AndroidQ | AudioPolicy
AudioPolicyService是负责音频策略的制定,AudioFlinger负责音频策略的具体执行,两个模块各司其职。
1.AudioPolicyService
对于应用开发者来说,需要播放音频的时候只会去创建个AudioTrack去实现,其中的参数有主要的streamType、sampleRate、format等,还有的默认就不会设置参数,他不会去关心你当前设备的具体音频播放模块是什么样的,是speaker还是lineout、btout。系统跑起来后有许多应用都要播放音频,有的是播放music,有的是播放ring,具体每个音频对应的音量、音效等都是需要一个策略来管理的,这就是AudioPolicyService的任务,当然不止我上面说的这些。
AudioPolicyService和AudioFlinger一样,也是一个server,其提供的功能我们从其接口来入手(接口决定了功能),接口为IAudioPolicyService:
class IAudioPolicyService : public IInterface
{
public:
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(AudioPolicyService);
...
virtual audio_io_handle_t getOutput(audio_stream_type_t stream) = 0;
...
}
AudioSystem中又封装了AudioPolicyService的功能,AudioSystem首先要获取AudioPolicyService的Proxy:
const sp<IAudioPolicyService> AudioSystem::get_audio_policy_service()
{
sp<IAudioPolicyService> ap;
sp<AudioPolicyServiceClient> apc;
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(gLockAPS);
if (gAudioPolicyService == 0) {
sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
sp<IBinder> binder;
do {
binder = sm->getService(String16("media.audio_policy"));
if (binder != 0)
break;
ALOGW("AudioPolicyService not published, waiting...");
usleep(500000); // 0.5 s
} while (true);
if (gAudioPolicyServiceClient == NULL) {
gAudioPolicyServiceClient = new AudioPolicyServiceClient();
}
binder->linkToDeath(gAudioPolicyServiceClient);
gAudioPolicyService = interface_cast<IAudioPolicyService>(binder);
...
}
ap = gAudioPolicyService;
}
...
return ap;
}
以getOutput为例,看下AudioSystem的功能封装
audio_io_handle_t AudioSystem::getOutput(audio_stream_type_t stream)
{
const sp<IAudioPolicyService>& aps = AudioSystem::get_audio_policy_service();
if (aps == 0) return 0;
return aps->getOutput(stream);
}
这样就最终会调用到AudioPolicyService的Server端,Server端通过继承BinderService和BnAudioPolicyService来实现Binder功能:
class AudioPolicyService :
public BinderService<AudioPolicyService>,
public BnAudioPolicyService,
public IBinder::DeathRecipient
{
...
}
AudioPolicyService在第一次被引用的时候会创建关键的对象AudioPolicyClient和AudioPolicyManager
void AudioPolicyService::onFirstRef()
{
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
// start audio commands thread
mAudioCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmAudio"), this);
// start output activity command thread
mOutputCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmOutput"), this);
mAudioPolicyClient = new AudioPolicyClient(this);
mAudioPolicyManager = createAudioPolicyManager(mAudioPolicyClient);
}
// load audio processing modules
sp<AudioPolicyEffects>audioPolicyEffects = new AudioPolicyEffects();
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
mAudioPolicyEffects = audioPolicyEffects;
}
mUidPolicy = new UidPolicy(this);
mUidPolicy->registerSelf();
mSensorPrivacyPolicy = new SensorPrivacyPolicy(this);
mSensorPrivacyPolicy->registerSelf();
}
相关类的关系图
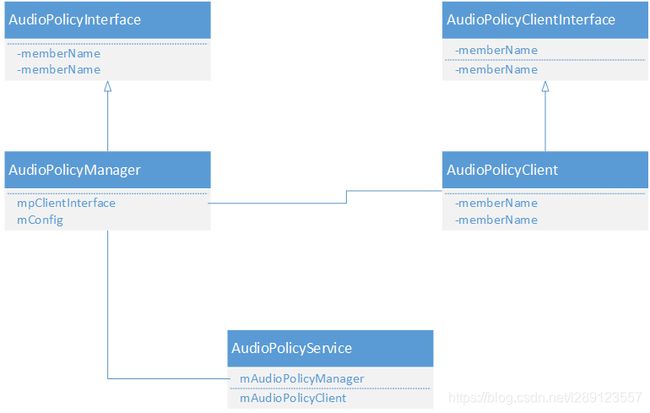
看这个图可以看到两个关键的接口AudioPolicyInterface和AudioPolicyClientInterface,这两个接口主要就是定义AudioPolicy该有的功能,关于这两个接口的命名我们来看下Android的解释
// The AudioPolicyInterface and AudioPolicyClientInterface classes define the communication interfaces
// between the platform specific audio policy manager and Android generic audio policy manager.
// The platform specific audio policy manager must implement methods of the AudioPolicyInterface class.
// This implementation makes use of the AudioPolicyClientInterface to control the activity and
// configuration of audio input and output streams.
//
// The platform specific audio policy manager is in charge of the audio routing and volume control
// policies for a given platform.
// The main roles of this module are:
// - keep track of current system state (removable device connections, phone state, user requests…).
// System state changes and user actions are notified to audio policy manager with methods of the AudioPolicyInterface.
// - process getOutput() queries received when AudioTrack objects are created: Those queries
// return a handler on an output that has been selected, configured and opened by the audio policy manager and that
// must be used by the AudioTrack when registering to the AudioFlinger with the createTrack() method.
// When the AudioTrack object is released, a putOutput() query is received and the audio policy manager can decide
// to close or reconfigure the output depending on other streams using this output and current system state.
// - similarly process getInput() and putInput() queries received from AudioRecord objects and configure audio inputs.
// - process volume control requests: the stream volume is converted from an index value (received from UI) to a float value
// applicable to each output as a function of platform specific settings and current output route (destination device). It
// also make sure that streams are not muted if not allowed (e.g. camera shutter sound in some countries).
//
// The platform specific audio policy manager is provided as a shared library by platform vendors (as for libaudio.so)
// and is linked with libaudioflinger.so
一般接口函数的调用流程遵循如下关系:AudioSystem-》AudioPolicyService-》AudioPolicyManager-》AudioPolicyClient-》AudioFlinger,接下来我们主要分析接口的实现。
2.AudioPolicyManager
AudioPolicyManager是AudioPolicy的管理者,主要就是实现audiopolicy的功能,所以他直接继承于AudioPolicyInterface。
我们来看一张图,发现没,两个类的方法大部分是一样的,这就说明AudioPolicyService一般会调用AudioPolicyManager中的方法来实现具体功能。在AudioPolicyService接口的具体实现中,区分了调用AudioPolicyManager和AudioPolicyClient的实现,调用AudioPolicyManager的实现是在文件AudioPolicyInterfaceImpl.cpp中。

在目录frameworks\av\services\audiopolicy中,有两个目录manager和managerdefault,分别是为了创建AudioPolicyManager和实现AudioPolicyManager的功能。
2.1 createAudioPolicyManager
extern "C" AudioPolicyInterface* createAudioPolicyManager(
AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
{
AudioPolicyManager *apm = new AudioPolicyManager(clientInterface);
status_t status = apm->initialize();
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
delete apm;
apm = nullptr;
}
return apm;
}
2.2 解析AudioPolicy配置文件
AudioPolicyManager::AudioPolicyManager(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
: AudioPolicyManager(clientInterface, false /*forTesting*/)
{
loadConfig();
}
void AudioPolicyManager::loadConfig() {
if (deserializeAudioPolicyXmlConfig(getConfig()) != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGE("could not load audio policy configuration file, setting defaults");
getConfig().setDefault();
}
}
AudioPolicy的配置文件有如下这些
audio_policy_configuration.xml
audio_policy_configuration_a2dp_offload_disabled.xml
audio_policy_configuration_bluetooth_legacy_hal.xml
…
配置文件太长,就不在这里粘贴了,我主要说下最后解析出来的配置文件对应到代码中哪些类型
- module节点对应到HwModule
- mixPort节点对应到AudioPort
- profile节点对应到AudioProfile
- gains对应到AudioGain,最后会一起加入到AudioPort中,这是其组成的一部分
- devicePort对应到DeviceDescriptor
- route对应到AudioRoute,最终会加入到HwModule中
具体每个类的相互关系如下图:

XML配置文件中,还有一类是关于音量的,这个是体现在VolumeCurve中
2.3 Manager
AudioPolicyService作为一个service,它一般负责命令的交互,具体到Policy的实际管理就是在类AudioPolicyManager中处理,AudioPolicyManager中负责太多的功能,要管理每个流的音量,设备的打开关闭,寻找合适的输出设备等等,我们来看其中的一个功能startOutput,它首先是通过AudioSystem来调用下来的
status_t AudioPolicyManager::startOutput(audio_port_handle_t portId)
{
...
status = startSource(outputDesc, client, &delayMs);
...
}
status_t AudioPolicyManager::startSource(const sp<SwAudioOutputDescriptor>& outputDesc,
const sp<TrackClientDescriptor>& client,
uint32_t *delayMs)
{
...
checkAndSetVolume(curves, client->volumeSource(),
...
}
status_t AudioPolicyManager::checkAndSetVolume(IVolumeCurves &curves,
VolumeSource volumeSource,
int index,
const sp<AudioOutputDescriptor>& outputDesc,
DeviceTypeSet deviceTypes,
int delayMs,
bool force)
{
...
if (isVoiceVolSrc || isBtScoVolSrc) {
...
mpClientInterface->setVoiceVolume(voiceVolume, delayMs);
...
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
这里又最终调用到AudioPolicyClient中的函数
3.AudioPolicyClient
AudioPolicyClient中的实现都在文件AudioPolicyClientImpl.cpp中
status_t AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyClient::setVoiceVolume(float volume, int delay_ms)
{
return mAudioPolicyService->setVoiceVolume(volume, delay_ms);
}