>com.examplegroupId>
<artifactId>project5artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>project5name>
<description>project5description>
<properties>
<java.version>17java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>6.0.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId>
<version>6.0.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-jartifactId>
<version>8.0.33version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatisartifactId>
<version>3.5.11version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-springartifactId>
<version>3.0.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.2.13version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.13.2version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-testartifactId>
<version>5.3.25version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectjgroupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaverartifactId>
<version>1.9.5version>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
Resource/jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456
config/SpringConfig.java
package com.example.project5.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@ComponentScan("com.example.project5")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class, MyBatisConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
config/JdbcConfig.java
package com.example.project5.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUsername(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
ds.setUrl(url);
return ds;
}
}
config/MyBatisConfig.java
package com.example.project5.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.example.project5.domain");
ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource);
return ssfb;
}
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer(){
MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("com.example.project5.dao");
return mapperScannerConfigurer;
}
}
dao/AccountDao.java
package com.example.project5.dao;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface AccountDao {
@Update("update account set money = money + #{money} where username = #{name}")
void addMoney(@Param("name") String username, @Param("money") Double money);
@Update("update account set money = money - #{money} where username = #{name}")
void outMoney(@Param("name") String username, @Param("money") Double money);
}
service/AccountService.java
package com.example.project5.service;
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账操作
* @param out 转出方
* @param in 转入方
* @param money 金额
*/
public void transfer(String out, String in, double money);
}
service/impl/AccountServiceImpl.java
package com.example.project5.service.impl;
import com.example.project5.dao.AccountDao;
import com.example.project5.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void transfer(String out, String in, double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(out, money);
accountDao.addMoney(in, money);
}
}
测试方法
package com.example.project5;
import com.example.project5.config.SpringConfig;
import com.example.project5.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class Project5ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void testTransfer() {
accountService.transfer("aaa", "bbb", 20);
}
}
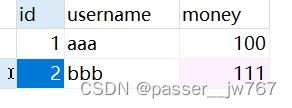
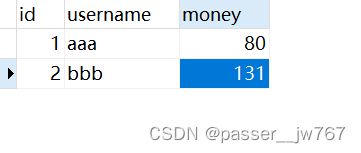
执行测试代码后,测试代码不会产生任何输出,但数据库中aaa的金额会由100变成80,bbb的金额会由111变成131:

问题分析
假如在AccountServiceImpl中手动制造一个错误:
package com.example.project5.service.impl;
import com.example.project5.dao.AccountDao;
import com.example.project5.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void transfer(String out, String in, double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(out, money);
int a = 1/0;
accountDao.addMoney(in, money);
}
}
这时候,程序在执行完outMoney方法,也就是aaa转出了20之后就不会继续执行了,这20并没有转入到bbb的账户之中,这就是事务的不一致性。接着上面的aaa金额为80,bbb的金额为131执行这个会报错的代码,结果是:
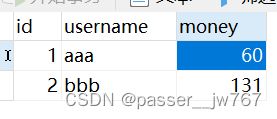
对运行的结果简单进行分析:

我们需要进行事务管理,使得数据层中的数据同加同减,而不是分开操作
事务管理三步
第一步:在业务层接口上加上注解@Transactional
package com.example.project5.service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账操作
* @param out 转出方
* @param in 转入方
* @param money 金额
*/
@Transactional
public void transfer(String out, String in, double money);
}
第二步:在JdbcConfig.java中注册事务管理器
package com.example.project5.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.lang.management.PlatformLoggingMXBean;
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUsername(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
ds.setUrl(url);
return ds;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}
}
第三步:在SpringConfig.java上加上开启事务管理的注解@EnableTransactionManagement
package com.example.project5.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@ComponentScan("com.example.project5")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class, MyBatisConfig.class})
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringConfig {
}
启用事务管理后,保持刚才会报错的AccountServiceImpl.java的代码,恢复aaa金额为80,bbb金额为131,并再次进行测试,此时数据库中的内容不会发生任何改变:
3. Spring事务角色
在事务没有开启的时候:

outMoney和inMoney分别对应一个事务,我们手动写的异常是写在事务T1和事务T2之间的,则事务T1执行完毕以后发生了异常,所以事务T2不再执行
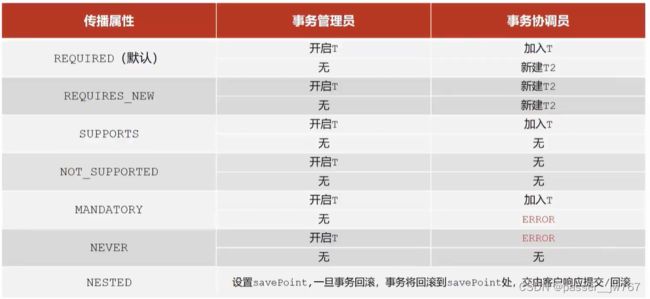
为了将两个事务统一起来,统一执行,或者统一不执行,我们在transfer方法上加了注解@Transactional,此时transfer本身是一个事务,我们将outMoney和inMoney都加入到这个事务中来:
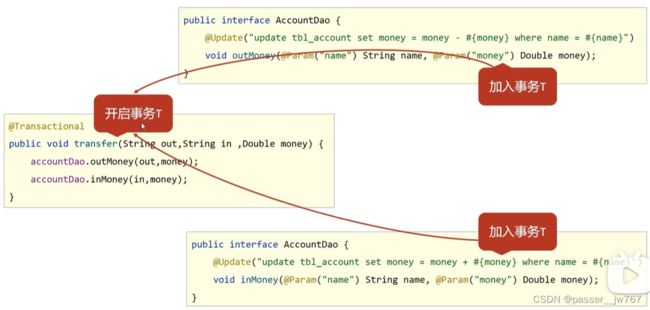
此时我们将transfer方法称为事务管理员,outMoney和inMoney称为事务协调员,具体定义如下:

4. Spring事务属性
事务配置
在@Transactional中还有很多属性
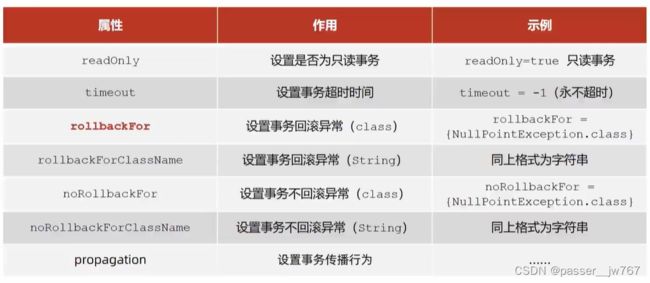
这里需要说明的是rollbackFor,默认的事务回滚,在我们没有定义rollbackFor的时候,只会在程序中出现运行时异常时候进行回滚,比如我们刚才手动指定的1/0就属于一个运行时抛出异常,假如修改这个异常如下:
package com.example.project5.service.impl;
import com.example.project5.dao.AccountDao;
import com.example.project5.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.io.IOException;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void transfer(String out, String in, double money) throws IOException {
accountDao.outMoney(out, money);
if(true) throw new IOException();
accountDao.addMoney(in, money);
}
}
再执行测试代码,就会发现数据库中的内容会从(aaa:80,bbb:131)->(aaa:60,bbb:131)
再次印证:没有定义rollbackFor的时候,只会在程序中出现运行时异常时候进行回滚
那么我们定义一下rollbackFor属性,如下:
package com.example.project5.service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账操作
* @param out 转出方
* @param in 转入方
* @param money 金额
*/
@Transactional(rollbackFor = {IOException.class})
public void transfer(String out, String in, double money) throws IOException;
}
再执行测试代码,就会发现数据库中的内容(aaa:60,bbb:131)->(aaa:60,bbb:131),没有发生改变,所以我们需要通过rollbackFor来指定一些非运行时异常,在定义rollbackFor以后,程序在遇到运行时异常仍会回滚。
案例:转账业务追加日志
案例代码
在上述案例代码中加上如下内容:
代码结构
数据库表
dao/LogDao.java
package com.example.project5.dao;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.Date;
@Repository
public interface LogDao {
@Insert("insert into log(content, date) VALUES(#{content}, #{date})")
void insertLog(@Param("content") String content, @Param("date") Date date);
}
service/LogService.java
注意,该方法上也要加上事务注解
package com.example.project5.service;
import java.util.Date;
public interface LogService {
@Transactional
void insertLog(String content, Date date);
}
service/LogServiceImpl.java
package com.example.project5.service.impl;
import com.example.project5.dao.LogDao;
import com.example.project5.service.LogService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Date;
@Service
public class LogServiceImpl implements LogService {
@Autowired
LogDao logDao;
@Override
public void insertLog(String content, Date date) {
logDao.insertLog(content, date);
}
}
修改service/impl/AccountServiceImpl.java如下
package com.example.project5.service.impl;
import com.example.project5.dao.AccountDao;
import com.example.project5.service.AccountService;
import com.example.project5.service.LogService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Date;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
AccountDao accountDao;
@Autowired
LogService logService;
@Override
public void transfer(String out, String in, double money) throws IOException {
try{
accountDao.outMoney(out, money);
accountDao.addMoney(in, money);
} finally {
logService.insertLog(out + "向" + in + "转账" + money + "元", new Date());
}
}
}
当捕捉到异常时执行日志记录。
将数据库中的金额恢复为:aaa->100,bbb->111,并执行测试代码,得到account表和log表的结果:

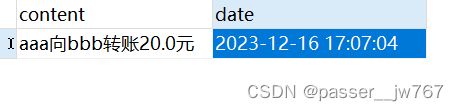
正常执行的时候,会修改数据库中的金额、向日志记录中添加日志
假设我们在AccountServiceImpl的try中加上:
accountDao.outMoney(out, money);
int a = 1/0;
accountDao.addMoney(in, money);
我们期望的结果是:不修改数据库中的金额、向日志记录中添加日志,使用修改后的代码再执行测试方法,得到结果是account表和log表中的内容都没有发生任何变化,所以我们归纳总结出存在的问题:
改进
我们需要定义事务的传播属性propagation,在LogService.java下重新写注解,改为:
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
此时,再次运行上面的代码,结果为:
account表中的内容不变,log表中新添了日志:
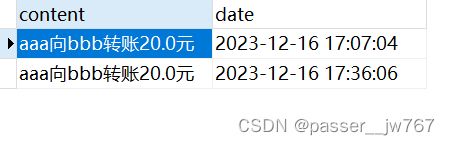
我认为这样的改进可以理解为,使用默认的propagation时,事务协调员都被添加到事务管理员的事务中,从而统一提交或统一回滚:

当我们在LogService上写明了事务的传播行为为Requires_New后,即使原有了事务,我们还是会为这个service实例开启一个新事务,如下,这样就不是统一受到事务t的控制了: