界面编程与视图(view)组件——三种UI界面开发方式
Android中三种UI界面的开发方式
一、使用编程方式开发UI界面的例子:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ViewActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
LinearLayout layout = new LinearLayout(this);
super.setContentView(layout);
layout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
final TextView tv = new TextView(this);
Button btn = new Button(this);
btn.setText(R.string.app_name);
btn.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
layout.addView(btn);
layout.addView(tv);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v){
tv.setText("hello"+new java.util.Date());
}
});
}
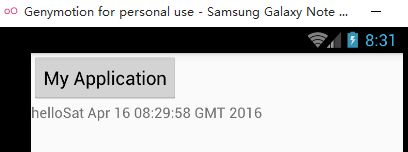
}运行截图:
使用代码创建UI界面,代码十分臃肿,不如xml布局文件来控制UI界面,不过在实际项目中更多采用代码和xml结合的方式控制UI界面,是界面更加美观、功能完善。
二、xml布局文件和Java代码混合控制UI界面例子——简单的图片浏览器
xml布局文件代码:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/root"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.john.myapplication.MainActivity">
LinearLayout>Java代码:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
int[] images = new int[]{
R.drawable.ajax,
R.drawable.html,
R.drawable.java,
R.drawable.javaee,
};
int imaNum=0;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinearLayout main= (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.root);
//创建ImageView组件
final ImageView image = new ImageView(this);
//将ImageView组件添加到LinearLayout布局中
main.addView(image);
//初始化显示的第一张图片
image.setImageResource(images[0]);
image.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v){
//改变显示的图片 image.setImageResource(images[++imaNum%images.length]);
}
});
}
}运行截图
三、开发自定义View
想要把UI界面设置的更加美观,开发自定义的View非常非常的重要,还是新手小白的我在这方面还在学习中,不能提出什么好的建议,这里给一个我在学习中用到的例子——跟随手指动的小球
Java代码:
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
public class DrawView extends View {
public float currentX=40;
public float currentY=50;
//定义并创建画笔
Paint p = new Paint();
public DrawView(Context context){
super(context);
}
public DrawView(Context context, AttributeSet set){
super(context,set);
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas canvas){
super.onDraw(canvas);
//设置画笔颜色
p.setColor(Color.RED);
canvas.drawCircle(currentX,currentY,15,p);
}
//为该组件的触碰事件重写事件的处理办法
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event){
currentX=event.getX();
currentY=event.getY();
//通知当前的组件重画自己
invalidate();
//返回true表明该处理方法已经处理该事件
return true;
}
}有两种方式可以使用这个我们自定义的组件
(1)直接通过代码使用自定义组件
Java代码:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinearLayout main= (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.root);
//创建DrawView组件
final DrawView draw = new DrawView(this);
draw.setMinimumWidth(300);
draw.setMinimumHeight(500);
main.addView(draw);
}
}(2)直接在xml使用自定义组件
xml代码:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/root"
android:orientation="vertical" tools:context="com.example.john.myapplication.MainActivity">
<com.example.john.myapplication.DrawView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
LinearLayout>在布局文件中已经添加自定义组件了,因此,在Java代码中只需要写
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}