【三维几何学习】使用VTK对网格输入特征进行可视化
使用VTK对网格输入特征进行可视化
- 引言
- 一、全部代码
- 二、可视化
引言

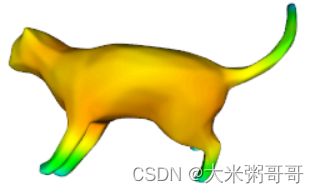
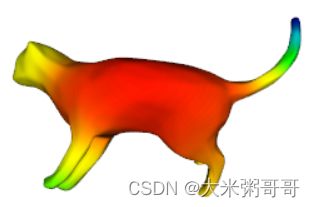
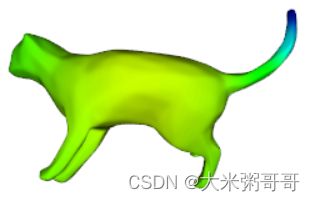
使用python调用VTK库对网格的输入特征进行可视化,方便后续实验与分析
上图可视化的输入特征是热核特征HKS的第一个通道,也可对其他输入进行可视化- 数据集可参考1:三角网格(Triangular Mesh)分类数据集
一、全部代码
compute_hks_autoscale函数参考自2:DiffusionNet
VTK可视化代码参考3:VTK使用颜色映射标量数据
import numpy as np
import potpourri3d as pp3d
import scipy
import scipy.sparse.linalg
import vtkmodules.all as vtk
import torch
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
class TriMesh:
def __init__(self, file):
# 属性
self.file = file # 文件完整路径
self.filename = None # 文件名称
self.vs = [] # 坐标索引
self.faces = [] # 顶点索引
self.features = None # 特征
self.vs, self.faces = pp3d.read_mesh(file)
self.faces_num = len(self.faces)
def compute_hks_autoscale(self, eig_k, count=16):
eps = 1e-8
L = pp3d.cotan_laplacian(self.vs, self.faces, denom_eps=1e-10)
massvec_np = pp3d.vertex_areas(self.vs, self.faces)
massvec_np += eps * np.mean(massvec_np)
L_eigsh = (L + scipy.sparse.identity(L.shape[0]) * eps).tocsc()
massvec_eigsh = massvec_np
Mmat = scipy.sparse.diags(massvec_eigsh)
eigs_sigma = eps
failcount = 0
while True:
try:
# We would be happy here to lower tol or maxiter since we don't need these to be super precise, but for some reason those parameters seem to have no effect
evals_np, evecs_np = scipy.sparse.linalg.eigsh(L_eigsh, k=eig_k, M=Mmat, sigma=eigs_sigma)
# Clip off any eigenvalues that end up slightly negative due to numerical weirdness
evals_np = np.clip(evals_np, a_min=0., a_max=float('inf'))
break
except Exception as e:
print(e)
if failcount > 3:
raise ValueError("failed to compute eigendecomp")
failcount += 1
print("--- decomp failed; adding eps ===> count: " + str(failcount))
L_eigsh = L_eigsh + scipy.sparse.identity(L.shape[0]) * (eps * 10 ** failcount)
evals = torch.from_numpy(evals_np)
evecs = torch.from_numpy(evecs_np)
# these scales roughly approximate those suggested in the hks paper
scales = torch.logspace(-2, 0., steps=count, device=evals.device, dtype=evals.dtype)
return self.compute_hks(evals, evecs, scales)
def compute_hks(self, evals, evecs, scales):
# expand batch
if len(evals.shape) == 1:
expand_batch = True
evals = evals.unsqueeze(0)
evecs = evecs.unsqueeze(0)
scales = scales.unsqueeze(0)
else:
expand_batch = False
# TODO could be a matmul
power_coefs = torch.exp(-evals.unsqueeze(1) * scales.unsqueeze(-1)).unsqueeze(1) # (B,1,S,K)
terms = power_coefs * (evecs * evecs).unsqueeze(2) # (B,V,S,K)
out = torch.sum(terms, dim=-1) # (B,V,S)
if expand_batch:
return out.squeeze(0)
else:
return out
def show_point_color(mesh: TriMesh, seg=[], Subdivision=False):
# 1. 添加数据
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
pColor = vtk.vtkFloatArray()
for v in mesh.vs:
points.InsertNextPoint(v)
pColor.InsertNextValue(v[0])
if len(seg) > 0:
pColor = vtk.vtkFloatArray()
for s in seg:
pColor.InsertNextValue(s)
polys = vtk.vtkCellArray()
for f in mesh.faces:
polys.InsertNextCell(len(f), f)
# 2. 创建PolyData
cube = vtk.vtkPolyData()
cube.SetPoints(points)
cube.SetPolys(polys)
cube.GetPointData().SetScalars(pColor)
# 2.5细分
if Subdivision:
l = vtk.vtkLinearSubdivisionFilter() # 先linear
l.SetInputData(cube)
l.SetNumberOfSubdivisions(1)
l.Update()
loop = vtk.vtkLoopSubdivisionFilter() # 后loop
loop.SetInputConnection(l.GetOutputPort())
loop.SetNumberOfSubdivisions(5)
loop.Update()
# lut = vtk.vtkLookupTable()
# lut.SetHueRange(0.125, 0.666) # 映射的颜色变换参数(自己调颜色)
mapper = vtk.vtkPolyDataMapper()
mapper.ScalarVisibilityOn()
mapper.SetColorModeToMapScalars()
# mapper.SetLookupTable(lut)
mapper.SetScalarRange(0, 1)
if Subdivision:
mapper.SetInputConnection(loop.GetOutputPort())
else:
mapper.SetInputData(cube)
# 3.创建Actor
actor = vtk.vtkActor()
actor.SetMapper(mapper)
# actor.GetProperty().SetEdgeColor(0, 0, 0)
# actor.GetProperty().SetEdgeVisibility(1) # 显示边
# 3.5 加入colormap
scalarBar = vtk.vtkScalarBarActor() # 设置color_bar
scalarBar.SetLookupTable(mapper.GetLookupTable())
scalarBar.SetTitle("")
scalarBar.SetNumberOfLabels(10) # 设置要显示的刻度标签数。自己设定色带的位置
scalarBar.SetMaximumNumberOfColors(10)# # 设置标题和条形之间的边距
# scalarBar.SetVerticalTitleSeparation(10)
# # 设置标题颜色
scalarBar.DrawTickLabelsOn()
scalarBar.GetTitleTextProperty().SetColor(0, 0, 0)
scalarBar.GetLabelTextProperty().SetColor(0, 0, 0)
# 4.创建Renderer
renderer = vtk.vtkRenderer()
renderer.SetBackground(1, 1, 1) # 背景白色
renderer.AddActor(actor) # 将actor加入
renderer.ResetCamera() # 调整显示
renderer.AddActor2D(scalarBar)
# 5.渲染窗口
renWin = vtk.vtkRenderWindow()
renWin.AddRenderer(renderer)
renWin.Render()
# 6.交互
renWinInteractor = vtk.vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
renWinInteractor.SetRenderWindow(renWin)
renWinInteractor.SetInteractorStyle(vtk.vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera())
renWinInteractor.Start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 读取网格
mesh = TriMesh('../../../datasets/shrec_10/alien/train/T5.obj') # 1 13 15
# 计算特征
face_hks = mesh.compute_hks_autoscale(eig_k=4).numpy()
# 某一通道的归一化
face_hks = face_hks[:, 0] / np.max(face_hks[:, 0])
# 可视化
show_point_color(mesh, face_hks, False)
二、可视化
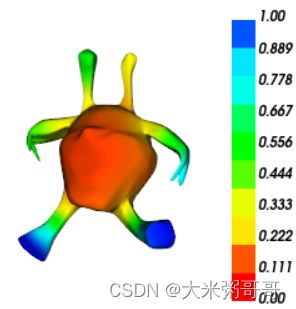
- eig_k=1毫无意义,就可视化而言eig_k=4效果是最好的
- 特征通道取前几个即可,最后的几个维度对于形状特征区分度较低
- 对于Cubes这种内嵌式的模型,少量的eig_k并不能很好的体现内嵌模型的特征
三角网格(Triangular Mesh)分类数据集 ↩︎
DiffusionNet ↩︎
VTK使用颜色映射标量数据 ↩︎