binservice之binder机制流程分析
binder机制
系统中很多机制都涉及到binder机制,所以对binder机制有一个大致的了解是必不可少的。
本文从bindService方法出发
流程分析为bindService->connection的onServiceConnected触发来了解一下binder机制
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
首先了解一下一些基本的概念
进程与进程之间是相互隔离的,每个进程都有自己的用户空间。
他们通过内核空间进行数据交互。
binder通信机制
通过内存映射将进程2的数据和内核空间的一块区域的数据进行映射
当进程1通过copy_from_user将数据拷贝到内核空间的时候,由于内核空间的数据和进程2用户空间的数据存在映射关系,直接就能刷新
binder机制通过aidl通信
aidl分为proxy,和stub。
客户端获取aidl实例(proxy),proxy用来发送数据,
服务端实现aidl实例(stub), stub用来接收数据
_data //发送到服务端的数据
_reply // 服务端返回的数据
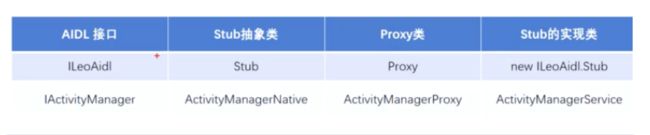
系统binder通信的流程涉及到的stub和proxy为下所示,后面的代码分析中会解析这个图中的各类各自负责的责任
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
mbase是Context,context的默认实现类为ContextImpl
所以打开ContextImpl中的bindService
//ContextImpl
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, Process.myUserHandle());
}
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
}
这里有几个地方要注意
IServiceConnection sd;
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
打开getServiceDispatcher
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
if (sd == null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
}
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
//直接看最后一行sd.getIServiceConnection();
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
return mIServiceConnection;
}
//而serviceconnection定义如下
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
所以这里得出结论
IServiceConnection sd = InnerConnection
接下来回到上面继续看bindServiceCommon
看另外的一个关键点
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
首先打开ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().
static public IActivityManager getDefault() {
return gDefault.get();
}
private static final Singleton gDefault = new Singleton() {
protected IActivityManager create() {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("activity");
IActivityManager am = asInterface(b);
return am;
}
};
public abstract class ActivityManagerNative extends Binder implements IActivityManager
{
static public IActivityManager asInterface(IBinder obj) {
return new ActivityManagerProxy(obj);
}
ActivityManagerProxy为proxy
同时ActivityManagerNative继承binder是属于stub类
而IActivityManager是一个接口属于aidl接口
ActivityManagerNative是一个抽象类它的子类是ActivityManagerService也就是stub的实现类
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
接下来继续看ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService这行代码
其实也就是触发的ActivityManagerProxy的bindService
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection,
int flags, String callingPackage, int userId) throws RemoteException {
mRemote.transact(BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
return res;
}
mRemote发送了一个BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION到stub类中
接下来到ActivityManagerNative的BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION中
case BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION: {
IServiceConnection conn = IServiceConnection.Stub.asInterface(b);
int res = bindService(app, token, service, resolvedType, conn, fl,
callingPackage, userId);
return true;
}
继续触发了bindService,也就是stub的实现类ActivityManagerService的
bindService
//ActivityManagerService
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
// 继续跟进bindServiceLocked位于ActiveServices类中
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//uid校验 binder机制特点
if (callerApp.info.uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
}
//如果service是BIND_AUTO_CREATE就会进入bringUpServiceLocked
//这里是创建service
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
//如果service创建了就会走下面
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
try {
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
return 1;
}
先看这一行关键代码
//注意这里是service创建了的情况下没创建的话走else里面的requestServiceBindingLocked方法
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder);
c.conn点进去发现final IServiceConnection conn;
conn是IServiceConnection
而在最开始我们已经得出结论
IServiceConnection=IServiceConnection sd = InnerConnection
也就是说这里触发的connect方法是位于InnerConnection中的connect方法
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
触发sd.connected方法
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
// If there is a new service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}
在doConnected方法的最后可以看到onServiceDisconnected和onServiceConnected
也就是说到这里binderservice到onServiceConnected的流程就结束了
有兴趣的可以继续往下看
分析bindservice是怎么触发onBind
和onRebind
分为四种情况

首先看第二种情况
关键代码如下
bringUpServiceLocked
//如果service是BIND_AUTO_CREATE就会进入bringUpServiceLocked
//这里是创建service
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
//第二种情况如果app!=null创建service流程
private final String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
}
}
//第一种情况创建进程startProcessLocked就是Zygote进程fork的过程就不深入分析了
if (app == null) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
}
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
}
app.thread是activitythread里面的applicationthread
app.thread点进去之后是IApplicationThread
public interface IApplicationThread extends IInterface {
}
IApplicationThread继承IInterface,这里又是一次binder机制
IApplicationThread是IInterface接口
ApplicationThreadNative是stub
ApplicationThreadProxy是proxy
那么scheduleCreateService其实触发的就是ApplicationThreadNative中的
scheduleCreateService方法也就是触发ApplicationThreadNative的实现类
ApplicationThread中的scheduleCreateService方法
ApplicationThread位于activitythread中
那么applicationthread中的scheduleCreateService如下
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
handler发送了一个事件CREATE_SERVICE
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceCreate");
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
}
}
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
service.onCreate();
通过反射创建了service然后调用oncreate方法
接下来看第三第四种情况
在bindServiceLocked中
//如果service创建了就会走下面
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
try {
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
return 1;
}
requestServiceBindingLocked方法
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
}
直接看application的scheduleBindService
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
}
}
到这里就能看到onBind和onRebind了
在service绑定了之后会触发
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
直接定位到activitymanagerservice中的publishService
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
然后看publishServiceLocked位于ActiveServices下面
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
}
最终又调用了这个方法,到这里就分析完了
总结一波
binder机制主要设计到4个类
一个aidl接口
一个proxy类
一个stub类
stub是抽象类有它自己的实现类
比如IActivityManager是aidl接口
ActivityManagerNative是stub抽象类
ActivityManagerProxy是proxy类
ActivityManagerService是stub的实现类
比如IApplicationThread是aidl接口
ApplicationThreadNative是stub抽象类
ApplicationThreadProxy是proxy类
位于ActivityThread中的ApplicationThread是stub的实现类
一般是先触发proxy方法,proxy触发stub抽想类的方法,他们都继承aidl接口触发stub方法后,找stub实现类对应的方法