CSS笔试面试题(一)
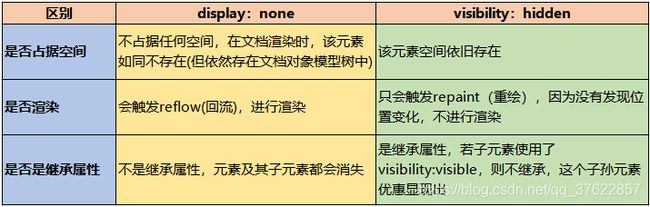
1.display:none和visibility:hidden的区别?
相同: 它们都能让元素不可见
区别:
display:none;会让元素完全从渲染树中消失,渲染的时候不占据任何空间;
visibility: hidden;不会让元素从渲染树消失,渲染师元素继续占据空间,只是内容不可见
display: none;是非继承属性,子孙节点消失由于元素从渲染树消失造成,
通过修改子孙节点属性无法显示;
visibility:hidden;是继承属性,子孙节点消失由于继承了 hidden,
通过设置 visibility: visible;可以让子孙节点显式
修改常规流中元素的 display 通常会造成文档重排。
修改 visibility 属性只会造成本元素的重绘
读屏器不会读取 display: none;元素内容;
会读取 visibility: hidden 元素内容
2.opacity和rgba的区别?
- opacity 作用于元素以及元素内的所有内容(包括文字)的透明度
- rgba() 只作用于元素自身的颜色或其背景色,子元素不会继承透明效果
3.使用css,让一个div(200px*200px)z在任何时候,都处于屏幕正中心?
4-1.css盒子模型,box-sizing属性的理解?
css的盒模型由content(内容)、padding(内边距)、border(边框)、margin(外边距)组成。
但盒子的大小由content+padding+border的这几部分决定。
box-sizing是一个CSS3属性,与盒子模型有着密切联系。即决定元素的宽高如何计算,box-sizing有三个属性:
box-sizing:content-box|border-box|inherit
•content-box:(默认模式)使得元素的宽高即为内容区的宽高
•border-box:计算content+padding+border=本身元素的大小,即缩小了content大小
•inherit:指定box-sizing属性的值,应该从父元素继承
4-2介绍一下标准的 CSS 的盒子模型?低版本 IE 的盒子模型有什么不同的?
- 有两种, IE 盒子模型、W3C 盒子模型;
- 盒模型: 内容(content)、填充(padding)、边界(margin)、 边框(border);
- 标准(W3C)盒模型:元素宽度 = width + padding + border + margin
- 怪异(IE)盒模型:元素宽度 = width + margin
- 区 别: IE 的 content 部分把 border 和 padding 计算了进去;
- 标准浏览器通过设置 css3 的 box-sizing: border-box 属性,触发“怪异模式”解析计算宽高
5-1.清除浮动,什么时候需要清除浮动,清除浮动都有哪些方法?
浮动的元素是脱离文档标准流的,如果我们不清楚浮动,name就会造成父元素高度坍塌,影响页面布局
清除浮动的方式:3、4、5
1.直接给父元素添加一个高度;
弊端:不是每次都知道父元素的高度
2.给父元素设置浮动
弊端:不是任何时候父元素都需要浮动,而且一旦父元素浮动,会影响后续的效果
3.为父元素设置overflow
取值:hidden或auto
弊端:如果有内容溢出显示,也会被一同隐藏
4.在父元素中,追加一个空的子元素div,并设置其clear:both;
这种方式是通过空白来撑开父元素的高度,没有副作用,单页面中会出现多余的结果
5.伪元素-------给高度坍塌的盒子,添加一个clearfix的类
.clearfix:after{
content:""; //添加一个内容
display:block; //转化为一个块元素
clear:both; //清除两侧的浮动
}
.clearfix{ //兼容低版本浏览器
Zoom:1;
}
使用伪元素的好处:不增加冗余的DOM节点,符合语义化
overflow:hidden可以触发BFC机制。
BFC:块级格式化上下文,创建BFC的元素就是一个独立的盒子,它规定了内部如何布局,并且与这个独立盒子里的布局
不受外部影响,当然它也不会影响到外面的元素,计算BFC的高度时,浮动元素也参与计算
5-2.谈谈浮动和清除浮动
浮动的框可以向左或向右移动,直到他的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动框的边框为止。由于浮动框不在文档的普通流中,所以文档的普通流的块框表现得就像浮动框不存在一样。浮动的块框会漂浮在文档普通流的块框上
解决方法
1. 父级 div 定义伪类:after 和 zoom (推荐使用,建议定义公共类,以减少 CSS 代码)
.clearfloat:after{
display:block;
clear:both;
content:"";
visibility:hidden;
height:0}
.clearfloat{zoom:1}
2. 在结尾处添加空 div 标签 clear:both
Left
Right
3. 父级 div 定义 height
4. 父级 div 定义 overflow:auto
5. 父级 div 定义 overflow:hidden
6. 父级 div 也一起浮动
7. 父级 div 定义 display:table
8. 结尾处加 br 标签 clear:both
6.如何让一个不定宽高的盒子水平垂直居中
定位的方式
.father{
position:relative;
}
.son{
position:absolute;
top:0;right:0;
bottom:0;left:0;
margin:auto;
}
CSS3属性
.father{
position:relative;
}
.son{
position:absolute;
top:50%;left:50%;
transform:tranlate(-50%,-50%);
}
Flex布局
.father{
display:flex;
justify-content:center;
align-items:center;
}
7.说说px、em、rem的区别?
px:像素,相对长度单位。像素px是相对于显示器屏幕分辨率而言的
em的值并不是固定的,会继承父级元素的字体大小,代表倍数 em = 像素值 / 父级 font-size
rem的值并不是固定的,始终是基于根元素的,也代表倍数
8.position的值有哪些?relative 和 absolute 定位原点是?
- absolute 生成绝对定位的元素,相对于值不为 static 的第一个父元素进行定位。
- fixed (老 IE 不支持) 生成绝对定位的元素,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。
- relative 生成相对定位的元素,相对于其正常位置进行定位。
- static 默认值。没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中(忽略 top, bottom, left, right - z-index 声明)。
- inherit 规定从父元素继承 position 属性的值
9.CSS中link和@import的区别
- link 是 HTML 方式, @import 是 CSS 方式
- link 最大限度支持并行下载,@import 过多嵌套导致串行下载,出现 FOUC
- link 可以通过 rel=“alternate stylesheet” 指定候选样式
- 浏览器对 link 支持早于@import ,可以使用 @import 对老浏览器隐藏样式
- @import 必须在样式规则之前,可以在 css 文件中引用其他文件
- 总体来说:link 优于@import
10.什么是响应式设计?响应式设计的基本原理是什么?如何兼容低版本的 IE?
-
响应式设计就是网站能够兼容多个终端,而不是为每个终端做一个特定的版本
-
基本原理是利用 CSS3 媒体查询,为不同尺寸的设备适配不同样式
-
对于低版本的 IE,可采用 JS 获取屏幕宽度,然后通过 resize 方法来实现兼容:
$(window).resize(function () { screenRespond(); }); screenRespond(); function screenRespond(){ var screenWidth = $(window).width(); if(screenWidth <= 1800){ $("body").attr("class", "w1800"); } if(screenWidth <= 1400){ $("body").attr("class", "w1400"); } if(screenWidth > 1800){ $("body").attr("class", ""); } }
11.为什么要初始化CSS样式?
因为浏览器兼容性问题,不同浏览器对有些标签的默认值是不同的,如果没对CSS初始化往往会出现浏览器之间的页面显示差异
初始化样式会对SEO(Search Engine Optimization,即搜索引擎优化)有一定的影响
12.CSS3有哪些新特性?
- 新增选择器 p:nth-child(n){color: rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.75)}
- 弹性盒模型 display: flex;
- 多列布局 column-count: 5;
- 媒体查询 @media (max-width: 480px) {.box: {column-count: 1;}}
- 个性化字体 @font-face{font-family: BorderWeb; src:url(BORDERW0.eot);}
- 颜色透明度 color: rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.75);
- 圆角 border-radius: 5px;
- 渐变 background:linear-gradient(red, green, blue);
- 阴影 box-shadow:3px 3px 3px rgba(0, 64, 128, 0.3);
- 倒影 box-reflect: below 2px;
- 文字装饰 text-stroke-color: red;
- 文字溢出 text-overflow:ellipsis;
- 背景效果 background-size: 100px 100px;
- 边框效果 border-image:url(bt_blue.png) 0 10;
- 平滑过渡 transition: all .3s ease-in .1s;
- 动画 @keyframes anim-1 {50% {border-radius: 50%;}} animation: anim-1 1s;
- 转换
- 旋转 transform: rotate(20deg);
- 倾斜 transform: skew(150deg, -10deg);
- 位移 transform: translate(20px, 20px);
- 缩放 transform: scale(.5);
13. ::before和::after中双冒号和单冒号有什么区别?解释一下这2个伪元素的作用?
单冒号(:)用于CSS3伪类,双冒号(::)用于CSS3伪元素。伪元素由双冒号和伪元素名称组成,双冒号是在当前规范中引入的,用于区分伪类和伪元素
14.CSS优化、提高性能的方法有哪些?
- 多个 css 合并,尽量减少 HTTP 请求
- 将 css 文件放在页面最上面
- 避免使用 CSS 表达式
- 选择器优化嵌套,尽量避免层级过深
- 充分利用 css 继承属性,减少代码量
- 属性值为 0 时,不加单位
- 属性值为小于 1 的小数时,省略小数点前面的 0
- css 雪碧图
- 移除空的css规则(Remove empty rules)
- 正确使用display的属性
- 不滥用浮动、web字体
- 不声明过多的font-size
- 不再选择符中使用ID标识符
- 遵守盒模型规则
- 尽量减少页面重排、重绘
- 抽象提取公共样式,减少代码量
17.css预处理器?
- CSS 预处理器基本思想:为 CSS 增加了一些编程的特性(变量、逻辑判断、函数等)
- 开发者使用这种语言进行进行 Web 页面样式设计,再编译成正常的 CSS 文件使用
- 使用 CSS 预处理器,可以使 CSS 更加简洁、适应性更强、可读性更佳,无需考虑兼容性
- 最常用的 CSS 预处理器语言包括:Sass(SCSS)和 LESS
###18.CSS 有哪些继承属性 - 关于文字排版的属性如:
- font
- word-break
- letter-spacing
- text-align
- text-rendering
- word-spacing
- white-space
- text-indent
- text-transform
- text-shadow
- line-height
- color
- visibility
- cursor
19.display,float,position 的关系
- 如果 display 为 none,那么 position 和 float 都不起作用,这种情况下元素不产生框
- 否则,如果 position 值为 absolute 或者 fixed,框就是绝对定位的,float 的计算值为 none,display 根据下面的表格进行调整
- 否则,如果 float 不是 none,框是浮动的,display 根据下表进行调整
- 否则,如果元素是根元素,display 根据下表进行调整
- 其他情况下 display 的值为指定值 总结起来:绝对定位、浮动、根元素都需要调整 display
- 表格 display属性转换:
- 指定值 inline-table 转成table
- 指定值 inline, table-row-group, table-column, table-column-group, table-header-group, table-footer-group, table-row, table-cell, table-caption, inline-block 转成block
- 其他任何的指定值都保持不变
20.外边距折叠(collapsing margins)
外边距重叠就是 margin-collapse
相邻的两个盒子(可能是兄弟关系也可能是祖先关系)的外边距可以结合成一个单独的外边距。 这种合并外边距的方式被称为折叠,结合而成的外边距称为折叠外边距
折叠结果遵循下列计算规则:
- 两个相邻的外边距都是正数时,折叠结果是它们两者之间较大的值
- 两个相邻的外边距都是负数时,折叠结果是两者绝对值的较大值
- 两个外边距一正一负时,折叠结果是两者的相加的和
21.CSS 选择器有哪些?
- id 选择器( # myid)
- 类选择器(.myclassname)
- 标签选择器(div, h1, p)
- 相邻选择器(h1 + p)
- 子选择器(ul > li)
- 后代选择器(li a)
- 通配符选择器( * )
- 属性选择器(a[rel = “external”])
- 伪类选择器(a:hover, li:nth-child)
22.CSS3 新增伪类有那些?
-
p:first-of-type 选择属于其父元素的首个
元素的每个元素。 -
p:last-of-type 选择属于其父元素的最后
元素的每个元素。 -
p:only-of-type 选择属于其父元素唯一的
元素的每个元素。 -
p:only-child 选择属于其父元素的唯一子元素的每个
元素。 -
p:nth-child(2) 选择属于其父元素的第二个子元素的每个
元素。 -
:after 在元素之前添加内容,也可以用来做清除浮动。
-
:before 在元素之后添加内容
-
:enabled 选择器匹配每个已启用的元素(大多用在表单元素上)。
-
:disabled 控制表单控件的禁用状态。
-
:checked 单选框或复选框被选中
23.如何居中 div?如何居中一个浮动元素?如何让绝对定位的 div 居中?
如果需要居中的元素为常规流中 inline 元素,为父元素设置 text-align: center;即可实现
如果需要居中的元素为常规流中 block 元素,1)为元素设置宽度,2)设置左右 margin 为 auto。3)IE6 下需在父元素上设置 text-align: center;,再给子元素恢复需要的值
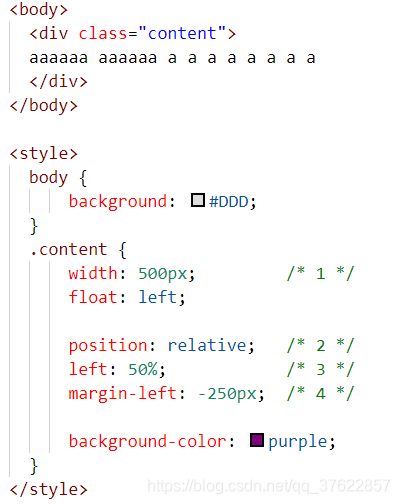
如果需要居中的元素为绝对定位元素,1)为元素设置宽度,2)偏移量设置为 50%,3)偏移方向外边距设置为元素宽度一半乘以-1

如果需要居中的元素为绝对定位元素,1)为元素设置宽度,2)设置左右偏移量都为 0,3)设置左右外边距都为 auto
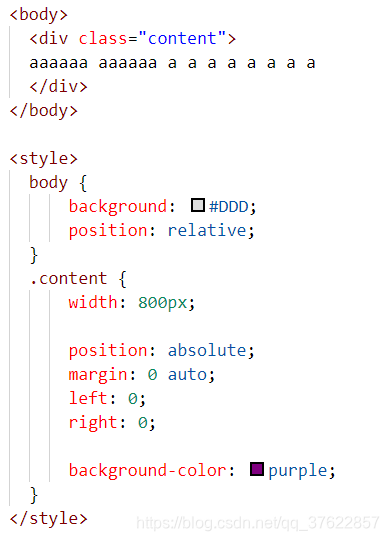
24.如何竖直居中一个元素
- 绝对定位居中
- 如果居中的是行内元素,可以设置父级 height 与 line-height 相等
- 设置 margin/padding 居中
- 相对位置偏移居中
- flex 居中 设置 align-items:center 即可
25.display 有哪些值?说明他们的作用
- block 象块类型元素一样显示。
- none 缺省值。象行内元素类型一样显示。
- inline-block 象行内元素一样显示,但其内容象块类型元素一样显示。
- list-item 象块类型元素一样显示,并添加样式列表标记。
- table 此元素会作为块级表格来显示
- inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 display 属性的值
26.用纯 CSS 创建一个三角形的原理是什么?
/* 把上、左、右三条边隐藏掉(颜色设为 transparent)*/
#demo {
width: 0;
height: 0;
border-width: 20px;
border-style: solid;
border-color: transparent transparent red transparent;
}
27.一个满屏品字布局如何设计?
简单的方式:
- 上面的 div 宽 100%,
- 下面的两个 div 分别宽 50%,
- 然后用 float 或者 inline 使其不换行即可
28.经常遇到的浏览器的兼容性有哪些?原因,解决方法是什么,常用 hack 的技巧 ?
- png24 位的图片在 iE6 浏览器上出现背景,解决方案是做成 PNG8.
- 浏览器默认的 margin 和 padding 不同。解决方案是加一个全局的*{margin:0;padding:0;}来统一
- IE 下,可以使用获取常规属性的方法来获取自定义属性,也可以使用 getAttribute()获取自定义属性;
- Firefox 下,只能使用 getAttribute()获取自定义属性。解决方法:统一通过 getAttribute()获取自定义属性
- IE 下,even 对象有 x,y 属性,但是没有 pageX,pageY 属性
- Firefox 下,event 对象有 pageX,pageY 属性,但是没有 x,y 属性
29.li 与 li 之间有看不见的空白间隔是什么原因引起的?有什么解决办法?(也称幽灵字符)
行框的排列会受到中间空白(回车\空格)等的影响,因为空格也属于字符,这些空白也会被应用样式,占据空间,所以会有间隔,把字符大小设为 0,就没有空格了
30-1.display:inline-block 间隙问题怎么解决?(携程)
移除空格、使用 margin 负值、使用 font-size:0、letter-spacing、word-spacing
30-2.inline、inline-block和block的区别?
- inline:块级元素转换为行内元素
- inline-block:转为内联元素
- block :行内元素转换为块级元素
31.display:inline-block 什么时候会显示间隙?
- 相邻的 inline-block 元素之间有换行或空格分隔的情况下会产生间距
- 非 inline-block 水平元素设置为 inline-block 也会有水平间距
- 可以借助 vertical-align:top; 消除垂直间隙
- 可以在父级加 font-size:0; 在子元素里设置需要的字体大小,消除垂直间隙
- 把 li 标签写到同一行可以消除垂直间隙,但代码可读性差
32.CSS 优先级算法如何计算?
- 优先级就近原则,同权重情况下样式定义最近者为准
- 载入样式以最后载入的为准
- 优先级为: !important > id > class > tag important 比 内联优先级高
33.css 定义的权重
以下是权重的规则:标签的权重为1,class的权重为10,id的权重为100,以下例子是演示各种定义的权重值:
/*权重为1*/
div{ }
/*权重为10*/
.class1{ }
/*权重为100*/
#id1{ }
/*权重为100+1=101*/
#id1 div{ }
/*权重为10+1=11*/
.class1 div{ }
/*权重为10+10+1=21*/
.class1 .class2 div{ }
如果权重相同,则最后定义的样式会起作用,但是应该避免这种情况出现。
34.box-sizing 常用的属性有哪些?分别有什么作用?
- box-sizing: content-box; // 默认的标准(W3C)盒模型元素效果
- box-sizing: border-box; // 触发怪异(IE)盒模型元素的效果
- box-sizing: inherit; // 继承父元素 box-sizing 属性的值
35.请列举几种隐藏元素的方法
- visibility: hidden; 这个属性只是简单的隐藏某个元素,但是元素占用的空间任然存在
- opacity: 0; CSS3 属性,设置 0 可以使一个元素完全透明
- position: absolute; 设置一个很大的 left 负值定位,使元素定位在可见区域之外
- display: none; 元素会变得不可见,并且不会再占用文档的空间。
- transform: scale(0); 将一个元素设置为缩放无限小,元素将不可见,元素原来所在的位置将被保留
- HTML5 属性,效果和 display:none;相同,但这个属性用于记录一个元素的状态
- height: 0; 将元素高度设为 0 ,并消除边框
- filter: blur(0); CSS3 属性,将一个元素的模糊度设置为 0,从而使这个
36.css 属性 content 有什么作用?
content 属性专门应用在 before/after 伪元素上,用于插入额外内容或样式
37.请解释一下 CSS3 的 Flexbox(弹性盒布局模型)以及适用场景?
Flexbox 用于不同尺寸屏幕中创建可自动扩展和收缩布局
38.请写出多种等高布局
- 在列的父元素上使用这个背景图进行 Y 轴的铺放,从而实现一种等高列的假像
- 模仿表格布局等高列效果:兼容性不好,在 ie6-7 无法正常运行
- css3 flexbox 布局: .container{display: flex; align-items: stretch;}
39.圣杯布局的实现原理?
要求:三列布局;中间主体内容前置,且宽度自适应;两边内容定宽
好处:重要的内容放在文档流前面可以优先渲染
原理:利用相对定位、浮动、负边距布局,而不添加额外标签
.container { padding-left: 150px; padding-right: 190px; } .main { float: left; width: 100%; } .left { float: left; width: 190px; margin-left: -100%; position: relative; left: -150px; } .right { float: left; width: 190px; margin-left: -190px; position: relative; right: -190px; }40.什么是双飞翼布局?实现原理?
双飞翼布局:
对圣杯布局(使用相对定位,对以后布局有局限性)的改进,消除相对定位布局原理:
主体元素上设置左右边距,预留两翼位置。左右两栏使用浮动和负边距归位,消除相对定位。.container { /*padding-left:150px;*/ /*padding-right:190px;*/ } .main-wrap { width: 100%; float: left; } .main { margin-left: 150px; margin-right: 190px; } .left { float: left; width: 150px; margin-left: -100%; /*position: relative;*/ /*left:-150px;*/ } .right { float: left; width: 190px; margin-left: -190px; /*position:relative;*/ /*right:-190px;*/ }40.reset.css 和 Normalize.css 理解
reset.css 意为重置默认样式。HTML 中绝大部分标签元素在网页显示中都有一个默认属性值,通常为了避免重复定义元素样式,需要进行重置默认样式
Eric Meyer(CSS Reset)推荐
html, body, div, span, applet, object, iframe, h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, p, blockquote, pre, a, abbr, acronym, address, big, cite, code, del, dfn, em, font, img, ins, kbd, q, s, samp, small, strike, strong, sub, sup, tt, var, b, u, i, center, dl, dt, dd, ol, ul, li, fieldset, form, label, legend, table, caption, tbody, tfoot, thead, tr, th, td { margin: 0; padding: 0; border: 0; outline: 0; font-size: 100%; vertical-align: baseline; background: transparent; } body { line-height: 1; } ol, ul { list-style: none; } blockquote, q { quotes: none; } blockquote:before, blockquote:after, q:before, q:after { content: ''; content: none; } /* remember to define focus styles! */ :focus { outline: 0; } /* remember to highlight inserts somehow! */ ins { text-decoration: none; } del { text-decoration: line-through; } /* tables still need ‘cellspacing=”0″‘ in the markup */ table { border-collapse: collapse; border-spacing: 0; }Normalize.css 只是一个很小的 css 文件,但它在默认的 HTML 元素样式上提供了跨浏览器的高度一致性。相比于传统的 css reset,Normalize.css 是一种现代的,为 HTML5 准备的优质替代方案。
Normalize.css 是一种 CSS reset 的替代方案。经过@necolas 和@jon neal 花了几百个小时来努力研究不同浏览器的默认样式的差异,这个项目终于变成了现在这样。
我们创造 normalize.css 有下几个目的:
- 保护有用的浏览器默认样式而不是完全去掉它们
- 一般化的样式:为大部分 HTML 元素提供
- 修复浏览器自身的 bug 并保证各浏览器的一致性
- 优化 CSS 可用性:用一些小技巧
- 解释代码:用注释和详细的文档来
41.什么是 FOUC(Flash of Unstyled Content)? 如何来避免 FOUC?
- 当使用 @import 导入 CSS 时,会导致某些页面在 IE 出现奇怪的现象: 没有样式的页面内容显示瞬间闪烁,这种现象称为“文档样式短暂失效”,简称为 FOUC
- 产生原因:当样式表晚于结构性 html 加载时,加载到此样式表时,页面将停止之前的渲染。
- 等待此样式表被下载和解析后,再重新渲染页面,期间导致短暂的花屏现象。
- 解决方法:使用 link 标签将样式表放在文档 head
42.浏览器是怎样解析 CSS 选择器的?
浏览器解析 CSS 选择器的方式是从右到左
43.在网页中的应该使用奇数还是偶数的字体?
在网页中的应该使用“偶数”字体:
- 偶数字号相对更容易和 web 设计的其他部分构成比例关系
- 使用奇数号字体时文本段落无法对齐
- 宋体的中文网页排布中使用最多的就是 12 和 14
44.margin 和 padding 分别适合什么场景使用?
- 需要在 border 外侧添加空白,且空白处不需要背景(色)时,使用 margin
- 需要在 border 内测添加空白,且空白处需要背景(色)时,使用 padding
45.抽离样式模块怎么写,说出思路?
CSS 可以拆分成 2 部分:公共 CSS 和 业务 CSS:
- 网站的配色,字体,交互提取出为公共 CSS。这部分 CSS 命名不应涉及具体的业务
- 对于业务 CSS,需要有统一的命名,使用公用的前缀。可以参考面向对象的 CSS
46.元素竖向的百分比设定是相对于容器的高度吗?
元素竖向的百分比设定是相对于容器的宽度,而不是高度
47.全屏滚动的原理是什么? 用到了 CSS 的那些属性?
- 原理类似图片轮播原理,超出隐藏部分,滚动时显示
- 可能用到的 CSS 属性:overflow:hidden; transform:translate(100%, 100%); display:none;
48.什么是视差滚动效果,如何给每页做不同的动画?
-
视差滚动是指多层背景以不同的速度移动,形成立体的运动效果,具有非常出色的视觉体验
-
一般把网页解剖为:背景层、内容层和悬浮层。当滚动鼠标滚轮时,各图层以不同速度移动,形成视差的
实现原理 -
以 “页面滚动条” 作为 “视差动画进度条”
-
以 “滚轮刻度” 当作 “动画帧度” 去播放动画的
-
监听 mousewheel 事件,事件被触发即播放动画,实现“翻页”效果
49.a 标签上四个伪类的执行顺序是怎么样的?
link > visited > hover > active
50.伪元素和伪类的区别和作用?
伪元素:
在内容元素的前后插入额外的元素或样式,但是这些元素实际上并不在文档中生成。它们只在外部显示可见,但不会在文档的源代码中找到它们,因此,称为“伪”元素。例如:p::before {content:"第一章:";} p::after {content:"Hot!";} p::first-line {background:red;} p::first-letter {font-size:30px;}伪类:
将特殊的效果添加到特定选择器上。它是已有元素上添加类别的,不会产生新的元素。例如:a:hover {color: #FF00FF} p:first-child {color: red}51.如何修改 Chrome 记住密码后自动填充表单的黄色背景?
- 产生原因:由于 Chrome 默认会给自动填充的 input 表单加上 input:-webkit-autofill 私有属性造成的
- 解决方案 1:在 form 标签上直接关闭了表单的自动填充:autocomplete=“off”
- 解决方案 2:input:-webkit-autofill { background-color: transparent; }
input [type=search] 搜索框右侧小图标如何美化?
input[type="search"]::-webkit-search-cancel-button{ -webkit-appearance: none; height: 15px; width: 15px; border-radius: 8px; background:url("images/searchicon.png") no-repeat 0 0; background-size: 15px 15px; }52.网站图片文件,如何点击下载?而非点击预览?
下载 下载###53.iOS safari 如何阻止“橡皮筋效果”?
$(document).ready(function(){ var stopScrolling = function(event) { event.preventDefault(); } document.addEventListener('touchstart', stopScrolling, false); document.addEventListener('touchmove', stopScrolling, false); });54.你对 line-height 是如何理解的?
- line-height 指一行字的高度,包含了字间距,实际上是下一行基线到上一行基线距离
- 如果一个标签没有定义 height 属性,那么其最终表现的高度是由 line-height 决定的
- 一个容器没有设置高度,那么撑开容器高度的是 line-height 而不是容器内的文字内容
- 把 line-height 值设置为 height 一样大小的值可以实现单行文字的垂直居中
- line-height 和 height 都能撑开一个高度,height 会触发 haslayout,而 line-height 不会
55.line-height 三种赋值方式有何区别?(带单位、纯数字、百分比)
- 带单位:px 是固定值,而 em 会参考父元素 font-size 值计算自身的行高
- 纯数字:会把比例传递给后代。例如,父级行高为 1.5,子元素字体为 18px,则子元素行高为 1.5 * 18 = 27px
- 百分比:将计算后的值传递给后代
56.设置元素浮动后,该元素的 display 值会如何变化?
设置元素浮动后,该元素的 display 值自动变成 block
57.怎么让 Chrome 支持小于 12px 的文字?
.shrink{ -webkit-transform:scale(0.8); -o-transform:scale(1); display:inline-block; }58.让页面里的字体变清晰,变细用 CSS 怎么做?(IOS 手机浏览器字体齿轮设置)
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;59.font-style 属性 oblique 是什么意思?
font-style: oblique; 使没有 italic 属性的文字实现倾斜60.如果需要手动写动画,你认为最小时间间隔是多久?
16.7ms 多数显示器默认频率是 60Hz,即 1 秒刷新 60 次,所以理论上最小间隔: 1s / 60 * 1000 = 16.7ms
61.overflow: scroll 时不能平滑滚动的问题怎么处理?
监听滚轮事件,然后滚动到一定距离时用 jquery 的 animate 实现平滑效果。
62.一个高度自适应的 div,里面有两个 div,一个高度 100px,希望另一个填满剩下的高度
- 方案 1: .
sub { height: calc(100%-100px); } - 方案 2:
container { position:relative; } .sub { position: absolute; top: 100px; bottom: 0; } - 方案 3:
.container { display:flex; flex-direction:column; } .sub { flex:1; }
63.CSS 中类 class 和 id 的区别
对于 CSS 而言,id 和 class 都是选择器,唯一不同的地方在于权重不同。
如果只说 CSS,上面那一句话就讲完了。
拓展出来,对于 html 而言,id 和 class 都是 dom 元素的属性值。
不同的地方在于 id 属性的值是唯一的,而 class 属性值可以重复。
id 还一个老特性是锚点功能,当浏览器地址栏有一个#xxx,页面会自动滚动到 id=xxx 的元素上面。更直接的:id 给 js 用,class 给 css 用(趋势)
64.如何优化网页的打印样式
其中 media 指定的属性就是设备,显示器上就是 screen,打印机则是 print,电视是 tv,投影仪是 projection。
但打印样式表也应有些注意事项:
- 打印样式表中最好不要用背景图片,因为打印机不能打印 CSS 中的背景。如要显示图片,请使用 html 插入到页面中。
- 最好不要使用像素作为单位,因为打印样式表要打印出来的会是实物,所以建议使用 pt 和 cm。
- 隐藏掉不必要的内容。(@print div{display:none;})
- 打印样式表中最好少用浮动属性,因为它们会消失。
65.请问为何要使用 transform 而非 absolute positioning,或反之的理由?为什么?
- 使用 transform 或 position 实现动画效果时是有很大差别。
- 使用 transform 时,可以让 GPU 参与运算,动画的 FPS 更高。
- 使用 position 时,最小的动画变化的单位是 1px,而使用 transform 参与时,可以做到更小(动画效果更加平滑)
- 功能都一样。但是 translate 不会引起浏览器的重绘和重排,这就相当 nice 了。
反之
- tranform 改变 fixed 子元素的定位对象
- transform 改变元素层叠顺序
66.请解释 CSS sprites,以及你要如何在页面或网站中实现它
- CSS Sprites 其实就是把网页中一些背景图片整合到一张图片文件中,再利用 CSS 的“background-image”,“background- repeat”,“background-position”的组合进行背景定位,background-position 可以用数字能精确的定位出背景图片的位置。
- CSS Sprites 为一些大型的网站节约了带宽,让提高了用户的加载速度和用户体验,不需要加载更多的图片。
67.你熟悉 SVG 样式的书写吗?

下面的属性在 SVG 和 CSS 中是一样的,只是在 SVG 的 transformations 和 dimensions 中稍有区别:-
font-family, font-size, font-style, font-variant 和 font-weight
-
width 和 height
-
scale, rotate, skew
###68.如果设计中使用了非标准的字体,你该如何去实现? -
用图片代替
-
web fonts 在线字库
-
@font-face
69.css hack 原理及常用 hack
原理:利用不同浏览器对 CSS 的支持和解析结果不一样编写针对特定浏览器样式。 常见的 hack 有 1)属性 hack。 2)选择器 hack。 3)IE 条件注释属性 hack:不同浏览器解析 bug 或方法
/* IE6 */ #once { _color: blue } /* IE6, IE7 */ #doce { *color: blue; /* or #color: blue */ } /* Everything but IE6 */ #diecisiete { color/**/: blue } /* IE6, IE7, IE8 */ #diecinueve { color: blue\9; } /* IE7, IE8 */ #veinte { color/*\**/: blue\9; } /* IE6, IE7 -- acts as an !important */ #veintesiete { color: blue !ie; } /* string after ! can be anything */选择器 hack:不同浏览器对选择器的支持不一样
/***** Selector Hacks ******/ /* IE6 and below */ * html #uno { color: red } /* IE7 */ *:first-child+html #dos { color: red } /* IE7, FF, Saf, Opera */ html>body #tres { color: red } /* IE8, FF, Saf, Opera (Everything but IE 6,7) */ html>/**/body #cuatro { color: red } /* Opera 9.27 and below, safari 2 */ html:first-child #cinco { color: red } /* Safari 2-3 */ html[xmlns*=""] body:last-child #seis { color: red } /* safari 3+, chrome 1+, opera9+, ff 3.5+ */ body:nth-of-type(1) #siete { color: red } /* safari 3+, chrome 1+, opera9+, ff 3.5+ */ body:first-of-type #ocho { color: red } /* saf3+, chrome1+ */ @media screen and (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio:0) { #diez { color: red } } /* iPhone / mobile webkit */ @media screen and (max-device-width: 480px) { #veintiseis { color: red } } /* Safari 2 - 3.1 */ html[xmlns*=""]:root #trece { color: red } /* Safari 2 - 3.1, Opera 9.25 */ *|html[xmlns*=""] #catorce { color: red } /* Everything but IE6-8 */ :root *> #quince { color: red } /* IE7 */ *+html #dieciocho { color: red } /* Firefox only. 1+ */ #veinticuatro, x:-moz-any-link { color: red } /* Firefox 3.0+ */ #veinticinco, x:-moz-any-link, x:default { color: red }IE 条件注释:适用于[IE5, IE9]常见格式如下
{ color: red } /* saf3+, chrome1+ */ @media screen and (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio:0) { #diez { color: red } } /* iPhone / mobile webkit */ @media screen and (max-device-width: 480px) { #veintiseis { color: red } } /* Safari 2 - 3.1 */ html[xmlns*=""]:root #trece { color: red } /* Safari 2 - 3.1, Opera 9.25 */ *|html[xmlns*=""] #catorce { color: red } /* Everything but IE6-8 */ :root *> #quince { color: red } /* IE7 */ *+html #dieciocho { color: red } /* Firefox only. 1+ */ #veinticuatro, x:-moz-any-link { color: red } /* Firefox 3.0+ */ #veinticinco, x:-moz-any-link, x:default { color: red }